Abstract
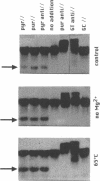
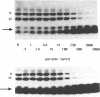
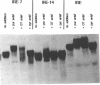
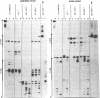
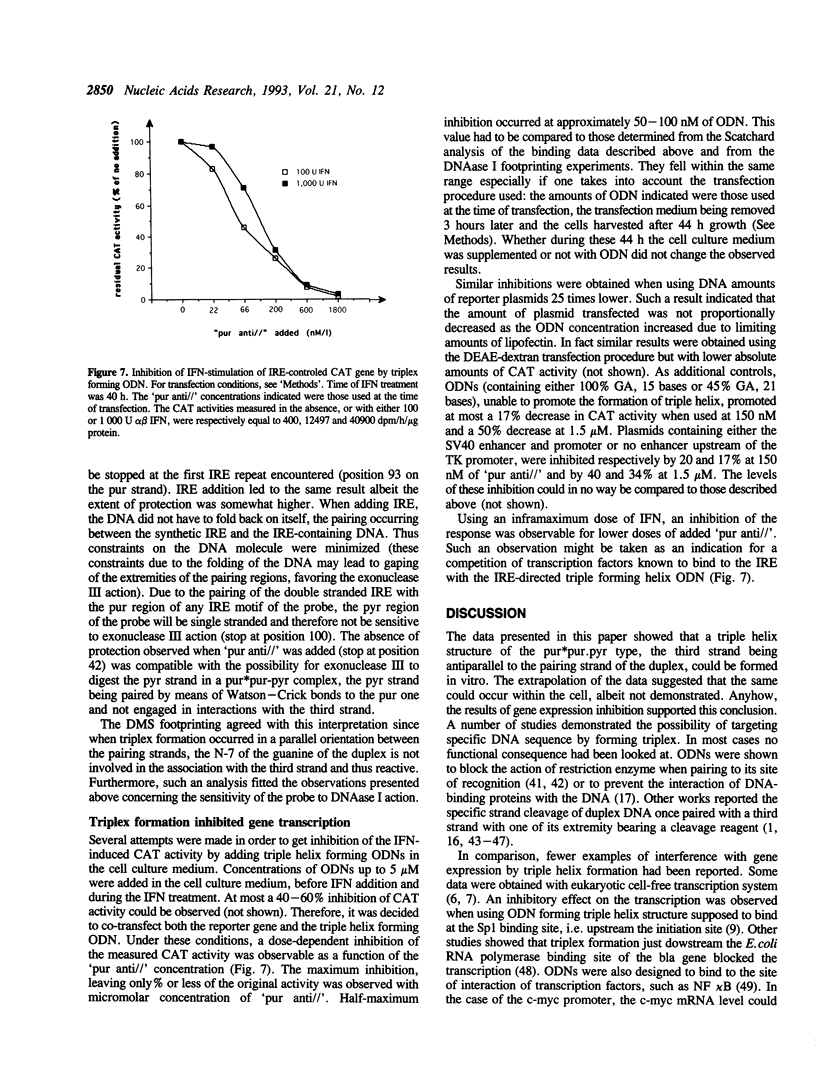
Several oligodeoxynucleotides (ODNs) were designed in order to interact with the purine rich element of the IRE (Interferon Responsive Element) of the 6-16 gene by triplex formation. An ODN of 21 bases, the sequence being identical to that of the purine strand of the IRE (48% G), but in reverse orientation, was able to interact with the IRE (KD: 20 nM). The binding was Mg2+ dependent. The two purine strands of the triplex were oriented antiparallel as confirmed by DNAase I and copper-phenanthroline footprinting experiments. An ODN in which A were replaced by T, also interacted with the same target, but with a lower affinity. Exonuclease III action indicated that the two IRE repeats of the 6-16 promoter interacted with each other through Hoogsteen base pairing, the third strand being parallel to the paired Watson-Crick strand. This led to a potential H-DNA structure which could be destabilized by adding ODNs able to form a triplex structure. 6-16 IRE driven-reporter gene constructs lost their interferon stimulability when co-transfected with triplex forming ODNs. The range of effective ODN concentrations was compatible with the affinity determined when measuring their direct interactions with the DNA.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnott S., Selsing E. Structures for the polynucleotide complexes poly(dA) with poly (dT) and poly(dT) with poly(dA) with poly (dT). J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 15;88(2):509–521. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90498-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beal P. A., Dervan P. B. Second structural motif for recognition of DNA by oligonucleotide-directed triple-helix formation. Science. 1991 Mar 15;251(4999):1360–1363. doi: 10.1126/science.2003222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernués J., Beltrán R., Casasnovas J. M., Azorín F. Structural polymorphism of homopurine--homopyrimidine sequences: the secondary DNA structure adopted by a d(GA.CT)22 sequence in the presence of zinc ions. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2087–2094. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03617.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blume S. W., Gee J. E., Shrestha K., Miller D. M. Triple helix formation by purine-rich oligonucleotides targeted to the human dihydrofolate reductase promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 11;20(7):1777–1784. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.7.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooney M., Czernuszewicz G., Postel E. H., Flint S. J., Hogan M. E. Site-specific oligonucleotide binding represses transcription of the human c-myc gene in vitro. Science. 1988 Jul 22;241(4864):456–459. doi: 10.1126/science.3293213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale T. C., Rosen J. M., Guille M. J., Lewin A. R., Porter A. G., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Overlapping sites for constitutive and induced DNA binding factors involved in interferon-stimulated transcription. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):831–839. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03444.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durland R. H., Kessler D. J., Gunnell S., Duvic M., Pettitt B. M., Hogan M. E. Binding of triple helix forming oligonucleotides to sites in gene promoters. Biochemistry. 1991 Sep 24;30(38):9246–9255. doi: 10.1021/bi00102a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duval-Valentin G., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Specific inhibition of transcription by triple helix-forming oligonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):504–508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- François J. C., Saison-Behmoaras T., Barbier C., Chassignol M., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Sequence-specific recognition and cleavage of duplex DNA via triple-helix formation by oligonucleotides covalently linked to a phenanthroline-copper chelate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9702–9706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- François J. C., Saison-Behmoaras T., Hélène C. Sequence-specific recognition of the major groove of DNA by oligodeoxynucleotides via triple helix formation. Footprinting studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 23;16(24):11431–11440. