ABSTRACT
Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus) is a frequent colonizer of the nasopharynx and one of the leading causative agents of otitis media, pneumonia, and meningitis. The current literature asserts that S. pneumoniae is transmitted person to person via respiratory droplets; however, environmental surfaces (fomites) have been linked to the spread of other respiratory pathogens. Desiccation tolerance has been to shown to be essential for long-term survival on dry surfaces. This study investigated the survival and infectivity of S. pneumoniae following desiccation under ambient conditions. We recovered viable bacteria after all desiccation periods tested, ranging from 1 h to 4 weeks. Experiments conducted under nutrient limitation indicate that desiccation is a condition separate from starvation. Desiccation of an acapsular mutant and 15 different clinical isolates shows that S. pneumoniae desiccation tolerance is independent of the polysaccharide capsule and is a species-wide phenomenon, respectively. Experiments demonstrating that nondesiccated and desiccated S. pneumoniae strains colonize the nasopharynx at comparable levels, combined with their ability to survive long-term desiccation, suggest that fomites may serve as alternate sources of pneumococcal infection.
IMPORTANCE
Even with the advent of multivalent capsular polysaccharide conjugate vaccines, S. pneumoniae continues to be a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Every year, there are approximately 7 million cases of pneumococcus-based otitis media in the United States alone, while pneumococcal invasive diseases are responsible for more than 1 million deaths globally. It is believed that the human upper respiratory tract is the sole niche of S. pneumoniae and, thus, that spread occurs via close contact with an infected individual. In this study, we characterized the desiccation tolerance of S. pneumoniae and found that it can survive for many weeks postdehydration and retain infectivity. Our results suggest that desiccation tolerance is an inherent trait of this genetically variable species and that fomites may be a source of transmission.
Introduction
The Gram-positive encapsulated bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae is a common inhabitant of the human nasopharynx but can shift from commensal to pathogen, causing invasive diseases, including otitis media, pneumonia, bacteremia, and meningitis (1, 2). Based on polysaccharide capsular differences, more than 90 serotypes of S. pneumoniae have been identified (3, 4). Even with the recent introduction of capsular polysaccharide-protein conjugate vaccines directed at multiple serotypes, S. pneumoniae remains a devastating pathogen worldwide (1, 5). The current medical view is that transmission of this pathogen occurs through direct contact with respiratory secretions from infected individuals (2).
Commonplace activities such as talking, coughing, and sneezing disseminate large amounts of bacteria into the external environment (6, 7), and research on respiratory tract pathogens has implicated dust and disintegrating sputum as reservoirs of bacterial transmission (8). Fomites, or environmental surfaces, have been described as probable or confirmed sources of infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus, Chlamydia trachomatis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumanii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, various enterococci, and other bacteria (9–15). Recent comprehensive literature searches on microbial persistence on dry surfaces identified more than 30 types of clinically relevant bacteria, including S. pneumoniae, that survive for anywhere from 30 minutes to over 30 months (8, 16).
Environmental survival often hinges on an organism’s ability to withstand periods of desiccation. “Animalcule” recovery from desiccation was first described by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek over three centuries ago (17–19). At present, the best-known and most-studied microbes that tolerate extended periods of desiccation are the cyanobacteria, extremophiles, and sporeformers (19–23). Desiccation tolerance is linked to a switch to a metabolically inactive state as well as the ability to repair protein oxidation and DNA damage upon rehydration (20, 22, 24, 25). If S. pneumoniae were shown to survive desiccation, this bacterial durability could change our understanding of its transmission. As the only known reservoir of S. pneumoniae is the human upper respiratory tract, few studies have examined its capacity to persist in the environment. Confounding issues in interpreting these prior data include the following: (i) different dissemination strategies were used between studies, and (ii) most work involved the direct desiccation of patient samples rather than bacteria alone (26).
Here, we characterize S. pneumoniae’s capacity to survive desiccation and explore the potential for fomites as a transmission source. We developed a desiccation protocol and studied S. pneumoniae viability over periods of desiccation ranging from 1 h to 28 days. We found that desiccation and starvation are separate processes and that desiccation tolerance likely is a species-wide phenomenon of S. pneumoniae that does not depend on the presence of the polysaccharide capsule. Not only can S. pneumoniae survive extended periods of desiccation under ambient conditions, but also it retains its infectivity, as assessed by murine nasopharyngeal colonization.
