Abstract
The biphenyl dioxygenase of Burkholderia xenovorans LB400 is a multicomponent Rieske-type oxygenase (RO) that catalyzes the dihydroxylation of biphenyl and many polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). The structural bases for the substrate specificity of the enzyme’s oxygenase component (BphAELB400) are largely unknown. BphAEp4, a variant previously obtained through directed evolution, transforms several chlorobiphenyls, including 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl, more efficiently than BphAELB400 yet differs from the parent oxygenase at only two positions: T335A/F336M. Herein, we compare the structure of BphAELB400 and BphAEp4 and examine the biochemical properties of two BphAELB400 variants with single substitutions, T335A or F336M. Our data show that residue 336 contacts the biphenyl and influences the regiospecificity of the reaction, but does not enhance the enzyme’s reactivity toward 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl. By contrast, residue 335 did not contact biphenyl, but contributed significantly to expansion of the enzyme’s substrate range. Crystal structures indicate that Thr335 imposes constraints through hydrogen bonds and non-bonded contacts to the segment from Val320 to Gln322. These contacts are lost when Thr is replaced by Ala, relieving intramolecular constraints and allowing for significant movement of this segment during binding of 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl, increasing the space available to accommodate the doubly-ortho-chlorinated congener 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl. This study provides important insight about how ROs can expand substrate range through mutations that increase the plasticity and/or mobility of protein segments lining the catalytic cavity.
Keywords: Polychlorinated biphenyl, Burkholderia xenovorans LB400, enzyme engineering, Rieske-type oxygenase, PCB
Introduction
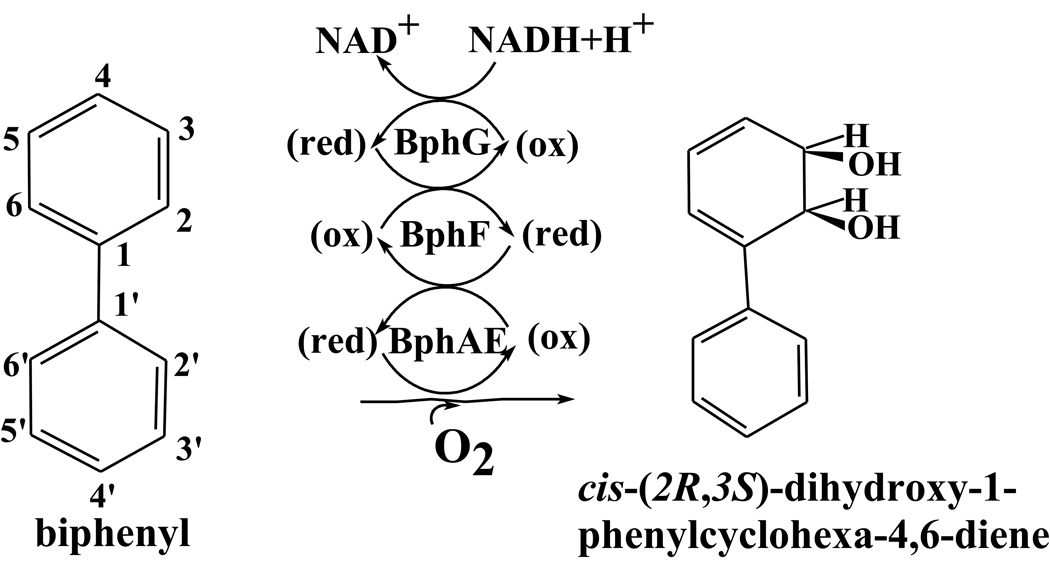
Biphenyl dioxygenase (BPDO) is a multicomponent Rieske-type oxygenase (RO). As other aryl-hydroxylating dioxygenases it has been extensively studied because it catalyzes the transformation of a range of non-physiological substrates. These include polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), which are of environmental concern1; 2, and heterocyclic compounds of pharmaceutical and agrochemical interest3; 4; 5; 6. BPDO catalyzes the first reaction of the bacterial biphenyl catabolic pathway. This three-component system catalyzes the insertion of two oxygen atoms onto vicinal carbons of biphenyl, yielding cis-(2R,3S)-dihydroxy-1-phenylcyclohexa-4,6-diene. In Burkholderia xenovorans LB4007, the three components are: the oxygenase, BphAELB400, an heterohexamer comprised of 3 α (BphALB400) and 3 β (BphELB400) subunits; the ferredoxin, BphFLB400; and the ferredoxin reductase component, BphGLB400 (Fig. 1). Each α subunit of the α3β3 hexamer contains a Rieske-type Fe2S2 cluster and a mononuclear iron center8. Electrons flow successively from NADH to the FAD center in BphG, thence to the Rieske clusters of BphF and of BphAE, and finally to the mononuclear iron catalytic center. The mechanism of dihydroxylation is thought to be very similar to that of naphthalene dioxygenase (NDO) from Pseudomonas sp. NCIB 9816-49.
