Abstract
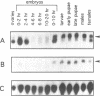
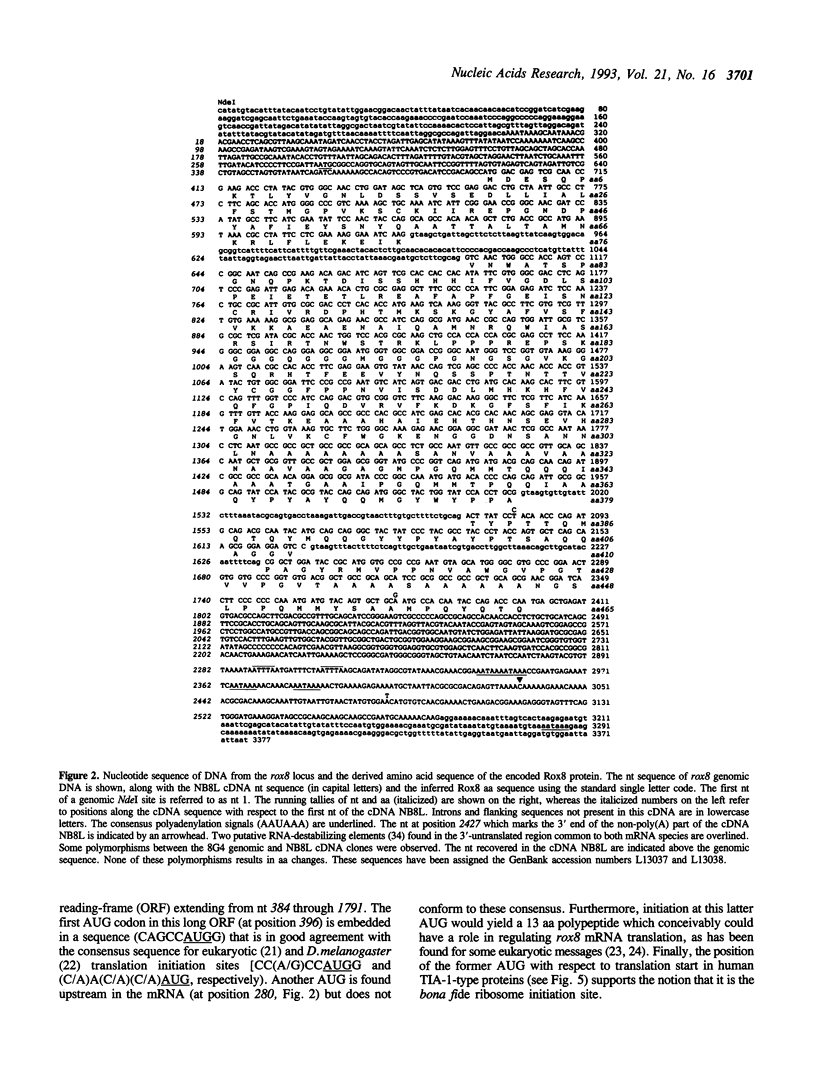
We report the molecular analysis of a novel Drosophila melanogaster gene, rox8, isolated in a PCR-based screen for sequences encoding RRM-type RNA-binding polypeptides. The rox8 gene is predicted to encode a 50-kilodalton protein displaying extensive amino acid sequence similarities (46% overall identity; 57 to 60% similarity) to the two recently described human TIA-1-type nucleolysins. These cytolytic granule associated proteins, which bind polyadenylated sequences in vitro and trigger DNA fragmentation in permeabilized target cells, are suspected to participate in the apoptotic cell death pathway induced by T-lymphocytes and natural killer cells. The structural relatedness of the three proteins includes three tandemly-repeated consensus RNA-recognition motifs at the N-terminal end and a putative membrane targeting signal at the C-terminal end. rox8 cytologically maps to 95D5-9 on the right arm of the third chromosome. Two rox8 transcripts of 3 and 3.3 kb in length, respectively, result from a developmentally-modulated alternative usage of different polyadenylation sites and are differentially accumulated throughout the fly life cycle. Molecular characterization of rox8 represents the first step in a genetic analysis of the potential roles of a TIA-1-related protein in RNA metabolism and/or programmed cell death in Drosophila.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams J. M., White K., Fessler L. I., Steller H. Programmed cell death during Drosophila embryogenesis. Development. 1993 Jan;117(1):29–43. doi: 10.1242/dev.117.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. H., Kafatos F. C. Functional cDNA libraries from Drosophila embryos. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 20;203(2):425–437. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavener D. R. Comparison of the consensus sequence flanking translational start sites in Drosophila and vertebrates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1353–1361. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dura J. M., Randsholt N. B., Deatrick J., Erk I., Santamaria P., Freeman J. D., Freeman S. J., Weddell D., Brock H. W. A complex genetic locus, polyhomeotic, is required for segmental specification and epidermal development in D. melanogaster. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):829–839. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90106-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. E., Yuan J. Y., Horvitz H. R. Mechanisms and functions of cell death. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:663–698. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giorgi F., Deri P. Cell death in ovarian chambers of Drosophila melanogaster. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1976 Jun;35(3):521–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grange T., de Sa C. M., Oddos J., Pictet R. Human mRNA polyadenylate binding protein: evolutionary conservation of a nucleic acid binding motif. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 25;15(12):4771–4787. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.12.4771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes S. R., Rebbert M. L., Mozer B. A., Forquignon F., Dawid I. B. pen repeat sequences are GGN clusters and encode a glycine-rich domain in a Drosophila cDNA homologous to the rat helix destabilizing protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1819–1823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Sharp P. M. CLUSTAL: a package for performing multiple sequence alignment on a microcomputer. Gene. 1988 Dec 15;73(1):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90330-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren R., Corces V., Morimoto R., Blackman R., Meselson M. Sequence homologies in the 5' regions of four Drosophila heat-shock genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3775–3778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren R., Livak K., Morimoto R., Freund R., Meselson M. Studies of cloned sequences from four Drosophila heat shock loci. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1359–1370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90246-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard S. C., Ivatt R. J. Synthesis and processing of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:555–583. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami A., Tian Q., Duan X., Streuli M., Schlossman S. F., Anderson P. Identification and functional characterization of a TIA-1-related nucleolysin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8681–8685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenan D. J., Query C. C., Keene J. D. RNA recognition: towards identifying determinants of specificity. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Jun;16(6):214–220. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90088-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. J., Baker B. S. Isolation of RRM-type RNA-binding protein genes and the analysis of their relatedness by using a numerical approach. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):174–183. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura K. I., Truman J. W. Postmetamorphic cell death in the nervous and muscular systems of Drosophila melanogaster. J Neurosci. 1990 Feb;10(2):403–401. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-02-00403.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller P. F., Hinnebusch A. G. Sequences that surround the stop codons of upstream open reading frames in GCN4 mRNA determine their distinct functions in translational control. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1217–1225. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M., Burks C., Hertz G., Stormo G. D., White O., Fields C. Splicing signals in Drosophila: intron size, information content, and consensus sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 25;20(16):4255–4262. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.16.4255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noselli S., Vincent A. The Drosophila melanogaster ribosomal protein L17A-encoding gene. Gene. 1992 Sep 10;118(2):273–278. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90199-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh S. K., Scott M. P., Sarnow P. Homeotic gene Antennapedia mRNA contains 5'-noncoding sequences that confer translational initiation by internal ribosome binding. Genes Dev. 1992 Sep;6(9):1643–1653. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.9.1643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. Poly(A) signals. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):671–674. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90495-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Query C. C., Bentley R. C., Keene J. D. A common RNA recognition motif identified within a defined U1 RNA binding domain of the 70K U1 snRNP protein. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):89–101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90175-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C. Social controls on cell survival and cell death. Nature. 1992 Apr 2;356(6368):397–400. doi: 10.1038/356397a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian Q., Streuli M., Saito H., Schlossman S. F., Anderson P. A polyadenylate binding protein localized to the granules of cytolytic lymphocytes induces DNA fragmentation in target cells. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):629–639. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90536-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaux D. The structure of an endocytosis signal. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;2(7):189–192. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90232-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. A., Fukuda M. Accumulation of membrane glycoproteins in lysosomes requires a tyrosine residue at a particular position in the cytoplasmic tail. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):955–966. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]