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.24.11431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Stark G. R. alpha-Interferon-induced transcription of HLA and metallothionein genes containing homologous upstream sequences. Nature. 1985 Apr 18;314(6012):637–639. doi: 10.1038/314637a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover J. N., Farah C. S., Pulleyblank D. E. Structural characterization of separated H DNA conformers. Biochemistry. 1990 Dec 18;29(50):11110–11115. doi: 10.1021/bi00502a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin L. C., Dervan P. B. Recognition of thymine adenine.base pairs by guanine in a pyrimidine triple helix motif. Science. 1989 Sep 1;245(4921):967–971. doi: 10.1126/science.2549639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigoriev M., Praseuth D., Robin P., Hemar A., Saison-Behmoaras T., Dautry-Varsat A., Thuong N. T., Hélène C., Harel-Bellan A. A triple helix-forming oligonucleotide-intercalator conjugate acts as a transcriptional repressor via inhibition of NF kappa B binding to interleukin-2 receptor alpha-regulatory sequence. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3389–3395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampel K. J., Crosson P., Lee J. S. Polyamines favor DNA triplex formation at neutral pH. Biochemistry. 1991 May 7;30(18):4455–4459. doi: 10.1021/bi00232a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoke G. D., Draper K., Freier S. M., Gonzalez C., Driver V. B., Zounes M. C., Ecker D. J. Effects of phosphorothioate capping on antisense oligonucleotide stability, hybridization and antiviral efficacy versus herpes simplex virus infection. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5743–5748. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Htun H., Dahlberg J. E. Topology and formation of triple-stranded H-DNA. Science. 1989 Mar 24;243(4898):1571–1576. doi: 10.1126/science.2648571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling L. L., Griffin L. C., Dervan P. B. Flanking sequence effects within the pyrimidine triple-helix motif characterized by affinity cleaving. Biochemistry. 1992 Mar 17;31(10):2829–2834. doi: 10.1021/bi00125a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohwi Y., Kohwi-Shigematsu T. Magnesium ion-dependent triple-helix structure formed by homopurine-homopyrimidine sequences in supercoiled plasmid DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3781–3785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Doan T., Perrouault L., Praseuth D., Habhoub N., Decout J. L., Thuong N. T., Lhomme J., Hélène C. Sequence-specific recognition, photocrosslinking and cleavage of the DNA double helix by an oligo-[alpha]-thymidylate covalently linked to an azidoproflavine derivative. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7749–7760. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel P. Biochemistry of interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:251–282. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macaya R. F., Gilbert D. E., Malek S., Sinsheimer J. S., Feigon J. Structure and stability of X.G.C mismatches in the third strand of intramolecular triplexes. Science. 1991 Oct 11;254(5029):270–274. doi: 10.1126/science.254.5029.270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher L. J., 3rd, Dervan P. B., Wold B. Analysis of promoter-specific repression by triple-helical DNA complexes in a eukaryotic cell-free transcription system. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 14;31(1):70–81. doi: 10.1021/bi00116a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher L. J., 3rd, Wold B., Dervan P. B. Inhibition of DNA binding proteins by oligonucleotide-directed triple helix formation. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):725–730. doi: 10.1126/science.2549631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel D., Chatelain G., Herault Y., Brun G. The long repetitive polypurine/polypyrimidine sequence (TTCCC)48 forms DNA triplex with PU-PU-PY base triplets in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 11;20(3):439–443. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.3.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser H. E., Dervan P. B. Sequence-specific cleavage of double helical DNA by triple helix formation. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):645–650. doi: 10.1126/science.3118463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orson F. M., Thomas D. W., McShan W. M., Kessler D. J., Hogan M. E. Oligonucleotide inhibition of IL2R alpha mRNA transcription by promoter region collinear triplex formation in lymphocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 25;19(12):3435–3441. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.12.3435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei D., Corey D. R., Schultz P. G. Site-specific cleavage of duplex DNA by a semisynthetic nuclease via triple-helix formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9858–9862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilch D. S., Levenson C., Shafer R. H. Structure, stability, and thermodynamics of a short intermolecular purine-purine-pyrimidine triple helix. Biochemistry. 1991 Jun 25;30(25):6081–6088. doi: 10.1021/bi00239a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter A. C., Chernajovsky Y., Dale T. C., Gilbert C. S., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. Interferon response element of the human gene 6-16. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):85–92. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02786.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postel E. H., Flint S. J., Kessler D. J., Hogan M. E. Evidence that a triplex-forming oligodeoxyribonucleotide binds to the c-myc promoter in HeLa cells, thereby reducing c-myc mRNA levels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):8227–8231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.8227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid L. E., Brasnett A. H., Gilbert C. S., Porter A. C., Gewert D. R., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. A single DNA response element can confer inducibility by both alpha- and gamma-interferons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):840–844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy C., Lebleu B. DNA protein interactions at the interferon-responsive promoter elements: potential for an H-DNA conformation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 11;19(3):517–524. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.3.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. P., Kent K., Bird J., Fishback J., Froehler B. Modified deoxyoligonucleotides stable to exonuclease degradation in serum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 25;19(4):747–750. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.4.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoji Y., Akhtar S., Periasamy A., Herman B., Juliano R. L. Mechanism of cellular uptake of modified oligodeoxynucleotides containing methylphosphonate linkages. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5543–5550. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigman D. S. Chemical nucleases. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 2;29(39):9097–9105. doi: 10.1021/bi00491a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel S. A., Dervan P. B. Single-site enzymatic cleavage of yeast genomic DNA mediated by triple helix formation. Nature. 1991 Mar 14;350(6314):172–174. doi: 10.1038/350172a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel S. A., Doucette-Stamm L. A., Riba L., Housman D. E., Dervan P. B. Site-specific cleavage of human chromosome 4 mediated by triple-helix formation. Science. 1991 Dec 13;254(5038):1639–1642. doi: 10.1126/science.1836279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veal J. M., Rill R. L. Noncovalent DNA binding of bis(1,10-phenanthroline)copper(I) and related compounds. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 29;30(4):1132–1140. doi: 10.1021/bi00218a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. R. Transcriptional regulation of interferon-stimulated genes. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Aug 15;200(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb21041.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yakubov L. A., Deeva E. A., Zarytova V. F., Ivanova E. M., Ryte A. S., Yurchenko L. V., Vlassov V. V. Mechanism of oligonucleotide uptake by cells: involvement of specific receptors? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6454–6458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon K., Hobbs C. A., Koch J., Sardaro M., Kutny R., Weis A. L. Elucidation of the sequence-specific third-strand recognition of four Watson-Crick base pairs in a pyrimidine triple-helix motif: T.AT, C.GC, T.CG, and G.TA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):3840–3844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. L., Krawczyk S. H., Matteucci M. D., Toole J. J. Triple helix formation inhibits transcription elongation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10023–10026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]