Abstract
Piriformospora indica is an endophytic fungus that colonizes roots of many plant species and promotes growth and resistance to certain plant pathogens. Despite its potential use in agriculture, little is known on the molecular basis of this beneficial plant-fungal interaction. In a genetic screen for plants, which do not show a P. indica- induced growth response, we isolated an Arabidopsis mutant in the OXI1 (Oxidative Signal Inducible1) gene. OXI1 has been characterized as a protein kinase which plays a role in pathogen response and is regulated by H2O2 and PDK1 (3-PHOSPHOINOSITIDE-DEPENDENT PROTEIN KINASE1). A genetic analysis showed that double mutants of the two closely related PDK1.1 and PDK1.2 genes are defective in the growth response to P. indica. While OXI1 and PDK1 gene expression is upregulated in P. indica-colonized roots, defense genes are downregulated, indicating that the fungus suppresses plant defense reactions. PDK1 is activated by phosphatidic acid (PA) and P. indica triggers PA synthesis in Arabidopsis plants. Under beneficial co-cultivation conditions, H2O2 formation is even reduced by the fungus. Importantly, phospholipase D (PLD)α1 or PLDδ mutants, which are impaired in PA synthesis do not show growth promotion in response to fungal infection. These data establish that the P. indica-stimulated growth response is mediated by a pathway consisting of the PLD-PDK1-OXI1 cascade.
Author Summary
Like many root-colonizing microbes, the primitive Basidiomycete fungus Piriformospora indica colonizes the roots of many plant species and promotes their growth. The lack of host specificity suggests that the plant response to this endopyhte is based on general signalling processes. In a genetic screen for Arabidopsis plants, which do not show a P. indica-induced growth response, we isolated a mutant in the OXI1 (Oxidative Signal Inducible1) gene. Previously, this protein kinase has been shown to play a role in pathogen response and is regulated by H2O2 and PDK1 (3-PHOSPHOINOSITIDE-DEPENDENT PROTEIN KINASE1). A genetic analysis showed that deletion of PDK1 also abolishes the growth response to P. indica. PDK1 is activated by phosphatidic acid (PA). P. indica triggers PA synthesis and mutants impaired in PA synthesis do not show growth promotion in response to fungal infection. Since defense processes are repressed by P. indica, we propose that a pathway consisting of the PLD-PDK1-OXI1 cascade mediates the P. indica-induced growth response.
Introduction
The endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica, a cultivable basidiomycete of Sebacinales, colonizes the roots of many plant species including Arabidopsis [1], [2]. Like other members of Sebacinales, P. indica is found worldwide in association with roots [3], and stimulates growth, biomass and seed production of the hosts [1], [2], [4]–[11]. The fungus promotes nitrate and phosphate uptake and metabolism [6], [12], [13]. P. indica also confers resistance against abiotic [7], [14], [15] and biotic stress [2], [16]. The broad host range of P. indica indicates that the beneficial interaction may be based on general recognition and signalling pathways. Little is yet understood about the molecular steps leading to P. indica-induced growth promotion. Plant growth can be induced by a fungal exudate component [9], suggesting the involvement of specific receptors at the plant cell surface. In support of this hypothesis, an atypical receptor kinase with leucine-rich repeats was identified to be required for the growth response in Arabidopsis [5]. Moreover, a rapid increase in the intracellular calcium concentration in the root cells indicates that an intracellular signalling cascade is triggered early upon plant-fungal interaction [9]. So far, however, no further components of the signalling pathway have been identified.
In mammals, the phospholipid-binding 3-PHOSPHOINOSITIDE-DEPENDENT PROTEIN KINASE1 (PDK1) sustains and regulates the balance between growth, cell division and apoptosis [17]–[19]. PDK1 is a member of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase A / protein kinase G / protein kinase C (AGC) kinase family [17] and the Arabidopsis homolog AtPDK1 is regulated by binding to the lipid phosphatidic acid (PA) [20], [21]. Phospholipase D (PLD)α1 is the main producer of PA in Arabidopsis roots [22]. In plants, PA is a second messenger [23], [24] that links lipid signalling to oxidative stress signalling [25], e.g. during abscisic acid-induced stomatal closure or defense against pathogens [26]–[28]. PDK1 is the only AGC kinase in plants with an identifiable lipid-binding domain [20], [21], [29], [30].
OXIDATIVE SIGNAL INDUCIBLE1 (OXI1) is a serine/threonine kinase necessary for oxidative burst-mediated signalling in Arabidopsis roots [20], [31]. OXI1 is a member of the AGC protein kinase family (also called AGC2-1 [30]) and its expression is induced by H2O2 [31]. OXI1 is required for full activation of the two mitogen-activating protein kinases 3 and 6 (MPK3 and MPK6) after treatment with reactive oxygen species (ROS) or elicitors and for different ROS-mediated processes including basal resistance to Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis (previously known as Peronospora parasitica) infection and root hair growth [31]. Among all AGC kinases in Arabidopsis [30], AGC2-2 might be considered as an OXI1 homolog, however this kinase has not yet been investigated. The active OXI1 phosphorylates and thus activates the downstream serine/threonine kinase PTI1-2 in response to ROS and phospholipid signals [21], and many of these signals derive from microbial pathogens or elicitors, such as cell wall fragments or specific protein factors released by pathogens [32], [33]. Besides ROS, OXI1 is also activated by PDK1 [20].
In this work, we report on the results of a genetic screen for Arabidopsis mutants, which do not respond to P. indica. By positional cloning, we have identified OXI1 as the responsible gene for the growth phenotype induced by P. indica. Since OXI1 is an AGC protein kinase that can be activated by H2O2 and PDK1, we also tested whether mutants in PDK1.1 and PDK1.2 are defective in the P. indica-induced growth phenotype. We found that pdk1.1 pdk1.2 double knock out mutants do not respond to P. indica. The fungus stimulates PA, but not H2O2 synthesis in Arabidopsis plants. PA is produced by several pathways including by PLD. When PA synthesis was reduced by inactivation of phospholipase D (PLD)α1 or PLDδ, the P. indica-induced growth promotion was compromised. These results suggest that P. indica stimulates growth by PA-mediated activation of PDK1, which subsequently activates OXI1.
