Abstract
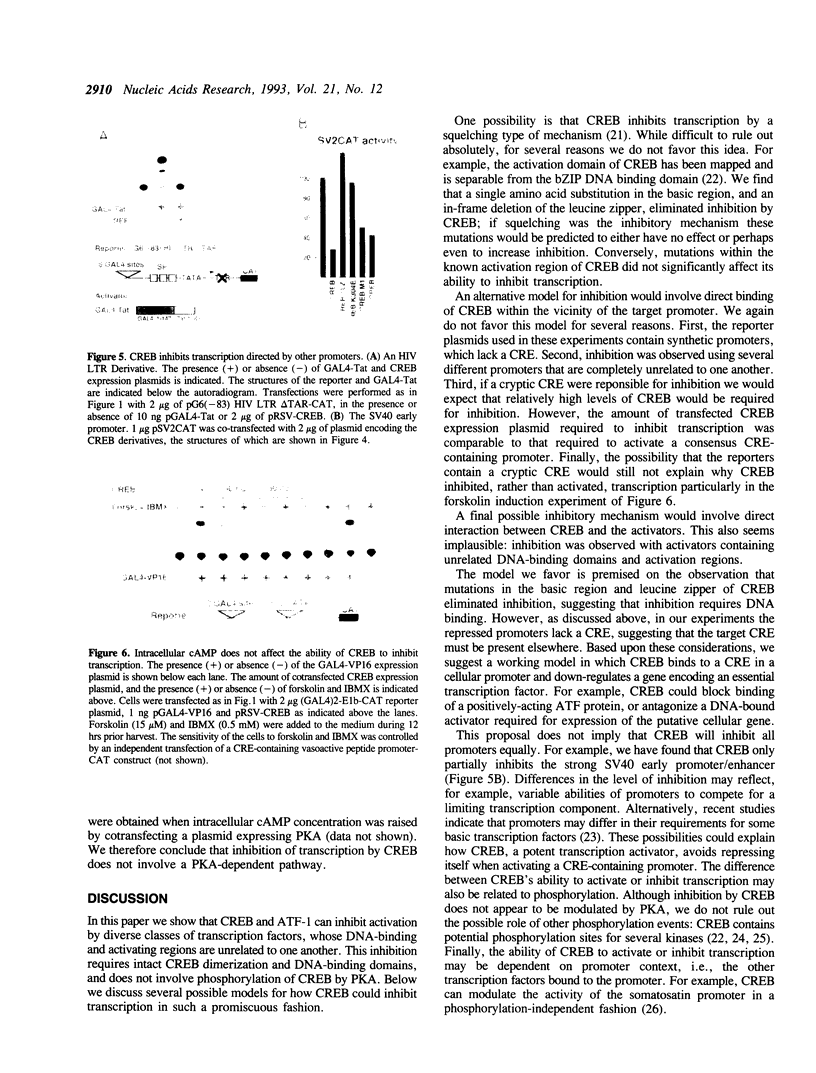
Cyclic AMP response element binding protein (CREB) activates transcription of cAMP response element (CRE)-containing promoters following an elevation of intracellular cAMP. Here we show that CREB and the highly related protein ATF-1 are also potent transcription inhibitors. Strikingly, CREB inhibits transcription of multiple activators, whose DNA-binding domains and activation regions are unrelated to one another. Inhibition requires that the CREB dimerization and DNA-binding domains are intact. However, inhibition is not dependent upon the presence of a CRE in the promoter, and does not involve heterodimer formation between CREB and the activator. The ability of an activator protein to inhibit transcription in such a promiscuous fashion has not been previously reported.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brindle P. K., Montminy M. R. The CREB family of transcription activators. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992 Apr;2(2):199–204. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80274-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond M. I., Miner J. N., Yoshinaga S. K., Yamamoto K. R. Transcription factor interactions: selectors of positive or negative regulation from a single DNA element. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1266–1272. doi: 10.1126/science.2119054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwarki V. J., Montminy M., Verma I. M. Both the basic region and the 'leucine zipper' domain of the cyclic AMP response element binding (CREB) protein are essential for transcriptional activation. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):225–232. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08099.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes N. S., Borrelli E., Sassone-Corsi P. CREM gene: use of alternative DNA-binding domains generates multiple antagonists of cAMP-induced transcription. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):739–749. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90503-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G., Ptashne M. Negative effect of the transcriptional activator GAL4. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):721–724. doi: 10.1038/334721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giniger E., Ptashne M. Transcription in yeast activated by a putative amphipathic alpha helix linked to a DNA binding unit. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):670–672. doi: 10.1038/330670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G. A., Menzel P., Leonard J., Fischer W. H., Montminy M. R. Characterization of motifs which are critical for activity of the cyclic AMP-responsive transcription factor CREB. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1306–1312. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G. A., Montminy M. R. Cyclic AMP stimulates somatostatin gene transcription by phosphorylation of CREB at serine 133. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):675–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G. A., Yamamoto K. K., Fischer W. H., Karr D., Menzel P., Biggs W., 3rd, Vale W. W., Montminy M. R. A cluster of phosphorylation sites on the cyclic AMP-regulated nuclear factor CREB predicted by its sequence. Nature. 1989 Feb 23;337(6209):749–752. doi: 10.1038/337749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habener J. F. Cyclic AMP response element binding proteins: a cornucopia of transcription factors. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Aug;4(8):1087–1094. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-8-1087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T. W., Liu F., Coukos W. J., Green M. R. Transcription factor ATF cDNA clones: an extensive family of leucine zipper proteins able to selectively form DNA-binding heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2083–2090. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonat C., Rahmsdorf H. J., Park K. K., Cato A. C., Gebel S., Ponta H., Herrlich P. Antitumor promotion and antiinflammation: down-modulation of AP-1 (Fos/Jun) activity by glucocorticoid hormone. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1189–1204. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90395-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpinski B. A., Morle G. D., Huggenvik J., Uhler M. D., Leiden J. M. Molecular cloning of human CREB-2: an ATF/CREB transcription factor that can negatively regulate transcription from the cAMP response element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4820–4824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamph W. W., Dwarki V. J., Ofir R., Montminy M., Verma I. M. Negative and positive regulation by transcription factor cAMP response element-binding protein is modulated by phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4320–4324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Q., Yun Y. D., Hoeffler J. P., Habener J. F. Cyclic-AMP-responsive transcriptional activation of CREB-327 involves interdependent phosphorylated subdomains. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4455–4465. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07896.