Abstract
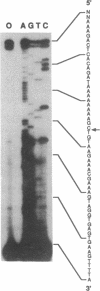
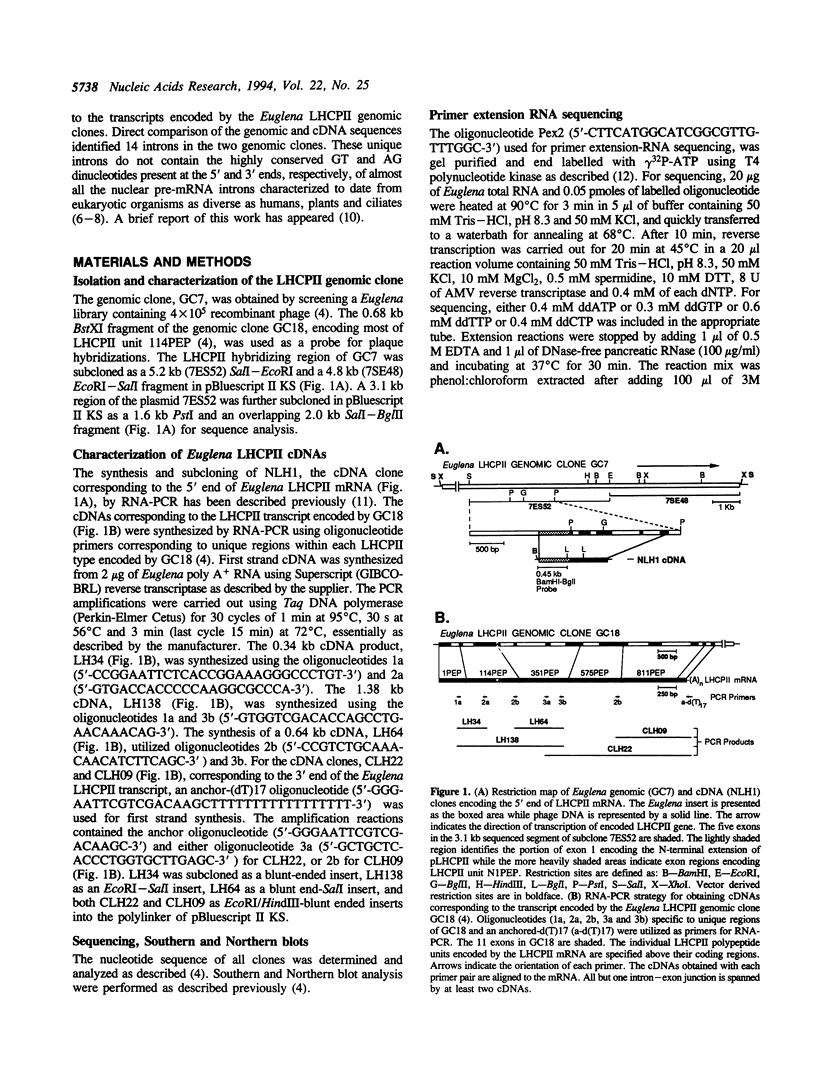
The precursor to the Euglena light harvesting chlorophyll a/b binding protein of photosystem II (LHCPII) is a polyprotein containing multiple copies of LHCPII covalently joined by a decapeptide linker. cDNA and genomic clones encoding the 5' and 3' end of a 6.6 kb LHCPII mRNA were sequenced. A 3.1 kb genomic region encoding 1.05 kb of the 5' end of LHCPII mRNA contains 4 introns. A 7.6 kb genomic region encoding 3.3 kb of the 3' end of LHCPII mRNA contains 10 introns. The 5' and 3' ends of the 14 identified Euglena introns lacked the conserved dinucleotides (5'-GT and AG-3') found at the termini of virtually every characterized nuclear pre-mRNA intron. A common consensus splice site selection sequence could not be identified. The Euglena introns do not have the structural characteristics of group I and group II introns. The only structural feature common to all Euglena introns was the ability of short stretches of nucleotides at the 5' and 3' ends of the introns to base pair, forming a stable stem-loop with the 5' and 3' splice site juxtaposed for splicing but displaced by 2 nucleotides. The 26 nucleotide sequence at the 5' end of LHCPII mRNA is absent from the genomic sequence and identical to the 5' end of one of the small Euglena SL-RNAs indicating that it is post-transcriptionally added by trans-splicing.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agabian N. Trans splicing of nuclear pre-mRNAs. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1157–1160. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90674-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agami R., Shapira M. Nucleotide sequence of the spliced leader RNA gene from Leishmania mexicana amazonensis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 11;20(7):1804–1804. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.7.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellofatto V., Cooper R., Cross G. A. Discontinuous transcription in Leptomonas seymouri: presence of intact and interrupted mini-exon gene families. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7437–7456. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal T., Thomas J. Cis and trans mRNA splicing in C. elegans. Trends Genet. 1988 Nov;4(11):305–308. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90107-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavener D. R., Ray S. C. Eukaryotic start and stop translation sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 25;19(12):3185–3192. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.12.3185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. Conserved sequences and structures of group I introns: building an active site for RNA catalysis--a review. Gene. 1988 Dec 20;73(2):259–271. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90492-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan R. L., Keller M., Canaday J., Weil J. H., Imbault P. Eight small subunits of Euglena ribulose 1-5 bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase are translated from a large mRNA as a polyprotein. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):333–338. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08115.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christopher D. A., Hallick R. B. Euglena gracilis chloroplast ribosomal protein operon: a new chloroplast gene for ribosomal protein L5 and description of a novel organelle intron category designated group III. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 11;17(19):7591–7608. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.19.7591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copertino D. W., Hall E. T., Van Hook F. W., Jenkins K. P., Hallick R. B. A group III twintron encoding a maturase-like gene excises through lariat intermediates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Mar 25;22(6):1029–1036. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.6.1029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copertino D. W., Hallick R. B. Group II and group III introns of twintrons: potential relationships with nuclear pre-mRNA introns. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Dec;18(12):467–471. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90008-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csank C., Taylor F. M., Martindale D. W. Nuclear pre-mRNA introns: analysis and comparison of intron sequences from Tetrahymena thermophila and other eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5133–5141. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs S. P. The chloroplasts of some algal groups may have evolved from endosymbiotic eukaryotic algae. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;361:193–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb46519.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Biochemical mechanisms of constitutive and regulated pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:559–599. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallick R. B., Hong L., Drager R. G., Favreau M. R., Monfort A., Orsat B., Spielmann A., Stutz E. Complete sequence of Euglena gracilis chloroplast DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 25;21(15):3537–3544. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.15.3537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houlné G., Schantz R. Characterization of cDNA sequences for LHCI apoproteins in Euglena gracilis: the mRNA encodes a large precursor containing several consecutive divergent polypeptides. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Aug;213(2-3):479–486. doi: 10.1007/BF00339619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson I. J. A reappraisal of non-consensus mRNA splice sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):3795–3798. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.3795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansson S., Gustafsson P. Type I and type II genes for the chlorophyll a/b-binding protein in the gymnosperm Pinus sylvestris (Scots pine): cDNA cloning and sequence analysis. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 Mar;14(3):287–296. doi: 10.1007/BF00028766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapotas N., Bellofatto V. Differential response to RNA trans-splicing signals within the phosphoglycerate kinase gene cluster in Trypanosoma brucei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Aug 25;21(17):4067–4072. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.17.4067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller M., Tessier L. H., Chan R. L., Weil J. H., Imbault P. In Euglena, spliced-leader RNA (SL-RNA) and 5S rRNA genes are tandemly repeated. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 11;20(7):1711–1715. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.7.1711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishore R., Muchhal U. S., Schwartzbach S. D. The presequence of Euglena LHCPII, a cytoplasmically synthesized chloroplast protein, contains a functional endoplasmic reticulum-targeting domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11845–11849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Comparison of initiation of protein synthesis in procaryotes, eucaryotes, and organelles. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):1–45. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.1-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesser C. F., Guthrie C. Mutations in U6 snRNA that alter splice site specificity: implications for the active site. Science. 1993 Dec 24;262(5142):1982–1988. doi: 10.1126/science.8266093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Q., Ma L., Burkhart W., Spremulli L. L. Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones for chloroplast translational initiation factor-3 from Euglena gracilis. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 1;269(13):9436–9444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAQSOOD M., BIOL M. I. Biological effects of ionizing radiation. Pak J Health. 1957 Jan;6(4):227–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Umesono K., Ozeki H. Comparative and functional anatomy of group II catalytic introns--a review. Gene. 1989 Oct 15;82(1):5–30. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montandon P. E., Stutz E. Structure and expression of the Euglena gracilis nuclear gene coding for the translation elongation factor EF-1 alpha. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 11;18(1):75–82. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muchhal U. S., Schwartzbach S. D. Characterization of a Euglena gene encoding a polyprotein precursor to the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b-binding protein of photosystem II. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 Jan;18(2):287–299. doi: 10.1007/BF00034956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman A. J., Norman C. U5 snRNA interacts with exon sequences at 5' and 3' splice sites. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):743–754. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90149-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen T. W. Trans-splicing in nematodes. Exp Parasitol. 1989 Nov;69(4):413–416. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(89)90191-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R., Siliciano P. G. Evidence for an essential non-Watson-Crick interaction between the first and last nucleotides of a nuclear pre-mRNA intron. Nature. 1993 Feb 18;361(6413):660–662. doi: 10.1038/361660a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rikin A., Schwartzbach S. D. Extremely large and slowly processed precursors to the Euglena light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b binding proteins of photosystem II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5117–5121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruby S. W., Abelson J. Pre-mRNA splicing in yeast. Trends Genet. 1991 Mar;7(3):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90276-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff J. A., Schwartzbach S. D., Osafune T., Hase E. Photocontrol and processing of LHCP II apoprotein in Euglena: possible role of Golgi and other cytoplasmic sites. J Photochem Photobiol B. 1991 Nov;11(2):219–236. doi: 10.1016/1011-1344(91)80262-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharif A. L., Smith A. G., Abell C. Isolation and characterisation of a cDNA clone for a chlorophyll synthesis enzyme from Euglena gracilis. The chloroplast enzyme hydroxymethylbilane synthase (porphobilinogen deaminase) is synthesised with a very long transit peptide in Euglena. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Sep 15;184(2):353–359. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15026.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogin M. L. Early evolution and the origin of eukaryotes. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1991 Dec;1(4):457–463. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80192-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogin M. L., Elwood H. J., Gunderson J. H. Evolutionary diversity of eukaryotic small-subunit rRNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1383–1387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sontheimer E. J., Steitz J. A. The U5 and U6 small nuclear RNAs as active site components of the spliceosome. Science. 1993 Dec 24;262(5142):1989–1996. doi: 10.1126/science.8266094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A. Splicing takes a holliday. Science. 1992 Aug 14;257(5072):888–889. doi: 10.1126/science.1386941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessier L. H., Chan R. L., Keller M., Weil J. H., Imbault P. The Euglena gracilis rbcS gene contains introns with unusual borders. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jun 15;304(2-3):252–255. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80631-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessier L. H., Keller M., Chan R. L., Fournier R., Weil J. H., Imbault P. Short leader sequences may be transferred from small RNAs to pre-mature mRNAs by trans-splicing in Euglena. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2621–2625. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07804.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]