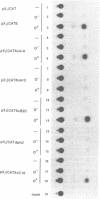
Abstract
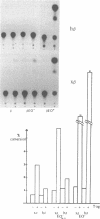
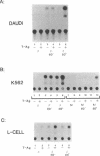
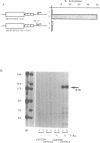
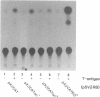
We demonstrate a general role for DNA replication in the activation of gene transcription in transient transfection assays. The effect is observed for a wide range of genes and cell types, transfected by a number of protocols and is independent of increased template copy number. Replication does not stimulate transcription driven by proximal promoter elements alone but requires a functional enhancer element. This synergy between an active replication origin and an enhancer is not confined to elements from viruses such as SV40, which undergo an early to late switch in gene expression that is tightly coupled to replication, since the enhancer-containing long terminal repeats from retroviruses are strongly stimulated by replication. Furthermore, synthetic enhancers consisting of multimerised binding sites for one or two factors are also subject to replication-activation. The diversity of synthetic and natural enhancers used in this study suggests that replication and transcription do not share a common protein factor. We propose that replication leads to chromatin modifications that facilitate enhancer action.
Full text
PDF

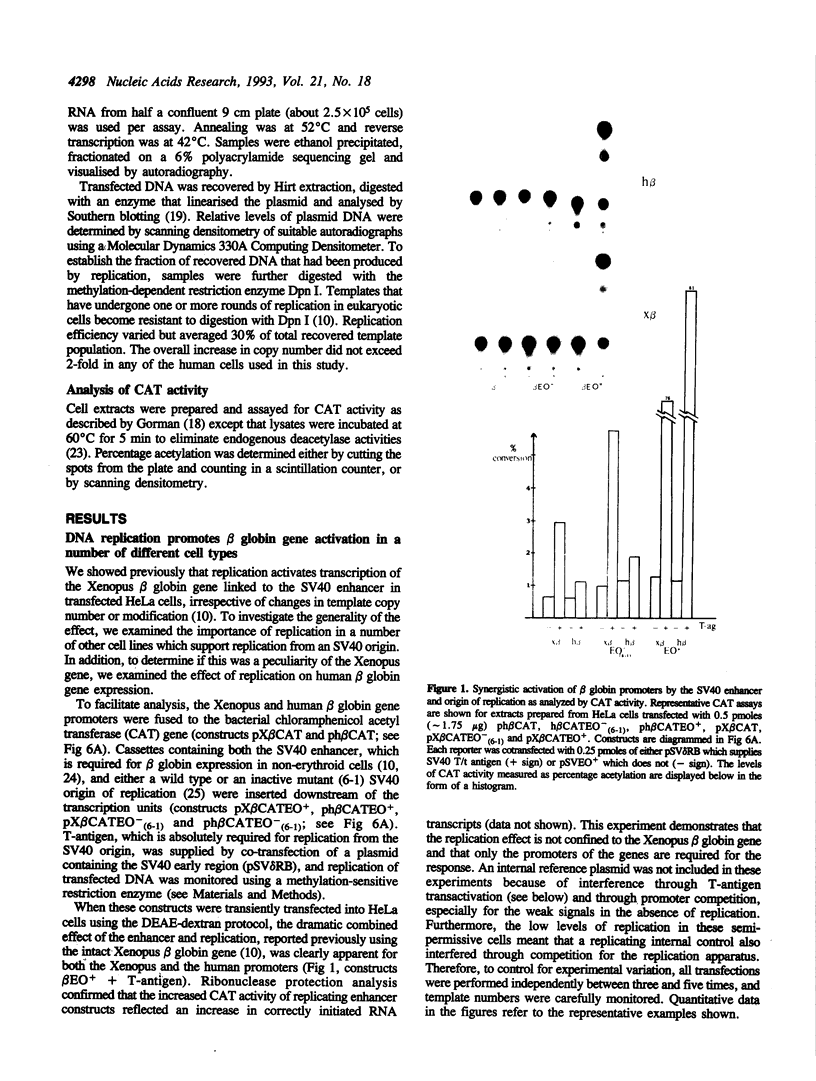
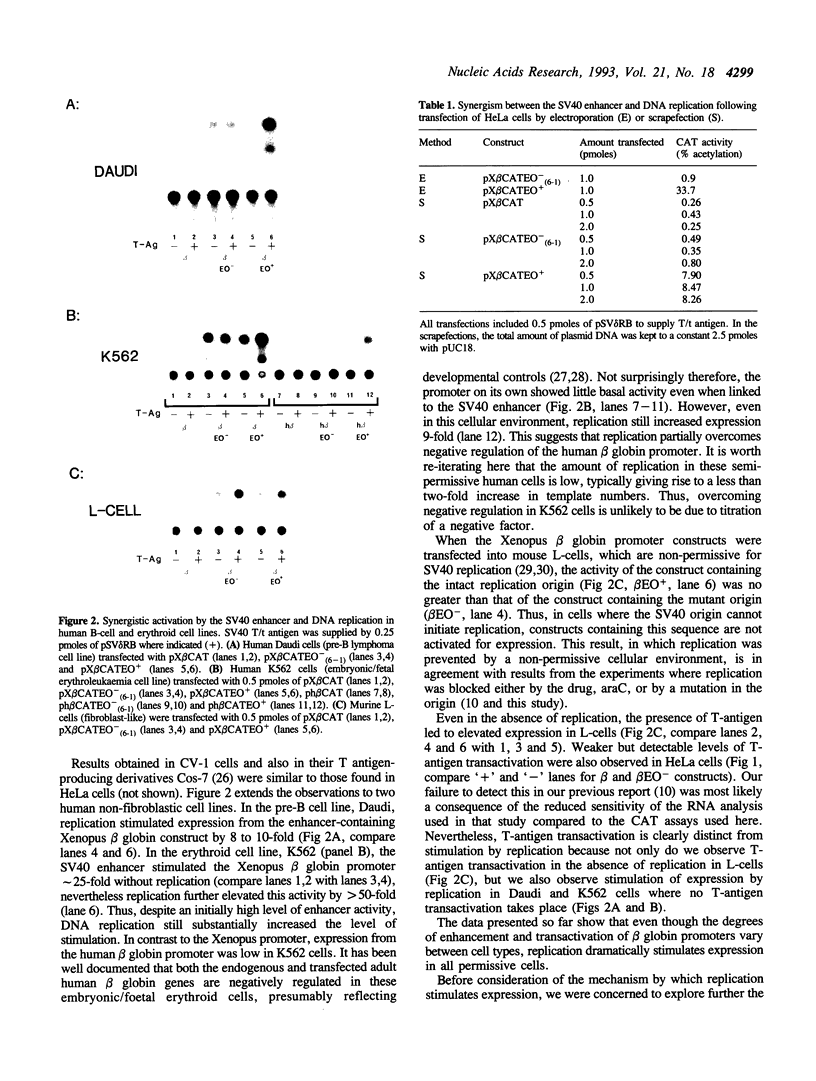
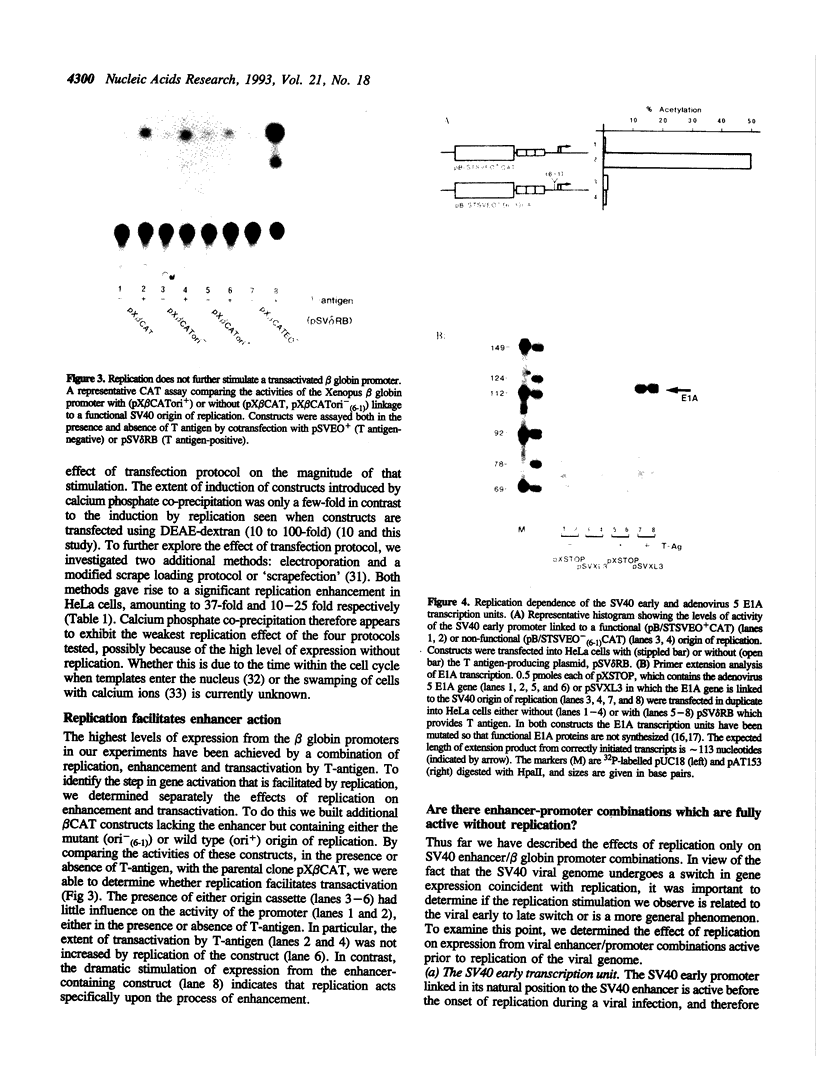



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almouzni G., Méchali M., Wolffe A. P. Competition between transcription complex assembly and chromatin assembly on replicating DNA. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):573–582. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08145.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braithwaite A. W., Sturzbecher H. W., Addison C., Palmer C., Rudge K., Jenkins J. R. Mouse p53 inhibits SV40 origin-dependent DNA replication. Nature. 1987 Oct 1;329(6138):458–460. doi: 10.1038/329458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao S. X., Mishoe H., Elion J., Berg P. E., Schechter A. N. Activation of the human epsilon- and beta-globin promoters by SV40 T antigen. Biochem J. 1989 Mar 15;258(3):769–776. doi: 10.1042/bj2580769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Yaniv M. Assembly of transfected DNA into chromatin: structural changes in the origin-promoter-enhancer region upon replication. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1243–1253. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01959.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charnay P., Maniatis T. Transcriptional regulation of globin gene expression in the human erythroid cell line K562. Science. 