RESULTS
S. pneumoniae can survive long periods of desiccation.
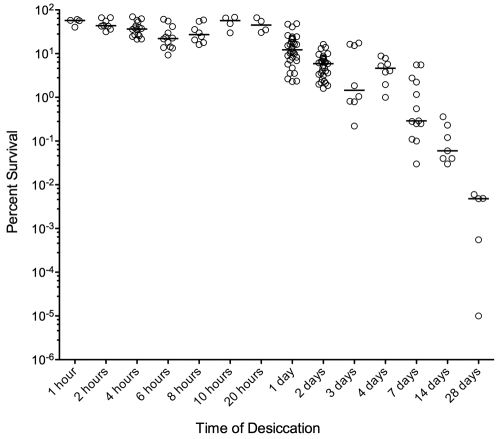
To examine the ability of S. pneumoniae to withstand dehydration, we developed a desiccation protocol. Encapsulated S. pneumoniae strain D39 (serotype 2) was grown overnight on blood agar, scraped off the plate, evenly divided, and spread thinly onto four polystyrene petri dish lids. The bacteria from one lid were immediately resuspended in Todd-Hewitt broth supplemented with yeast extract (THY; initial time point [T0]), and the other three lids were desiccated in the dark under ambient conditions for predetermined times prior to rehydration. The number of viable cells per lid was determined by plating serial dilutions on blood agar and counting the resultant colonies, and the percent survival was calculated by dividing the time point by the T0 viable count. Our results show that S. pneumoniae survives desiccation periods of at least 4 weeks at ambient temperature and humidity (Fig. 1).
FIG 1 .
S. pneumoniae D39 survival after desiccation. Bacteria were rehydrated and plated after 1 hour to 28 days of desiccation to determine viability. Data were pooled from multiple biological replicate experiments. Open circles represent individual samples, and bars show the medians.
In the desiccation experiment described above using colonies scraped from blood agar plates, the starting population was likely to be very heterogeneous with respect to growth rate and, thus, physiological state. To examine a more homogenous starting population, we tested exponentially growing S. pneumoniae cells from broth culture for desiccation over a 7-day period. We observed the same level of bacterial viability at 4- and 7-day time points as that found when using plate-grown bacteria (data not shown), suggesting that the physiological state does not dictate an ability to survive longer periods of desiccation.
Desiccation and starvation are separable stresses.
Numerous forces that contribute to bacterial cell death over time are at work during desiccation (21, 22, 27). It is possible that cell death of S. pneumoniae is due primarily to nutrient deprivation, regardless of other factors. To test this, we conducted simultaneous experiments under two conditions, desiccation and starvation with maintenance of hydration. The desiccated samples were treated as described above, while the starved samples were spread onto phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) agar plates rather than polystyrene petri dishes. All samples were placed in the dark under ambient conditions for 6, 24, or 48 h prior to collection for comparison to the T0 viable count. We saw a significant difference in bacterial recovery between the desiccated and starved samples (Fig. 2), with the starved samples losing viability at a much higher rate than the desiccated samples. The starved samples underwent a shift from slightly higher survival after 6 h (P < 0.05) to lower survival at 24 h (P < 0.05) and 48 h (P < 0.001), confirming that nutrient deprivation is a different phenomenon than dehydration.
FIG 2 .
S. pneumoniae D39 survival after desiccation versus nutrient deprivation. Bacteria were recovered 6, 24, or 48 hours after desiccation or starvation on PBS agar, and viability was determined. Closed circles represent desiccated samples, open circles represent starved samples, and bars show the medians. The probability that medians differ at each time point is shown by asterisks. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.001 (two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni posttest correction).
S. pneumoniae desiccation tolerance is not dependent on the polysaccharide capsule.
As research has indicated that Gram-positive bacteria survive desiccation better than their Gram-negative counterparts (28–30), we wondered if the polysaccharide capsule of S. pneumoniae contributes to its ability to withstand desiccation. A capsule is present in essentially all S. pneumoniae clinical isolates and is required for efficient host colonization as well as invasive disease (4, 31, 32). To assess the role of the capsule in desiccation tolerance, we compared the survival of D39 to that of an acapsular derivative, AC326. We saw no significant difference in bacterial viability at any time point at up to 1 week of desiccation (Fig. 3), leading us to conclude that the capsule is not an important factor in surviving desiccation. An anti-type 2 capsule Western blot demonstrated the presence of the capsule in cells desiccated for 1, 2, or 7 days, confirming that the lack of phenotypic difference between D39 and the acapsular strain is not due to D39 downregulating production of the capsule, and thus appearing acapsular, during desiccation (data not shown).
FIG 3 .
Desiccation tolerance of S. pneumoniae D39 (encapsulated) and its acapsular derivative AC326. Bacteria were recovered 4 to 168 hours after desiccation. Data for D39 with the capsule (white) and without the capsule (gray) are shown as the median values (n = 4), and bars represent the ranges.
Desiccation tolerance is a property shared by diverse pneumococcal strains.