Results
Beneficial interaction between P. indica and Arabidopsis requires OXI1
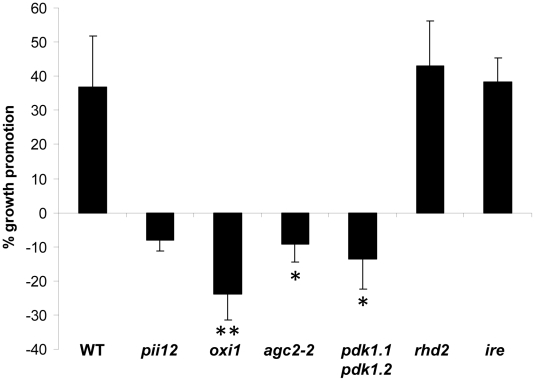
Arabidopsis plants co-cultivated with P. indica are taller than the uncolonized controls [1], [2]. On the basis of this growth phenotype, we searched for ethylmethane sulfonate-induced mutants, which grow like uncolonized plants or are smaller in the presence of the fungus. One of these mutants, called Piriformospora indica-insensitive12 (pii12), was smaller in the presence of the fungus (Figure 1) and mapped to a region on chromosome 3 that included oxi1. Moreover, the pii12 mutant had reduced root hair lengths and reduced oxi1 mRNA levels in roots and shoots when compared to the wild-type (Figure S1 in Text S1). Sequence analysis uncovered that the mutant lacks a 19 bp segment upstream of the putative translation start site, while the coding region was intact. To clarify whether OXI1 is responsible for the absence of the P. indica-induced growth response in Arabidopsis, pii12 was complemented with the full-length cDNA of OXI1. Three independent transformants had higher OXI1 mRNA levels when compared to pii12 and showed a growth response to the fungus, which was comparable to the wild type (Figure S2 in Text S1). An independent T-DNA insertion line for oxi1 was used for further analysis, because it completely lacked OXI1 mRNA (Figure S3A in Text S1). Like pii12, growth promotion by P. indica was inhibited in oxi1 plants (Figure 1 and Figure S2 in Text S1). These results confirm that a deletion in the OXI1 promoter region is responsible for the absence of the growth response of Arabidopsis plants to P. indica. We conclude that P. indica-induced growth promotion in Arabidopsis requires OXI1.
Figure 1. P. indica-mediated increase in fresh weight (%) of wild-type (WT) and mutant plants.
Data are based on 5–9 independent experiments with 10 plants per treatment. Bars represent SEs (significant difference to WT; * p<0.05; ** p<0.001).
H2O2 production is not stimulated upon fungal infection of Arabidopsis roots
Previously, it was shown that OXI1 is induced by H2O2 in the roots [31]. However, H2O2 measurements and staining of colonized wild type roots with nitrobluetetrazolium chloride (NBT) uncovered that P. indica does not induce H2O2 accumulation [9]. Under growth promoting conditions, we even observed a repression of H2O2 accumulation in the roots (Figure S4C in Text S1). Also high concentrations of fungal hyphae, which are no longer beneficial for the plants, did not result in H2O2 production in the roots (H2O2 levels, no fungal treatment: 17.4±2.1 nmol/g fresh weight; non-beneficial interaction: 17.1±1.7 nmol/g fresh weight; n = 9 independent experiments).
Root hair mutant ire and rhd2 plants are not compromised in P. indica-induced growth promotion of Arabidopsis
The inability of oxi1 plants to respond to P. indica might be caused by their shorter root hairs [31]. However, mRNA levels for the P. indica translation elongation factor1 (Pitef1) were comparable in oxi1 and wild-type roots (Figure S5 in Text S1), indicating that root colonization does not differ from the wild-type in oxi1.
We also investigated the interaction of P. indica with two other mutants with reduced root hair phenotypes: the AGC kinase ire and the NADPH oxidase rhd2 ([34], [35] Figure S3B in Text S1). Growth of these mutants was promoted by P. indica (Figure 1), and the degree of root colonization was again comparable to the wild-type (Figure S5 in Text S1). Therefore, the root hair phenotype does not seem to be responsible for the impaired interaction of oxi1 with P. indica. Furthermore, among the RHD genes expressed in Arabidopsis roots, RHD2 shows the highest expression level and RHD2 is responsible for most of the H2O2 production in the roots [35]. Thus, the lower H2O2 production in rhd2 roots does not compromise the beneficial plant-fungal interaction.
AGC2-2, a homolog of OXI1, is required for P. indica-induced growth promotion
AGC2-2 (At4g13000) is the closest homolog of OXI1 (see phylogenetic tree in [30]) and shares >60% sequence identity to OXI1. Both kinases contain an aspartic acid residue in their active site (D149 in OXI1 and D146 in AGC2-2) and share a conserved PDK1 binding site, the FxxF motif, at their C-terminal ends [20]. However, in contrast to the OXI1 mRNA level, the AGC2-2 mRNA level is not regulated by ROS (https://www.genevestigator.com). agc2-2 plants did not show any visible phenotype, produced the same amount of seeds, and – in contrast to oxi1 [31] - root hairs of agc2-2 plants were not shorter than those of wild-type plants (Figure S1B in Text S1). However, despite the fact that root colonization was not affected by the agc2-2 mutation (Figure S5 in Text S1), agc2-2 plants were compromised in the growth response to the fungus (Figure 1). Thus, besides OXI1, the so far uncharacterized AGC2-2 is important for P. indica-mediated growth promotion in Arabidopsis. Attempts to generate homozygous oxi1 agc2-2 double knock out lines failed: among 98 F2 plants obtained from crosses of the two mutants, all plants, which were homozygote for either oxi1 or agc2-2 were heterozygote for the other kinase gene. This suggests that both OXI1 and AGC2-2 might play a role in embryogenesis in Arabidopsis.
PDK1 is required for P. indica-induced growth promotion
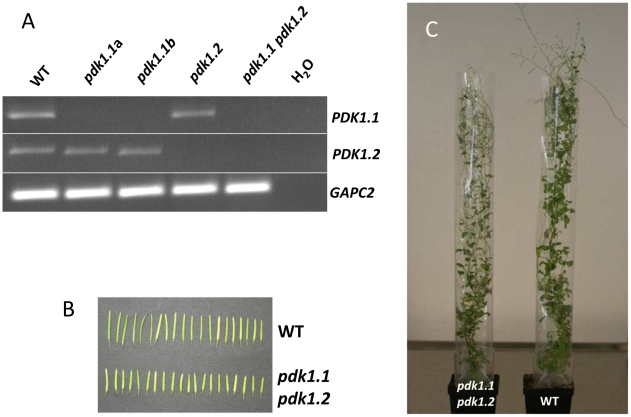
We next tried to identify the upstream components of the OXI1 cascade that is responsible for the fungal growth effect in plants. Previously, it was shown that PDK1 and H2O2 can activate OXI1 in Arabidopsis [20], [21]. Because P. indica infection did not alter H2O2 levels in Arabidopsis, we turned our attention to the two closely related PDK1 genes, PDK1.1 and PDK1.2 (92% homology at the amino acid level), which are present in the Arabidopsis genome (cf. phylogenetic tree of AGC kinases in [30]). Both PDK1 genes are expressed in roots. We generated a pdk1.1 pdk1.2 double knock out line. RT-PCR analysis confirmed that neither PDK1.1 nor PDK1.2 transcripts can be detected in the double mutant line (Figure 2A). A phenotypic analysis revealed that pdk1.1 pdk1.2 plants are smaller than the wild-type (Figure 2C), have shorter siliques (Figure 2B) and produce only 41%±6.8% (n = 23) of the seeds of the wild-type. Importantly, fungal induced growth promotion in pdk1.1 pdk1.2 plants was clearly compromised (Figure 1), whereas root colonization was comparable to the wild-type (Figure S5 in Text S1). Therefore, besides general functions in growth regulation, the combination of PDK1.1 and PDK1.2 is required for P. indica-induced growth promotion in Arabidopsis.
