Abstract
Replication protein A (RP-A) is a heterotrimeric single-stranded DNA binding protein with important functions in DNA replication, DNA repair and DNA recombination. We have found that RP-A from calf thymus can unwind DNA in the absence of ATP and MgCl2, two essential cofactors for bona fide DNA helicases (Georgaki, A., Strack, B., Podust, V. and Hübscher, U. FEBS Lett. 308, 240-244, 1992). DNA unwinding by RP-A was found to be sensitive to MgCl2, ATP, heating and freezing/thawing. Escherichia coli single stranded DNA binding protein at concentrations that coat the single stranded regions had no influence on DNA unwinding by RP-A suggesting that RP-A binds fast and tightly to single-stranded DNA. DNA unwinding by RP-A did not show directionality. Experiments with monoclonal antibodies strongly suggested that the 70kDa subunit is responsible for DNA unwinding. Phosphorylation of the 32kDa subunit of RP-A by chicken cdc2 kinase facilitated DNA unwinding indicating that this posttranslational modification might be important for modulating this activity of RP-A. Finally, DNA unwinding of a primer recognition complex for DNA polymerase delta which is composed of proliferating cell nuclear antigen, replication factor C and ATP bound to a singly-primed M13DNA slightly inhibited DNA unwinding. An important role for DNA unwinding by RP-A in processes such as initiation of DNA replication, fork propagation, DNA repair and DNA recombination is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arezzo F., Rose K. M. Tryptic peptide analysis of nanogram quantities of proteins: radioiodination of proteins detected by silver staining in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1987 Dec;167(2):387–393. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90181-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boehmer P. E., Dodson M. S., Lehman I. R. The herpes simplex virus type-1 origin binding protein. DNA helicase activity. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 15;268(2):1220–1225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boehmer P. E., Lehman I. R. Herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP8: helix-destabilizing properties. J Virol. 