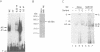Abstract
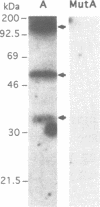
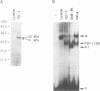
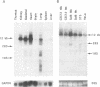
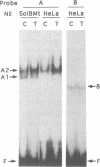
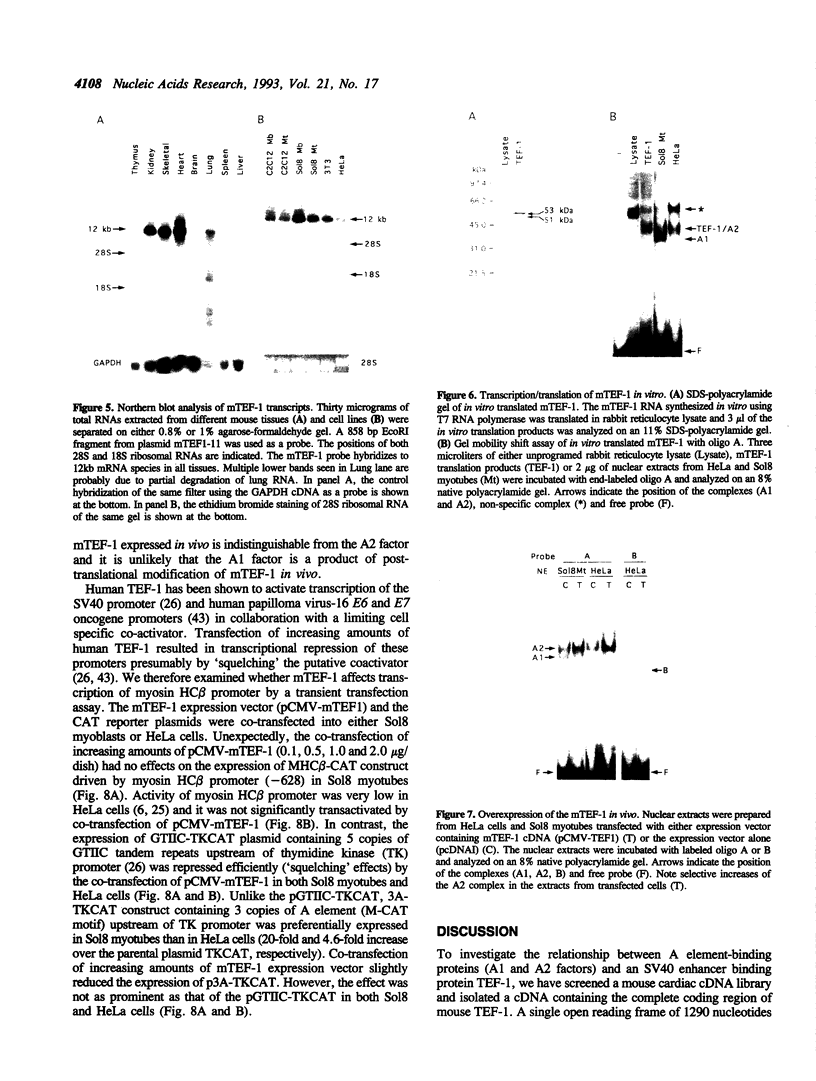
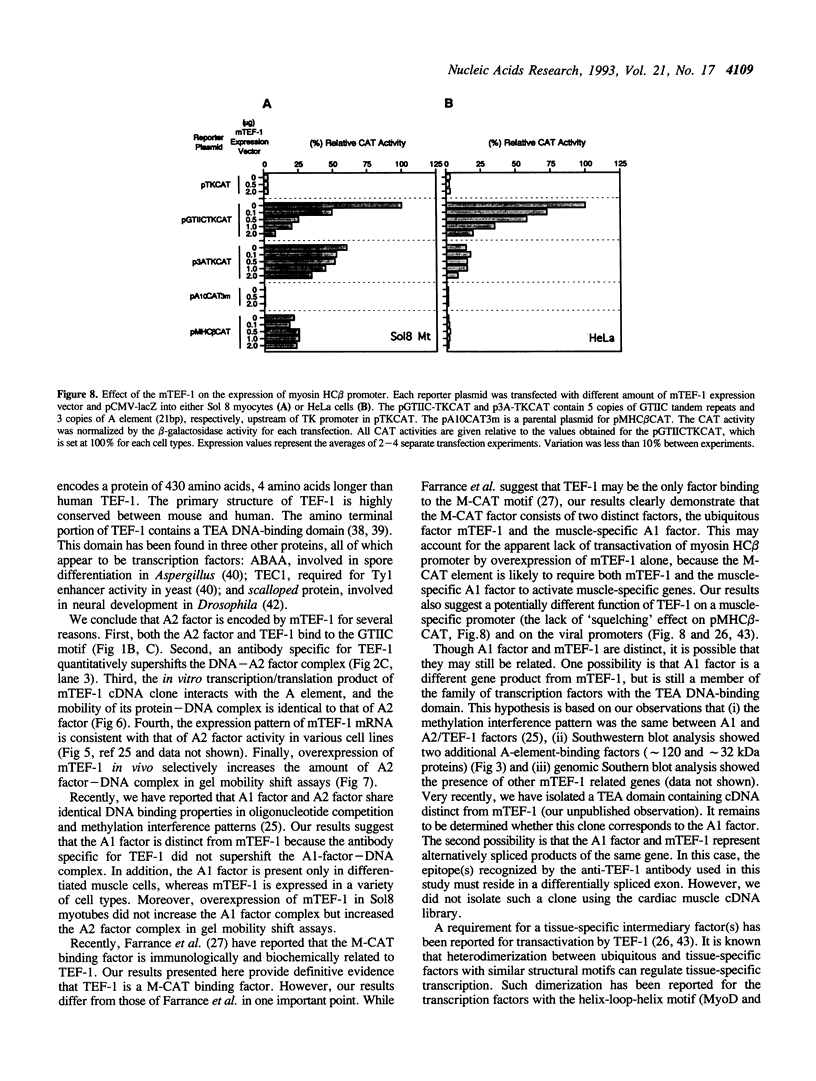
The A element, a fourteen base pair sequence in the rabbit myosin heavy chain (HC) beta promoter (-276/-263), contains the M-CAT motif, a cis-acting element found in several muscle-specific genes. The A element is essential for muscle-specific transcription of the myosin HC beta gene. Recently, we have identified both muscle-specific and ubiquitous factors (A1 and A2 factors, respectively) that bind to the A element. Since the sequence of the A element is very similar to the GTIIC motif in the SV40 enhancer, we examined the relationship between A-element-binding factors and a GTIIC binding factor TEF-1, recently isolated from HeLa cells. The GTIIC motif was bound by the A1 and A2 factors in muscle nuclear extracts and competed with the A element for DNA-protein complex formation. Antibody against human TEF-1 'supershifted' the ubiquitous A2 factor-DNA complex, but did not alter the mobility of the muscle-specific A1 factor-DNA complex. We isolated a murine cDNA clone (mTEF-1) from a cardiac cDNA library. The clone is highly homologous to Hela cell TEF-1. The in vitro transcription/translation product of mTEF-1 cDNA bound to the A element, and the DNA binding property of mTEF-1 was identical to that of the A2 factor. Transfection of mTEF-1 cDNA into muscle and non-muscle cells confirmed that mTEF-1 corresponds to A2, but not to A1 factors. The mTEF-1 mRNA is expressed abundantly in skeletal and cardiac muscles, kidney and lung, but it is also expressed at lower levels in other tissues. These results suggest that the M-CAT binding factors consist of two different factors; the ubiquitous A2 is encoded by mTEF-1, but the muscle-specific A1 factor is distinct from mTEF-1.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blatt C., DePamphilis M. L. Striking homology between mouse and human transcription enhancer factor-1 (TEF-1). Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Feb 11;21(3):747–748. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.3.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxer L. M., Prywes R., Roeder R. G., Kedes L. The sarcomeric actin CArG-binding factor is indistinguishable from the c-fos serum response factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):515–522. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Buschhausen-Denker G., Bober E., Tannich E., Arnold H. H. A novel human muscle factor related to but distinct from MyoD1 induces myogenic conversion in 10T1/2 fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):701–709. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03429.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürglin T. R. The TEA domain: a novel, highly conserved DNA-binding motif. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):11–12. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90132-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell S., Inamdar M., Rodrigues V., Raghavan V., Palazzolo M., Chovnick A. The scalloped gene encodes a novel, evolutionarily conserved transcription factor required for sensory organ differentiation in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1992 Mar;6(3):367–379. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.3.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cribbs L. L., Shimizu N., Yockey C. E., Levin J. E., Jakovcic S., Zak R., Umeda P. K. Muscle-specific regulation of a transfected rabbit myosin heavy chain beta gene promoter. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10672–10678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cserjesi P., Olson E. N. Myogenin induces the myocyte-specific enhancer binding factor MEF-2 independently of other muscle-specific gene products. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4854–4862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. Expression of a single transfected cDNA converts fibroblasts to myoblasts. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):987–1000. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90585-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrance I. K., Mar J. H., Ordahl C. P. M-CAT binding factor is related to the SV40 enhancer binding factor, TEF-1. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):17234–17240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flink I. L., Edwards J. G., Bahl J. J., Liew C. C., Sole M., Morkin E. Characterization of a strong positive cis-acting element of the human beta-myosin heavy chain gene in fetal rat heart cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):9917–9924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisterfer-Lowrance A. A., Kass S., Tanigawa G., Vosberg H. P., McKenna W., Seidman C. E., Seidman J. G. A molecular basis for familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: a beta cardiac myosin heavy chain gene missense mutation. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):999–1006. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90274-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossett L. A., Kelvin D. J., Sternberg E. A., Olson E. N. A new myocyte-specific enhancer-binding factor that recognizes a conserved element associated with multiple muscle-specific genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5022–5033. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang J. J., Chambon P., Davidson I. Characterization of the transcription activation function and the DNA binding domain of transcriptional enhancer factor-1. EMBO J. 1993 Jun;12(6):2337–2348. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05888.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiji T., Lace M. J., Parkkinen S., Anderson R. D., Haugen T. H., Cripe T. P., Xiao J. H., Davidson I., Chambon P., Turek L. P. Transcriptional enhancer factor (TEF)-1 and its cell-specific co-activator activate human papillomavirus-16 E6 and E7 oncogene transcription in keratinocytes and cervical carcinoma cells. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2271–2281. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05286.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laloux I., Dubois E., Dewerchin M., Jacobs E. TEC1, a gene involved in the activation of Ty1 and Ty1-mediated gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: cloning and molecular analysis. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3541–3550. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Davis R. L., Wright W. E., Kadesch T., Murre C., Voronova A., Baltimore D., Weintraub H. Functional activity of myogenic HLH proteins requires hetero-oligomerization with E12/E47-like proteins in vivo. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):305–315. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90620-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. C., Chow K. L., Fang P., Schwartz R. J. Activation of skeletal alpha-actin gene transcription: the cooperative formation of serum response factor-binding complexes over positive cis-acting promoter serum response elements displaces a negative-acting nuclear factor enriched in replicating myoblasts and nonmyogenic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5090–5100. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mar J. H., Ordahl C. P. M-CAT binding factor, a novel trans-acting factor governing muscle-specific transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4271–4283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirabito P. M., Adams T. H., Timberlake W. E. Interactions of three sequentially expressed genes control temporal and spatial specificity in Aspergillus development. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):859–868. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90800-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Vaessin H., Caudy M., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N., Cabrera C. V., Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D., Lassar A. B. Interactions between heterologous helix-loop-helix proteins generate complexes that bind specifically to a common DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock R., Treisman R. Human SRF-related proteins: DNA-binding properties and potential regulatory targets. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12A):2327–2341. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12a.2327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes S. J., Konieczny S. F. Identification of MRF4: a new member of the muscle regulatory factor gene family. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2050–2061. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sartorelli V., Webster K. A., Kedes L. Muscle-specific expression of the cardiac alpha-actin gene requires MyoD1, CArG-box binding factor, and Sp1. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1811–1822. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassoon D., Lyons G., Wright W. E., Lin V., Lassar A., Weintraub H., Buckingham M. Expression of two myogenic regulatory factors myogenin and MyoD1 during mouse embryogenesis. Nature. 1989 Sep 28;341(6240):303–307. doi: 10.1038/341303a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu N., Dizon E., Zak R. Both muscle-specific and ubiquitous nuclear factors are required for muscle-specific expression of the myosin heavy-chain beta gene in cultured cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):619–630. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu N., Prior G., Umeda P. K., Zak R. cis-acting elements responsible for muscle-specific expression of the myosin heavy chain beta gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 11;20(7):1793–1799. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.7.1793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva C. M., Tully D. B., Petch L. A., Jewell C. M., Cidlowski J. A. Application of a protein-blotting procedure to the study of human glucocorticoid receptor interactions with DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1744–1748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanigawa G., Jarcho J. A., Kass S., Solomon S. D., Vosberg H. P., Seidman J. G., Seidman C. E. A molecular basis for familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: an alpha/beta cardiac myosin heavy chain hybrid gene. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):991–998. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90273-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W. R., Nadal-Ginard B., Mahdavi V. A MyoD1-independent muscle-specific enhancer controls the expression of the beta-myosin heavy chain gene in skeletal and cardiac muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22678–22688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Identification and purification of a polypeptide that binds to the c-fos serum response element. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2711–2717. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02564.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uetsuki T., Nabeshima Y., Fujisawa-Sehara A., Nabeshima Y. Regulation of the chicken embryonic myosin light-chain (L23) gene: existence of a common regulatory element shared by myosin alkali light-chain genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2562–2569. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandromme M., Gauthier-Rouvière C., Carnac G., Lamb N., Fernandez A. Serum response factor p67SRF is expressed and required during myogenic differentiation of both mouse C2 and rat L6 muscle cell lines. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(6):1489–1500. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.6.1489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voss J. W., Wilson L., Rosenfeld M. G. POU-domain proteins Pit-1 and Oct-1 interact to form a heteromeric complex and can cooperate to induce expression of the prolactin promoter. Genes Dev. 1991 Jul;5(7):1309–1320. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.7.1309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Davis R., Tapscott S., Thayer M., Krause M., Benezra R., Blackwell T. K., Turner D., Rupp R., Hollenberg S. The myoD gene family: nodal point during specification of the muscle cell lineage. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):761–766. doi: 10.1126/science.1846704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R., Urlaub G., Chasin L. DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright W. E., Sassoon D. A., Lin V. K. Myogenin, a factor regulating myogenesis, has a domain homologous to MyoD. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):607–617. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90583-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao J. H., Davidson I., Matthes H., Garnier J. M., Chambon P. Cloning, expression, and transcriptional properties of the human enhancer factor TEF-1. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):551–568. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90088-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Y. T., Breitbart R. E., Smoot L. B., Lee Y., Mahdavi V., Nadal-Ginard B. Human myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2 comprises a group of tissue-restricted MADS box transcription factors. Genes Dev. 1992 Sep;6(9):1783–1798. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.9.1783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]