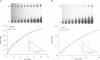Abstract
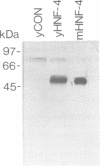
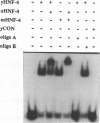
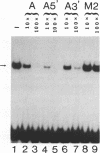
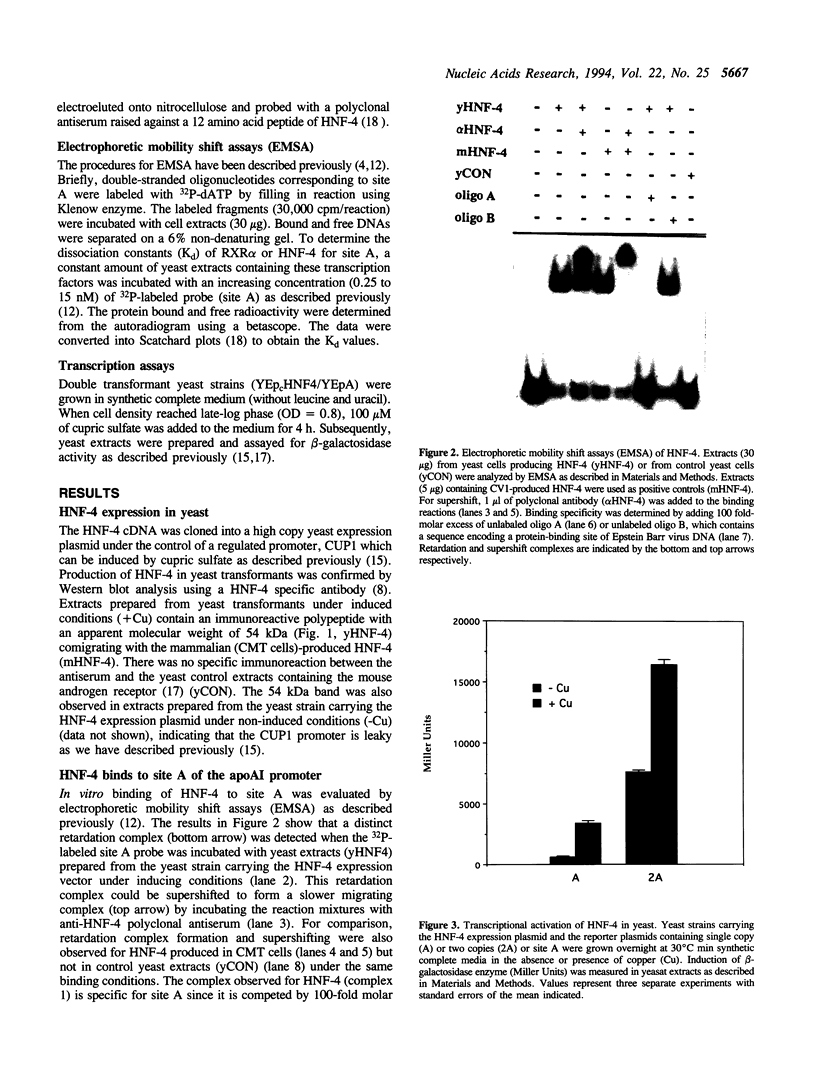
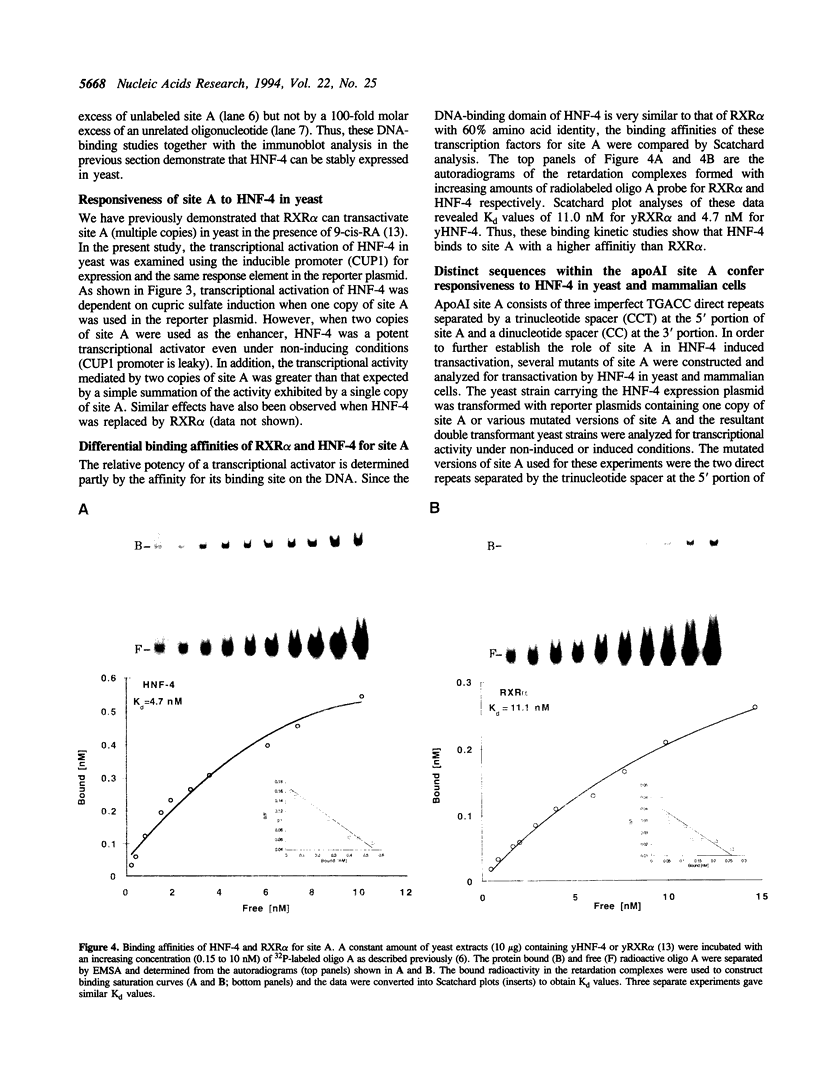
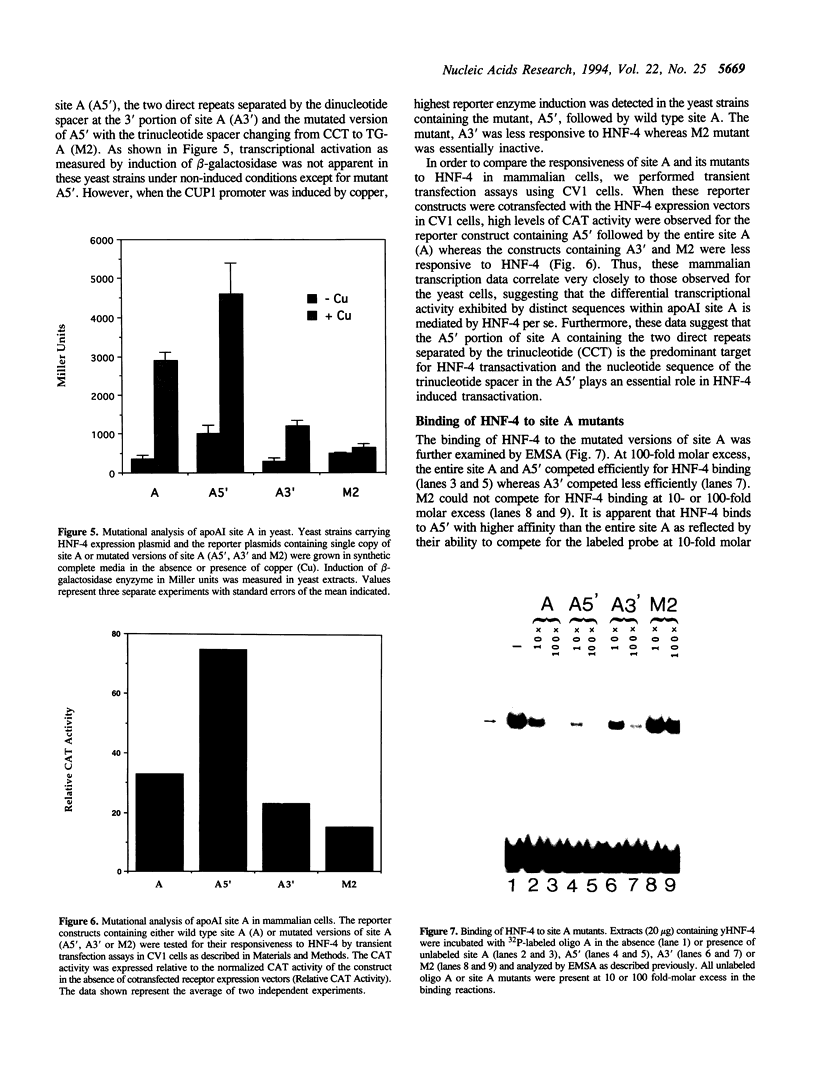
Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4 (HNF-4), a liver-enriched orphan receptor of the nuclear receptor superfamily, is required for the expression of a wide variety of liver-specific genes including apoAI. To explore the possibility that site A of the apoAI gene enhancer might also be the target for HNF-4 without the interference of endogenous mammalian cell proteins that also bind to site A, we tested the ability of HNF-4 to activate transcription from site A in yeast cells. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSA) and Scatchard plot analysis demonstrated that yeast produced HNF-4 binds to site A with an affinity two times higher than that of yeast produced RXR alpha. Mapping analysis indicated that the 5' portion of site A containing two imperfect direct repeats (TGAACCCTTGACC) and the sequence of the trinucleotide spacer (CCT) between these imperfect repeats are critical determinants for selective binding and transactivation by HNF-4. Similar observations were obtained when these mutated versions of site A were evaluated by transient cotransfection assays in CV1 cells. We conclude that the unique structural determinants of site A in conjunction with the differential binding affinity of HNF-4 for site A may play a fundamental role in apoAI gene regulation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chan J., Nakabayashi H., Wong N. C. HNF-4 increases activity of the rat Apo A1 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Mar 11;21(5):1205–1211. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.5.1205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D. J., Rifkind B. M. High-density lipoprotein--the clinical implications of recent studies. N Engl J Med. 1989 Nov 9;321(19):1311–1316. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198911093211907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddad I. A., Ordovas J. M., Fitzpatrick T., Karathanasis S. K. Linkage, evolution, and expression of the rat apolipoprotein A-I, C-III, and A-IV genes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):13268–13277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heery D. M., Zacharewski T., Pierrat B., Gronemeyer H., Chambon P., Losson R. Efficient transactivation by retinoic acid receptors in yeast requires retinoid X receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):4281–4285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.4281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladias J. A., Karathanasis S. K. Regulation of the apolipoprotein AI gene by ARP-1, a novel member of the steroid receptor superfamily. Science. 