1983 Jun 17;220(4603):1281–1283. doi: 10.1126/science.6574602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabb D. W., Dixon J. E. A method for increasing the sensitivity of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase assays in extracts of transfected cultured cells. Anal Biochem. 1987 May 15;163(1):88–92. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90096-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean A., Ley T. J., Humphries R. K., Fordis M., Schechter A. N. Inducible transcription of five globin genes in K562 human leukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5515–5519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enver T., Brewer A. C., Patient R. K. Role for DNA replication in beta-globin gene activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1301–1308. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenfeld G. Chromatin as an essential part of the transcriptional mechanism. Nature. 1992 Jan 16;355(6357):219–224. doi: 10.1038/355219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromental C., Kanno M., Nomiyama H., Chambon P. Cooperativity and hierarchical levels of functional organization in the SV40 enhancer. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):943–953. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90109-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard R. D., Guggenheimer R. A., Gluzman Y. Analysis of nonpermissivity in mouse cells overexpressing simian virus 40 T antigen. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):851–857. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.851-857.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y., Sambrook J. F., Frisque R. J. Expression of early genes of origin-defective mutants of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3898–3902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Rigby P. W., Lane D. P. Negative regulation of viral enhancers in undifferentiated embryonic stem cells. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):519–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90109-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Weintraub H. Propagation of globin DNAase I-hypersensitive sites in absence of factors required for induction: a possible mechanism for determination. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90019-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Clarke J. The SV40 enhancer is composed of multiple functional elements that can compensate for one another. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):461–470. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90332-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmquist G. P. Role of replication time in the control of tissue-specific gene expression. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Feb;40(2):151–173. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtzer H., Weintraub H., Mayne R., Mochan B. The cell cycle, cell lineages, and cell differentiation. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1972;7:229–256. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60073-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries E. H., Temin H. M. Requirement for cell division for initiation of transcription of Rous sarcoma virus RNA. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):531–546. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.531-546.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Khoury G., Gorman C., Howard B., Gruss P. Host-specific activation of transcription by tandem repeats from simian virus 40 and Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6453–6457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui T., Murayama M., Mita T. Adenovirus 2 peptide IX gene is expressed only on replicated DNA molecules. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4149–4154. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil P. L., Murphy R. F., Lanni F., Taylor D. L. A method for incorporating macromolecules into adherent cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1556–1564. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. M., Nasmyth K. A. Role of DNA replication in the repression of silent mating type loci in yeast. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):247–251. doi: 10.1038/312247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Control of cellular and viral transcription during adenovirus infection. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1986;19(4):307–322. doi: 10.3109/10409238609082543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolau C., Sene C. Liposome-mediated DNA transfer in eukaryotic cells. Dependence of the transfer efficiency upon the type of liposomes used and the host cell cycle stage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Oct 11;721(2):185–190. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(82)90067-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ondek B., Gloss L., Herr W. The SV40 enhancer contains two distinct levels of organization. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):40–45. doi: 10.1038/333040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phares W., Franza B. R., Jr, Herr W. The kappa B enhancer motifs in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and simian virus 40 recognize different binding activities in human Jurkat and H9 T cells: evidence for NF-kappa B-independent activation of the kappa B motif. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7490–7498. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7490-7498.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine R., Levy D. E., Reich N., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional stimulation by CaPO4-DNA precipitates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 25;16(4):1371–1378. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.4.