Abstract
We have significantly improved a method originally developed by Liang and Pardee [Science 257 (1992) 967-971] to display a broad spectrum of expressed genes and to detect differences in expression between different cell types. We have analysed various aspects of the technique and have modified it for both, the application to fast and efficient identification of genes and the use with automatic analysis systems. Based on the mathematical background we have devised the appropriate number of optimal PCR primers. We have also introduced nondenaturating gels for separating double stranded fragments as single bands. By applying the method to regenerating mouse liver, we have identified, out of a total of 38,000 bands, about 70 fragments where the expression of the corresponding genes seems to be differentially regulated at different time points. Application of the method to an automatic DNA sequencer was successfully done. Thus, we have confirmed the usefulness and increased the power of the RNA display technique, which we named differential display reverse transcription PCR (DDRT-PCR), and have extended the range of its application.
Full text
PDF


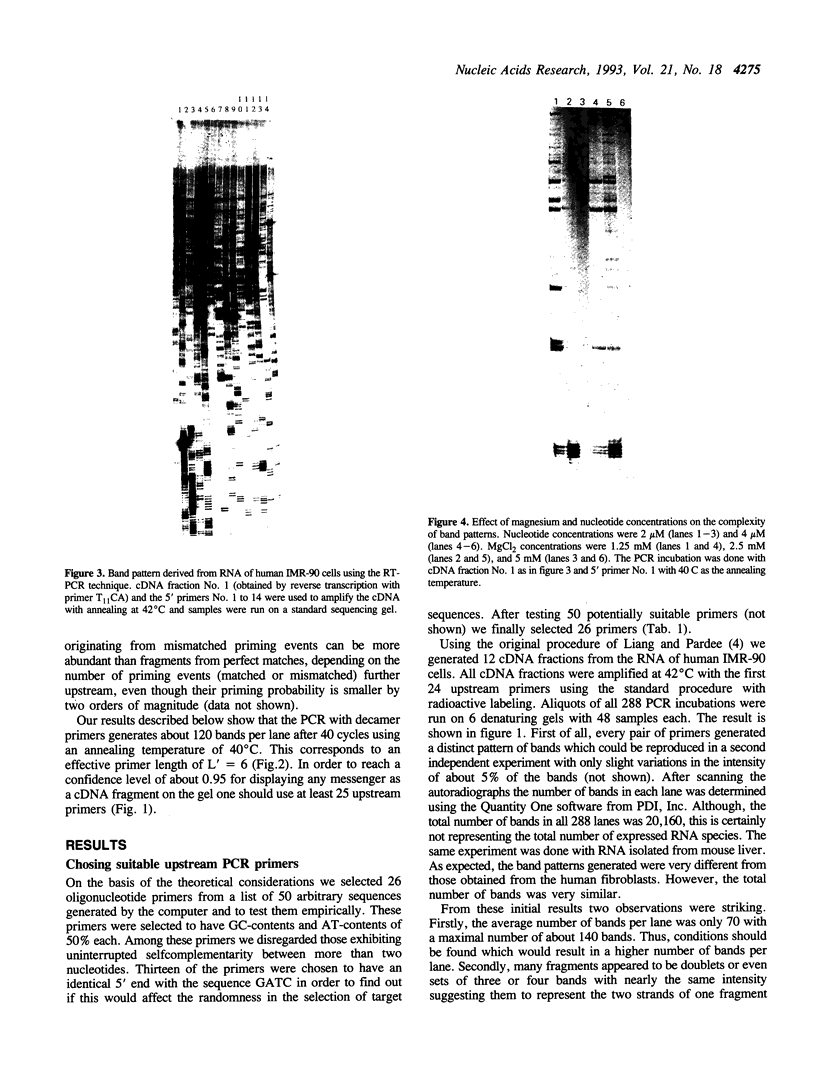

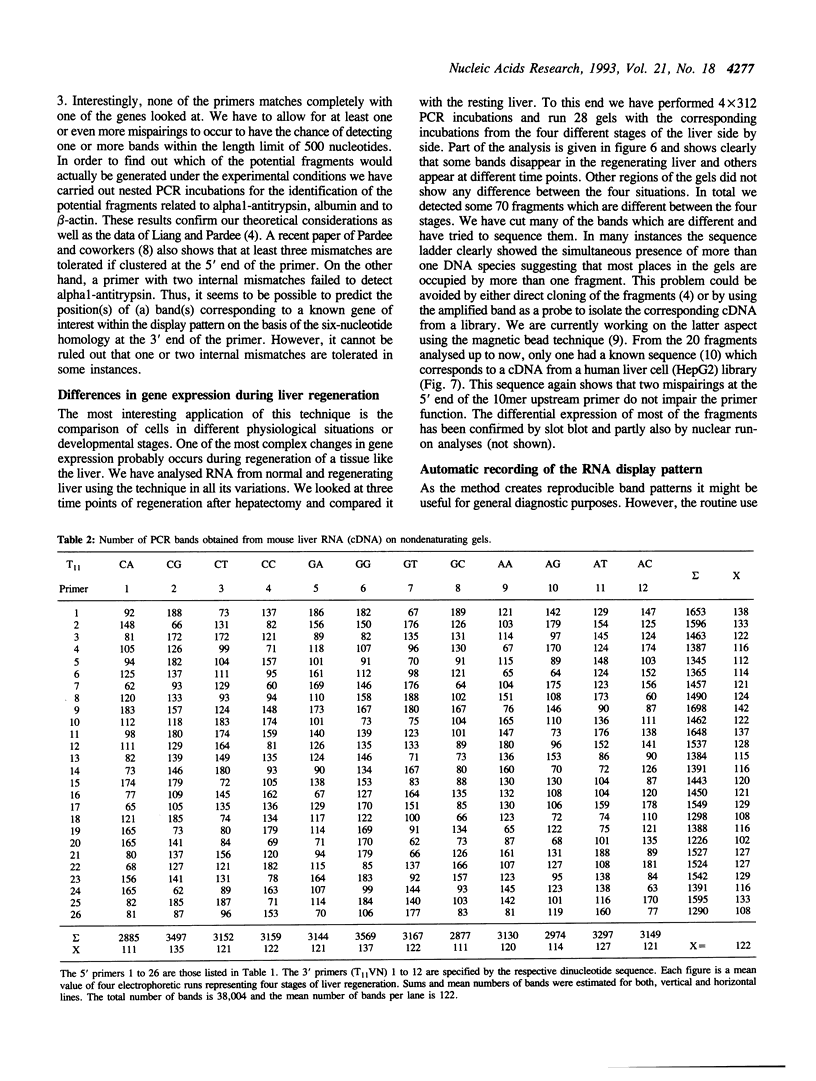



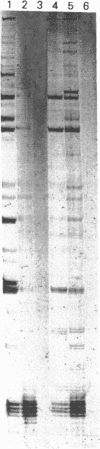
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn B., Sedlacek Z., Manca A., Kioschis P., Konecki D., Lehrach H., Poustka A. A strategy for the selection of transcribed sequences in the Xq28 region. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Jul;1(4):235–242. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.4.235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang P., Averboukh L., Keyomarsi K., Sager R., Pardee A. B. Differential display and cloning of messenger RNAs from human breast cancer versus mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 1992 Dec 15;52(24):6966–6968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang P., Pardee A. B. Differential display of eukaryotic messenger RNA by means of the polymerase chain reaction. Science. 1992 Aug 14;257(5072):967–971. doi: 10.1126/science.1354393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okubo K., Hori N., Matoba R., Niiyama T., Fukushima A., Kojima Y., Matsubara K. Large scale cDNA sequencing for analysis of quantitative and qualitative aspects of gene expression. Nat Genet. 1992 Nov;2(3):173–179. doi: 10.1038/ng1192-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St John T. P., Davis R. W. Isolation of galactose-inducible DNA sequences from Saccharomyces cerevisiae by differential plaque filter hybridization. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):443–452. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss M., Hering S., Lubbe L., Griffin B. E. Immortalization and transformation of human fibroblasts by regulated expression of polyoma virus T antigens. Oncogene. 1990 Aug;5(8):1223–1229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagle D. A., Swaroop M., Lovett M., Collins F. S. Magnetic bead capture of expressed sequences encoded within large genomic segments. Nature. 1993 Feb 25;361(6414):751–753. doi: 10.1038/361751a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann C. R., Orr W. C., Leclerc R. F., Barnard E. C., Timberlake W. E. Molecular cloning and selection of genes regulated in Aspergillus development. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):709–715. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90434-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]