Abstract
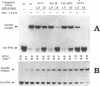
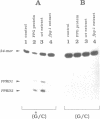
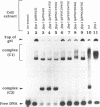
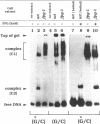
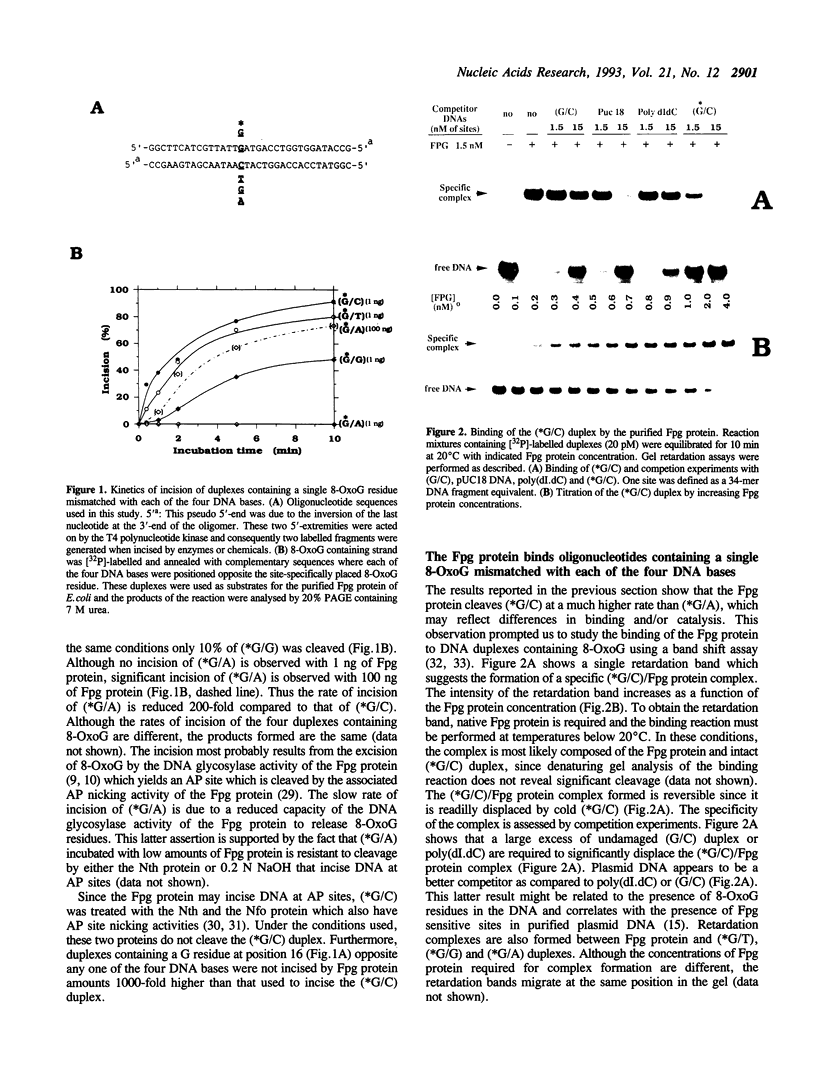
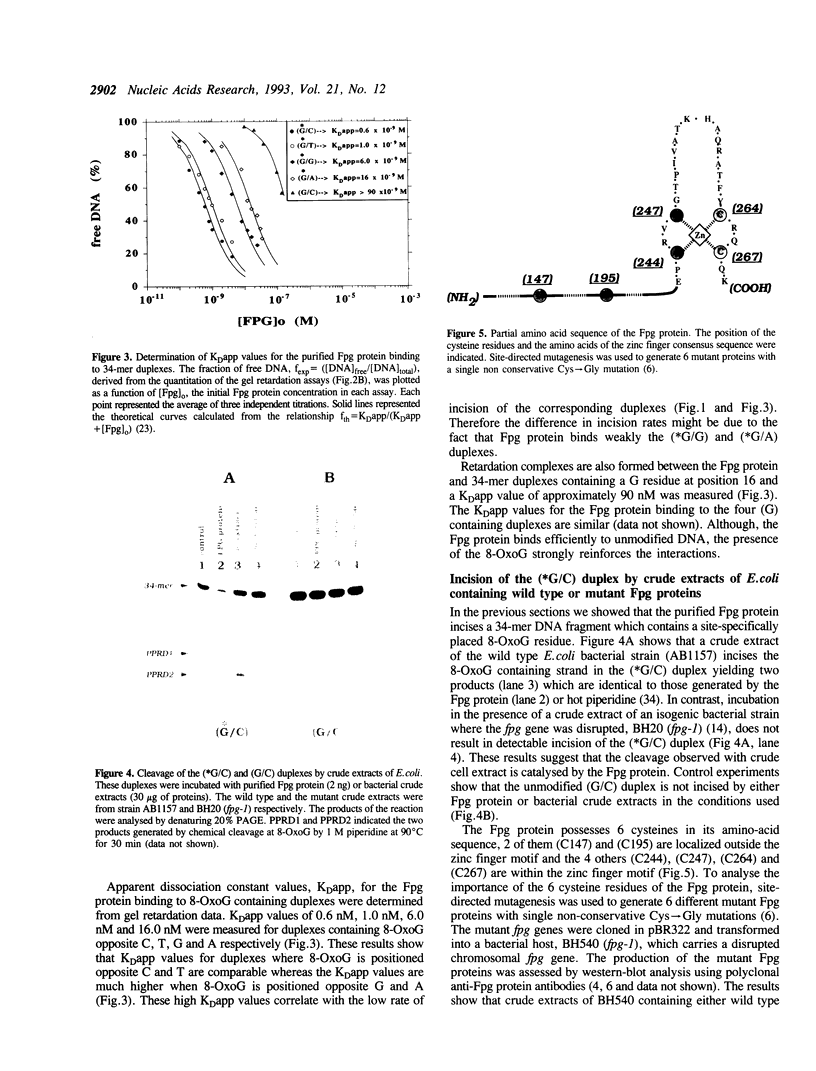
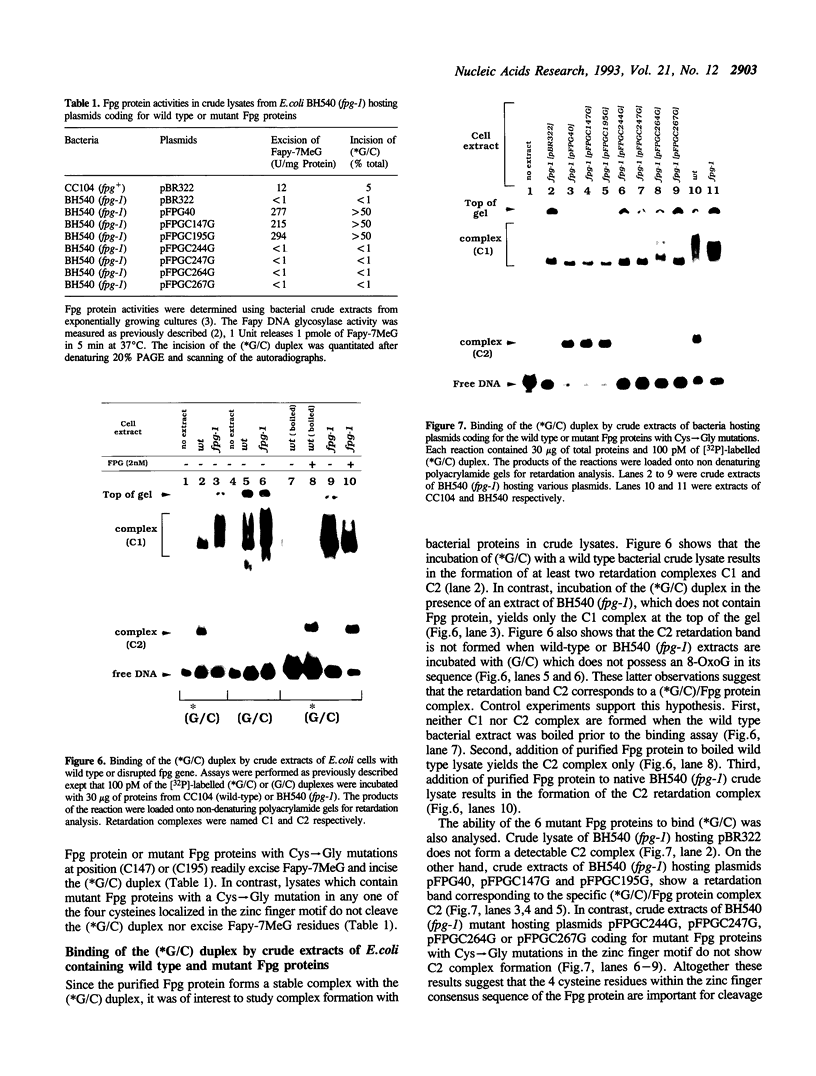
A 34-mer oligonucleotide containing a single 7,8-dihydro-8-oxoguanine (8-OxoG) residue was used to study the enzymatic and DNA binding properties of the Fpg protein from E. coli. The highest rates of incision of the 8-OxoG containing strand by the Fpg protein were observed for duplexes where 8-OxoG was opposite C (*G/C) or T (*G/T). In contrast, the rates of incision of duplexes containing 8-OxoG opposite G (*G/G) and A (*G/A) were 5-fold and 200-fold slower. Gel retardation studies showed that the Fpg protein had a strong affinity for duplexes where the 8-OxoG was opposite pyrimidines and less affinity for duplexes where the 8-OxoG was opposite purines. KDapp values were 0.6 nM (*G/C), 1.0 nM (*G/T), 6.0 nM (*G/G) and 16.0 nM (*G/A). The Fpg protein also binds to unmodified (G/C) duplex and a KDapp of 90 nM was measured. The cleavage and binding of the (*G/C) duplex were also studied using bacterial crude lysates. Wild type E. coli crude extract incised the 8-OxoG containing strand and formed a specific retardation complex with the (*G/C) duplex. These two reactions were mediated by the Fpg protein, since they were not observed with a crude extract from a bacterial strain whose fpg gene was inactivated. Furthermore, we have studied the properties of 6 mutant Fpg proteins with Cys-->Gly mutations. The results showed that the 2 Fpg proteins with Cys-->Gly mutations outside the zinc finger sequence cleaved the 8-OxoG containing strand, formed complexes with the (*G/C) duplex and suppressed the mutator phenotype of the fpg-1 mutant. In contrast, the 4 Fpg proteins with Cys-->Gly mutations within the zinc finger motif neither cleave nor bind the (*G/C) duplex, nor do these proteins suppress the fpg-1 mutator phenotype.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailly V., Verly W. G., O'Connor T., Laval J. Mechanism of DNA strand nicking at apurinic/apyrimidinic sites by Escherichia coli [formamidopyrimidine]DNA glycosylase. Biochem J. 1989 Sep 1;262(2):581–589. doi: 10.1042/bj2620581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boiteux S., Belleney J., Roques B. P., Laval J. Two rotameric forms of open ring 7-methylguanine are present in alkylated polynucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5429–5439. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boiteux S., Bichara M., Fuchs R. P., Laval J. Excision of the imidazole ring-opened form of N-2-aminofluorene-C(8)-guanine adduct in poly(dG-dC) by Escherichia coli formamidopyrimidine-DNA glycosylase. Carcinogenesis. 1989 Oct;10(10):1905–1909. doi: 10.1093/carcin/10.10.1905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boiteux S., Costa de Oliveira R., Laval J. The Escherichia coli O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase does not repair promutagenic O6-methylguanine residues when present in Z-DNA. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 25;260(15):8711–8715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boiteux S., Gajewski E., Laval J., Dizdaroglu M. Substrate specificity of the Escherichia coli Fpg protein (formamidopyrimidine-DNA glycosylase): excision of purine lesions in DNA produced by ionizing radiation or photosensitization. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 14;31(1):106–110. doi: 10.1021/bi00116a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boiteux S., Huisman O. Isolation of a formamidopyrimidine-DNA glycosylase (fpg) mutant of Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jan;215(2):300–305. doi: 10.1007/BF00339732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boiteux S., O'Connor T. R., Laval J. Formamidopyrimidine-DNA glycosylase of Escherichia coli: cloning and sequencing of the fpg structural gene and overproduction of the protein. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3177–3183. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02629.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breimer L. H. Enzymatic excision from gamma-irradiated polydeoxyribonucleotides of adenine residues whose imidazole rings have been ruptured. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 24;12(16):6359–6367. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.16.6359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breimer L. H., Lindahl T. DNA glycosylase activities for thymine residues damaged by ring saturation, fragmentation, or ring contraction are functions of endonuclease III in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5543–5548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breimer L. H. Molecular mechanisms of oxygen radical carcinogenesis and mutagenesis: the role of DNA base damage. Mol Carcinog. 1990;3(4):188–197. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940030405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaing B., Boiteux S., Zelwer C. DNA containing a chemically reduced apurinic site is a high affinity ligand for the E. coli formamidopyrimidine-DNA glycosylase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 11;20(3):389–394. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.3.