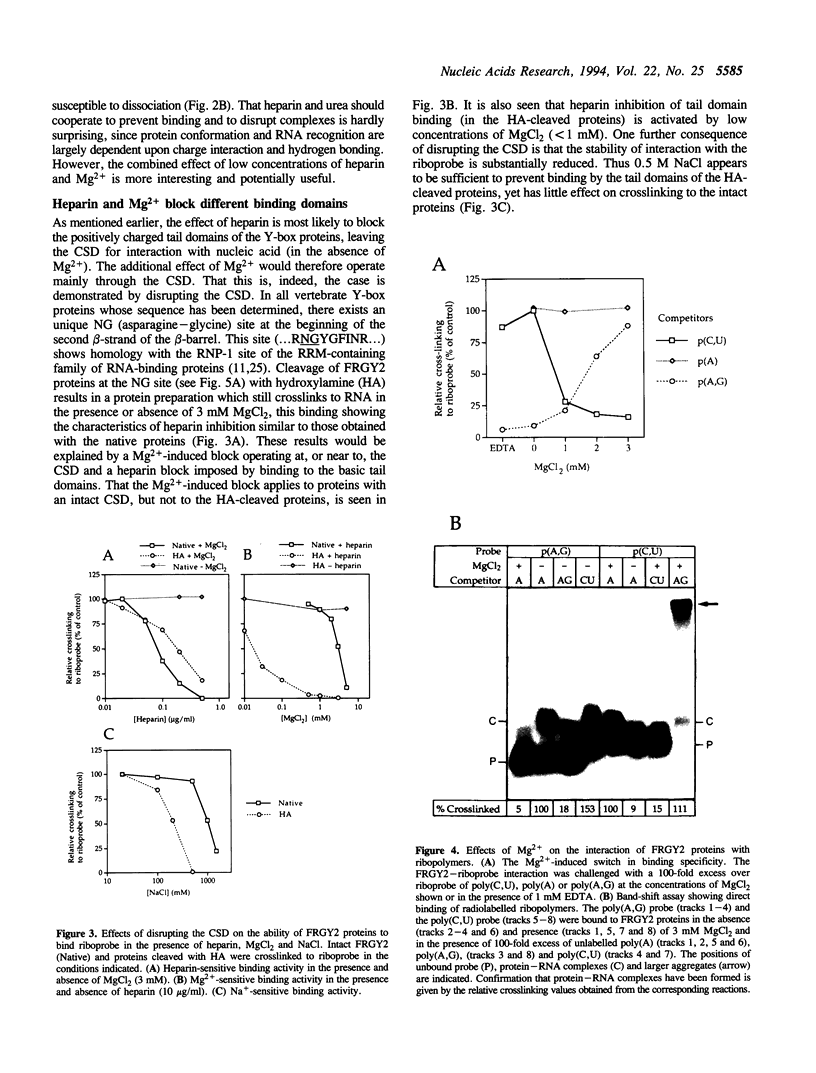
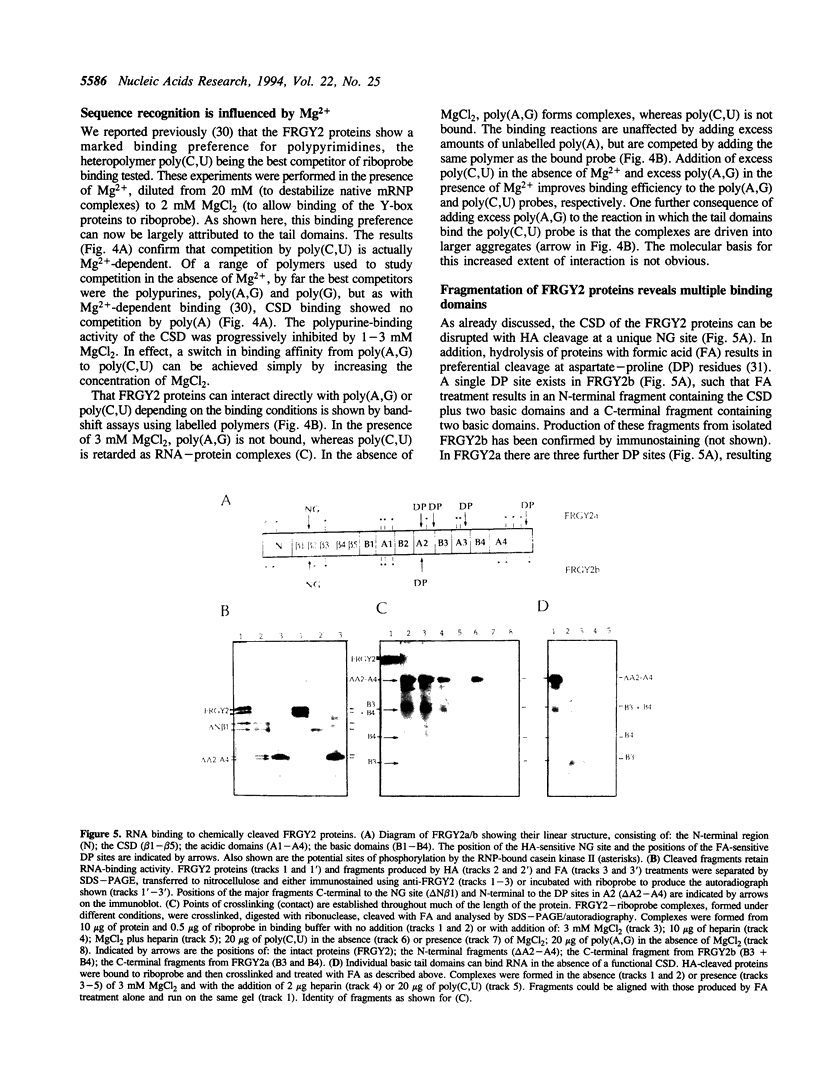
Abstract
Eukaryotic Y-box proteins are reported to interact with a wide variety of nucleic acid structures to act as transcription factors and mRNA masking proteins. The modular structure of Y-box proteins includes a highly conserved N-terminal cold-shock domain (CSD, equivalent to the bacterial cold-shock proteins) plus four basic C-terminal domains containing arginine clusters and aromatic residues. In addition, the basic domains are separated by acidic regions which contain several potential sites for serine/threonine phosphorylation. The interaction of Y-box proteins, isolated from Xenopus oocytes (FRGY2 type), with RNA molecules has been studied by UV crosslinking and protein fragmentation. We have identified two distinct binding activities. The CSD interacts preferentially with the polypurines poly(A,G) and poly(G) but not poly(A), this activity being sensitive to 5 mM MgCl2 but not to 5 mM spermidine. In the presence of 1 mM MgCl2 or 1 mM spermidine, the basic domains interact preferentially with poly(C,U), this activity being sensitive to 0.5 M NaCl. Binding of the basic domains is also sensitive to low concentrations of heparin. The basic domains can be crosslinked individually to labelled RNA. These results are discussed with reference to the various specificities noted in the binding of Y-box proteins to RNA and DNA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bendall A. J., Molloy P. L. Base preferences for DNA binding by the bHLH-Zip protein USF: effects of MgCl2 on specificity and comparison with binding of Myc family members. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Jul 25;22(14):2801–2810. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.14.2801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burd C. G., Dreyfuss G. Conserved structures and diversity of functions of RNA-binding proteins. Science. 1994 Jul 29;265(5172):615–621. doi: 10.1126/science.8036511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings A., Barrett P., Sommerville J. Multiple modifications in the phosphoproteins bound to stored messenger RNA in Xenopus oocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Dec 14;1014(3):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(89)90229-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschamps S., Viel A., Denis H., le Maire M. Purification of two thermostable components of messenger ribonucleoprotein particles (mRNPs) from Xenopus laevis oocytes, belonging to a novel class of RNA-binding proteins. FEBS Lett. 1991 Apr 22;282(1):110–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80456-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschamps S., Viel A., Garrigos M., Denis H., le Maire M. mRNP4, a major mRNA-binding protein from Xenopus oocytes is identical to transcription factor FRG Y2. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):13799–13802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Didier D. K., Schiffenbauer J., Woulfe S. L., Zacheis M., Schwartz B. D. Characterization of the cDNA encoding a protein binding to the major histocompatibility complex class II Y box. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7322–7326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doniger J., Landsman D., Gonda M. A., Wistow G. The product of unr, the highly conserved gene upstream of N-ras, contains multiple repeats similar to the cold-shock domain (CSD), a putative DNA-binding motif. New Biol. 1992 Apr;4(4):389–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn A., Durand B., Marfing C., Le Meur M., Benoist C., Mathis D. Conserved major histocompatibility complex class II boxes--X and Y--are transcriptional control elements and specifically bind nuclear proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6249–6253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enfield D. L., Ericsson L. H., Fujikawa K., Walsh K. A., Neurath H., Titani K. Amino acid sequence of the light chain of bovine factor X1 (Stuart factor). Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 19;19(4):659–667. doi: 10.1021/bi00545a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firulli A. B., Maibenco D. C., Kinniburgh A. J. The identification of a tandem H-DNA structure in the c-myc nuclease sensitive promoter element. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 May 29;185(1):264–270. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80985-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gai X. X., Lipson K. E., Prystowsky M. B. Unusual DNA binding characteristics of an in vitro translation product of the CCAAT binding protein mYB-1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 11;20(3):601–606. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.3.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant C. E., Deeley R. G. Cloning and characterization of chicken YB-1: regulation of expression in the liver. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):4186–4196. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.4186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graumann P., Marahiel M. A. The major cold shock protein of Bacillus subtilis CspB binds with high affinity to the ATTGG- and CCAAT sequences in single stranded oligonucleotides. FEBS Lett. 1994 Jan 31;338(2):157–160. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80355-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa S. L., Doetsch P. W., Hamilton K. K., Martin A. M., Okenquist S. A., Lenz J., Boss J. M. DNA binding properties of YB-1 and dbpA: binding to double-stranded, single-stranded, and abasic site containing DNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 25;19(18):4915–4920. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.18.4915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz E. M., Maloney K. A., Ley T. J. A human protein containing a "cold shock" domain binds specifically to H-DNA upstream from the human gamma-globin genes. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 13;269(19):14130–14139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquemin-Sablon H., Triqueneaux G., Deschamps S., le Maire M., Doniger J., Dautry F. Nucleic acid binding and intracellular localization of unr, a protein with five cold shock domains. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Jul 11;22(13):2643–2650. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.13.2643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandala J. C., Guntaka R. V. Cloning of Rous sarcoma virus enhancer factor genes. I. Evidence that RSV-EF-I is related to Y-box (inverted CCAAT) binding proteins and binds to multiple motifs in the RSV enhancer. Virology. 1994 Feb;198(2):514–523. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashanchi F., Duvall J. F., Dittmer J., Mireskandari A., Reid R. L., Gitlin S. D., Brady J. N. Involvement of transcription factor YB-1 in human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I basal gene expression. J Virol. 1994 Jan;68(1):561–565. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.1.561-565.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolluri R., Torrey T. A., Kinniburgh A. J. A CT promoter element binding protein: definition of a double-strand and a novel single-strand DNA binding motif. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 11;20(1):111–116. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.1.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon Y. K., Murray M. T., Hecht N. B. Proteins homologous to the Xenopus germ cell-specific RNA-binding proteins p54/p56 are temporally expressed in mouse male germ cells. Dev Biol. 1993 Jul;158(1):99–100. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Teana A., Brandi A., Falconi M., Spurio R., Pon C. L., Gualerzi C. O. Identification of a cold shock transcriptional enhancer of the Escherichia coli gene encoding nucleoid protein H-NS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10907–10911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laing L. G., Gluick T. C., Draper D. E. Stabilization of RNA structure by Mg ions. Specific and non-specific effects. J Mol Biol. 1994 Apr 15;237(5):577–587. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenz J., Okenquist S. A., LoSardo J. E., Hamilton K. K., Doetsch P. W. Identification of a mammalian nuclear factor and human cDNA-encoded proteins that recognize DNA containing apurinic sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3396–3400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
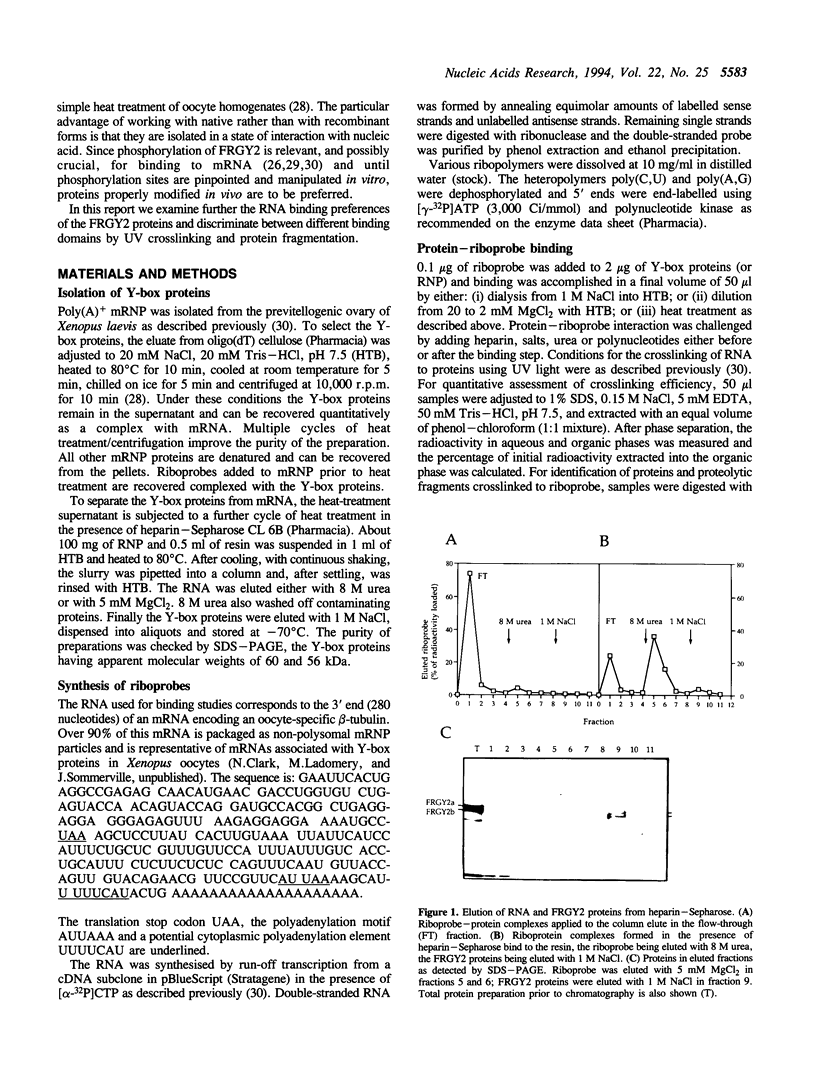
- Marello K., LaRovere J., Sommerville J. Binding of Xenopus oocyte masking proteins to mRNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 11;20(21):5593–5600. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.21.5593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. T., Krohne G., Franke W. W. Different forms of soluble cytoplasmic mRNA binding proteins and particles in Xenopus laevis oocytes and embryos. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;112(1):1–11. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. T., Schiller D. L., Franke W. W. Sequence analysis of cytoplasmic mRNA-binding proteins of Xenopus oocytes identifies a family of RNA-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):11–15. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newkirk K., Feng W., Jiang W., Tejero R., Emerson S. D., Inouye M., Montelione G. T. Solution NMR structure of the major cold shock protein (CspA) from Escherichia coli: identification of a binding epitope for DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):5114–5118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.5114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nute P. E., Mahoney W. C. Complete amino acid sequence of the gamma chain from the major fetal hemoglobin of the pig-tailed macaque, Macaca nemestrina. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 6;18(3):467–472. doi: 10.1021/bi00570a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozer J., Faber M., Chalkley R., Sealy L. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA clone for the CCAAT transcription factor EFIA reveals a novel structural motif. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22143–22152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranjan M., Tafuri S. R., Wolffe A. P. Masking mRNA from translation in somatic cells. Genes Dev. 1993 Sep;7(9):1725–1736. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.9.1725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindelin H., Jiang W., Inouye M., Heinemann U. Crystal structure of CspA, the major cold shock protein of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):5119–5123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.5119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindelin H., Marahiel M. A., Heinemann U. Universal nucleic acid-binding domain revealed by crystal structure of the B. subtilis major cold-shock protein. Nature. 1993 Jul 8;364(6433):164–168. doi: 10.1038/364164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnuchel A., Wiltscheck R., Czisch M., Herrler M., Willimsky G., Graumann P., Marahiel M. A., Holak T. A. Structure in solution of the major cold-shock protein from Bacillus subtilis. Nature. 1993 Jul 8;364(6433):169–171. doi: 10.1038/364169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommerville J. RNA-binding proteins: masking proteins revealed. Bioessays. 1992 May;14(5):337–339. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
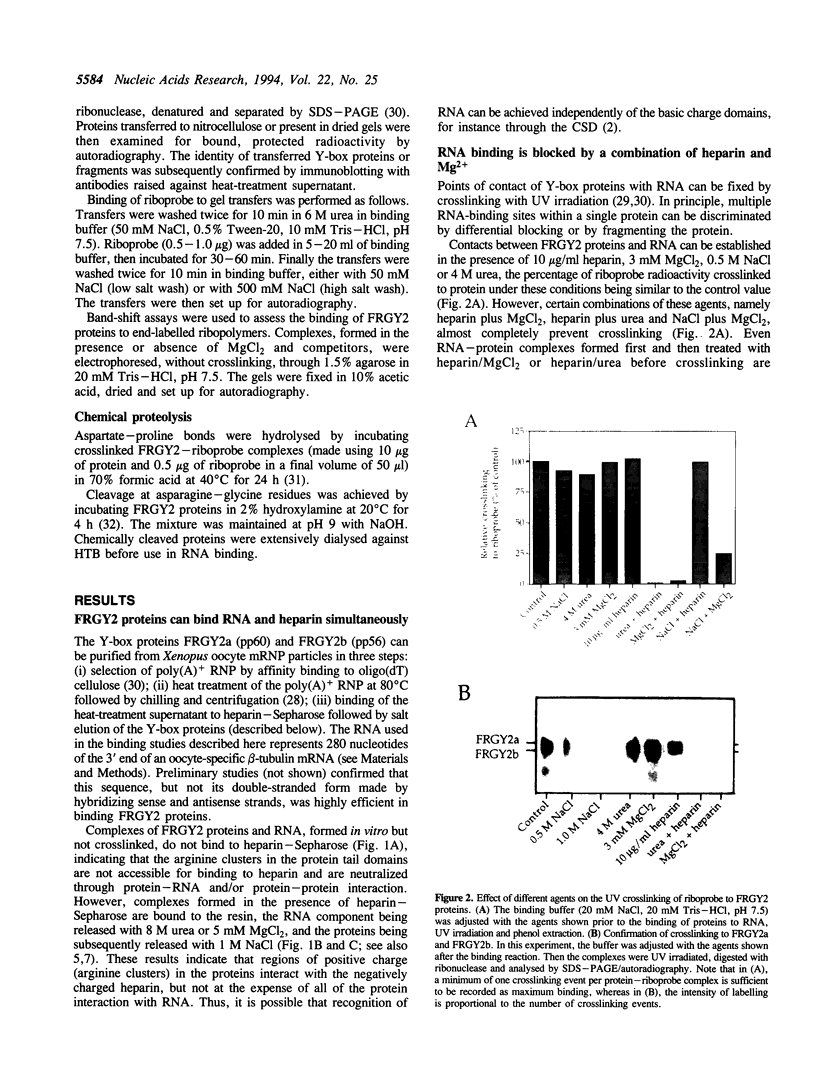
- Spitkovsky D. D., Royer-Pokora B., Delius H., Kisseljov F., Jenkins N. A., Gilbert D. J., Copeland N. G., Royer H. D. Tissue restricted expression and chromosomal localization of the YB-1 gene encoding a 42 kD nuclear CCAAT binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 25;20(4):797–803. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.4.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tafuri S. R., Familari M., Wolffe A. P. A mouse Y box protein, MSY1, is associated with paternal mRNA in spermatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):12213–12220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tafuri S. R., Wolffe A. P. Xenopus Y-box transcription factors: molecular cloning, functional analysis and developmental regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):9028–9032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.9028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wistow G. Cold shock and DNA binding. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):823–824. doi: 10.1038/344823c0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P. Structural and functional properties of the evolutionarily ancient Y-box family of nucleic acid binding proteins. Bioessays. 1994 Apr;16(4):245–251. doi: 10.1002/bies.950160407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Tafuri S., Ranjan M., Familari M. The Y-box factors: a family of nucleic acid binding proteins conserved from Escherichia coli to man. New Biol. 1992 Apr;4(4):290–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]