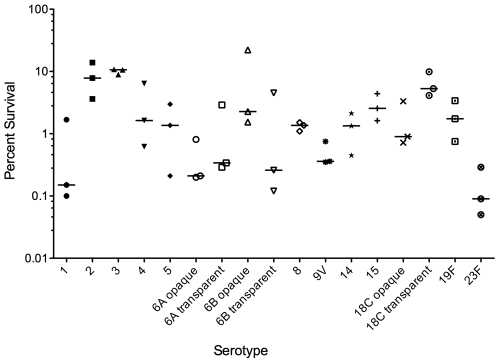
S. pneumoniae has a highly plastic genome, with up to 10% of variation between strains (2, 33–35). Since we eliminated the capsule as the basis for desiccation tolerance, it is possible that some genetic specificity of the D39 strain enhances its ability to survive desiccation. To determine if desiccation tolerance is shared or not by other strains, we performed 48-h desiccation experiments on 17 strains representing 14 different serotypes. All 17 strains tested survived desiccation at viabilities ranging from 0.1 to 10% (Fig. 4). For three of the serotypes (6A, 6B, and 18C), we tested both opaque- and transparent-colony-phase variants and saw no correlation between phase and desiccation tolerance. As capsular polysaccharide expression differs greatly between these two phase variants and is related to virulence in a mouse model (36), this supports our previous conclusion that the capsule is not a key factor in S. pneumoniae desiccation tolerance. Additionally, our experiments indicate that the ability to withstand the stresses of desiccation is a trait shared by numerous strains of S. pneumoniae.
FIG 4 .
Desiccation tolerance of 17 S. pneumoniae strains. Bacteria were recovered after 48 hours of desiccation. Each data point represents an independent experiment, and bars indicate the medians.
Desiccated S. pneumoniae retains infectivity.
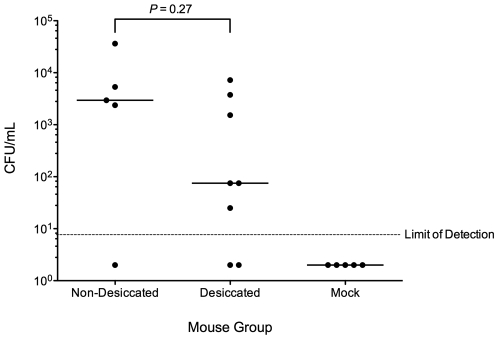
To extrapolate the importance of fomites as a source of S. pneumoniae transmission, it first must be established that, upon rehydration, desiccated bacteria are capable of colonization. Because S. pneumoniae is naturally virulent in mice and can colonize the nasopharynx asymptomatically, as in humans, we used this murine model to test whether desiccation affects colonization. We intranasally inoculated 8- to 12-week-old female Swiss-Webster mice with 5 µl/nare of PBS (mock) or PBS-suspended nondesiccated S. pneumoniae D39 (grown overnight on blood agar plates) or desiccated S. pneumoniae D39 (for 48 h). Three days postinoculation, the mice were killed, and the nasal lavage fluid was plated on blood agar containing 3 µg/ml gentamicin, to which S. pneumoniae is naturally resistant. The mock group had no detectable S. pneumoniae colonies, but the bacteria desiccated for 48 h colonized the murine nasopharynx well (Fig. 5). In the nondesiccated wild-type group, 80% of mice (4/5) had detectable levels of colonization, while 75% of mice (6/8) in the desiccated group were measurably colonized. The relatively low dose of inoculum used (~1.5 × 104 to 3.2 × 104 CFU/mouse) likely increased the spread seen in the data, as the mice had a better chance of clearing the bacteria than if the dose used was higher. Although the median load of bacteria recovered was higher for the nondesiccated challenge group, there was no significant difference in colonization levels between it and the desiccated group (P = 0.27), indicating that desiccation does not exert a major negative impact on the ability of S. pneumoniae to colonize hosts.
FIG 5 .
Murine nasopharyngeal colonization by desiccated versus nondesiccated S. pneumoniae. Shown are bacterial loads in nasal lavage fluid at 72 hours post-intranasal inoculation with 1.5 × 104 CFU (nondesiccated) and 3.2 × 104 CFU (desiccated) S. pneumoniae D39. Closed circles represent individual mice, and bars indicate the medians (P value determined by Mann-Whitney U test).
DISCUSSION
To our knowledge, this is the first study to describe both the desiccation tolerance of S. pneumoniae under ambient conditions and the ability of those desiccated bacteria to be infectious upon rehydration. Using a polystyrene surface as a fomite model, we demonstrate the environmental survival of S. pneumoniae over a period of 4 weeks. Although there was a decline in bacterial survival over time, the median total concentration of viable cells even after 14 days of desiccation fell within a previously suggested 50% infective dose (ID50) range for invasive pneumococcal disease (IPD) for this pathogen (37, 38). Since more bacteria are generally needed for invasive disease than for intranasal inoculation, this number may be sufficient for nasopharyngeal colonization, the first step toward infection (39). However, numerous variables will likely impact the frequency of transmission via fomites in natural settings.
