Abstract
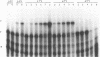
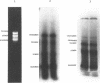
A synthetic gene encoding the hepatitis C virus (HCV) nucleocapsid protein was constructed and expressed in E. coli. To synthesize this gene, we developed a new method that results in the enzymatic synthesis of long polydeoxyribonucleotides from oligodeoxyribonucleotides. The method, designated as the 'Exchangeable Template Reaction' (ETR), uses oligonucleotides as templates for DNA polymerase. A special mechanism was designed to exchange the templates during the polymerase reaction. The mechanism relies on the formation of a single-stranded 3'-protrusion at the 'growing point' of the elongating DNA such that it can be subsequently annealed, in a sequence-specific manner, with the next synthetic oligonucleotide. When annealed to the 3'-protrusion, the added oligonucleotide becomes a template for DNA polymerase, and the protruding 3'-end of the double-stranded DNA is used as the primer. The HCV nucleocapsid gene was assembled with DNA ligase from three fragments synthesized by ETR. The data verify that this method is efficient. The main advantage of ETR is the ability to combine more than two oligonucleotides in one tube together with polymerase and an enzymatic activity that produces a 3'-protrusion (e.g., BstXI) rather than the sequential addition of each component. The data demonstrate that as many as five oligonucleotides can be used simultaneously, resulting in a synthesized DNA fragment of designed sequence. The synthetic gene expressed in E. coli produced a 27 kDa protein that specifically interacted with antibodies from sera obtained from HCV-infected individuals.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams S. E., Johnson I. D., Braddock M., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M., Edwards R. M. Synthesis of a gene for the HIV transactivator protein TAT by a novel single stranded approach involving in vivo gap repair. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 25;16(10):4287–4298. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.10.4287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal K. L., Büchi H., Caruthers M. H., Gupta N., Khorana H. G., Kleppe K., Kumar A., Ohtsuka E., Rajbhandary U. L., Van de Sande J. H. Total synthesis of the gene for an alanine transfer ribonucleic acid from yeast. Nature. 1970 Jul 4;227(5253):27–34. doi: 10.1038/227027a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell L. D., Smith J. C., Derbyshire R., Finlay M., Johnson I., Gilbert R., Slocombe P., Cook E., Richards H., Clissold P. Chemical synthesis, cloning and expression in mammalian cells of a gene coding for human tissue-type plasminogen activator. Gene. 1988 Mar 31;63(2):155–163. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90521-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H. B., Weng J. M., Jiang K., Bao J. S. A new method for the synthesis of a structural gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):871–878. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo Q. L., Richman K. H., Han J. H., Berger K., Lee C., Dong C., Gallegos C., Coit D., Medina-Selby R., Barr P. J. Genetic organization and diversity of the hepatitis C virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2451–2455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciccarelli R. B., Loomis L. A., McCoon P. E., Holzschu D. L. Insertional gene synthesis, a novel method of assembling consecutive DNA sequences within specific sites in plasmids. Construction of the HIV-1 tat gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 11;18(5):1243–1248. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.5.1243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denèfle P., Kovarik S., Guitton J. D., Cartwright T., Mayaux J. F. Chemical synthesis of a gene coding for human angiogenin, its expression in Escherichia coli and conversion of the product into its active form. Gene. 1987;56(1):61–70. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90158-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derbyshire K. M., Salvo J. J., Grindley N. D. A simple and efficient procedure for saturation mutagenesis using mixed oligodeoxynucleotides. Gene. 1986;46(2-3):145–152. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90398-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dretzen G., Bellard M., Sassone-Corsi P., Chambon P. A reliable method for the recovery of DNA fragments from agarose and acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):295–298. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90296-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebeling F., Naukkarinen R., Leikola J. Recombinant immunoblot assay for hepatitis C virus antibody as predictor of infectivity. Lancet. 1990 Apr 21;335(8695):982–983. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91055-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edge M. D., Green A. R., Heathcliffe G. R., Meacock P. A., Schuch W., Scanlon D. B., Atkinson T. C., Newton C. R., Markham A. F. Total synthesis of a human leukocyte interferon gene. Nature. 1981 Aug 20;292(5825):756–762. doi: 10.1038/292756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti L., Karnik S. S., Khorana H. G., Nassal M., Oprian D. D. Total synthesis of a gene for bovine rhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):599–603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freier S. M., Kierzek R., Jaeger J. A., Sugimoto N., Caruthers M. H., Neilson T., Turner D. H. Improved free-energy parameters for predictions of RNA duplex stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9373–9377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada S., Watanabe Y., Takeuchi K., Suzuki T., Katayama T., Takebe Y., Saito I., Miyamura T. Expression of processed core protein of hepatitis C virus in mammalian cells. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3015–3021. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3015-3021.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hijikata M., Kato N., Ootsuyama Y., Nakagawa M., Shimotohno K. Gene mapping of the putative structural region of the hepatitis C virus genome by in vitro processing analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5547–5551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostomský Z., Smrt J., Arnold L., Tocík Z., Paces V. Solid-phase assembly of cow colostrum trypsin inhibitor gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 25;15(12):4849–4856. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.12.4849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger J. A., Turner D. H., Zuker M. Improved predictions of secondary structures for RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7706–7710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayaraman K., Fingar S. A., Shah J., Fyles J. Polymerase chain reaction-mediated gene synthesis: synthesis of a gene coding for isozyme c of horseradish peroxidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4084–4088. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayaraman K., Puccini C. J. A PCR-mediated gene synthesis strategy involving the assembly of oligonucleotides representing only one of the strands. Biotechniques. 1992 Mar;12(3):392–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayaraman K., Shah J., Fyles J. PCR mediated gene synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 12;17(11):4403–4403. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.11.4403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato N., Hijikata M., Ootsuyama Y., Nakagawa M., Ohkoshi S., Sugimura T., Shimotohno K. Molecular cloning of the human hepatitis C virus genome from Japanese patients with non-A, non-B hepatitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9524–9528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khorana H. G. Total synthesis of a gene. Science. 1979 Feb 16;203(4381):614–625. doi: 10.1126/science.366749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khudiakov Iu E., Kalinina T. I., Nepliueva V. S., Smirnov V. D. Korreliatsiia mezhdu éffektivnost'iu initsiatsii transliatsii i vtorichnoi strukturoi mRNK u gibridnogo gena cro-lacIZ. Mol Biol (Mosk) 1987 Nov-Dec;21(6):1504–1512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumder K. Ligation-free gene synthesis by PCR: synthesis and mutagenesis at multiple loci of a chimeric gene encoding OmpA signal peptide and hirudin. Gene. 1992 Jan 2;110(1):89–94. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90448-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandecki W., Mollison K. W., Bolling T. J., Powell B. S., Carter G. W., Fox J. L. Chemical synthesis of a gene encoding the human complement fragment C5a and its expression in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3543–3547. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. H., Purcell R. H. Hepatitis C virus shares amino acid sequence similarity with pestiviruses and flaviviruses as well as members of two plant virus supergroups. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2057–2061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muraiso K., Hijikata M., Kato N., Shimotohno K., Okazaki N., Ohkoshi S., Uura M., Kaneko S., Kobayashi K., Omata M. Detection of hepatitis C virus infection by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay system using core protein expressed in Escherichia coli. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1991 Aug;82(8):879–882. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1991.tb01914.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muraiso K., Hijikata M., Ohkoshi S., Cho M. J., Kikuchi M., Kato N., Shimotohno K. A structural protein of hepatitis C virus expressed in E. coli facilitates accurate detection of hepatitis C virus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Oct 30;172(2):511–516. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90702-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plagemann P. G. Hepatitis C virus. Arch Virol. 1991;120(3-4):165–180. doi: 10.1007/BF01310473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink H., Liersch M., Sieber P., Meyer F. A large fragment approach to DNA synthesis: total synthesis of a gene for the protease inhibitor eglin c from the leech Hirudo medicinalis and its expression in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 24;12(16):6369–6387. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.16.6369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi J. J., Kierzek R., Huang T., Walker P. A., Itakura K. An alternate method for synthesis of double-stranded DNA segments. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9226–9229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpulla R. C., Narang S., Wu R. Use of a new retrieving adaptor in the cloning of a synthetic human insulin A-chain gene. Anal Biochem. 1982 Apr;121(2):356–365. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90493-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sproat B. S., Gait M. J. Chemical synthesis of a gene for somatomedin C. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 25;13(8):2959–2977. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.8.2959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Okamoto H., Kishimoto S., Munekata E., Tachibana K., Akahane Y., Yoshizawa H., Mishiro S. Demonstration of a hepatitis C virus-specific antigen predicted from the putative core gene in the circulation of infected hosts. J Gen Virol. 1992 Mar;73(Pt 3):667–672. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-3-667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takamizawa A., Mori C., Fuke I., Manabe S., Murakami S., Fujita J., Onishi E., Andoh T., Yoshida I., Okayama H. Structure and organization of the hepatitis C virus genome isolated from human carriers. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1105–1113. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1105-1113.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi K., Kubo Y., Boonmar S., Watanabe Y., Katayama T., Choo Q. L., Kuo G., Houghton M., Saito I., Miyamura T. The putative nucleocapsid and envelope protein genes of hepatitis C virus determined by comparison of the nucleotide sequences of two isolates derived from an experimentally infected chimpanzee and healthy human carriers. J Gen Virol. 1990 Dec;71(Pt 12):3027–3033. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-12-3027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlmann E. An alternative approach in gene synthesis: use of long selfpriming oligodeoxynucleotides for the construction of double-stranded DNA. Gene. 1988 Nov 15;71(1):29–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90074-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Poel C. L., Cuypers H. T., Reesink H. W., Weiner A. J., Quan S., Di Nello R., Van Boven J. J., Winkel I., Mulder-Folkerts D., Exel-Oehlers P. J. Confirmation of hepatitis C virus infection by new four-antigen recombinant immunoblot assay. Lancet. 1991 Feb 9;337(8737):317–319. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90942-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner M. P., Scheraga H. A. A method for the cloning of unpurified single-stranded oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 12;17(17):7113–7113. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.17.7113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wosnick M. A., Barnett R. W., Carlson J. E. Total chemical synthesis and expression in Escherichia coli of a maize glutathione-transferase (GST) gene. Gene. 1989 Mar 15;76(1):153–160. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Poel C. L., Reesink H. W., Schaasberg W., Leentvaar-Kuypers A., Bakker E., Exel-Oehlers P. J., Lelie P. N. Infectivity of blood seropositive for hepatitis C virus antibodies. Lancet. 1990 Mar 10;335(8689):558–560. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90347-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]