Figure 2. Characterization of PDK1 mutants.
(A) PDK1.1, PDK1.2 and GAPC2 transcript amounts were determined by RT-PCR with gene-specific primer pairs. The pdk1.1 pdk1.2 line does not contain pdk1 transcripts. Two independent pdk1.1 lines (a and b), pdk1.2 and pdk1.1 pdk1.2 were analysed. (B) Siliques and (C) phenotypes of pdk1.1 pdk1.2 and wild-type plants are shown.
PLDα1 and PLDδ are required for P. indica-mediated growth promotion
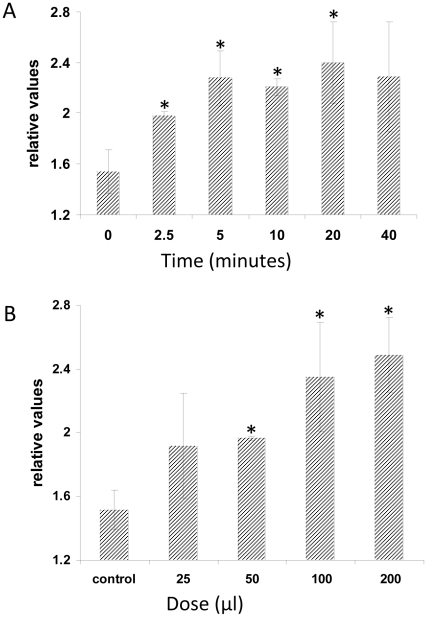
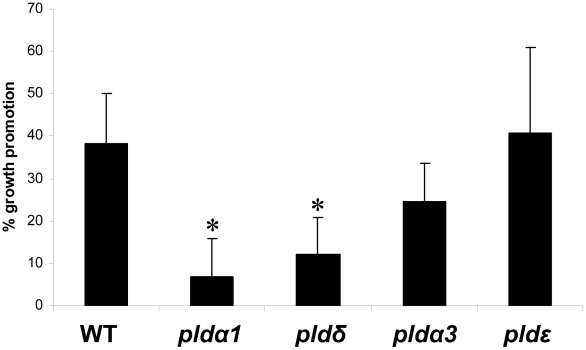
After having established that PDK1 is an important component of the P. indica-induced growth response pathway, we tried to go even further up in the cascade to identify the regulator of the PDK1s. PDK1 in Arabidopsis is activated by PA. PA is synthesized by PLD and by PLC/diacylglycerol kinase. PA in roots is mainly generated by PLD activity [28], [36]. The Arabidopsis genome contains 12 genes for PLDs, which are classified into six types, PLDα (1–3), β (1 and 2), γ (1–3), δ, ε and ζ (1 and 2) [37]. The most abundantly expressed pld genes in roots are pldα1 and pldδ [22], [38]. PLDα1 is responsible for most of the PA production in roots, and the PA content is severely reduced in the roots of pldα1 knock out mutants [22]. Furthermore, wounding-induced PA production is completely eliminated in the pldα1 pldδ double knock out line [39]. Application of a P. indica exudate fraction, which promotes plant growth [9] stimulates PA accumulation in a time- and dose-dependent manner in the roots (Figure 3). Furthermore, the growth response of pldα1 and pldδ insertion lines to P. indica was severely impaired (Figure 4). In comparison, the response of pldα3 und pldε (Figure 4, Figure S3C in Text S1) plants to P. indica was similar to wild type. These results indicate that signals from the fungus activate PA synthesis via PLDα1 and PLDδ in the roots.
Figure 3. Plant PA levels increase in response to treatment with P. indica exudate.
Five-days old seedlings were 32Pi-labelled overnight and then treated with P. indica exudates. (A) Time series of plant PA amounts induced by 50 µl P. indica exudates. (B) Dose response curve of plant PA production in response to different amounts of P. indica exudate. Lipids were extracted, analysed by thin layer chromatography and PA levels were quantified by phosphoimaging. 32P-PA control levels were ∼1.5% of the total 32P-labelled lipids. The values represent: radioactivity [+P. indica extract/+buffer]. Bars represent SEs, based on 3 independent experiments. Bars marked with an asterisk are significantly different compared to wild type (p<0.05).
Figure 4. P. indica-induced increases in fresh weight (%) of wild-type and pld mutants.
Data are based on at least three independent experiments with 10 plants per treatment. SEs are shown. Bars marked with an asterisk are significantly different compared to wild type (p<0.05).
Expression of defense-related genes is downregulated but independent of the OXI1 pathway under beneficial conditions
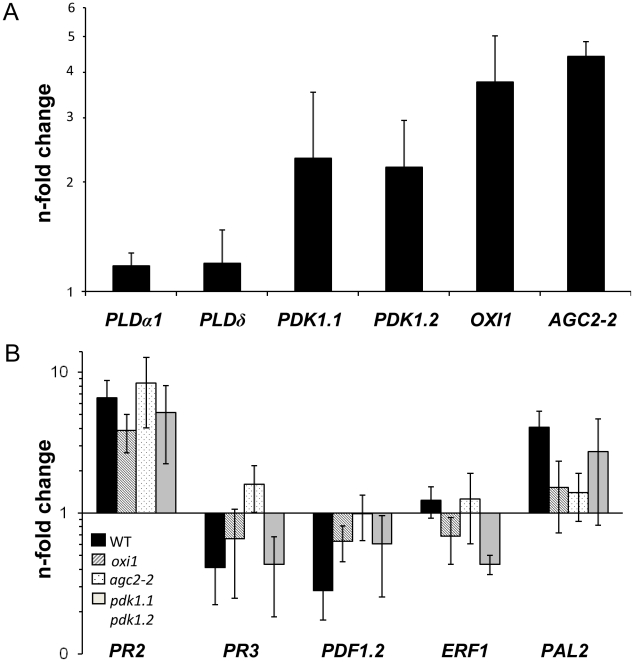
Compared to uncolonized roots, the two PDK1 mRNA levels were ∼2-fold higher and the OXI1 and AGC2-2 mRNA levels increased ∼4-fold in P. indica-colonized roots (Figure 5A). In contrast, three classical defense genes, which are targets of PDK1 and OXI1 signalling after pathogen infections (PR3, PDF1.2, ERF1 [20], [21], [31]), are downregulated in P. indica-colonized wild-type roots (Figure 5B). Thus, upregulation of the PDK1 and OXI1 mRNA by P. indica does not result in the activation of the three defense genes. The expression level of defense genes is also downregulated in the colonized pdk1.1 pdk1.2, oxi1 and agc2-2 plants. PR2 is mildly upregulated by the fungus, but this occurs also in the colonized mutants (Figure 5B). Thus, the regulation of the defense genes occurs independently of the OXI1 pathway under beneficial co-cultivation conditions of the two symbionts.
Figure 5. Expression levels of PDK1, OXI1 and AGC2-2 genes and defense genes in colonized wild-type or mutant roots relative to uncolonized control plants.
Panel A shows PDK1, OXI1 and AGC2-2 expression levels and panel B shows expression levels of several defense genes. RNA was extracted from roots and real-time PCR analyses were performed with the housekeeping gene UBQ5 as control. Calculations were performed according to [63]. Bars show the mean out of at least four independent experiments with SEs. Data are presented on a log scale.