1991 Feb 1;251(4993):561–565. doi: 10.1126/science.1899293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mak P., Fuernkranz H. A., Ge R., Karathanasis S. K. Retinoid X receptor homodimers function as transcriptional activators in yeast. Gene. 1994 Jul 22;145(1):129–133. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90335-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mak P., McDonnell D. P., Weigel N. L., Schrader W. T., O'Malley B. W. Expression of functional chicken oviduct progesterone receptors in yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae). J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21613–21618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mak P., Young C. Y., Tindall D. J. A novel yeast expression system to study androgen action. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1994;49:347–352. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571149-4.50023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger D., White J. H., Chambon P. The human oestrogen receptor functions in yeast. Nature. 1988 Jul 7;334(6177):31–36. doi: 10.1038/334031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger S., Halaas J. L., Breslow J. L., Sladek F. M. Orphan receptor HNF-4 and bZip protein C/EBP alpha bind to overlapping regions of the apolipoprotein B gene promoter and synergistically activate transcription. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 5;268(22):16831–16838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mietus-Snyder M., Sladek F. M., Ginsburg G. S., Kuo C. F., Ladias J. A., Darnell J. E., Jr, Karathanasis S. K. Antagonism between apolipoprotein AI regulatory protein 1, Ear3/COUP-TF, and hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 modulates apolipoprotein CIII gene expression in liver and intestinal cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1708–1718. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moehle C. M., Aynardi M. W., Kolodny M. R., Park F. J., Jones E. W. Protease B of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: isolation and regulation of the PRB1 structural gene. Genetics. 1987 Feb;115(2):255–263. doi: 10.1093/genetics/115.2.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- När A. M., Boutin J. M., Lipkin S. M., Yu V. C., Holloway J. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. The orientation and spacing of core DNA-binding motifs dictate selective transcriptional responses to three nuclear receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1267–1279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90021-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan T. C., Hao Q. L., Yamin T. T., Dai P. H., Chen B. S., Chen S. L., Kroon P. A., Chao Y. S. Rabbit apolipoprotein A-I mRNA and gene. Evidence that rabbit apolipoprotein A-I is synthesized in the intestine but not in the liver. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Dec 30;170(1-2):99–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13672.