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Lee B. A., Monks J. Multiple SP1 binding sites confer enhancer-independent, replication-activated transcription of HIV-1 and globin gene promoters. New Biol. 1992 Apr;4(4):369–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J. F., Fisher F., Goding C. R., Jones N. C. Mutational analysis of the adenovirus E1a gene: the role of transcriptional regulation in transformation. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2053–2060. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02470.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. H., Kegler D. M., Ziff E. B. Vector expression of adenovirus type 5 E1a proteins: evidence for E1a autoregulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2684–2696. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svaren J., Chalkley R. The structure and assembly of active chromatin. Trends Genet. 1990 Feb;6(2):52–56. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90074-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Grossniklaus U., Herr W., Hernandez N. Activation of the U2 snRNA promoter by the octamer motif defines a new class of RNA polymerase II enhancer elements. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1764–1778. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. P., Mathews M. B. DNA replication and the early to late transition in adenovirus infection. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):523–533. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90362-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Green M. R., Maniatis T. cis and trans activation of globin gene transcription in transient assays. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7428–7432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vales L. D., Darnell J. E., Jr Promoter occlusion prevents transcription of adenovirus polypeptide IX mRNA until after DNA replication. Genes Dev. 1989 Jan;3(1):49–59. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H. Formation of stable transcription complexes as assayed by analysis of individual templates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5819–5823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Brown D. D. DNA replication in vitro erases a Xenopus 5S RNA gene transcription complex. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):217–227. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90444-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P. Implications of DNA replication for eukaryotic gene expression. J Cell Sci. 1991 Jun;99(Pt 2):201–206. doi: 10.1242/jcs.99.2.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers J., Schaffner W., Tyndall C., Lupton S., Kamen R. Polyoma virus DNA replication requires an enhancer. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):242–246. doi: 10.1038/312242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]