Expression of defense-related genes is upregulated under non-beneficial conditions
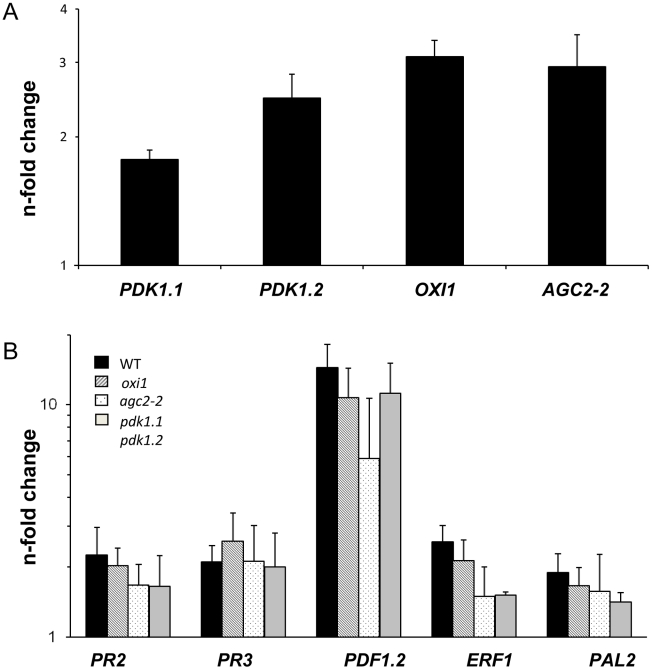
To test whether the PDK1, OXI1 and AGC2-2 kinases activate defense processes under non-beneficial conditions, we inoculated Arabidopsis plants with high doses of P. indica. Seven days after transfer to a dense fungal lawn, the seedlings still continued to grow (Figure S4A in Text S1), but visible accumulation of anthocyanin in the aerial parts were indicative of a stress response in the plants. No H2O2 accumulation would be detected under these co-cultivation conditions (Figure S4B in Text S1), however the PDK1, OXI1 and AGC2-2 mRNA levels were moderately upregulated (Figure 6A). In contrast to beneficial co-cultivation conditions, also defense genes, and in particular PDF1.2, were upregulated. However, this response was similar in wild type, oxi1, agc2-2 and pdk1.1 pdk1.2 mutants (Figure 6B). Therefore, upregulation of defense genes under non-physiological co-cultivation conditions is not mediated by the OXI1 pathway as well (Figure 6B).
Figure 6. Expression levels of PDK1, OXI1 and AGC2-2 genes and defense genes after treatment with a high dosis of P. indica (for details, cf. Methods and Materials and Figure S4A,B in Text S1).
Panel A shows PDK1, OXI1 and AGC2-2 expression levels and panel B shows expression levels of several defense genes. RNA was extracted from roots and real-time PCR analyses were performed with the housekeeping gene GAPC2 as control. Calculations were performed according to [63]. Bars show fold-induction of RNA values from wild type and agc mutant roots 7 days after co-cultivation on a fungal lawn relative to the RNA levels from seedlings grown in the absence of the fungus. Bars show the mean out of at least three independent experiments with SEs. Data are presented on a log scale.
Discussion
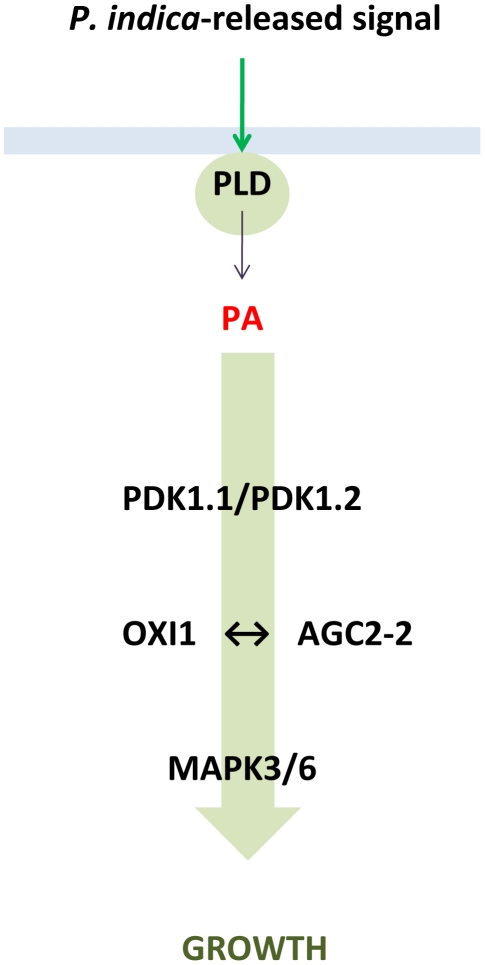
Growth promotion induced by P. indica in Arabidopsis depends on various compounds including phytohormones such as auxin and cytokinins [40], a balanced activation of defense responses in the roots [7], [41], the redox state in the cytoplasm [10] and sufficient nutrient supply [6]. In this work, we demonstrate that the OXI1 pathway is another important component, which mediates the beneficial interaction between P. indica and Arabidopsis. Moreover, we identified PLDα1, PLDδ and PDK1 as components, which are required for P. indica-induced growth promotion in Arabidopsis. Under beneficial co-cultivation conditions, P. indica stimulates PA synthesis, but not H2O2 production in Arabidopsis plants. The genetic evidence presented here and the biochemical data available for the OXI1 signalling pathway in pathogenic systems [20], [21], [28], [36] suggest that P. indica regulates plant growth via PA-stimulated PDK1 activation that subsequently triggers activation of the OXI1 and AGC2-2 protein kinases (Figure 7). The regulation of defense gene expression in response to nonbeneficial P. indica doses occurs also in pdk1.1 pdk1.2, oxi1 and agc2-2 mutants, indicating that the defense gene regulation is mediated by a pathway that functions independently of the OXI1 cascade.
Figure 7. Proposed model describing the role of PLD, PA, AGC and MAP kinases in the beneficial interaction between P. indica and Arabidopsis.
For MPK, see [9].