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Leonard J., Serup P., Gonzalez G., Edlund T., Montminy M. The LIM family transcription factor Isl-1 requires cAMP response element binding protein to promote somatostatin expression in pancreatic islet cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6247–6251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M., Manley J. L. Transcriptional repression of eukaryotic promoters. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):405–408. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F., Green M. R. A specific member of the ATF transcription factor family can mediate transcription activation by the adenovirus E1a protein. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1217–1224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90686-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin K. J., Lillie J. W., Green M. R. Evidence for interaction of different eukaryotic transcriptional activators with distinct cellular targets. Nature. 1990 Jul 12;346(6280):147–152. doi: 10.1038/346147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofir R., Dwarki V. J., Rashid D., Verma I. M. CREB represses transcription of fos promoter: role of phosphorylation. Gene Expr. 1991 Apr;1(1):55–60. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parvin J. D., Timmers H. T., Sharp P. A. Promoter specificity of basal transcription factors. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1135–1144. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90084-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renkawitz R. Transcriptional repression in eukaryotes. Trends Genet. 1990 Jun;6(6):192–197. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90176-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Ma J., Triezenberg S., Ptashne M. GAL4-VP16 is an unusually potent transcriptional activator. Nature. 1988 Oct 6;335(6190):563–564. doi: 10.1038/335563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Ptashne M. A vector for expressing GAL4(1-147) fusions in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7539–7539. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Rangarajan P., Kliewer S., Ransone L. J., Bolado J., Yang N., Verma I. M., Evans R. M. Functional antagonism between oncoprotein c-Jun and the glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1217–1226. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90397-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheng M., Thompson M. A., Greenberg M. E. CREB: a Ca(2+)-regulated transcription factor phosphorylated by calmodulin-dependent kinases. Science. 1991 Jun 7;252(5011):1427–1430. doi: 10.1126/science.1646483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y., Seto E., Chang L. S., Shenk T. Transcriptional repression by YY1, a human GLI-Krüppel-related protein, and relief of repression by adenovirus E1A protein. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):377–388. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90189-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K. Heat shock factor and the heat shock response. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):363–366. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90452-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southgate C. D., Green M. R. The HIV-1 Tat protein activates transcription from an upstream DNA-binding site: implications for Tat function. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2496–2507. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanese N., Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Coactivators for a proline-rich activator purified from the multisubunit human TFIID complex. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12A):2212–2224. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12a.2212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto A., Nyunoya H., Morita T., Sato T., Shimotohno K. Isolation of cDNAs for DNA-binding proteins which specifically bind to a tax-responsive enhancer element in the long terminal repeat of human T-cell leukemia virus type I. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1420–1426. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1420-1426.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. K., Gonzalez G. A., Menzel P., Rivier J., Montminy M. R. Characterization of a bipartite activator domain in transcription factor CREB. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):611–617. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90664-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Yen H. F., Chambard J. C., Sun Y. L., Smeal T., Schmidt T. J., Drouin J., Karin M. Transcriptional interference between c-Jun and the glucocorticoid receptor: mutual inhibition of DNA binding due to direct protein-protein interaction. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1205–1215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90396-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura T., Fujisawa J., Yoshida M. Multiple cDNA clones encoding nuclear proteins that bind to the tax-dependent enhancer of HTLV-1: all contain a leucine zipper structure and basic amino acid domain. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2537–2542. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07434.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]