1993 Feb;67(2):711–715. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.2.711-715.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brill S. J., Stillman B. Replication factor-A from Saccharomyces cerevisiae is encoded by three essential genes coordinately expressed at S phase. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1589–1600. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D., Kelly T. J. Animal virus DNA replication. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:671–717. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins K. L., Kelly T. J. Effects of T antigen and replication protein A on the initiation of DNA synthesis by DNA polymerase alpha-primase. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2108–2115. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coverley D., Kenny M. K., Lane D. P., Wood R. D. A role for the human single-stranded DNA binding protein HSSB/RPA in an early stage of nucleotide excision repair. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 11;20(15):3873–3880. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.15.3873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Din S., Brill S. J., Fairman M. P., Stillman B. Cell-cycle-regulated phosphorylation of DNA replication factor A from human and yeast cells. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):968–977. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornreiter I., Erdile L. F., Gilbert I. U., von Winkler D., Kelly T. J., Fanning E. Interaction of DNA polymerase alpha-primase with cellular replication protein A and SV40 T antigen. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):769–776. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05110.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutta A., Stillman B. cdc2 family kinases phosphorylate a human cell DNA replication factor, RPA, and activate DNA replication. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2189–2199. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05278.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fotedar R., Roberts J. M. Cell cycle regulated phosphorylation of RPA-32 occurs within the replication initiation complex. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2177–2187. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05277.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gassmann M., Thömmes P., Weiser T., Hübscher U. Efficient production of chicken egg yolk antibodies against a conserved mammalian protein. FASEB J. 1990 May;4(8):2528–2532. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.8.1970792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
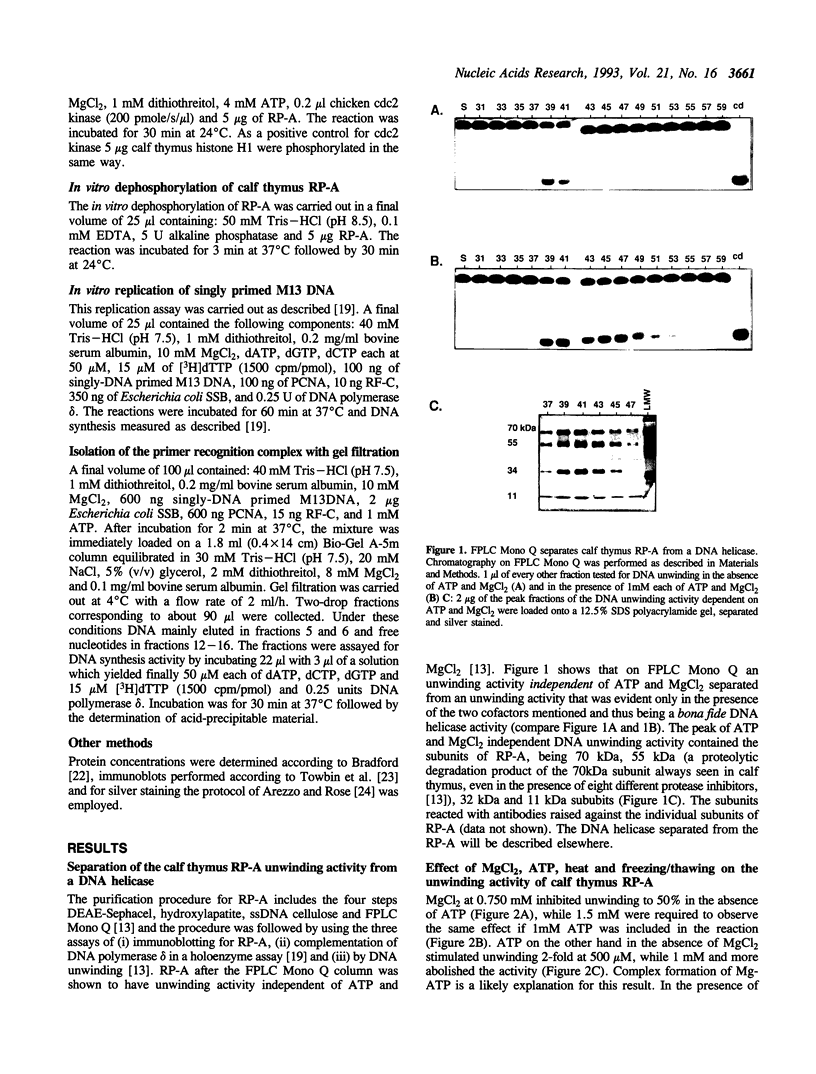
- Georgaki A., Strack B., Podust V., Hübscher U. DNA unwinding activity of replication protein A. FEBS Lett. 1992 Aug 24;308(3):240–244. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81283-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
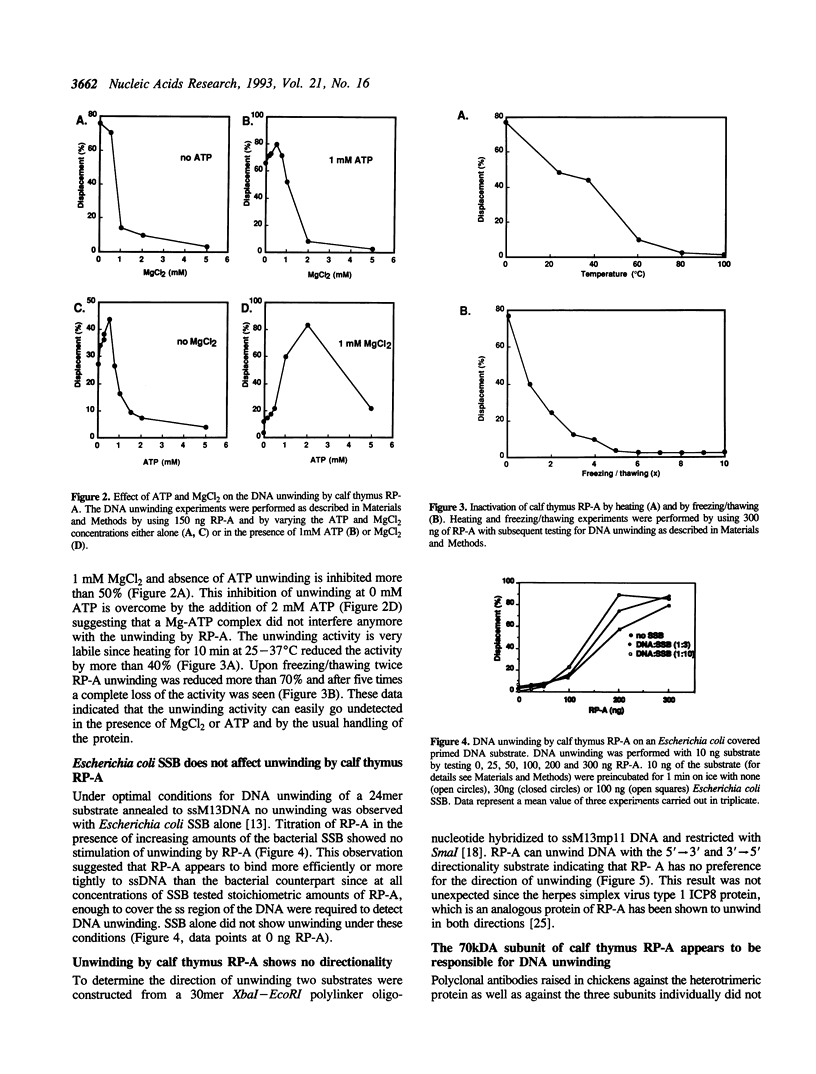
- Kenny M. K., Lee S. H., Hurwitz J. Multiple functions of human single-stranded-DNA binding protein in simian virus 40 DNA replication: single-strand stabilization and stimulation of DNA polymerases alpha and delta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9757–9761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny M. K., Schlegel U., Furneaux H., Hurwitz J. The role of human single-stranded DNA binding protein and its individual subunits in simian virus 40 DNA replication. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7693–7700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C., Snyder R. O., Wold M. S. Binding properties of replication protein A from human and yeast cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3050–3059. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
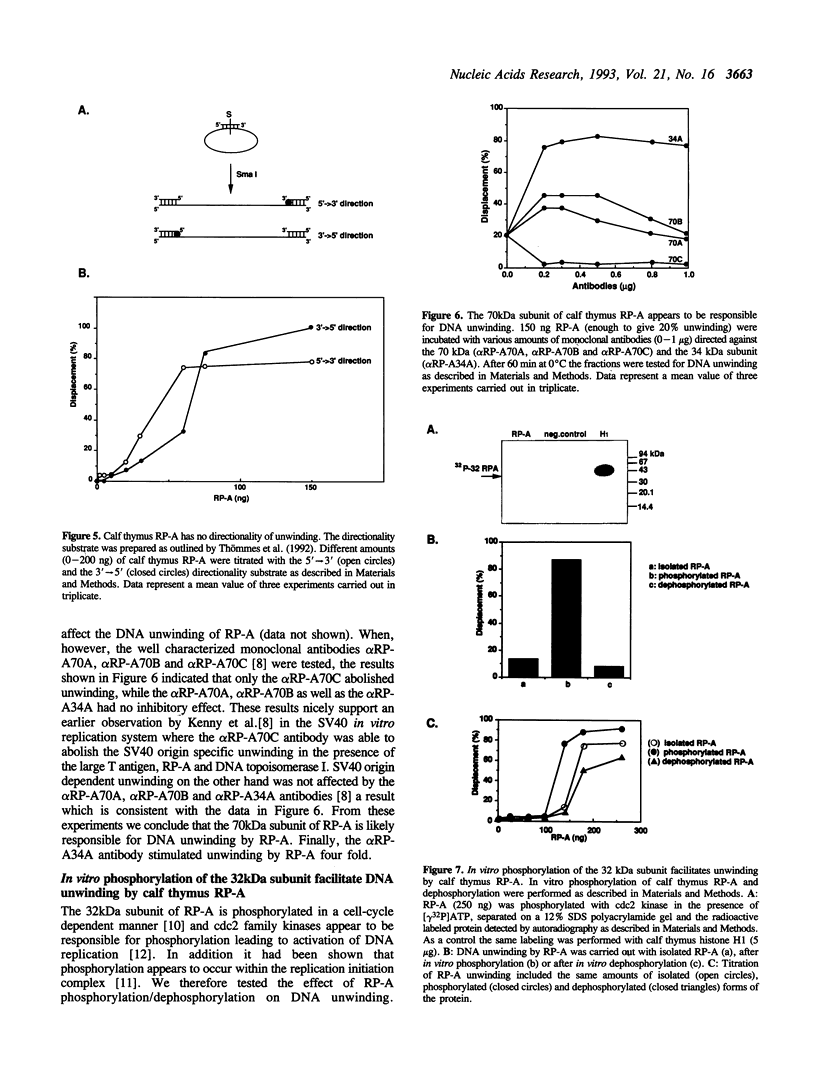