Figure 1.
The BPDO components and encoding genes in B. xenovorans LB400.
BPDOLB400 is one of the most potent biocatalysts of natural origin for the dioxygenation of chlorobiphenyls10. However, several di- and trichlorinated biphenyls are poorly transformed by this enzyme, including 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl, one of the major metabolites resulting from the reductive dehalogenation process conducted during anaerobic dehalorespiration11; 12. Moreover, as pointed out by previous authors11; 13, the congeners containing two chlorines in the ortho position of a single ring (2,6-dichlorobiphenyls) are strikingly resistant to co-metabolic degradation by aerobic bacteria. Only rare bacteria of natural origin and recombinant bacteria producing engineered BPDOs were shown to transform this congener14; 15; 16.
Recently, the BphAEp4 variant was created from BphAELB400 by substitution at two residues, T335A and F336M15. This variant catalyzes the oxygenation of many PCB congeners, including 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl, more efficiently than BphAELB40015. Structures of Pandorea pnomenusa B-356 BphAE (BphAEB356), of Rhodococcus jostii BphA1A2 (BphA1A2RHA1), of Sphingobium yanoikuyae B1 (BphA1A2B1) and of cumene and toluene dioxygenases have been reported16; 17; 18; 19; 20. Structural analyses have shown that residue Ile326 of BphA1RHA1 (corresponding to Phe336 of BphALB400) makes contact with the substrate but residue Gly325 of BphA1RHA1 (corresponding to Thr335 of BphAELB400) is too distant to interact directly with substrate. Similarly, residue 377 of BphALB40014; 15; 21; 22 and several others23 that, according to models of BphAE, have no contact with the substrate, were shown to modulate the reaction turnover rates and regiospecificity toward chlorobiphenyls. However, the mechanisms by which these residues influence the enzyme's catalytic properties remain unclear.
In the classic model of enzyme-substrate interaction as a lock-and-key, the catalytic cavity defines the space that fits exactly the dimension and shape of the substrate, placing its reactive atoms into a productive position toward the catalytic center. This model predicts the enzyme’s catalytic cavity can be remodeled to fit a new substrate by altering residues that line the catalytic pocket. However, this model is inadequate for enzymes that bind many different substrates in a productive orientation, especially those with bulky substituents, such as chlorobiphenyls. Moreover, the mechanisms by which relaxed enzymes such as BPDO evolve to expand their substrate range are still undetermined. Understanding how the residues influencing ROs' specificity and catalytic properties interact with substrate-analogs will help decipher some of the mechanisms by which these relaxed enzymes evolve and will also help design strategies to engineer improved biocatalysts exhibiting expanded substrate specificities. In this study, in an attempt to identify the mutation(s) in BphAEp4 that contribute most to its expanded substrate range and to gain more insight into the role played by residues 335 and 336 of BphALB400, we have examined the biochemical properties of two BphAELB400 variants with single substitutions, T335A or F336M, and we have determined and compared the three dimensional structures of BphAELB400 and its biphenyl-bound form with those of variant BphAEp4 and its 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl-bound form.