OXI1 and AGC2-2
The pii12 and oxi1 mutants are impaired in P. indica-induced growth promotion (Figure 1, Figure S2 in Text S1). The OXI1 kinase was shown to be induced by H2O2 and to activate defense responses against pathogen infections [20], [21], [31], [42]. However, H2O2 production is repressed in P. indica-colonized roots under beneficial co-cultivation conditions (Figure S4C in Text S1) and some defense genes are downregulated under beneficial conditions (Figure 5B). Exposure of Arabidopsis seedlings to high doses of the fungal hyphae induces a mild defense response, which occurs also in oxi1 mutants (Figure 6B). Thus, OXI1 is required for the growth response but is not involved in defense gene activation in this beneficial interaction (cf. below). Interestingly, the OXI1 overexpressor lines behaved like the wild-type (Figure S2 in Text S1) suggesting that wild-type amounts of the kinase are sufficient for the beneficial interaction. Furthermore, AGC2-2, a so far uncharacterized homolog of OXI1, is also required for the beneficial interaction. AGC2-2 is not induced by H2O2, but by P. indica in wild-type roots (Figure 5A). Since attempts to isolate a homozygote oxi1 agc2-2 double mutant failed and since the two single knock out lines fail to respond to P. indica, the two kinases have important and presumably different functions. Interestingly, this highly related pair of protein kinases resembles the OXI1-activated MAPKs MPK3 and MPK6, for which MPK3 is inducible by pathogens, while MPK6 is constitutively expressed and mpk3 mpk6 double mutants are embryo-lethal [9], [43]. In mammalian systems, AGC kinases play important roles in growth and proliferation. The activation mechanism of AGC kinases from both kingdoms by lipids and their conserved epitopes [17] support the idea that OXI1 and AGC2-2 play a crucial role in regulating cell growth, division and/or elongation in response to the signals from P. indica.
Because oxi1 mutants are also compromised in root hair growth, we tested two mutants with shorter root hairs, ire and rhd2. However, none of these mutants were impaired in the growth response to the fungus (Figure 1). Moreover, because rhd2 is also impaired in full production of H2O2 in roots, the inability of oxi1 to respond to P. indica is not caused by the reduced root hair phenotype or lower H2O2 levels in the roots.
PDK1s, PLDs and PA
PA is an important second messenger and is involved in regulating plant growth, proliferation, biomass production, cell expansion, as well as responses to biotic and abiotic stresses [23], [24], [26]-[28], [36], [44]–[48]. In response to stresses, PA balances and fine-tunes the appropriate plant response to environmental signals [28], [36]. PA accumulation is induced by exudate preparations from P. indica in a dose- and time-dependent manner (Figure 3), suggesting that the roots sense signalling molecules released from the fungus. The requirement of the PA-activated PDK1s for the beneficial interaction suggests a participation in growth regulation, similar to mammalians [49]–[51]. Nitrate and phosphate uptake and metabolism is stimulated by P. indica and required for growth promotion [6], [12], [13]. PA also plays important roles in nitrogen [48], [52]–[54] and phosphate signalling [55], [56]. These results might provide a link between the P. indica-induced positive growth phenotype and the primary metabolism. Further experiments are necessary to investigate a role of PDK1, OXI1 and AGC2-2 in this respect.
Interestingly, in mammals and yeast, PDK1 is a central regulatory kinase, which phosphorylates and thus activates AGC kinases in response to rises in the levels of the second messenger phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate [19], [57]. pdk1 knock-out mice are embryo-lethal [58]. Since the Arabidopsis pdk1.1 pdk1.2 double knock-out line is viable, activation of AGC kinases might be different in plant and mammalian systems [19], [57], [58].
PA is synthesized by PLD or phospholipase C/diacylgycerol kinase (PLC/DAG) [36]. PLDα1 and PLDδ are abundantly expressed in roots. We observed that their inactivation severely reduces P. indica-induced growth promotion (Figure 4). pldα1 was shown previously to contain lower PA levels in the roots [22], has reduced wounding-induced PA production, and this response is completely eliminated in the pldα1 pldδ double knock out line [39]. PLDα1 and PA have also been implicated in regulating NADPH oxidase activity and the production of H2O2 in ABA-mediated stomatal closure [25]. The plasma-membrane-bound PLDδ is activated in response to H2O2 [59]. However, since H2O2 is not accumulating in response to P. indica, the lipases might have a different function and are differently regulated in this beneficial interaction. PLDα1 and PLDδ expression is not induced by P. indica. PLDα1 activity is regulated by dynamic changes in intracellular Ca2+ levels (cf. [28]), and the Ca2+ levels in the root cytoplasm increases even faster in response to the same exudate fraction from P. indica that induces PA accumulation (Figure 3; [9]). These results suggest that signals from P. indica are decoded via the two intracellular second messengers PA and Ca2+. It remains to be determined how PA and Ca2+ cooperate to induce the appropriate plant responses, and which mechanisms determine whether they activate responses leading to a beneficial interaction or defense activation.
In conclusion, we demonstrate that in the beneficial interaction between P. indica and Arabidopsis the OXI1 pathway constitutes a protein kinase signalling pathway that confers growth stimulation (Figure 7). We propose a model whereby roots sense signals derived from P. indica by activating a signalling pathway that results in PA-mediated activation of PDK1, which subsequently activates the OXI1 and AGC2-2 protein kinases. Since MPK6 is a downstream target of OXI1 [31] and required for P. indica-mediated growth promotion [9], it is possible that MPK6 might be an additional component of this pathway. Future studies on the targets of the OXI1 pathway should help to clarify by which mechanism growth promotion occurs in plants and how this knowledge could be used to improve yield and productivity in agriculture. It also remains to be determined whether promotion of plant growth by mycorrhizal fungi or plant-growth promoting bacteria requires the same pathway, and how the Arabidopsis mutants analysed in this study respond to pathogens.
Materials and Methods
Growth conditions of plants and fungi, co-cultivation experiments
Wild-type Arabidopsis thaliana seeds and seeds from the homozygote T-DNA insertion lines were surface-sterilized and placed on Petri dishes containing MS nutrient medium [60]. After cold treatment at 4°C for 48 h, plates were incubated for 7 days at 22°C under continuous illumination (100 µmol m−2 sec−1). P. indica was cultured as described previously [1], [4] on Kaefer medium. Nine day-old A. thaliana seedlings were transferred to nylon disks (mesh size 70 µm) and placed on top of a modified PNM culture medium (5 mM KNO3, 2 mM MgSO4, 2 mM Ca(NO3)2, 0.01 µM FeSO4, 70 µM H3BO3, 14 µM MnCl2, 0.5 µM CuSO4, 1 µM ZnSO4, 0,2 µM Na2MoO4, 0.01 µM CoCl2, 10.5 g L−1 agar, pH 5.6), in 90 mm Petri dishes. Fungal plugs of 5 mm in diameter were placed at a distance of 1 cm from the roots. Control seedlings remain untreated. Plates were incubated at 22°C under continuous illumination from the side (80 µmol m−2 sec−1).
The following homozygote T-DNA insertion lines were used: rhd2 (At5g51060; [35] obtained from Prof. V. Zársky, Prague, Czech Republic), ire (At5g62310) Salk_043276, oxi1 (At3g25250) Gabi_355H08, agc2-2 (At4g13000) Salk_083220, pdk1.1a (At5g04510) Salk_113251, pdk1.1b (At5g04510) Salk_007800, pdk1.2 (At3g10540) Sail_450_B01, pldα1-1 (At3g15730, [61]) Salk_067533, pldδ (At4g35790, [61]) Salk_023247, pldα3 (At5g25370) Salk_122059, pldε (At1g55180) Koncz68434. pdk1.1 pdk1.2 was generated by crosses between pdk1.1 and pdk1.2.