- Melendy T., Stillman B. An interaction between replication protein A and SV40 T antigen appears essential for primosome assembly during SV40 DNA replication. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3389–3395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami Y., Hurwitz J. Functional interactions between SV40 T antigen and other replication proteins at the replication fork. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):11008–11017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podust V. N., Georgaki A., Strack B., Hübscher U. Calf thymus RF-C as an essential component for DNA polymerase delta and epsilon holoenzymes function. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 25;20(16):4159–4165. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.16.4159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seo Y. S., Lee S. H., Hurwitz J. Isolation of a DNA helicase from HeLa cells requiring the multisubunit human single-stranded DNA-binding protein for activity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):13161–13170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thömmes P., Ferrari E., Jessberger R., Hübscher U. Four different DNA helicases from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6063–6073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
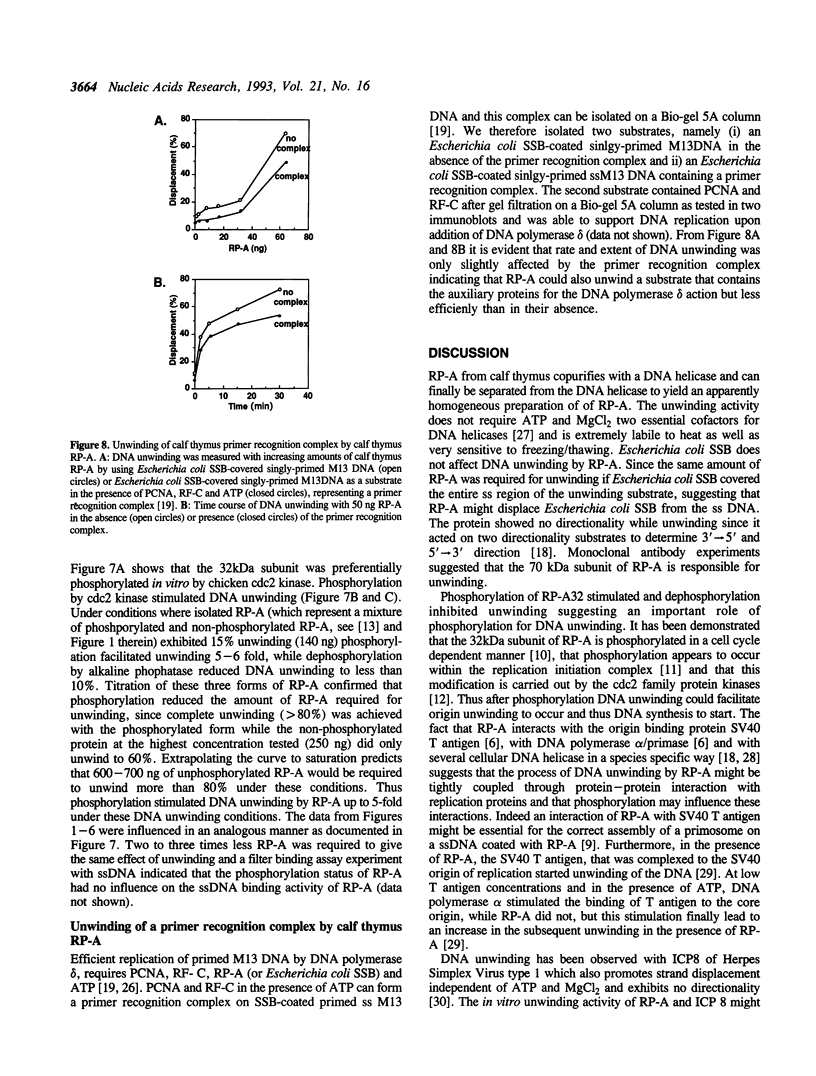
- Thömmes P., Hübscher U. Eukaryotic DNA helicases: essential enzymes for DNA transactions. Chromosoma. 1992 Jun;101(8):467–473. doi: 10.1007/BF00352468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Melendy T., Stillman B. Sequential initiation of lagging and leading strand synthesis by two different polymerase complexes at the SV40 DNA replication origin. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):534–539. doi: 10.1038/346534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Stillman B. Multiple replication factors augment DNA synthesis by the two eukaryotic DNA polymerases, alpha and delta. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3883–3889. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08567.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser T., Gassmann M., Thömmes P., Ferrari E., Hafkemeyer P., Hübscher U. Biochemical and functional comparison of DNA polymerases alpha, delta, and epsilon from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10420–10428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