It is important to make a distinction between the process of desiccation tolerance and its intrinsic nutrient limitation. It could be argued that the death of S. pneumoniae over time on fomites is simply a result of starvation and not due to stresses associated with desiccation and rehydration. However, two points argue against this hypothesis. First, we saw significantly less longer-term recovery of starved but hydrated cells versus that of desiccated cells, which indicates that nutrient deprivation and desiccation are distinct stresses. Our data are further supported by results from a previous study, in which S. pneumoniae mixed with dust, pus, and blood was viable approximately twice as long under dry versus moist conditions (26). Second, despite the absence of nutrients on fomites, we were able to recover viable cells after long time periods (up to 28 days) of desiccation. This suggests that the bacteria enter into some kind of stasis, enabling them to tolerate the stresses of desiccation. Desiccation may trigger an evolved survival pathway of S. pneumoniae, or survival may simply be attributed to a fortuitously protective cellular architecture. An investigation of the bacterial factors that mediate desiccation tolerance should be able to distinguish between these possibilities.
Numerous species of Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria have been shown to persist under desiccating conditions, although the literature suggests that Gram-positive bacteria exhibit enhanced tolerance to dry conditions (29, 30). One factor shared by many Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria is the presence of an extracellular polysaccharide. In S. pneumoniae, the polysaccharide capsule is a virulence factor, helping cells penetrate the mucus layer overlaying mucosal epithelia and escape phagocytosis (32, 36, 39). Using an acapsular mutant strain, we demonstrated that the capsule is not required for S. pneumoniae D39 desiccation tolerance. This corresponds with the results from our desiccation experiment on serotypes 6A, 6B, and 18C, in which we observed no clear trend associated with capsular phase variance. The variants of serotype 6A demonstrated near-identical recovery, while the other two serotypes displayed opposite recovery patterns between opaque and transparent variants.
Similar variation in desiccation tolerance was seen across other S. pneumoniae serotypes, including those seven previously identified as the most common in cases of IPD globally (40). We observed recovery across all 17 tested strains, accounting for 14 unique serotypes. Thus, a resistance to the stresses of desiccation appears to be a phenomenon intrinsic to the S. pneumoniae species. This is especially interesting, considering the wide genetic diversity among S. pneumoniae strains. Its natural transformable ability, combined with its high rate of recombination, enables S. pneumoniae to adapt readily to both antibiotic and vaccine selective pressures (1, 5, 41). Several years after the introduction and widespread administration of the heptavalent polysaccharide capsule vaccine (PCV7), IPD caused by the seven vaccine serotypes markedly decreased (42, 43). Simultaneous with this decrease was the emergence of multidrug-resistant nonvaccine serotypes, especially multidrug-resistant 19A, as leading causes of IPD (5, 41, 44, 45). Our data support the hypothesis that desiccation tolerance is a species-wide phenomenon; therefore, this ability is vertically transmitted in S. pneumoniae and likely would not be gained or lost as a result of its frequent horizontal transfer events.
Fomites have been linked to the transmission of other Gram-positive, nonsporulating pathogens. Methicillin-resistant S. aureus was shown to survive 1 to 90 days on common hospital materials (12) and has been proposed to cause infections via direct fomite-person transmission (26). Twenty weeks after desiccation of blood containing group A streptococci, growth in fresh blood indicated that the bacteria retained both viability and virulence (46). The hypothesis that S. pneumoniae may survive in the environment and use fomites as sources of transmission is not unprecedented. In fact, Walther and Ewald’s “sit and wait” hypothesis, which predicts that virulence correlates with durability in the external environment, identified a high-virulence, high-survival group of human respiratory tract pathogens that includes variola (smallpox) virus, Bordetella pertussis, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Corynebacterium diphtheriae, and S. pneumoniae (8). Here we tested this hypothesis by investigating the capacity of desiccated S. pneumoniae to colonize the murine nasopharynx. Colonization at levels not significantly different from those of nondesiccated S. pneumoniae argues in favor of the hypothesis that fomites serve as an alternate source of spread of S. pneumoniae.