Experiments on vermiculite
6 week-old adult plants were used for interaction studies with P. indica. Arabidopsis seedlings, grown for 14 days on MS media, were transferred to vermiculite (rather than soil), because this allowed to harvest the intact roots including the lateral roots. The growth response of the plants to P. indica on soil and on vermiculite is comparable (data not shown). The vermiculite was mixed with the fungus (1%, w/v) which was dissolved in PNM medium. 70 ml of liquid PNM medium or inoculated PNM medium was used per plant. The fungal mycelium was obtained from two weeks old liquid cultures after the medium was removed and the mycelium was washed with an excess of distilled water. Cultivation occurred in pots in a temperature-controlled growth chamber at 22°C under short-day conditions (light intensity: 80 µmol m−2 sec−1). The sizes of the plants were monitored weekly and after six weeks the fresh weights of the shoots were determined and the roots harvested for RNA or DNA extraction.
Experiments with the fungal lawn
12-day-old seedlings were directly transferred from MS medium to a plate with a fungal lawn. The fungal lawn was obtained by placing a fungal plug on Kaefer medium and the fungus was allowed to grow for 14 days at 24°C in the dark, before the seedlings were transferred to the plate. Control seedlings were transferred to Kaefer medium without the fungus. The plates were incubated for 7 days at 22°C under continuous illumination (80 µmol m−2 sec−1) from above. Fresh weights were determined (data not shown) and RNA was extracted of the root material.
RNA analysis
RNA was isolated from the roots with an RNA isolation kit (RNeasy, Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). For quantitative RT-PCR, RNA from Arabidopsis roots grown in the absence or presence of P. indica was used. Reverse transcription of 1 µg of total RNA was performed with oligodT Primer. First strand synthesis was performed with a kit from Qiagen (Omniscript, Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). RT-PCR was conducted with the primer pairs given in Figure S6 in Text S1. P. indica was monitored with a primer pair for the translation elongation factor 1 (Pitef1; [62]). The colonized (and control) roots were removed from vermiculite, rinsed 6 times with an excess of sterile water and were frozen in liquid nitrogen for RNA or DNA extraction. One of the two plant genes (GAPC2 and UBQ5) was used as housekeeping genes for Arabiopsis roots.
Semiquantitative analysis was performed after 27 PCR cycles: the products were analysed on 2% agarose gels, stained with ethidium bromide, and visualized bands were quantified with the ImageQuant 5.0 (GE Healthcare Life Sciences). Real-time quantitative RT-PCR was performed using the iCycler iQ real-time PCR detection system and iCycler software version 2.2 (Bio-Rad, Munich, Germany). For the amplification of the PCR products, iQ SYBR Supermix (Bio-Rad) was used according to the manufactureŕs instructions in a final volume of 23 µl. The iCycler was programmed to 95°C 2 min, 35× (95°C 30 s, 55°C 40 s, 72°C 45 s), 72°C 10 min followed by a melting curve programme (55–95°C in increasing steps of 0.5°C). All reactions were repeated twice. The mRNA levels for each cDNA probe were normalized with respect to the GAPC2 and UBQ5 message levels. Fold induction values were calculated with the ΔΔCP equation of Pfaffl (2001) [63]. The ratio of a target gene was calculated in the treated sample versus the untreated control in comparison to a reference gene. The primer pairs are given in Figure S6 in Text S1.
H2O2 measurements
H2O2 was determined by an assay coupled to the peroxidase [64]. Roots (0,1 g) were homogenized in 1 mL 1 M HClO4/insoluble PVP (5%). The supernatant was clarified by centrifugation, adjusted to pH 5.6 with 5 M K2CO3 solution and incubated with 1U ascorbate oxidase for 10 min to oxidize the ascorbate. The reaction in 0.1 M phosphate buffer (pH 6.5), 3.3 mM 3-(dimethylamino) benzoic acid, 0.07 mM 3-methyl-2-benzothiazoline hydrazone and 0.3 U peroxidase was started by adding the oxidized extracts and followed by absorbance change at 590 nm and 25°C. NBT staining has been described previously [9].
PA measurements
Arabidopsis seedlings (5-days-old) were labeled overnight in 400 µL buffer (2.5 mM MES-KOH, 1 mM KCl, pH 5.7) containing 10 µCi of carrier-free PO4 3−. Samples (3 seedlings each) were treated by adding 100 µL water with or without elicitor for the times and concentrations indicated. Treatments were stopped by adding 50 µL 50% perchloric acid (w/v) and shaking the samples vigorously for 5 min. Liquid was then removed and replaced by 375 µL of CHCl3/MeOH/HCl [50∶100∶1 (v/v)] followed by 100 µL 0.9 % NaCl (w/v), to extract the lipids while shaking (10 min). A two-phase system was induced by the addition of 375 µL of CHCl3 and 200 µL of 0.9% (w/v) NaCl. The remainder of the extraction was performed as described before [32]. For quantitative analysis, lipids were separated by thin-layer chromatography (TLC) using heat-activated, potassium oxalate/EDTA-impregnated, silica TLC plates (Merck, 20×20×0.1 cm) and an alkaline solvent system of CHCl3/MeOH/25%NH4OH/H2O [90∶70∶4∶16 (v/v)], essentially as described in [65]. Phospholipids were visualized and quantified by phosphoimaging (Molecular Dynamics, Sunnyvale, CA, USA).
Statistics
All data were analysed with one-side, unpaired students t-Test (p≤0.05) in Excel.
Accession numbers
OXI1 (other names: AGC2; AGC2-1; OXIDATIVE SIGNAL-INDUCIBLE1; ATOXI1; MJL12.22), At3g25250, NP_189162.1; AGC2-2 (other names: F25G13.90; F25G13_90), At4g13000, NP_193036.1; PDK1.1 (other names: 3'-PHOSPHOINOSITIDE-DEPENDENT PROTEIN KINASE 1; ATPDK1; PDK1; T32M21.110), At5g04510, NP_568138.1; PDK1.2 (other names: PDK2; F13M14.18), At3g10540, NP_187665.2; RHD2 (other names: A. THALIANA RESPIRATORY BURST OXIDASE HOMOLOG C; ATRBOHC; K3K7.25; RBOHC; ROOT HAIR DEFECTIVE 2), At5g51060, NP_199919.1; IRE (other names: INCOMPLETE ROOT HAIR ELONGATION), At5g62310, NP_201037.1; PLDα1 (other names: MSJ11.13; PHOSPHOLIPASE D ALPHA 1; PLD), At3g15730, NP_188194.1; PLDδ (other names: ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA PHOSPHOLIPASE D DELTA; ATPLDDELTA; F4B14.60; PLDDELTA), At4g35790, NP_849501.1; PLDα3 (other names: F18G18.110; PHOSPHOLIPASE D ALPHA 3; PLDALPHA3), At5g25370, NP_197919.1; PLDε (other names: F7A10.25; PHOSPHOLIPASE D ALPHA 4; PLDALPHA4; PLDEPSILON), At1g55180, NP_175914.1
Information from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ and http://www.arabidopsis.org/
Supporting Information
Supporting information.
(DOC)
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Claudia Röppischer, Sarah Mußbach and Wendy Roels for excellent technical assistance.
