Abstract
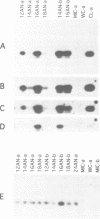
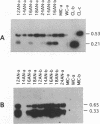
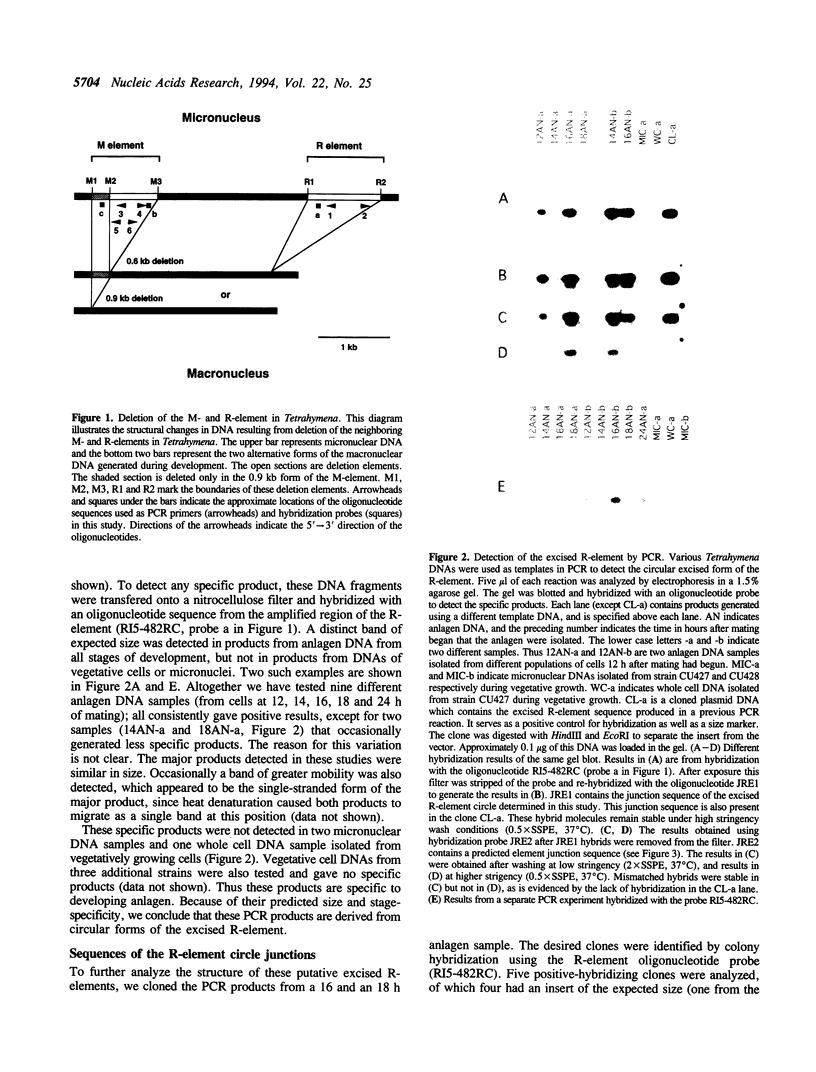
Extensive programmed DNA deletion occurs in ciliates during development. In this study we examine the excised forms of two previously characterized deletion elements, the R- and M-element, in Tetrahymena. Using divergently oriented primers in polymerase chain reactions we have detected the junctions formed by joining the two ends of these elements, providing evidence for the presence of circular excised forms. These circular forms were detected in developing macronuclear DNA from 12-24 h after mating began, but not in micronuclear or whole cell DNA of vegetative cells. They are present at very low abundance, detectable after PCR only through hybridization with specific probes. Sequence analysis shows that the circle junctions occur at or very near the known ends of the elements. There is sequence microheterogeneity in these junctions, which does not support a simple reciprocal exchange model for DNA deletion. A model involving staggered cuts and variable mismatch repair is proposed to explain these results. This model also explains the sequence microheterogeneity previously detected among the junction sequences retained in the macronuclear chromosome.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allis C. D., Dennison D. K. Identification and purification of young macronuclear anlagen from conjugating cells of Tetrahymena thermophila. Dev Biol. 1982 Oct;93(2):519–533. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90139-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austerberry C. F., Allis C. D., Yao M. C. Specific DNA rearrangements in synchronously developing nuclei of Tetrahymena. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7383–7387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austerberry C. F., Snyder R. O., Yao M. C. Sequence microheterogeneity is generated at junctions of programmed DNA deletions in Tetrahymena thermophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7263–7272. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austerberry C. F., Yao M. C. Nucleotide sequence structure and consistency of a developmentally regulated DNA deletion in Tetrahymena thermophila. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):435–443. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austerberry C. F., Yao M. C. Sequence structures of two developmentally regulated, alternative DNA deletion junctions in Tetrahymena thermophila. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3947–3950. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns P. J., Brussard T. B. Pair formation in tetrahymena pyriformis, an inducible developmental system. J Exp Zool. 1974 Jun;188(3):337–344. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401880309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godiska R., James C., Yao M. C. A distant 10-bp sequence specifies the boundaries of a programmed DNA deletion in Tetrahymena. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12A):2357–2365. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12a.2357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godiska R., Yao M. C. A programmed site-specific DNA rearrangement in Tetrahymena thermophila requires flanking polypurine tracts. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1237–1246. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90688-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorovsky M. A. Macro- and micronuclei of Tetrahymena pyriformis: a model system for studying the structure and function of eukaryotic nuclei. J Protozool. 1973 Feb;20(1):19–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1973.tb05995.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinonen T. Y., Pearlman R. E. A germ line-specific sequence element in an intron in Tetrahymena thermophila. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 1;269(26):17428–17433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter D. J., Williams K., Cartinhour S., Herrick G. Precise excision of telomere-bearing transposons during Oxytricha fallax macronuclear development. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2101–2112. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn C. L., Krikau M. F., Shyman S. Developmentally coordinated en masse excision of a highly repetitive element in E. crassus. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1009–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90757-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaraczewski J. W., Jahn C. L. Elimination of Tec elements involves a novel excision process. Genes Dev. 1993 Jan;7(1):95–105. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.1.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karrer K. M. Germ line-specific DNA sequences are present on all five micronuclear chromosomes in Tetrahymena thermophila. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;3(11):1909–1919. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.11.1909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh M., Hirono M., Takemasa T., Kimura M., Watanabe Y. A micronucleus-specific sequence exists in the 5'-upstream region of calmodulin gene in Tetrahymena thermophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 May 25;21(10):2409–2414. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.10.2409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klobutcher L. A., Turner L. R., LaPlante J. Circular forms of developmentally excised DNA in Euplotes crassus have a heteroduplex junction. Genes Dev. 1993 Jan;7(1):84–94. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.1.84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribas-Aparicio R. M., Sparkowski J. J., Proulx A. E., Mitchell J. D., Klobutcher L. A. Nucleic acid splicing events occur frequently during macronuclear development in the protozoan Oxytricha nova and involve the elimination of unique DNA. Genes Dev. 1987 Jun;1(4):323–336. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.4.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saveliev S. V., Cox M. M. The fate of deleted DNA produced during programmed genomic deletion events in Tetrahymena thermophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Dec 25;22(25):5695–5701. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.25.5695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tausta S. L., Klobutcher L. A. Detection of circular forms of eliminated DNA during macronuclear development in E. crassus. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1019–1026. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90758-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. M., Ellingson J. L., Catt D. M., Berger P. J., Karrer K. M. A small family of elements with long inverted repeats is located near sites of developmentally regulated DNA rearrangement in Tetrahymena thermophila. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;14(9):5939–5949. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.9.5939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K., Doak T. G., Herrick G. Developmental precise excision of Oxytricha trifallax telomere-bearing elements and formation of circles closed by a copy of the flanking target duplication. EMBO J. 1993 Dec;12(12):4593–4601. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06148.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao M. C., Choi J., Yokoyama S., Austerberry C. F., Yao C. H. DNA elimination in Tetrahymena: a developmental process involving extensive breakage and rejoining of DNA at defined sites. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90236-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao M. C. Elimination of specific DNA sequences from the somatic nucleus of the ciliate Tetrahymena. J Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;92(3):783–789. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.3.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao M. C., Gorovsky M. A. Comparison of the sequences of macro- and micronuclear DNA of Tetrahymena pyriformis. Chromosoma. 1974;48(1):1–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00284863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama R. W., Yao M. C. Elimination of DNA sequences during macronuclear differentiation in Tetrahymena thermophila, as detected by in situ hybridization. Chromosoma. 1982;85(1):11–22. doi: 10.1007/BF00344591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]