It has been noted that increased postdesiccation recovery rates are seen when bacterial cells are more concentrated at the time of dissemination (16, 22, 47, 48), and so it is conceivable that the bacterial viability in our experiments is artificially high based on the density of bacteria spread on the polystyrene surface (2.2 × 108 CFU over an area of ~600 mm2). In experiments testing the number of beta-hemolytic streptococci expelled by respiratory activeties, Hamburger and Green showed that nose blowing, more than coughing or sneezing, forces out the most bacteria (6). In patients with beta-hemolytic streptococcus-positive nose cultures, nose blowing resulted in an average expulsion of 1.1 × 107 CFU and a maximum of over 1 × 109 CFU (6); therefore, it is possible that an S. pneumoniae (alpha-hemolytic streptococcus) carrier could expel concentrations approximating those used in our experiments. Additionally, they recovered an average of 7.9 × 105 CFU from the hands of nasal carriers 3 h after they were last washed and found that these individuals transferred beta-hemolytic streptococci to other surfaces they touched (6). These surfaces, as well as dried handkerchiefs used during nose blowing, served as major sources of airborne beta-hemolytic streptococci (6). We propose, then, that fomites may serve as reservoirs for S. pneumoniae, which we show can survive for weeks in a desiccated state and after which are still capable of colonizing the nasopharynx of susceptible hosts.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacterial strains.
The S. pneumoniae strains used in this study are listed in Table 1. Mid-exponential-growth-phase S. pneumoniae bacteria were stored as “starter cultures” in microcentrifuge tubes at −80°C in THY plus 12% glycerol in 0.25- to 0.4-ml aliquots.
TABLE 1 .
Strains used in this study
| Strain | Genotype or description |
Serotype (type of variant) |
Reference or source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC326 | Acapsular D39 | 2 | 49 |
| AC353 | TIGR4, Smr derivative | 4 | 50 |
| AC1356 | Clinical isolate | 1 | J. Weiser |
| AC1357 | Clinical isolate | 6A (opaque) | J. Weiser |
| AC1358 | Clinical isolate | 6A (transparent) | J. Weiser |
| AC1359 | Clinical isolate | 6B (opaque) | J. Weiser |
| AC1360 | Clinical isolate | 6B (transparent) | J. Weiser |
| AC1361 | Clinical isolate | 5 | J. Weiser |
| AC1362 | Clinical isolate | 23F | J. Weiser |
| AC1363 | Clinical isolate | 8 | J. Weiser |
| AC1364 | Clinical isolate | 14 | J. Weiser |
| AC1365 | Clinical isolate | 9V | J. Weiser |
| AC1366 | Clinical isolate | 18C (opaque) | J. Weiser |
| AC1367 | Clinical isolate | 18C (transparent) | J. Weiser |
| AC1368 | Clinical isolate | 3 | J. Weiser |
| AC1369 | Clinical isolate | 19F | J. Weiser |
| AC1371 | Clinical isolate | 15 | J. Weiser |
| AC1770 | D39 | 2 | 51 |
Desiccation.
An S. pneumoniae starter culture containing ~107 CFU was thawed, the entire contents were plated on Trypticase soy agar plus 5% sheep’s blood (Northeast Laboratory) (blood agar), and after 16 h of growth at 37°C in a 5% CO2 incubator, the bacterial lawn was scraped off the plate surface and pooled in the center of the plate using a plastic straightedge (catalog no. 165-3320, Bio-Rad Gel Releaser). The bacteria were then split evenly by eye into four pools, and each of which was spread thinly and evenly using the plastic straightedge onto the inner side of a 100-mm by 15-mm polystyrene petri dish lid (Fisher). There was approximately 108 CFU spread on each lid. Immediately after spreading, the bacteria on one lid were resuspended with 1.5 ml THY, serially diluted in THY, and plated to determine the number of CFU, constituting the initial time point (T0). The remaining three lids were closed over the petri dish bottoms and placed in the dark at room temperature for specific times (1 h to 28 days) until being similarly resuspended and serially diluted to determine the number of CFU. Desiccations were conducted in the dark based on previous research implicating photooxidative damage as a cause of enzyme, protein, and DNA damage during desiccations under light conditions (22). The percent remaining viable bacteria was calculated by dividing the time point number of CFU by the T0 number of CFU. Ambient temperature and relative humidity were monitored throughout the duration of each experiment. The range for all experiments was 21 to 25°C and 18 to 45% relative humidity. Neither the temperature nor humidity variation observed impacted the degree of desiccation tolerance.
Mid-exponential-growth-phase desiccation.
An S. pneumoniae starter culture containing ~107 CFU was thawed and used to seed a 10-ml culture of THY plus Oxyrase (Oxyrase, Inc.). After 4 h of growth to mid-exponential phase (optical density at 600 nm [OD600] = 0.4) at 37°C in a 5% CO2 incubator, the culture was split evenly into 20 aliquots (480 µl each) that were spun for 7 minutes at 1500 × g at room temperature. The supernatants were removed except for 50 µl, and each pellet was resuspended and transferred to the inner side of a 100-mm by 15-mm polystyrene petri dish lid, onto which it was spread thinly and evenly using the plastic straightedge. Approximately 2 × 107 CFU were spread on each lid. Immediately after the pellet was spread, the petri dishes were dried open in the biosafety cabinet with airflow on for 30 minutes. Next, the bacteria on the four lids were individually resuspended with 1.5 ml THY, serially diluted in THY, and plated to determine the number of CFU, constituting the initial time point (T0). The remaining lids were closed over the petri dish bottoms and placed in the dark at room temperature for 1, 2, 4, or 7 days until being similarly resuspended and serially diluted to determine the CFU. The percent remaining viable bacteria was calculated by dividing the time point number of CFU by the T0 number of CFU. During the experiment, the ranges of temperature and relative humidity were 23 to 24°C and 21 to 25%, respectively.