Results
Metabolism of 2,6-dichorobiphenyl by BphAELB400 variants
In a previous report BphAEp4 (A335M336) was shown to perform better than BphAELB400 (T335F336) toward 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl15. In this study, we created BphAEp401 (A335F336) and BphAEp402 (T335M336) to identify which of the two substitutions has greater influence on activity toward 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl. The ability of all enzymes to catalyze the oxygenation of this substrate was assessed using a whole cell assay with IPTG-induced recombinant Escherichia coli strains. SDS-PAGE analysis indicated that E. coli DH11S pDB31[LB400-bphFG] harboring pQE31[bphAELB400] or either one of the recombinant plasmids pQE31[bphAEp4], pQE31[bphAEp401] or pQE31[bphAEp402] produced similar amounts of enzyme (not shown). Furthermore, based on the amount of 2,3-dihydro-2,3-dihydroxybiphenyl monitored after addition of biphenyl to resting cell suspensions of recombinant E. coli expressing these enzymes, the mutations did not affect the ability to oxidize biphenyl and no 3,4-dihydro-3,4-dihydroxybiphenyl was produced.
In a previous study it was shown that BphAEp4 metabolizes 2,2'-dichlorobiphenyl to generate principally 3,4-dihydro-3,4-dihydroxy-2,2'-dichlorobiphenyl instead of 2,3-dihydroxy-2'-chlorobiphenyl, as produced by BphAELB40015. GC-MS analyses of the metabolites generated by cells producing BphAEp401 revealed that this mutant yielded 2,3-dihydroxy-2'-chlorobiphenyl as the major metabolite, whereas BphAEp402 produced principally the 3,4-dihydro-3,4-dihydroxy-2,2’-dichlorobiphenyl (Fig. 2a). Therefore, the F336M substitution influenced the regiospecificity toward 2,2'-dichlorobiphenyl, but neither of the mutations (F336M or T335A) curtailed the capacity of the enzyme to dihydroxylate this substrate.
Figure 2.
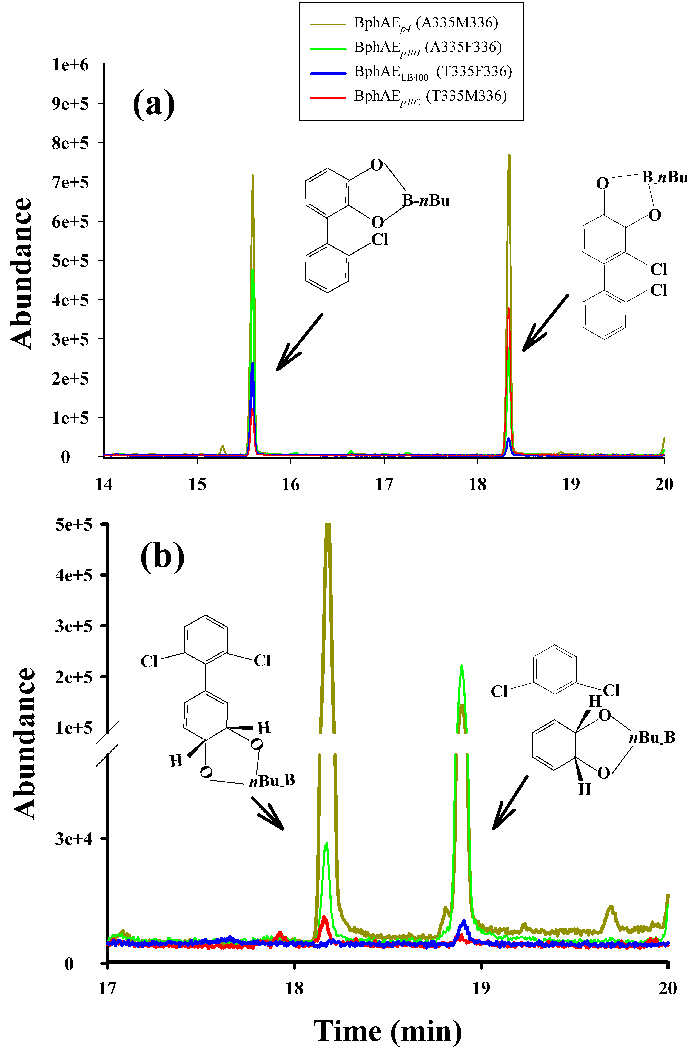
GC-MS spectra of butylboronate-derived metabolites produced (a) from 2,2'-dichlorobiphenyl and (b) from 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl by BphAELB400 and its variants.
