Abstract
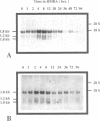
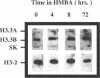
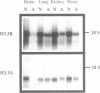
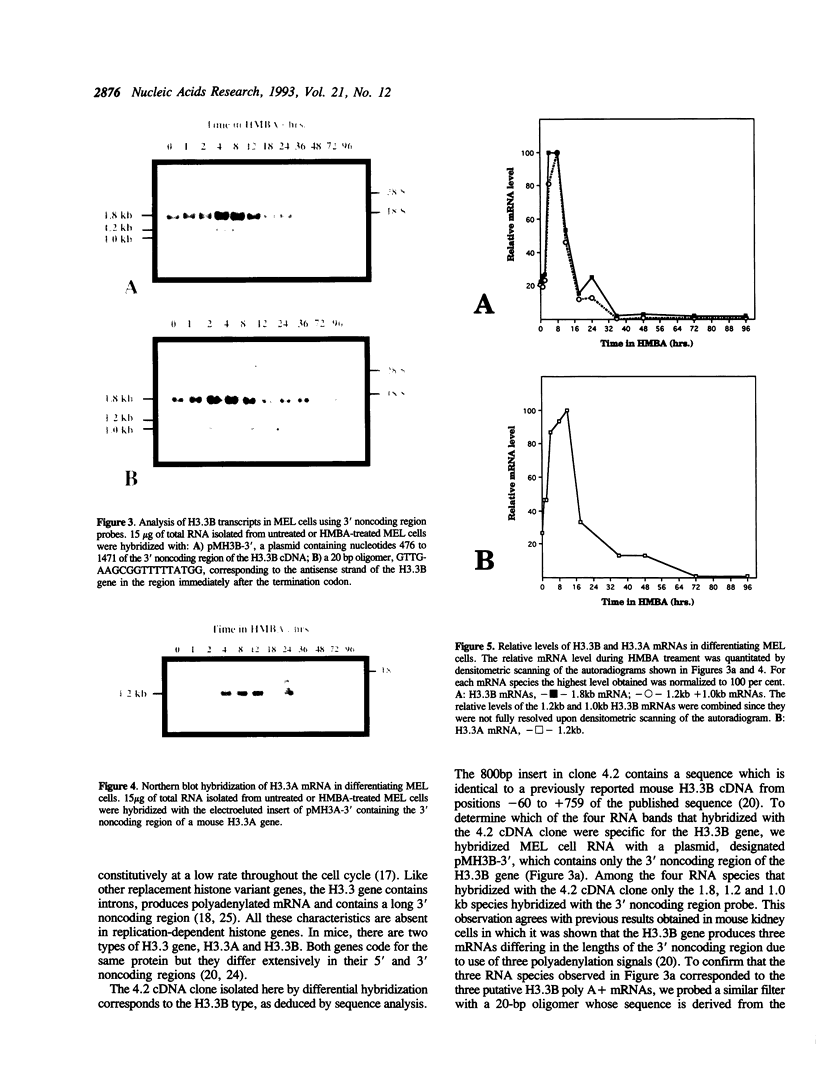
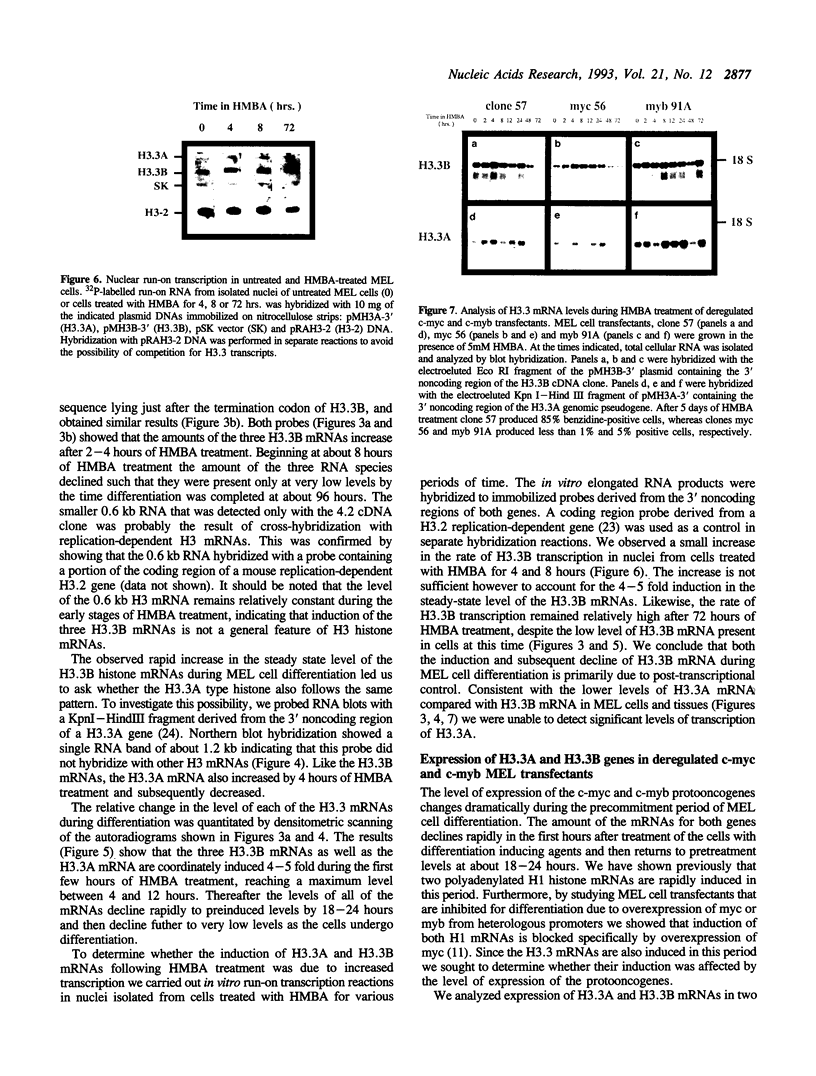
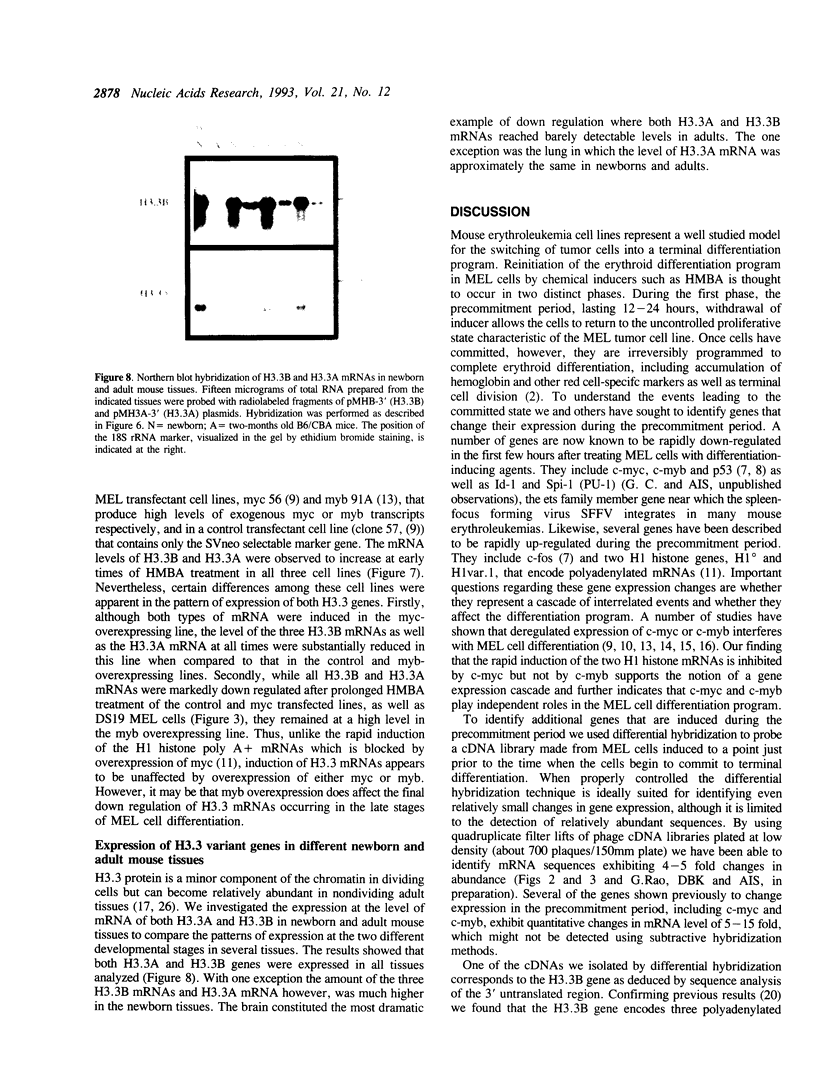
Differential hybridization to a cDNA library made from the mRNA of differentiating mouse erythroleukemia (MEL) cells has been used to identify sequences that are induced during the early stages of MEL cell differentiation. One of the differentially expressed genes identified encodes the H3.3 histone subtype. We show here that the three polyadenylated mRNAs produced from the H3.3B gene, as well as the single mRNA produced from the related H3.3A gene, are coordinately induced during the first few hours of MEL cell differentiation and subsequently down regulated as cells undergo terminal differentiation. Nuclear run-on transcription experiments indicate that the accumulation and decay of these mRNAs are controlled at the post-transcriptional level. Unlike the polyadenylated mRNAs of two H1 histone genes that exhibit similar kinetics of induction and decay controlled by c-myc, induction of the H3.3 mRNAs is unaffected by deregulated expression of c-myc.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alterman R. B., Sprecher C., Graves R., Marzluff W. F., Skoultchi A. I. Regulated expression of a chimeric histone gene introduced into mouse fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2316–2324. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. T., Wellman S. E., Sittman D. B. Changes in the levels of three different classes of histone mRNA during murine erythroleukemia cell differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2879–2886. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brush D., Dodgson J. B., Choi O. R., Stevens P. W., Engel J. D. Replacement variant histone genes contain intervening sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1307–1317. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalmers M., Wells D. Extreme sequence conservation characterizes the rabbit H3.3A histone cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):3075–3075. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.3075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z., Banks J., Rifkind R. A., Marks P. A. Inducer-mediated commitment of murine erythroleukemia cells to differentiation: a multistep process. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):471–475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng G. H., Nandi A., Clerk S., Skoultchi A. I. Different 3'-end processing produces two independently regulated mRNAs from a single H1 histone gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7002–7006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng G. H., Skoultchi A. I. Rapid induction of polyadenylated H1 histone mRNAs in mouse erythroleukemia cells is regulated by c-myc. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2332–2340. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke M. F., Kukowska-Latallo J. F., Westin E., Smith M., Prochownik E. V. Constitutive expression of a c-myb cDNA blocks Friend murine erythroleukemia cell differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):884–892. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppola J. A., Cole M. D. Constitutive c-myc oncogene expression blocks mouse erythroleukaemia cell differentiation but not commitment. Nature. 1986 Apr 24;320(6064):760–763. doi: 10.1038/320760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dmitrovsky E., Kuehl W. M., Hollis G. F., Kirsch I. R., Bender T. P., Segal S. Expression of a transfected human c-myc oncogene inhibits differentiation of a mouse erythroleukaemia cell line. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):748–750. doi: 10.1038/322748a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend C., Scher W., Holland J. G., Sato T. Hemoglobin synthesis in murine virus-induced leukemic cells in vitro: stimulation of erythroid differentiation by dimethyl sulfoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):378–382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielli F., Aden D. P., Carrel S. C., von Bahr C., Rane A., Angeletti C. A., Hancock R. Histone complements of human tissues, carcinomas, and carcinoma-derived cell lines. Mol Cell Biochem. 1984 Nov;65(1):57–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganguly S., Skoultchi A. I. Absolute rates of globin gene transcription and mRNA formation during differentiation of cultured mouse erythroleukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12167–12173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusella J., Geller R., Clarke B., Weeks V., Housman D. Commitment to erythroid differentiation by friend erythroleukemia cells: a stochastic analysis. Cell. 1976 Oct;9(2):221–229. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90113-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hraba-Renevey S., Kress M. Expression of a mouse replacement histone H3.3 gene with a highly conserved 3' noncoding region during SV40- and polyoma-induced Go to S-phase transition. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 11;17(7):2449–2461. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.7.2449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kume T. U., Takada S., Obinata M. Probability that the commitment of murine erythroleukemia cell differentiation is determined by the c-myc level. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 20;202(4):779–786. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90558-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachman H. M., Cheng G. H., Skoultchi A. I. Transfection of mouse erythroleukemia cells with myc sequences changes the rate of induced commitment to differentiate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6480–6484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachman H. M., Skoultchi A. I. Expression of c-myc changes during differentiation of mouse erythroleukaemia cells. Nature. 1984 Aug 16;310(5978):592–594. doi: 10.1038/310592a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks P. A., Ramsay R., Sheffery M., Rifkind R. A. Changes in gene expression during hexamethylene bisacetamide induced erythroleukemia differentiation. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1987;251:253–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks P. A., Rifkind R. A. Erythroleukemic differentiation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:419–448. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.002223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochownik E. V., Kukowska J. Deregulated expression of c-myc by murine erythroleukaemia cells prevents differentiation. 1986 Aug 28-Sep 3Nature. 322(6082):848–850. doi: 10.1038/322848a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Profous-Juchelka H. R., Reuben R. C., Marks P. A., Rifkind R. A. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of globin gene accumulation in murine erythroleukemia cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):229–232. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay R. G., Ikeda K., Rifkind R. A., Marks P. A. Changes in gene expression associated with induced differentiation of erythroleukemia: protooncogenes, globin genes, and cell division. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6849–6853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeiro R., Darnell J. E. Competition hybridization by "pre-saturation" of HeLa cell DNA. J Mol Biol. 1969 Sep 28;44(3):551–562. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90379-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellman S. E., Casano P. J., Pilch D. R., Marzluff W. F., Sittman D. B. Characterization of mouse H3.3-like histone genes. Gene. 1987;59(1):29–39. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90263-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells D., Kedes L. Structure of a human histone cDNA: evidence that basally expressed histone genes have intervening sequences and encode polyadenylylated mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2834–2838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]