Starvation.
S. pneumoniae D39 was scraped off a blood agar plate and split evenly into 4 pools as described above, and each of which was spread onto PBS agar (1.5% agar [Fisher] in 1× PBS [Boston Bioproducts]). The plates were closed and incubated at room temperature in the dark. The percent remaining viable bacteria at multiple times was calculated as described in the desiccation experiments.
Anticapsule Western blot.
As described in the desiccation experiments, an S. pneumoniae starter culture was thawed, plated on blood agar, and grown for 16 h before the lawn was scraped off the plate, split evenly into four pools, and spread onto petri dish lids. One lid (T0) was immediately resuspended with 1.5 ml THY, and a small volume (20 µl) was used to serially dilute and plate for the number of CFU while the remaining volume was spun for 7 minutes at 1500 × g at room temperature. The supernatant was discarded, the pellet was washed with 500 µl THY, the sample was spun as done previously, the supernatant was removed, and the pellet was frozen at −80°C until use. The remaining three lids were closed over the petri dish bottoms and desiccated in the dark under ambient conditions for 1, 2, or 7 days, at which time they were similarly resuspended, serially diluted, plated for the number of CFU, and spun to freeze the cell pellets.
The cell pellets were thawed and resuspended in 20 µl 10 mM Tris (pH 7.5), 10 µl proteinase K buffer (50 mM EDTA, 0.5% Tween 20, 0.5% Triton X-100, 50 mM Tris [pH 8]), and 2 µl proteinase K (20 mg/ml). After 30 minutes of incubation at 37°C, each sample was mixed with 38 µl 10 mM Tris (pH 7.5) and 17.5 µl sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) sample buffer (50 mM Tris [pH 6.8], 12.5 mM EDTA, 2% SDS, 10% glycerol, 1% β-mercaptoethanol, 0.02% bromophenol blue) and heated for 10 minutes at 99°C. The samples were loaded (20 µl each) onto a 10% SDS-PAGE gel, which was run for 75 minutes at 120 V before being transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane (Invitrogen) using a semidry transfer apparatus (Bio-Rad) for 70 minutes at 25 V. Ponceau staining was used for 30 s to confirm effective proteinase K treatment before being washed off with distilled water (dH2O). Using the Snap i.d. protein detection system (Millipore), the membrane was blocked with 30 ml 1× NapBlock (G Biosciences) in 1× Tris-buffered saline (TBS). The membrane was incubated for 10 minutes with polyclonal rabbit anti-type 2 capsule antiserum (Statens Serum Institut) at 1:1,000 in 1× TBS. After being washed with 90 ml 1× TBS, the membrane was incubated for 10 minutes with Cy5 goat anti-rabbit IgG (Invitrogen) at 1.7:1,000 in 1× TBS while protected from light and then washed with 90 ml 1× TBS and visualized using FLA-9000 Starion (Fujifilm).
Mouse model of nasopharyngeal colonization.
In all animal experiments, 8- to 12-week-old female outbred Swiss-Webster mice (Charles River Laboratories or Taconic Laboratories) were used. Mice were mock infected with 1× PBS or infected with either nondesiccated or 48-h desiccated S. pneumoniae D39. The nondesiccated S. pneumoniae was prepared by plating one starter culture on blood agar. After 16 h of growth, the colonies were resuspended in 1× PBS and adjusted to ~1 × 105 CFU/ml. The desiccated S. pneumoniae was prepared as described in a desiccation experiment, except at 48 h postdesiccation, the bacteria were resuspended in 1× PBS and adjusted to ~1 × 105 CFU/ml by OD600 measurement.
Mice were lightly anesthetized by inhalation of 2.5% isofluorane and inoculated (5 µl per nare) with 1× PBS, nondesiccated S. pneumoniae D39, or desiccated S. pneumoniae D39. Mice were killed by CO2 asphyxiation 3 days later. Bacteria colonizing the nasopharynx were recovered by lavage with 0.5 ml sterile 1× PBS through an opening made in the trachea. The lavage fluid was serially diluted and plated on blood agar containing gentamicin (3 µg/ml).
Statistical analysis.