Footnotes
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
IC, JV, and BS were supported by the IMPRS for Chemical Ecology, Jena. Work was supported by the SFB 604. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Peškan-Berghöfer T, Shahollari B, Giong PH, Hehl S, Markert C, et al. Association of Piriformospora indica with Arabidopsis thaliana roots represents a novel system to study beneficial plant-microbe interactions and involves early plant protein modifications in the endoplasmic reticulum and at the plasma membrane. Physiol Plant. 2004;122:465–477. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Oelmüller R, Sherameti I, Tripathi S, Varma A. Piriformospora indica, a cultivable root endophyte with multiple biotechnological applications. Symbiosis. 2009;49:1–17. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Selosse MA, Dubois MP, Alvarez N. Do Sebacinales commonly associate with plant roots as endophytes? Mycol Res. 2009;113:1062–1069. doi: 10.1016/j.mycres.2009.07.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Verma S, Varma A. Piriformospora indica, gen. et sp. nov., a new root-colonizing fungus. Mycologia. 1998;90:896–903. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Shahollari B, Vadassery J, Varma A, Oelmüller R. A leucine-rich repeat protein is required for growth promotion and enhanced seed production mediated by the endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2007;50:1–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03028.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sherameti I, Shahollari B, Venus Y, Altschmied L, Varma A, et al. The endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica stimulates the expression of nitrate reductase and the starch-degrading enzyme glucan-water dikinase in tobacco and Arabidopsis roots through a homeodomain transcription factor that binds to a conserved motif in their promoters. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:26241–26247. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M500447200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sherameti I, Venus Y, Drzewiecki C, Tripathi S, Dan VM, et al. PYK10, a beta-glucosidase located in the endoplasmatic reticulum, is crucial for the beneficial interaction between Arabidopsis thaliana and the endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica. Plant J. 2008;54:428–439. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sherameti I, Tripathi S, Varma A, Oelmüller R. The root-colonizing endophyte Piriformospora indica confers drought tolerance in Arabidopsis by stimulating the expression of drought stress-related genes in leaves. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2008;21:799–807. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-21-6-0799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Vadassery J, Ranf S, Drzewiecki C, Mithöfer A, Mazars C, et al. A cell wall extract from the endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica promotes growth of Arabidopsis seedlings and induces intracellular calcium elevation in roots. Plant J. 2009;59:193–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.03867.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Vadassery J, Tripathi S, Prasad R, Varma A, Oelmüller R. Monodehydroascorbate reductase 2 and dehydroascorbate reductase 5 are crucial for a mutualistic interaction between Piriformospora indica and Arabidopsis. J Plant Physiol. 2009;166:1263–1274. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2008.12.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Waller F, Achatz B, Baltruschat H, Fodor J, Becker K, et al. The endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica reprograms barley to salt-stress tolerance, disease resistance, and higher yield. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:13386–13391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0504423102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Shahollari B, Peškan-Berghöfer T, Oelmüller R. Receptor kinases with leucine-rich repeats are enriched in Triton X-100 insoluble plasma membrane microdomains from plants. Physiol Plant. 2004;122:397–403. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Yadav V, Kumar M, Deep DK, Kumar H, Sharma R, et al. A phosphate transporter from the root endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica plays a role in phosphate transport to the host plant. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:26532–26544. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.111021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 14.Baltruschat H, Fodor J, Harrach BD, Niemczyk E, Barna B, et al. Salt tolerance of barley induced by the root endophyte Piriformospora indica is associated with a strong increase in antioxidants. New Phytol. 2008;180:501–510. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02583.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sun C, Johnson JM, Cai D, Sherameti I, Oelmüller R, et al. Piriformospora indica confers drought tolerance in Chinese cabbage leaves by stimulating antioxidant enzymes, the expression of drought-related genes and the plastid-localized CAS protein. J Plant Physiol. 2010;167:1009–1017. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2010.02.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Stein E, Molitor A, Kogel KH, Waller F. Systemic resistance in Arabidopsis conferred by the mycorrhizal fungus Piriformospora indica requires jasmonic acid signaling and the cytoplasmic function of NPR1. Plant Cell Physiol. 2008;49:1747–1751. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcn147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Alessi DR. Discovery of PDK1, one of the missing links in insulin signal transduction. Colworth Medal Lecture. Biochem Soc Trans. 2001;29:1–14. doi: 10.1042/0300-5127:0290001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Storz P, Toker A. 3'-phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1 (PDK-1) in PI 3-kinase signaling. Front Biosci. 2002;7:d886–902. doi: 10.2741/storz. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mora A, Komander D, van Aalten DM, Alessi DR. PDK1, the master regulator of AGC kinase signal transduction. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2004;15:161–170. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2003.12.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Anthony RG, Henriques R, Helfer A, Meszaros T, Rios G, et al. A protein kinase target of a PDK1 signalling pathway is involved in root hair growth in Arabidopsis. EMBO J. 2004;23:572–581. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Anthony RG, Khan S, Costa J, Pais MS, Bögre L. The Arabidopsis protein kinase PTI1-2 is activated by convergent phosphatidic acid and oxidative stress signaling pathways downstream of PDK1 and OXI1. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:37536–37546. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M607341200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Devaiah SP, Roth MR, Baughman E, Li M, Tamura P, et al. Quantitative profiling of polar glycerolipid species from organs of wild-type Arabidopsis and a phospholipase Dα1 knockout mutant. Phytochemistry. 2006;67:1907–1924. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2006.06.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Munnik T, Meijer HJ, Ter Riet B, Hirt H, Frank W, et al. Hyperosmotic stress stimulates phospholipase D activity and elevates the levels of phosphatidic acid and diacylglycerol pyrophosphate. Plant J. 2000;22:147–154. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2000.00725.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Laxalt AM, Munnik T. Phospholipid signalling in plant defence. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2002;5:332–338. doi: 10.1016/s1369-5266(02)00268-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Zhang Y, Zhu H, Zhang Q, Li M, Yan M, et al. Phospholipase Dα1 and phosphatidic acid regulate NADPH oxidase activity and production of reactive oxygen species in ABA-mediated stomatal closure in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2009;21:2357–2377. doi: 10.1105/tpc.108.062992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Testerink C, Munnik T. Phosphatidic acid: a multifunctional stress signaling lipid in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2005;10:368–375. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2005.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wang X, Devaiah SP, Zhang W, Welti R. Signaling functions of phosphatidic acid. Prog Lipid Res. 2006;45:250–278. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2006.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Li M, Hong Y, Wang X. Phospholipase D- and phosphatidic acid-mediated signaling in plants. BBA - Mol Cell Biol L. 2009;1791:927–935. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2009.02.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Deak M, Casamayor A, Currie RA, Downes CP, Alessi DR. Characterisation of a plant 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 homologue which contains a pleckstrin homology domain. FEBS Lett. 1999;451:220–226. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(99)00556-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Bögre L, Okrész L, Henriques R, Anthony RG. Growth signalling pathways in Arabidopsis and the AGC protein kinases. Trends Plant Sci. 2003;8:424–431. doi: 10.1016/S1360-1385(03)00188-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Rentel MC, Lecourieux D, Ouaked F, Usher SL, Petersen L, et al. OXI1 kinase is necessary for oxidative burst-mediated signalling in Arabidopsis. Nature. 