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottman J. N., Widom R. L., Nadal-Ginard B., Mahdavi V., Karathanasis S. K. A retinoic acid-responsive element in the apolipoprotein AI gene distinguishes between two different retinoic acid response pathways. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3814–3820. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sastry K. N., Seedorf U., Karathanasis S. K. Different cis-acting DNA elements control expression of the human apolipoprotein AI gene in different cell types. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):605–614. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schena M., Yamamoto K. R. Mammalian glucocorticoid receptor derivatives enhance transcription in yeast. Science. 1988 Aug 19;241(4868):965–967. doi: 10.1126/science.3043665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladek F. M. Orphan receptor HNF-4 and liver-specific gene expression. Receptor. 1993 Fall;3(3):223–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladek F. M., Zhong W. M., Lai E., Darnell J. E., Jr Liver-enriched transcription factor HNF-4 is a novel member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2353–2365. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Cooperative binding of steroid hormone receptors contributes to transcriptional synergism at target enhancer elements. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):443–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90919-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Murakami K. K., Thompson C. C., Evans R. M. Direct repeats as selective response elements for the thyroid hormone, retinoic acid, and vitamin D3 receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1255–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90020-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widom R. L., Ladias J. A., Kouidou S., Karathanasis S. K. Synergistic interactions between transcription factors control expression of the apolipoprotein AI gene in liver cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):677–687. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widom R. L., Rhee M., Karathanasis S. K. Repression by ARP-1 sensitizes apolipoprotein AI gene responsiveness to RXR alpha and retinoic acid. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3380–3389. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. K., Lehmann J., Hoffmann B., Dawson M. I., Cameron J., Graupner G., Hermann T., Tran P., Pfahl M. Homodimer formation of retinoid X receptor induced by 9-cis retinoic acid. Nature. 1992 Aug 13;358(6387):587–591. doi: 10.1038/358587a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong W., Sladek F. M., Darnell J. E., Jr The expression pattern of a Drosophila homolog to the mouse transcription factor HNF-4 suggests a determinative role in gut formation. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):537–544. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05685.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]