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. C., Cahill D. S., Kasai H., Nishimura S., Loeb L. A. 8-Hydroxyguanine, an abundant form of oxidative DNA damage, causes G----T and A----C substitutions. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):166–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chetsanga C. J., Lindahl T. Release of 7-methylguanine residues whose imidazole rings have been opened from damaged DNA by a DNA glycosylase from Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3673–3684. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung M. H., Kiyosawa H., Ohtsuka E., Nishimura S., Kasai H. DNA strand cleavage at 8-hydroxyguanine residues by hot piperidine treatment. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Oct 15;188(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)92341-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham R. P., Saporito S. M., Spitzer S. G., Weiss B. Endonuclease IV (nfo) mutant of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1120–1127. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1120-1127.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham R. P., Weiss B. Endonuclease III (nth) mutants of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):474–478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cupples C. G., Miller J. H. A set of lacZ mutations in Escherichia coli that allow rapid detection of each of the six base substitutions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5345–5349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czeczot H., Tudek B., Lambert B., Laval J., Boiteux S. Escherichia coli Fpg protein and UvrABC endonuclease repair DNA damage induced by methylene blue plus visible light in vivo and in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3419–3424. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3419-3424.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dizdaroglu M. Chemical determination of free radical-induced damage to DNA. Free Radic Biol Med. 1991;10(3-4):225–242. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(91)90080-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves R. J., Felzenszwalb I., Laval J., O'Connor T. R. Excision of 5'-terminal deoxyribose phosphate from damaged DNA is catalyzed by the Fpg protein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14429–14435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inaoka T., Ishida M., Ohtsuka E. Affinity of single- or double-stranded oligodeoxyribonucleotides containing a thymine photodimer for T4 endonuclease V. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2609–2614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai H., Crain P. F., Kuchino Y., Nishimura S., Ootsuyama A., Tanooka H. Formation of 8-hydroxyguanine moiety in cellular DNA by agents producing oxygen radicals and evidence for its repair. Carcinogenesis. 1986 Nov;7(11):1849–1851. doi: 10.1093/carcin/7.11.1849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaspar R. L., Rychlik W., White M. W., Rhoads R. E., Morris D. R. Simultaneous cytoplasmic redistribution of ribosomal protein L32 mRNA and phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E after mitogenic stimulation of Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3619–3622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J. C., Bleeker M. J., Saris C. P., Roelen H. C., Brugghe H. F., van den Elst H., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H., Westra J. G., Kriek E. Repair and replication of plasmids with site-specific 8-oxodG and 8-AAFdG residues in normal and repair-deficient human cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Sep 11;20(17):4437–4443. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.17.4437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouchakdjian M., Bodepudi V., Shibutani S., Eisenberg M., Johnson F., Grollman A. P., Patel D. J. NMR structural studies of the ionizing radiation adduct 7-hydro-8-oxodeoxyguanosine (8-oxo-7H-dG) opposite deoxyadenosine in a DNA duplex. 8-Oxo-7H-dG(syn).dA(anti) alignment at lesion site. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 5;30(5):1403–1412. doi: 10.1021/bi00219a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchino Y., Mori F., Kasai H., Inoue H., Iwai S., Miura K., Ohtsuka E., Nishimura S. Misreading of DNA templates containing 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine at the modified base and at adjacent residues. Nature. 1987 May 7;327(6117):77–79. doi: 10.1038/327077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagravère C., Malfoy B., Leng M., Laval J. Ring-opened alkylated guanine is not repaired in Z-DNA. 1984 Aug 30-Sep 5Nature. 310(5980):798–800. doi: 10.1038/310798a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laval J., Boiteux S., O'Connor T. R. Physiological properties and repair of apurinic/apyrimidinic sites and imidazole ring-opened guanines in DNA. Mutat Res. 1990 Nov-Dec;233(1-2):73–79. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(90)90152-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J. D., Johnson A. W., Demple B. Homogeneous Escherichia coli endonuclease IV. Characterization of an enzyme that recognizes oxidative damage in DNA. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8066–8071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaels M. L., Pham L., Cruz C., Miller J. H. MutM, a protein that prevents G.C----T.A transversions, is formamidopyrimidine-DNA glycosylase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 11;19(13):3629–3632. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.13.3629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor T. R., Laval J. Physical association of the 2,6-diamino-4-hydroxy-5N-formamidopyrimidine-DNA glycosylase of Escherichia coli and an activity nicking DNA at apurinic/apyrimidinic sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5222–5226. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortigão J. F., Rösch H., Selter H., Fröhlich A., Lorenz A., Montenarh M., Seliger H. Antisense effect of oligodeoxynucleotides with inverted terminal internucleotidic linkages: a minimal modification protecting against nucleolytic degradation. Antisense Res Dev. 1992 Summer;2(2):129–146. doi: 10.1089/ard.1992.2.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich A., Nordheim A., Wang A. H. The chemistry and biology of left-handed Z-DNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:791–846. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.004043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J. E., Price S., Maidt L., Gutteridge J. M., Floyd R. A. Methylene blue plus light mediates 8-hydroxy 2'-deoxyguanosine formation in DNA preferentially over strand breakage. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):631–635. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibutani S., Takeshita M., Grollman A. P. Insertion of specific bases during DNA synthesis past the oxidation-damaged base 8-oxodG. Nature. 1991 Jan 31;349(6308):431–434. doi: 10.1038/349431a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tchou J., Kasai H., Shibutani S., Chung M. H., Laval J., Grollman A. P., Nishimura S. 8-oxoguanine (8-hydroxyguanine) DNA glycosylase and its substrate specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4690–4694. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tudek B., Laval J., Boiteux S. SOS-independent mutagenesis in lacZ induced by methylene blue plus visible light. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Jan;236(2-3):433–439. doi: 10.1007/BF00277144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood M. L., Dizdaroglu M., Gajewski E., Essigmann J. M. Mechanistic studies of ionizing radiation and oxidative mutagenesis: genetic effects of a single 8-hydroxyguanine (7-hydro-8-oxoguanine) residue inserted at a unique site in a viral genome. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 31;29(30):7024–7032. doi: 10.1021/bi00482a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]