2004;427:858–861. doi: 10.1038/nature02353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.van der Luit AH, Piatti T, van Doorn A, Musgrave A, Felix G, et al. Elicitation of suspension-cultured tomato cells triggers the formation of phosphatidic acid and diacylglycerol pyrophosphate. Plant Physiol. 2000;123:1507–1516. doi: 10.1104/pp.123.4.1507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Yamaguchi T, Minami E, Ueki J, Shibuya N. Elicitor-induced activation of phospholipases plays an important role for the induction of defense responses in suspension-cultured rice cells. Plant Cell Physiol. 2005;46:579–587. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pci065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Oyama T, Shimura Y, Okada K. The IRE gene encodes a protein kinase homologue and modulates root hair growth in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2002;30:289–299. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2002.01290.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Foreman J, Demidchik V, Bothwell JH, Mylona P, Miedema H, et al. Reactive oxygen species produced by NADPH oxidase regulate plant cell growth. Nature. 2003;422:442–446. doi: 10.1038/nature01485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Arisz SA, Testerink C, Munnik T. Plant PA signaling via diacylglycerol kinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1791:869–875. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2009.04.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Qin C, Wang X. The Arabidopsis phospholipase D family. Characterization of a calcium-independent and phosphatidylcholine-selective PLDζ1 with distinct regulatory domains. Plant Physiol. 2002;128:1057–1068. doi: 10.1104/pp.010928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Zhang W, Wan X, Hong Y, Li W, Wang X. Berlin Heidelberg, Germany: Springer-Verlag; 2010. Plant phospholipase D. pp. 39–62. In Lipid Signaling in Plants (ed T Munnik) [Google Scholar]
- 39.Bargmann BO, Laxalt AM, ter Riet B, Testerink C, Merquiol E, et al. Reassessing the role of phospholipase D in the Arabidopsis wounding response. Plant Cell Environ. 2009;32:837–850. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2009.01962.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Vadassery J, Ritter C, Venus Y, Camehl I, Varma A, et al. The role of auxins and cytokinins in the mutualistic interaction between Arabidopsis and Piriformospora indica. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2008;21:1371–1383. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-21-10-1371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Camehl I, Sherameti I, Venus Y, Bethke G, Varma A, et al. Ethylene signalling and ethylene-targeted transcription factors are required to balance beneficial and nonbeneficial traits in the symbiosis between the endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica and Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol. 2010;185:1062–1073. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.03149.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Petersen LN, Ingle RA, Knight MR, Denby KJ. OXI1 protein kinase is required for plant immunity against Pseudomonas syringae in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot. 2009;60:3727–3735. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erp219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Wang H, Ngwenyama N, Liu Y, Walker JC, Zhang S. Stomatal development and patterning are regulated by environmentally responsive mitogen-activated protein kinases in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2007;19:63–73. doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.048298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Wang X. Regulatory functions of phospholipase D and phosphatidic acid in plant growth, development, and stress responses. Plant Physiol. 2005;139:566–573. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.068809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Bargmann BO, Munnik T. The role of phospholipase D in plant stress responses. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2006;9:515–522. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2006.07.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Xue H, Chen X, Li G. Involvement of phospholipid signaling in plant growth and hormone effects. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2007;10:483–489. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2007.07.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Hong Y, Pan X, Welti R, Wang X. Phospholipase Dα3 is involved in the hyperosmotic response in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2008;20:803–816. doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.056390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Hong Y, Devaiah SP, Bahn SC, Thamasandra BN, Li M, et al. Phospholipase Dε and phosphatidic acid enhance Arabidopsis nitrogen signaling and growth. Plant J. 2009;58:376–387. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.03788.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Fang Y, Vilella-Bach M, Bachmann R, Flanigan A, Chen J. Phosphatidic acid-mediated mitogenic activation of mTOR signaling. Science. 2001;294:1942–1945. doi: 10.1126/science.1066015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Huang P, Frohman MA. The potential for phospholipase D as a new therapeutic target. Expert Opin Ther Tar. 2007;11:707–716. doi: 10.1517/14728222.11.5.707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Foster DA, Xu L. Phospholipase D in cell proliferation and cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 2003;1:789–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Crawford NM. Nitrate: nutrient and signal for plant growth. Plant Cell. 1995;7:859–868. doi: 10.1105/tpc.7.7.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Walch-Liu P, Ivanov, II, Filleur S, Gan Y, Remans T, et al. Nitrogen regulation of root branching. Ann Bot. 2006;97:875–881. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcj601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Hirel B, Le Gouis J, Ney B, Gallais A. The challenge of improving nitrogen use efficiency in crop plants: towards a more central role for genetic variability and quantitative genetics within integrated approaches. J Exp Bot. 2007;58:2369–2387. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erm097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Li M, Welti R, Wang X. Quantitative profiling of Arabidopsis polar glycerolipids in response to phosphorus starvation. Roles of phospholipases Dζ1 and Dζ2 in phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis and digalactosyldiacylglycerol accumulation in phosphorus-starved plants. Plant Physiol. 2006;142:750–761. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.085647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Cruz-Ramirez A, Oropeza-Aburto A, Razo-Hernandez F, Ramirez-Chavez E, Herrera-Estrella L. Phospholipase Dζ2 plays an important role in extraplastidic galactolipid biosynthesis and phosphate recycling in Arabidopsis roots. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:6765–6770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0600863103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Bayascas JR. PDK1: the major transducer of PI 3-kinase actions. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010;346:9–29. doi: 10.1007/82_2010_43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Lawlor MA, Mora A, Ashby PR, Williams MR, Murray-Tait V, et al. Essential role of PDK1 in regulating cell size and development in mice. EMBO J. 2002;21:3728–3738. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdf387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Zhang W, Wang C, Qin C, Wood T, Olafsdottir G, et al. The oleate-stimulated phospholipase D, PLDδ, and phosphatidic acid decrease H2O2-induced cell death in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2003;15:2285–2295. doi: 10.1105/tpc.013961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Murashige T, Skoog F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant. 1962;15:473–497. [Google Scholar]
- 61.Bargmann BO, Laxalt AM, ter Riet B, van Schooten B, Merquiol E, et al. Multiple PLDs required for high salinity and water deficit tolerance in plants. Plant Cell Physiol. 2009;50:78–89. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcn173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Bütehorn B, Rhody D, Franken P. Isolation and characterisation of Pitef1 encoding the translation elongation factor EF-1a of the root endophyte Piriformospora indica. Plant Biol. 2000;2:687–692. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Pfaffl MW. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001;29:e45. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.9.e45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Veljovic-Jovanovic S, Noctor G, Foyer CH. Are leaf hydrogen peroxide concentrations commonly overestimated? The potential influence of artefactual interference by tissue phenolics and ascorbate. Plant Physiol Bioch. 2002;40:501–507. [Google Scholar]
- 65.Munnik T, Musgrave A, de Vrije T. Rapid turnover of polyphosphoinositides in carnation flower petals. Planta. 1994;193:89–98. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supporting information.
(DOC)