Abstract
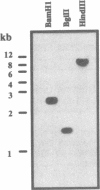
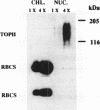
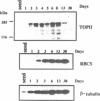
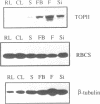
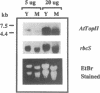
Topoisomerase II (TOPII) is an important enzyme involved in DNA replication and chromosome condensation. The level of TOPII expression has been correlated with the proliferative state of eukaryotic cells. Here we report the cloning and characterization of a cDNA clone AtTopII encoding the first reported TOPII from higher plants. AtTopII is 4603 base pairs (bp) in length and encodes an open reading frame of 1473 amino acid residues. One interesting feature of AtTopII is the presence of a 110 bp direct repeat in the last one-third of the cDNA. Analysis of the genomic sequence within this region by PCR revealed that this duplication includes a small intron of 89 bp. Conservation of sequences within this repeated intron suggests that this in-frame duplication may be a relatively recent event. The deduced amino acid sequence of AtTopII shows strong homologies to TOPII sequences reported from other eukaryotes, particularly in the regions that are highly conserved among different species. Southern blot analysis with Arabidopsis DNA indicates that AtTopII is a single-copy gene while Northern blots detected a 5.0 kb transcript, the level of which is substantially higher in young seedlings than in mature plants. Using a polyclonal antiserum raised against the C-terminal one-third of AtTOPII, we found that the protein is localized in the nucleus and its level is correlated with the proliferative state of the particular tissue.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman P., Glover C. V., Osheroff N. Phosphorylation of DNA topoisomerase II by casein kinase II: modulation of eukaryotic topoisomerase II activity in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3164–3168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adachi Y., Luke M., Laemmli U. K. Chromosome assembly in vitro: topoisomerase II is required for condensation. Cell. 1991 Jan 11;64(1):137–148. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90215-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carballo M., Giné R., Santos M., Puigdomènech P. Characterization of topoisomerase I and II activities in nuclear extracts during callogenesis in immature embryos of Zea mays. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 Jan;16(1):59–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00017917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardenas M. E., Dang Q., Glover C. V., Gasser S. M. Casein kinase II phosphorylates the eukaryote-specific C-terminal domain of topoisomerase II in vivo. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1785–1796. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05230.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caron P. R., Watt P., Wang J. C. The C-terminal domain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae DNA topoisomerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 May;14(5):3197–3207. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.5.3197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlesworth B., Sniegowski P., Stephan W. The evolutionary dynamics of repetitive DNA in eukaryotes. Nature. 1994 Sep 15;371(6494):215–220. doi: 10.1038/371215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crenshaw D. G., Hsieh T. Function of the hydrophilic carboxyl terminus of type II DNA topoisomerase from Drosophila melanogaster. I. In vitro studies. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):21328–21334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiNardo S., Voelkel K., Sternglanz R. DNA topoisomerase II mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: topoisomerase II is required for segregation of daughter molecules at the termination of DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2616–2620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Laskey R. A. Protein import into the cell nucleus. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:367–390. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duguet M., Lavenot C., Harper F., Mirambeau G., De Recondo A. M. DNA topoisomerases from rat liver: physiological variations. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 25;11(4):1059–1075. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.4.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto T., Wang J. C. Yeast DNA topoisomerase II is encoded by a single-copy, essential gene. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1073–1080. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90057-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halligan B. D., Edwards K. A., Liu L. F. Purification and characterization of a type II DNA topoisomerase from bovine calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2475–2482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heck M. M., Earnshaw W. C. Topoisomerase II: A specific marker for cell proliferation. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2569–2581. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm C., Goto T., Wang J. C., Botstein D. DNA topoisomerase II is required at the time of mitosis in yeast. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):553–563. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins J. R., Ayton P., Jones T., Davies S. L., Simmons D. L., Harris A. L., Sheer D., Hickson I. D. Isolation of cDNA clones encoding the beta isozyme of human DNA topoisomerase II and localisation of the gene to chromosome 3p24. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 11;20(21):5587–5592. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.21.5587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junghans H., Metzlaff M. A simple and rapid method for the preparation of total plant DNA. Biotechniques. 1990 Feb;8(2):176–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F. DNA topoisomerase poisons as antitumor drugs. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:351–375. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynn R., Giaever G., Swanberg S. L., Wang J. C. Tandem regions of yeast DNA topoisomerase II share homology with different subunits of bacterial gyrase. Science. 1986 Aug 8;233(4764):647–649. doi: 10.1126/science.3014661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manzara T., Carrasco P., Gruissem W. Developmental and organ-specific changes in promoter DNA-protein interactions in the tomato rbcS gene family. Plant Cell. 1991 Dec;3(12):1305–1316. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.12.1305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perisic O., Lam E. A tobacco DNA binding protein that interacts with a light-responsive box II element. Plant Cell. 1992 Jul;4(7):831–838. doi: 10.1105/tpc.4.7.831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinna L. A. Casein kinase 2: an 'eminence grise' in cellular regulation? Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Sep 24;1054(3):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahyoun N., Wolf M., Besterman J., Hsieh T., Sander M., LeVine H., 3rd, Chang K. J., Cuatrecasas P. Protein kinase C phosphorylates topoisomerase II: topoisomerase activation and its possible role in phorbol ester-induced differentiation of HL-60 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1603–1607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlötterer C., Tautz D. Slippage synthesis of simple sequence DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 25;20(2):211–215. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiozaki K., Yanagida M. Functional dissection of the phosphorylated termini of fission yeast DNA topoisomerase II. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(5):1023–1036. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.5.1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staiger C., Doonan J. Cell division in plants. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;5(2):226–231. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90107-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan D. M., Glisson B. S., Hodges P. K., Smallwood-Kentro S., Ross W. E. Proliferation dependence of topoisomerase II mediated drug action. Biochemistry. 1986 Apr 22;25(8):2248–2256. doi: 10.1021/bi00356a060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussex I. M. Developmental programming of the shoot meristem. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):225–229. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90895-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. J., Mosig G. An ATP-dependent supercoiling topoisomerase of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii affects accumulation of specific chloroplast transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):873–891. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura T., Ohkura H., Adachi Y., Morino K., Shiozaki K., Yanagida M. DNA topoisomerase II is required for condensation and separation of mitotic chromosomes in S. pombe. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):917–925. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90518-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:665–697. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. DNA topoisomerases: why so many? J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):6659–6662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyckoff E., Natalie D., Nolan J. M., Lee M., Hsieh T. Structure of the Drosophila DNA topoisomerase II gene. Nucleotide sequence and homology among topoisomerases II. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jan 5;205(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90361-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]