Abstract
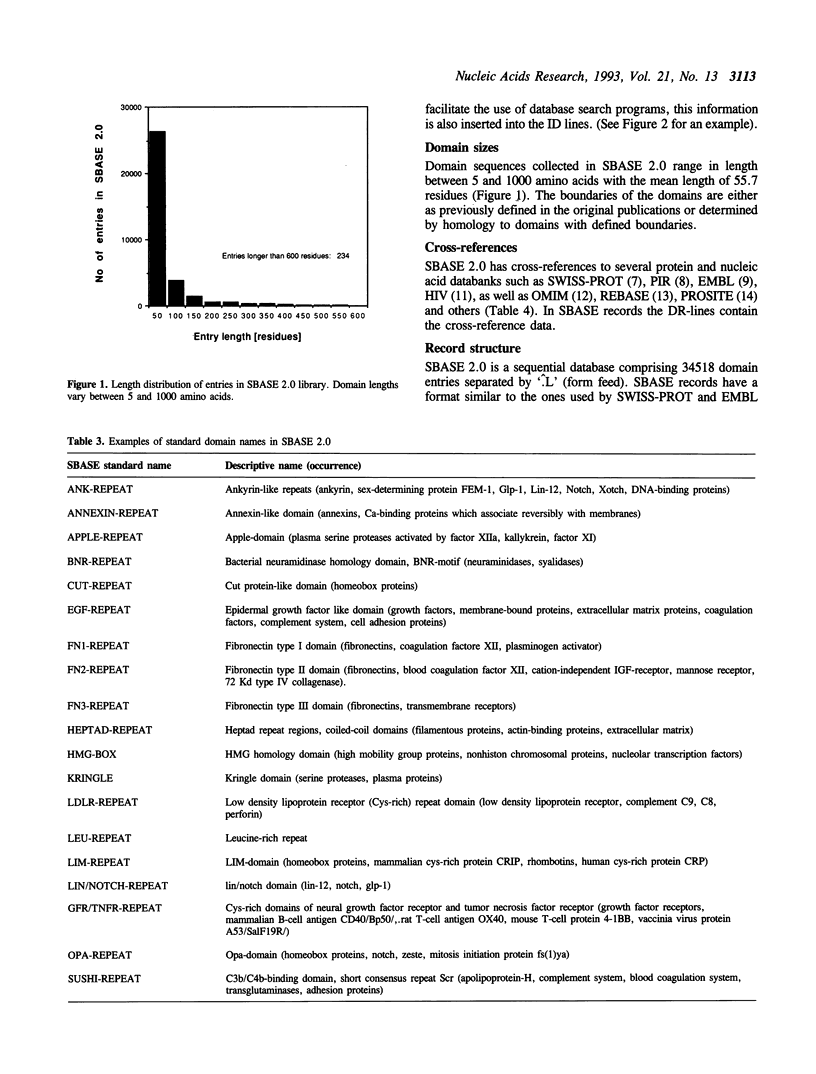
SBASE 2.0 is the second release of SBASE, a collection of annotated protein domain sequences. SBASE entries represent various structural, functional, ligand-binding and topogenic segments of proteins [Pongor, S. et al. (1993) Prot. Eng., in press]. This release contains 34,518 entries provided with standardized names and it is cross-referenced to the major protein and nucleic acid databanks as well as to the PROSITE catalog of protein sequence patterns [Bairoch, A. (1992) Nucl. Acids Res., 20 suppl, 2013-2018]. SBASE can be used for establishing domain homologies using different database-search tools such as FASTA [Lipman and Pearson (1985) Science, 227, 1436-1441], FASTDB [Brutlag et al. (1990) Comp. Appl. Biosci., 6, 237-245] or BLAST3 [Altschul and Lipman (1990) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 87, 5509-5513] which is especially useful in the case of loosely defined domain types for which efficient consensus patterns can not be established. SBASE 2.0 and a set of search and retrieval tools are freely available on request to the authors or by anonymous 'ftp' file transfer from mean value of ftp.icgeb.trieste.it.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Lipman D. J. Protein database searches for multiple alignments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5509–5513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bairoch A., Boeckmann B. The SWISS-PROT protein sequence data bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 11;20 (Suppl):2019–2022. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.suppl.2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bairoch A. PROSITE: a dictionary of sites and patterns in proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 11;20 (Suppl):2013–2018. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.suppl.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker W. C., George D. G., Mewes H. W., Tsugita A. The PIR-International Protein Sequence Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 11;20 (Suppl):2023–2026. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.suppl.2023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker W. C., Hunt L. T., George D. G. Identifying domains in protein sequences. Protein Seq Data Anal. 1988;1(5):363–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M., Norman D. G., Campbell I. D. Protein modules. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Jan;16(1):13–17. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90009-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brutlag D. L., Dautricourt J. P., Maulik S., Relph J. Improved sensitivity of biological sequence database searches. Comput Appl Biosci. 1990 Jul;6(3):237–245. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/6.3.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burks C., Cinkosky M. J., Fischer W. M., Gilna P., Hayden J. E., Keen G. M., Kelly M., Kristofferson D., Lawrence J. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 11;20 (Suppl):2065–2069. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.suppl.2065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Henikoff J. G. Automated assembly of protein blocks for database searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 11;19(23):6565–6572. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.23.6565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Fuchs R., Stoehr P. J., Cameron G. N. The EMBL Data Library. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 11;20 (Suppl):2071–2074. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.suppl.2071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. J., Macelis D. Restriction enzymes and their isoschizomers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 11;20 (Suppl):2167–2180. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.suppl.2167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon G., Paladini R., Tisminetzky S., Cserzö M., Hátsági Z., Tossi A., Pongor S. Improved detection of homology in distantly related proteins: similarity of adducin with actin-binding proteins. Protein Seq Data Anal. 1992;5(1):39–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Annau T. M., Chandrasegaran S. Finding sequence motifs in groups of functionally related proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):826–830. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. F., Smith T. F. Automatic generation of primary sequence patterns from sets of related protein sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):118–122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



