Abstract
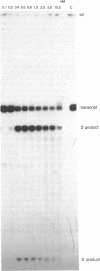
To identify the divalent metal ions that can support the self-cleavage activity of the genomic ribozyme of human hepatitis delta virus (HDV), we tested the activity of various divalent metal ions in the ribozyme reactions catalyzed by HDV88 (683-770 nt) and 88DI3 (HDV88 with the sequence from 740-752 nt deleted). Among various metal ions tested, Mg2+, Mn2+, Ca2+ and Sr2+ efficiently supported the self-cleavage reactions of the HDV88 and 88DI3 ribozymes. In the case of the 88DI3 ribozyme, other divalent metal ions, such as Cd2+, Ba2+, Co2+, Pb2+ and Zn2+, were also able to support the self-cleavage reaction to some extent (< 10%). In the presence of spermidine (0.5 mM), the cleavage reaction was promoted at lower concentrations of effective divalent metal ions. The HDV ribozyme represents the only example of ribozyme to date of a ribozyme that catalyzes the self-cleavage reaction in the presence of Ca2+ ions as efficiently as it does in the presence of Mg2+ ions.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Been M. D., Perrotta A. T., Rosenstein S. P. Secondary structure of the self-cleaving RNA of hepatitis delta virus: applications to catalytic RNA design. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 1;31(47):11843–11852. doi: 10.1021/bi00162a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belinsky M. G., Britton E., Dinter-Gottlieb G. Modification interference analysis of a self-cleaving RNA from hepatitis delta virus. FASEB J. 1993 Jan;7(1):130–136. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.1.8422959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. The chemistry of self-splicing RNA and RNA enzymes. Science. 1987 Jun 19;236(4808):1532–1539. doi: 10.1126/science.2438771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahm S. C., Uhlenbeck O. C. Role of divalent metal ions in the hammerhead RNA cleavage reaction. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 1;30(39):9464–9469. doi: 10.1021/bi00103a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier-Takada C., Haydock K., Allen L., Altman S. Metal ion requirements and other aspects of the reaction catalyzed by M1 RNA, the RNA subunit of ribonuclease P from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1986 Apr 8;25(7):1509–1515. doi: 10.1021/bi00355a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmquist B. Elimination of adventitious metals. Methods Enzymol. 1988;158:6–12. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)58042-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazakov S., Altman S. A trinucleotide can promote metal ion-dependent specific cleavage of RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):7939–7943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.7939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar P. K., Suh Y. A., Miyashiro H., Nishikawa F., Kawakami J., Taira K., Nishikawa S. Random mutations to evaluate the role of bases at two important single-stranded regions of genomic HDV ribozyme. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 11;20(15):3919–3924. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.15.3919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar P. K., Suh Y. A., Taira K., Nishikawa S. Point and compensation mutations to evaluate essential stem structures of genomic HDV ribozyme. FASEB J. 1993 Jan;7(1):124–129. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.1.8422958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo M. Y., Sharmeen L., Dinter-Gottlieb G., Taylor J. Characterization of self-cleaving RNA sequences on the genome and antigenome of human hepatitis delta virus. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4439–4444. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4439-4444.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman N., Joyce G. F. Evolution in vitro of an RNA enzyme with altered metal dependence. Nature. 1993 Jan 14;361(6408):182–185. doi: 10.1038/361182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Chang M. F., Shieh C. K., Kamahora T., Vannier D. M., Govindarajan S., Lai M. M. Molecular cloning and sequencing of a human hepatitis delta (delta) virus RNA. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):343–346. doi: 10.1038/329343a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrotta A. T., Been M. D. A pseudoknot-like structure required for efficient self-cleavage of hepatitis delta virus RNA. Nature. 1991 Apr 4;350(6317):434–436. doi: 10.1038/350434a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccirilli J. A., Vyle J. S., Caruthers M. H., Cech T. R. Metal ion catalysis in the Tetrahymena ribozyme reaction. Nature. 1993 Jan 7;361(6407):85–88. doi: 10.1038/361085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenstein S. P., Been M. D. Self-cleavage of hepatitis delta virus genomic strand RNA is enhanced under partially denaturing conditions. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 4;29(35):8011–8016. doi: 10.1021/bi00487a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharmeen L., Kuo M. Y., Dinter-Gottlieb G., Taylor J. Antigenomic RNA of human hepatitis delta virus can undergo self-cleavage. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2674–2679. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2674-2679.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D., Burgin A. B., Haas E. S., Pace N. R. Influence of metal ions on the ribonuclease P reaction. Distinguishing substrate binding from catalysis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2429–2436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto N., Kierzek R., Turner D. H. Kinetics for reaction of a circularized intervening sequence with CU, UCU, CUCU, and CUCUCU: mechanistic implications from the dependence on temperature and on oligomer and Mg2+ concentrations. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 23;27(17):6384–6392. doi: 10.1021/bi00417a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh Y. A., Kumar P. K., Nishikawa F., Kayano E., Nakai S., Odai O., Uesugi S., Taira K., Nishikawa S. Deletion of internal sequence on the HDV-ribozyme: elucidation of functionally important single-stranded loop regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 25;20(4):747–753. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.4.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thill G., Blumenfeld M., Lescure F., Vasseur M. Self-cleavage of a 71 nucleotide-long ribozyme derived from hepatitis delta virus genomic RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 11;19(23):6519–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.23.6519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchimaru T., Uebayasi M., Tanabe K., Taira K. Theoretical analyses on the role of Mg2+ ions in ribozyme reactions. FASEB J. 1993 Jan;7(1):137–142. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.1.8422960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uebayasi M., Uchimaru T., Tanabe K., Nishikawa S., Taira K. Preferential chelation of cationic ligands to axial-equatorial oxygens over equatorial-equatorial dianionic oxygens: implication to the mechanism of action of ribozymes. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser. 1991;(25):107–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. N., Lai M. M. Reversible cleavage and ligation of hepatitis delta virus RNA. Science. 1989 Feb 3;243(4891):652–654. doi: 10.1126/science.2492677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]