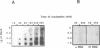Abstract
Reaction between a circular single stranded and a linear double stranded DNA molecule (ssDNA and dsDNA) provides an efficient system to study recombination mediated by RecA protein. However, classical assays using reaction in solution require highly purified enzymes. This limits biochemical studies of mutant RecA proteins from Escherichia coli or of RecA proteins from other organisms. We describe here an assay that is specific for RecA activity even in bacterial crude extracts. In this assay, the ssDNA is bound to a nitrocellulose membrane, proteins are loaded on this membrane and it is then incubated with a labeled homologous dsDNA. Joint molecules are visualized by autoradiography. We have shown that, despite the reduced mobility of the DNA due to its binding to the membrane, RecA protein is able to promote formation of stable plectonemic joints, in a homology dependent manner. Fourteen other proteins involved in DNA metabolism were checked and did not produce a signal in our assay. Moreover, in Dot blot analysis as well as after native electrophoresis and electrotransfer on a ssDNA coated membrane, production of a signal was strictly dependent on the presence of active RecA protein in the bacterial crude extracts used. We named this assay Pairing On Membrane blot (POM blot).
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beattie K. L., Wiegand R. C., Radding C. M. Uptake of homologous single-stranded fragments by superhelical DNA. II. Characterization of the reaction. J Mol Biol. 1977 Nov;116(4):783–803. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90271-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox M. M., Lehman I. R. Enzymes of general recombination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:229–262. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox M. M., Lehman I. R. recA protein of Escherichia coli promotes branch migration, a kinetically distinct phase of DNA strand exchange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3433–3437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutreix M., Burnett B., Bailone A., Radding C. M., Devoret R. A partially deficient mutant, recA1730, that fails to form normal nucleoprotein filaments. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Apr;232(3):489–497. doi: 10.1007/BF00266254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honigberg S. M., Radding C. M. The mechanics of winding and unwinding helices in recombination: torsional stress associated with strand transfer promoted by RecA protein. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):525–532. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90074-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jwang B., Radding C. M. Torsional stress generated by RecA protein during DNA strand exchange separates strands of a heterologous insert. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7596–7600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radding C. M. Helical RecA nucleoprotein filaments mediate homologous pairing and strand exchange. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jul 7;1008(2):131–145. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(80)90001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roca A. I., Cox M. M. The RecA protein: structure and function. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1990;25(6):415–456. doi: 10.3109/10409239009090617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata T., DasGupta C., Cunningham R. P., Radding C. M. Purified Escherichia coli recA protein catalyzes homologous pairing of superhelical DNA and single-stranded fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1638–1642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang S. S., Chow S. A., Radding C. M. Networks of DNA and RecA protein are intermediates in homologous pairing. Biochemistry. 1985 Jun 18;24(13):3226–3232. doi: 10.1021/bi00334a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. C. Enzymes and molecular mechanisms of genetic recombination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:603–640. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.003131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]