Abstract
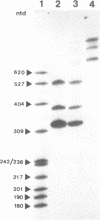
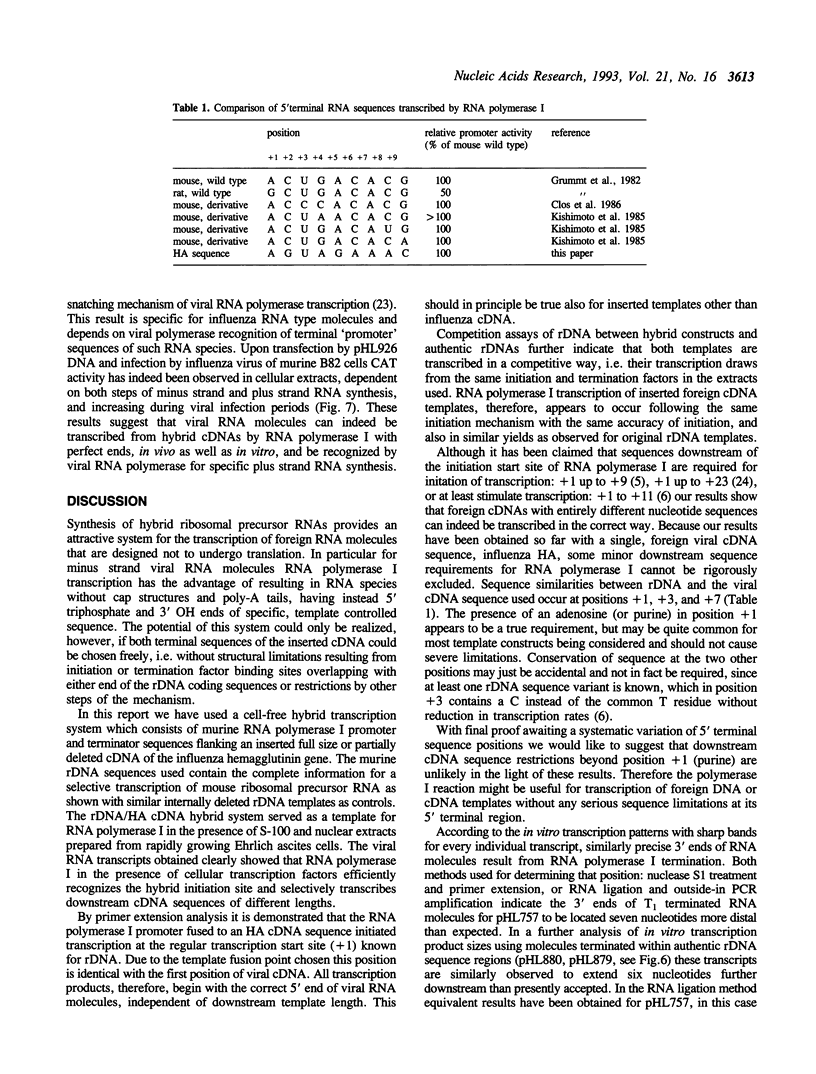
RNA polymerase I has been used for transcription of influenza hemagglutinin (HA) cDNA precisely linked in the anti-sense configuration to both mouse rDNA promoter and terminator segments. In transcription reactions based on Ehrlich ascites cell nuclear extracts, specific uniform RNA products are synthesized in high rates that are comparable to original rDNA template transcriptions. Primer extension reactions show the 5' ends of these RNA transcripts to be located exactly at position +1, corresponding to the 5' end of negative strand HA viral RNA. RNA 3' ends in a first series of constructs were found extended beyond the accepted location of pre-rRNA 3' ends, in using both hybrid cDNA and original rDNA templates. But upon deletion of six basepairs from the rDNA termination region RNA polymerase I transcription has been adapted to yield correctly terminated influenza viral RNA in vitro. This result has been confirmed in an in vivo experiment via synthesis of an anti-sense viral RNA molecule containing the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) gene, which in turn is recognized at its terminal sequence by viral RNA dependent RNA polymerase for plus strand mRNA synthesis and expression of CAT activity.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bogomolova A. E., Nikolaev L. G. Identification of a sequence-specific protein binding the 5'-transcribed spacer of rat ribosomal genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 11;19(23):6633–6637. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.23.6633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braam J., Ulmanen I., Krug R. M. Molecular model of a eucaryotic transcription complex: functions and movements of influenza P proteins during capped RNA-primed transcription. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):609–618. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90393-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clos J., Normann A., Ohrlein A., Grummt I. The core promoter of mouse rDNA consists of two functionally distinct domains. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 10;14(19):7581–7595. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.19.7581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comai L., Tanese N., Tjian R. The TATA-binding protein and associated factors are integral components of the RNA polymerase I transcription factor, SL1. Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):965–976. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90039-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürste J. P., Pansegrau W., Frank R., Blöcker H., Scholz P., Bagdasarian M., Lanka E. Molecular cloning of the plasmid RP4 primase region in a multi-host-range tacP expression vector. Gene. 1986;48(1):119–131. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90358-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Kuhn A., Bartsch I., Rosenbauer H. A transcription terminator located upstream of the mouse rDNA initiation site affects rRNA synthesis. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):901–911. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90805-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Maier U., Ohrlein A., Hassouna N., Bachellerie J. P. Transcription of mouse rDNA terminates downstream of the 3' end of 28S RNA and involves interaction of factors with repeated sequences in the 3' spacer. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):801–810. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90253-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Rosenbauer H., Niedermeyer I., Maier U., Ohrlein A. A repeated 18 bp sequence motif in the mouse rDNA spacer mediates binding of a nuclear factor and transcription termination. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):837–846. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90558-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I. Specific transcription of mouse ribosomal DNA in a cell-free system that mimics control in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):727–731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernández P., Martín-Parras L., Martínez-Robles M. L., Schvartzman J. B. Conserved features in the mode of replication of eukaryotic ribosomal RNA genes. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1475–1485. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05791.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa Y., Safrany G., Hisatake K., Tanaka N., Maeda Y., Kato H., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Structure of the core promoter of human and mouse ribosomal RNA gene. Asymmetry of species-specific transcription. J Mol Biol. 1991 Mar 5;218(1):55–67. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90873-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn A., Grummt I. 3'-end formation of mouse pre-rRNA involves both transcription termination and a specific processing reaction. Genes Dev. 1989 Feb;3(2):224–231. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.2.224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luytjes W., Krystal M., Enami M., Parvin J. D., Palese P. Amplification, expression, and packaging of foreign gene by influenza virus. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1107–1113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90766-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Mahony D. J., Smith S. D., Xie W., Rothblum L. I. Analysis of the phosphorylation, DNA-binding and dimerization properties of the RNA polymerase I transcription factors UBF1 and UBF2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 25;20(6):1301–1308. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.6.1301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parvin J. D., Palese P., Honda A., Ishihama A., Krystal M. Promoter analysis of influenza virus RNA polymerase. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5142–5152. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5142-5152.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romaniuk P. J., Uhlenbeck O. C. Joining of RNA molecules with RNA ligase. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:52–59. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnapp A., Grummt I. Transcription complex formation at the mouse rDNA promoter involves the stepwise association of four transcription factors and RNA polymerase I. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24588–24595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seong B. L., Brownlee G. G. A new method for reconstituting influenza polymerase and RNA in vitro: a study of the promoter elements for cRNA and vRNA synthesis in vitro and viral rescue in vivo. Virology. 1992 Jan;186(1):247–260. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90079-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smid A., Finsterer M., Grummt I. Limited proteolysis unmasks specific DNA-binding of the murine RNA polymerase I-specific transcription termination factor TTFI. J Mol Biol. 1992 Oct 5;227(3):635–647. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90213-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Tower J. Transcription of cloned eukaryotic ribosomal RNA genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:801–830. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tower J., Culotta V. C., Sollner-Webb B. Factors and nucleotide sequences that direct ribosomal DNA transcription and their relationship to the stable transcription complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3451–3462. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil P. A., Segall J., Harris B., Ng S. Y., Roeder R. G. Faithful transcription of eukaryotic genes by RNA polymerase III in systems reconstituted with purified DNA templates. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):6163–6173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie W. Q., Rothblum L. I. Domains of the rat rDNA promoter must be aligned stereospecifically. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1266–1275. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto O., Takakusa N., Mishima Y., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Determination of the promoter region of mouse ribosomal RNA gene by an in vitro transcription system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):299–303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]