In resting a cell assay, after 18 hours of incubation, recombinant E. coli cells expressing BphAEp4 transformed 25±5% of the initial amount (50 µM) of 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl added to the bacterial suspension, under the same conditions cells expressing BphAEp401 transformed 15±3% of this substrate. Cells expressing BphAEp402 and those expressing BphAELB400 metabolized 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl very poorly, transforming less than 1% of the substrate to produce trace amounts of metabolites whereas those expressing BphAEp4 and BphAEp401 clearly produced two metabolites (Fig. 2b). In previous work, BphAEB-35616 was shown to produce two metabolites from 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl, and the major one was predicted to be 2’,3’-dihydro-2’,3’-dihydroxy-2,6-dichlorobiphenyl on the basis of the crystal structure of the BphAEB-356:2,6-chlorobiphenyl complex which was consistent with an ortho-meta oxygenation of this substrate. When BphAEp4 catalyzed the oxygenation of 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl, GC-MS analysis showed the minor metabolite was the same as the major metabolite produced by BphAEB-356, i.e., 2’,3’-dihydro-2’,3’-dihydroxy-2,6-dichlorobiphenyl. Analysis of the crystal structure of the BphAEp4:2,6-dichlorobiphenyl-complex (see below) is consistent with the fact that BphAEp4 produces 3’,4’-dihydroxy-3’,4’-dihydro-2,6-dichlorobiphenyl as major metabolite. Cells expressing BphAEp401 produced the same metabolites as those expressing BphAEp4, but in lower yield: the sum of areas under GC-MS peaks of metabolites was about one third of the value obtained for cells expressing BphAEp4. Moreover, the ratio of the metabolites, and thus the regiospecificity of these enzymes toward 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl, differed significantly.
In summary, of the mutations T335A and F336M, the data indicate T335A contributed more to the increased-reactivity of BphAEp4 toward 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl. It is not clear if the F336M mutation alone influences the regiospecificity because the amounts of metabolites produced by cells expressing BphAEp402 are too small. However, it is clear that the additional substitution of F336M along with T335A is effective to alter the regiospecificity. Together, these observations suggest that the side chain at position 336 appears to influence the regiospecificity of the enzyme toward 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl.
Crystal structure BphAELB400: general features
BphAELB400 crystals have the triclinic space group P1 with unit-cell parameters a = 132.6, b = 132.4, c = 133.0 Å, and α = 102.6, β = 102.7 and γ = 104.6°. Analysis of the probable protein and solvent content of the unit cell suggested the possibility of twelve αβ dimers (four α3β3-hexamers) in the asymmetric unit with a Matthews coefficient VM = 2.41 Å3 Da−1 and a solvent content of 50%; these basic aspects of the crystal packing were confirmed by determination of the structure. Crystallographic data and statistics are reported in Table 1.
Table 1.
