Abstract
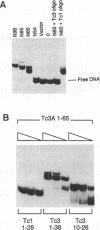
Tc3 is a member of the Tc1/mariner family of transposable elements. All these elements have terminal inverted repeats, encode related transposases and insert exclusively into TA dinucleotides. We have studied the DNA binding properties of Tc3 transposase and found that an N-terminal domain of 65 amino acids binds specifically to two regions within the 462 bp Tc3 inverted repeat; one region is located at the end of the inverted repeat, the other is located approximately 180 bp from the end. Methylation interference experiments indicate that this N-terminal DNA binding domain of the Tc3 transposase interacts with nucleotides on one face of the DNA helix over adjacent major and minor grooves.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abad P., Quiles C., Tares S., Piotte C., Castagnone-Sereno P., Abadon M., Dalmasso A. Sequences homologous to Tc(s) transposable elements of Caenorhabditis elegans are widely distributed in the phylum nematoda. J Mol Evol. 1991 Sep;33(3):251–258. doi: 10.1007/BF02100676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amemura J., Ichikawa H., Ohtsubo E. Tn3 transposition immunity is conferred by the transposase-binding domain in the terminal inverted-repeat sequence of Tn3. Gene. 1990 Mar 30;88(1):21–24. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90055-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brezinsky L., Wang G. V., Humphreys T., Hunt J. The transposable element Uhu from Hawaiian Drosophila--member of the widely dispersed class of Tc1-like transposons. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18(8):2053–2059. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.8.2053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caizzi R., Caggese C., Pimpinelli S. Bari-1, a new transposon-like family in Drosophila melanogaster with a unique heterochromatic organization. Genetics. 1993 Feb;133(2):335–345. doi: 10.1093/genetics/133.2.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J., Forbes E., Anderson P. The Tc3 family of transposable genetic elements in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1989 Jan;121(1):47–55. doi: 10.1093/genetics/121.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craigie R., Mizuuchi M., Mizuuchi K. Site-specific recognition of the bacteriophage Mu ends by the Mu A protein. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):387–394. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daboussi M. J., Langin T., Brygoo Y. Fot1, a new family of fungal transposable elements. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Mar;232(1):12–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00299131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derbyshire K. M., Grindley N. D. Binding of the IS903 transposase to its inverted repeat in vitro. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3449–3455. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05424.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doak T. G., Doerder F. P., Jahn C. L., Herrick G. A proposed superfamily of transposase genes: transposon-like elements in ciliated protozoa and a common "D35E" motif. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 1;91(3):942–946. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.3.942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fayet O., Ramond P., Polard P., Prère M. F., Chandler M. Functional similarities between retroviruses and the IS3 family of bacterial insertion sequences? Mol Microbiol. 1990 Oct;4(10):1771–1777. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00555.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franz G., Savakis C. Minos, a new transposable element from Drosophila hydei, is a member of the Tc1-like family of transposons. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 11;19(23):6646–6646. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.23.6646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Fernàndez J., Marfany G., Baguñ J., Saló E. Infiltration of mariner elements. Nature. 1993 Jul 8;364(6433):109–110. doi: 10.1038/364109a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierl A., Lütticke S., Saedler H. TnpA product encoded by the transposable element En-1 of Zea mays is a DNA binding protein. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4045–4053. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03298.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haniford D., Kleckner N. Tn 10 transposition in vivo: temporal separation of cleavages at the two transposon ends and roles of terminal basepairs subsequent to interaction of ends. EMBO J. 1994 Jul 15;13(14):3401–3411. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06643.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris L. J., Baillie D. L., Rose A. M. Sequence identity between an inverted repeat family of transposable elements in Drosophila and Caenorhabditis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):5991–5998. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.5991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris L. J., Prasad S., Rose A. M. Isolation and sequence analysis of Caenorhabditis briggsae repetitive elements related to the Caenorhabditis elegans transposon Tc1. J Mol Evol. 1990 Apr;30(4):359–369. doi: 10.1007/BF02101890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heierhorst J., Lederis K., Richter D. Presence of a member of the Tc1-like transposon family from nematodes and Drosophila within the vasotocin gene of a primitive vertebrate, the Pacific hagfish Eptatretus stouti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6798–6802. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Detection of Caenorhabditis transposon homologs in diverse organisms. New Biol. 1992 Apr;4(4):382–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman O., Errada P. R., Signon L., Kleckner N. Mutational analysis of IS10's outside end. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2101–2109. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03619.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kans J. A., Casadaban M. J. Nucleotide sequences required for Tn3 transposition immunity. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):1904–1914. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.1904-1914.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan E., Mack J. P., Katz R. A., Kulkosky J., Skalka A. M. Retroviral integrase domains: DNA binding and the recognition of LTR sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 25;19(4):851–860. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.4.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogstad P. A., Champoux J. J. Sequence-specific binding of DNA by the Moloney murine leukemia virus integrase protein. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2796–2801. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2796-2801.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunze R., Starlinger P. The putative transposase of transposable element Ac from Zea mays L. interacts with subterminal sequences of Ac. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3177–3185. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08476.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K. Transpositional recombination: mechanistic insights from studies of mu and other elements. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:1011–1051. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.005051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson H. M., Lampe D. J., MacLeod E. G. A mariner transposable element from a lacewing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 11;20(23):6409–6409. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.23.6409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson H. M. The mariner transposable element is widespread in insects. Nature. 1993 Mar 18;362(6417):241–245. doi: 10.1038/362241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. H., Lade B. N., Chui D. S., Lin S. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Vectors for selective expression of cloned DNAs by T7 RNA polymerase. Gene. 1987;56(1):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanssens P., Opsomer C., McKeown Y. M., Kramer W., Zabeau M., Fritz H. J. Efficient oligonucleotide-directed construction of mutations in expression vectors by the gapped duplex DNA method using alternating selectable markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4441–4454. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tausta S. L., Klobutcher L. A. Detection of circular forms of eliminated DNA during macronuclear development in E. crassus. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1019–1026. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90758-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tudor M., Lobocka M., Goodell M., Pettitt J., O'Hare K. The pogo transposable element family of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Mar;232(1):126–134. doi: 10.1007/BF00299145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos J. C., van Luenen H. G., Plasterk R. H. Characterization of the Caenorhabditis elegans Tc1 transposase in vivo and in vitro. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7A):1244–1253. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7a.1244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiater L. A., Grindley N. D. Gamma delta transposase and integration host factor bind cooperatively at both ends of gamma delta. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1907–1911. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03024.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerbib D., Prentki P., Gamas P., Freund E., Galas D. J., Chandler M. Functional organization of the ends of IS1: specific binding site for an IS 1-encoded protein. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Sep;4(9):1477–1486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Luenen H. G., Colloms S. D., Plasterk R. H. Mobilization of quiet, endogenous Tc3 transposons of Caenorhabditis elegans by forced expression of Tc3 transposase. EMBO J. 1993 Jun;12(6):2513–2520. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05906.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Luenen H. G., Colloms S. D., Plasterk R. H. The mechanism of transposition of Tc3 in C. elegans. Cell. 1994 Oct 21;79(2):293–301. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]