Differences in survival between starved and desiccated samples were tested using two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Bonferroni posttest correction. Survival data of 48-h desiccated acapsular (AC326) and encapsulated (AC1770) strain D39 were shown to be normally distributed by the D’Agostino-Pearson omnibus normality test, and differences were then tested using the unpaired Student t test. Differences in colonization of mice were tested using the Mann-Whitney two-tailed U test.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank the members of the Camilli laboratory, especially Tim van Opijnen, for helpful comments during the course of this work.
A.C. is a Howard Hughes Medical Institute investigator.
Footnotes
Citation Walsh RL, Camilli A. 2011. Streptococcus pneumoniae is desiccation tolerant and infectious upon rehydration. mBio 2(3):e00092-11. doi:10.1128/mBio.00092-11
REFERENCES
- 1. Kadioglu A, Weiser JN, Paton JC, Andrew PW. 2008. The role of Streptococcus pneumoniae virulence factors in host respiratory colonization and disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 6:288–301 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. van der Poll T, Opal SM. 2009. Pathogenesis, treatment, and prevention of pneumococcal pneumonia. Lancet 374:1543–1556 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Park IH, et al. 2007. Discovery of a new capsular serotype (6C) within serogroup 6 of Streptococcus pneumoniae. J. Clin. Microbiol. 45:1225–1233 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Weiser JN. 2010. The pneumococcus: why a commensal misbehaves. J. Mol. Med. 88:97–102 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Croucher NJ, et al. 2011. Rapid pneumococcal evolution in response to clinical interventions. Science 331:430–434 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Hamburger M, Jr, Green MJ. 1946. The problem of the dangerous carrier of hemolytic streptococci; observations upon the role of the hands, of blowing the nose, of sneezing, and of coughing in the dispersal of these microorganisms. J. Infect. Dis. 79:33–44 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Xie X, Li Y, Zhang T, Fang HH. 2006. Bacterial survival in evaporating deposited droplets on a teflon-coated surface. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 73:703–712 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Walther BA, Ewald PW. 2004. Pathogen survival in the external environment and the evolution of virulence. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 79:849–869 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Akinyemi KO, Atapu AD, Adetona OO, Coker AO. 2009. The potential role of mobile phones in the spread of bacterial infections. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 3:628–632 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Jawad A, Seifert H, Snelling AM, Heritage J, Hawkey PM. 1998. Survival of Acinetobacter baumannii on dry surfaces: comparison of outbreak and sporadic isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 36:1938–1941 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Miller LG, Diep BA. 2008. Clinical practice: colonization, fomites, and virulence: rethinking the pathogenesis of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 46:752–760 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Neely AN, Maley MP. 2000. Survival of enterococci and staphylococci on hospital fabrics and plastic. J. Clin. Microbiol. 38:724–726 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Novak KD, Kowalski RP, Karenchak LM, Gordon YJ. 1995. Chlamydia trachomatis can be transmitted by a nonporous plastic surface in vitro. Cornea 14:523–526 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Scott E, Bloomfield SF. 1990. The survival and transfer of microbial contamination via cloths, hands and utensils. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 68:271–278 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Tolba O, et al. 2007. Survival of epidemic strains of nosocomial- and community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus on coins. Am. J. Infect. Control 35:342–346 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Kramer A, Schwebke I, Kampf G. 2006. How long do nosocomial pathogens persist on inanimate surfaces? A systematic review. BMC Infect. Dis. 6:130 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Crowe LM, Crowe JH. 1992. Anhydrobiosis: a strategy for survival. Adv. Space Res. 12:239–247 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Keilin D. 1959. The problem of anabiosis or latent life: history and current concept. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 150:149–191 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Potts M. 2001. Desiccation tolerance: a simple process? Trends Microbiol. 9:553–559 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Billi D, Friedmann EI, Hofer KG, Caiola MG, Ocampo-Friedmann R. 2000. Ionizing-radiation resistance in the desiccation-tolerant cyanobacterium Chroococcidiopsis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66:1489–1492 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Billi D, Potts M. 2002. Life and death of dried prokaryotes. Res. Microbiol. 153:7–12 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Potts M. 1994. Desiccation tolerance of prokaryotes. Microbiol. Rev. 58:755–805 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Sghaier H, Narumi I, Satoh K, Ohba H, Mitomo H. 2007. Problems with the current deinococcal hypothesis: an alternative theory. Theory Biosci. 126:43–45 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Fredrickson JK, et al. 2008. Protein oxidation: key to bacterial desiccation resistance? ISME J. 2:393–403 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Krisko A, Radman M. 2010. Protein damage and death by radiation in Escherichia coli and Deinococcus radiodurans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 107:14373–14377 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Mitscherlich E, Marth EH. 1984. Microbial survival in the environment. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Germany [Google Scholar]