Crystallographic data and refinement results for BphAELB400 and BphAEp4 structures
| BphAELB400 | BphAELB400: Biphenyl |
BphAEp4 | BphAEp4: 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crystallographic data | ||||
| Space group | P1 | P1 | P1 | P21 |
| Wavelength | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Resolution | 2.5 | 2.4 | 2.2 | 2.2 |
| Cell dimensions | ||||
| a (Å) | 132.56 | 132.82 | 133.47 | 86.73 |
| b (Å) | 132.35 | 132.65 | 133.59 | 276.76 |
| c (Å) | 132.98 | 130.42 | 133.23 | 93.32 |
| α (°) | 102.60 | 102.65 | 102.51 | 90.00 |
| β (°) | 102.69 | 101.11 | 104.99 | 117.37 |
| γ (°) | 104.61 | 105.31 | 102.75 | 90.00 |
| Unique reflections | 255418 | 329852 | 377867 | 177300 |
| Completeness (%) (Last shell) |
89.0 (30.0) | 93.0 (74.0) | 90.0 (64.3) | 86.0 (51.4) |
| Rsym(%)a (Last Shell) | 10.0 (41.2) | 6.5 (27.9) | 6.1 (34.6) | 8.0 (35.4) |
| I/σ (Last shell) | 6.8 (1.4) | 13.8 (2.2) | 8.9 (2.0) | 18.6 (1.5) |
| Multiplicity (Last shell) | 2.8 (1.2) | 2.7 (1.2) | 2.4 (1.2) | 2.6 (1.2) |
| Refinement | ||||
| No. of reflections | 254621/ 122731 | 291398/14569 | 358861/17943 | 144572/7228 |
| (working/test) | ||||
| No. of residues | 7356 | 7356 | 7356 | 3678 |
| Water molecules | 2022 | 2014 | 2540 | 2031 |
| Resolution range (Å) | 2.5 | 2.4 | 2.2 | 2.2 |
| Rcryst (%) | 20.0 | 22.0 | 21.4 | 21.2 |
| Rfree (%) | 26.8 | 25.6 | 26.6 | 25.3 |
| Average B-factors (Å2) | AB 47.3 | AB 43.8 | AB 20.4 | AB 45.9 |
| CD 47.7 | CD 43.8 | CD 20.7 | CD 46.5 | |
| EF 47.4 | EF 43.8 | EF 20.6 | EF 46.2 | |
| GH 47.4 | GH 43.8 | GH 19.9 | GH 46.4 | |
| IJ 46.9 | IJ 43.8 | IJ 19.7 | IJ 47.1 | |
| KL 47.3 | KL 43.8 | KL 20.6 | KL 48.3 | |
| MN 43.1 | MN 43.9 | MN 20.7 | ||
| OP 43.2 | OP 43.9 | OP 16.6 | ||
| QR 44.0 | QR 43.9 | QR 20.5 | ||
| ST 52.7 | ST 43.8 | ST 19.9 | ||
| UV 51.1 | UV 43.7 | UV 19.0 | ||
| WX 54.1 | WX 43.7 | WX 22.7 | ||
| Water atoms | 42.1 | 37.5 | 20.6 | 37.0 |
| All atoms | 47.6 | 43.7 | 20.0 | 46.6 |
| rmsd on bond lengths (Å) | 0.014 | 0.006 | 0.009 | 0.006 |
| rmsd on bond angles (°) | 1.56 | 0.90 | 1.12 | 0.87 |
| Ramachandran plot (%) | ||||
| Preferred | 91.7 | 94.7 | 94.9 | 94.8 |
| Allowed | 7.0 | 4.7 | 4.7 | 4.7 |
| Outliers | 1.3 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.5 |
The crystal structure of BphAELB400 was refined to final R and Rfree values of 20.0% and 26.8% at a resolution of 2.5 Å. The final model includes residues Asn18 to Phe143 and Phe153 to Pro459 of the α subunit and Phe9 to Phe188 of the β subunit. The center part of the α subunit (residues 144–152) was excluded from the final model because it was a disordered region and there was no electron density. Triplets of αβ dimers associate to generate four α3β3 hexamers with non-crystallographic three-fold symmetry. The αβ dimers as represented by chains AB-CD-EF, GH-IJ-KL, MN-OP-QR and ST-UV-WX respectively form the four functional hexamers. As other aryl-hydroxylating dioxygenases16; 17; 18; 24; 25; 26, BphAELB400 assembles as a mushroom shaped α3β3 hexamer with the α subunits forming the cap and the β subunits forming the stem. As expected, the folds of the α and β subunits are also very similar to those presented by the structures of the homologs referenced above. Each α subunit carries a Rieske-type [2Fe-2S] His2Cys2 cluster and coordinates a mononuclear Fe(II) ion via the side chains of conserved His, His, and Asp residues; the Fe also binds one water molecule.