- 27. Lievense LC, van’t Riet K. 1994. Convective drying of bacteria. II. Factors influencing survival. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 51:71–89 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Habimana O, et al. 2010. Micro ecosystems from feed industry surfaces: a survival and biofilm study of Salmonella versus host resident flora strains. BMC Vet. Res. 6:48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Janning B, in't Veld PH. 1994. Susceptibility of bacterial strains to desiccation: a simple method to test their stability in microbiological reference materials. Anal. Chim. Acta 286:469–476 [Google Scholar]
- 30. Møretrc T, et al. 2010. Factors affecting survival of Shigatoxin-producing Escherichia coli on abiotic surfaces. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 138:71–77 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. AlonsoDeVelasco E, Verheul AF, Verhoef J, Snippe H. 1995. Streptococcus pneumoniae: virulence factors, pathogenesis, and vaccines. Microbiol. Rev. 59:591–603 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Nelson AL, et al. 2007. Capsule enhances pneumococcal colonization by limiting mucus-mediated clearance. Infect. Immun. 75:83–90 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Hakenbeck R, et al. 2001. Mosaic genes and mosaic chromosomes: intra- and interspecies genomic variation of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect. Immun. 69:2477–2486 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Hava DL, LeMieux J, Camilli A. 2003. From nose to lung: the regulation behind Streptococcus pneumoniae virulence factors. Mol. Microbiol. 50:1103–1110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Lanie JA, et al. 2007. Genome sequence of Avery’s virulent serotype 2 strain D39 of Streptococcus pneumoniae and comparison with that of unencapsulated laboratory strain R6. J. Bacteriol. 189:38–51 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Kim JO, Weiser JN. 1998. Association of intrastrain phase variation in quantity of capsular polysaccharide and teichoic acid with the virulence of Streptococcus pneumoniae. J. Infect. Dis. 177:368–377 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Schmid-Hempel P, Frank SA. 2007. Pathogenesis, virulence, and infective dose. PLoS Pathog. 3:1372–1373 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Yershov AL, Jordan BS, Guymon CH, Dubick MA. 2005. Relationship between the inoculum dose of Streptococcus pneumoniae and pneumonia onset in a rabbit model. Eur. Respir. J. 25:693–700 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Bogaert D, De Groot R, Hermans PW. 2004. Streptococcus pneumoniae colonisation: the key to pneumococcal disease. Lancet Infect. Dis. 4:144–154 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Johnson HL, et al. 2010. Systematic evaluation of serotypes causing invasive pneumococcal disease among children under five: the pneumococcal global serotype project. PLoS Med. 7:e1000348 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Henriques-Normark B, Blomberg C, Dagerhamn J, Bättig P, Normark S. 2008. The rise and fall of bacterial clones: Streptococcus pneumoniae. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 6:827–837 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Dagan R, Klugman KP. 2008. Impact of conjugate pneumococcal vaccines on antibiotic resistance. Lancet Infect. Dis. 8:785–795 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Hicks LA, et al. 2007. Incidence of pneumococcal disease due to non-pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV7) serotypes in the United States during the era of widespread PCV7 vaccination, 1998-2004. J. Infect. Dis. 196:1346–1354 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Pelton SI, et al. 2007. Emergence of 19A as virulent and multidrug resistant Pneumococcus in Massachusetts following universal immunization of infants with pneumococcal conjugate vaccine. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 26:468–472 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Pillai DR, et al. 2009. Genome-wide dissection of globally emergent multi-drug resistant serotype 19A Streptococcus pneumoniae. BMC Genomics 10:642 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Reitmeyer JC, Ewert A, Crawford MA, Reitmeyer GR, Mock L. 1993. Survival of group A streptococci in dried human blood. J. Med. Microbiol. 38:61–63 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Mary P, Moschetto N, Tailliez R. 1993. Production and survival during storage of spray-dried Bradyrhizobium japonicum cell concentrates. J. Appl. Microbiol. 74:340–344 [Google Scholar]
- 48. Watson SP, Clements MO, Foster SJ. 1998. Characterization of the starvation-survival response of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 180:1750–1758 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Shoemaker NB, Guild WR. 1974. Destruction of low efficiency markers is a slow process occurring at a heteroduplex stage of transformation. Mol. Gen. Genet. 128:283–290 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Hava DL, Camilli A. 2002. Large-scale identification of serotype 4 Streptococcus pneumoniae virulence factors. Mol. Microbiol. 45:1389–1406 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Walker JA, Allen RL, Falmagne P, Johnson MK, Boulnois GJ. 1987. Molecular cloning, characterization, and complete nucleotide sequence of the gene for pneumolysin, the sulfhydryl-activated toxin of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect. Immun. 55:1184–1189 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]