Crystals of BphAELB400 were exposed to solid biphenyl and subjected to crystallographic analysis, which produced a structure of the complex refined to 2.4 Å resolution and a final R-factor of 21.8% (Rfree=25.2%) (Table 1). The biphenyl molecule could be identified clearly in initial difference Fourier maps. Binding of biphenyl in the active site and near the mononuclear Fe(II) requires only local structural adjustments and thus did not alter the basic aspects of crystal packing.
Comparison of the crystal structures of native and biphenyl-bound BphAELB400
The presence of twelve independent αβ dimers requires analysis of the variations in protein conformation observed in the crystals. Superposition of the twelve native BphAELB400 dimers shows that they are all very similar in the core of the α subunit. This is also the case for the biphenyl-bound enzyme (Fig. 1a of supplementary material). Thus, for either substrate-free or biphenyl-bound BphAELB400, the Cα atoms of the twelve protomers can be superposed in pairs with root-mean-square deviation of 0.2–0.4 Å (Supplementary material, Table 1). The average B-factor values were 29.2 Å2 and 45.9 Å2 for the substrate-free and biphenyl-bound forms. The least ordered residues are located at the edges of the molecule (Fig. 2a–h of supplementary material). Among the segments showing greatest disorder, four are of interest.
The segment comprising residues 247–263 of the α subunit is a loop covering the active site mouth, and it corresponds to residues 223–240 of the α subunit of NDO and of BphA1A2B1. In crystal structures of NDO and of BphA1A2B1 this segment was significantly displaced upon substrate binding24; 26. However, superposition of the twelve biphenyl-bound BphAELB400 αβ dimers with the twelve dimers of the substrate-free enzyme does not reveal a consistent change in conformation associated with substrate binding. That is, substrate binding did not impose any specific conformational change on this segment.
The segment comprising residues 280–287 of the α subunit has high B-factors in all chains of native and biphenyl-bound forms of BphAELB400 and shows conformational variability. The B-factors of all the chains in native BphAELB400 is lower (~ 37 Å2) in comparison to the biphenyl complex of BphAELB400 (~ 50 Å2). These residues correspond to segment 270–277 of BphA1A2RHA1, which was reported to show significant displacement after substrate binding18; thus this segment might also play a role in substrate binding. However, in contrast to BphA1A2RHA1, we have no evidence this segment is displaced when BphAELB400 binds biphenyl since the dominant conformation is the same in the presence and absence of substrates.
Finally, the N-terminal segment comprising residues 9–17 of the β subunit also exhibits high B-factors. In different contexts, this segment interacts with the active site mouth segment 247–263 of an α subunit belonging to a neighboring α3β3 hexamer or it is pulled toward a loop comprised of residues 158–164 of an adjacent β subunit from the same α3β3 hexamer. Thus, for the centrally positioned hexamer MNOPQR, segment 9–17 of chains N, P and R interacts with segment 247–263 of chains A, K and S of dimers AB, KL and ST, respectively. This movement will be discussed further below.
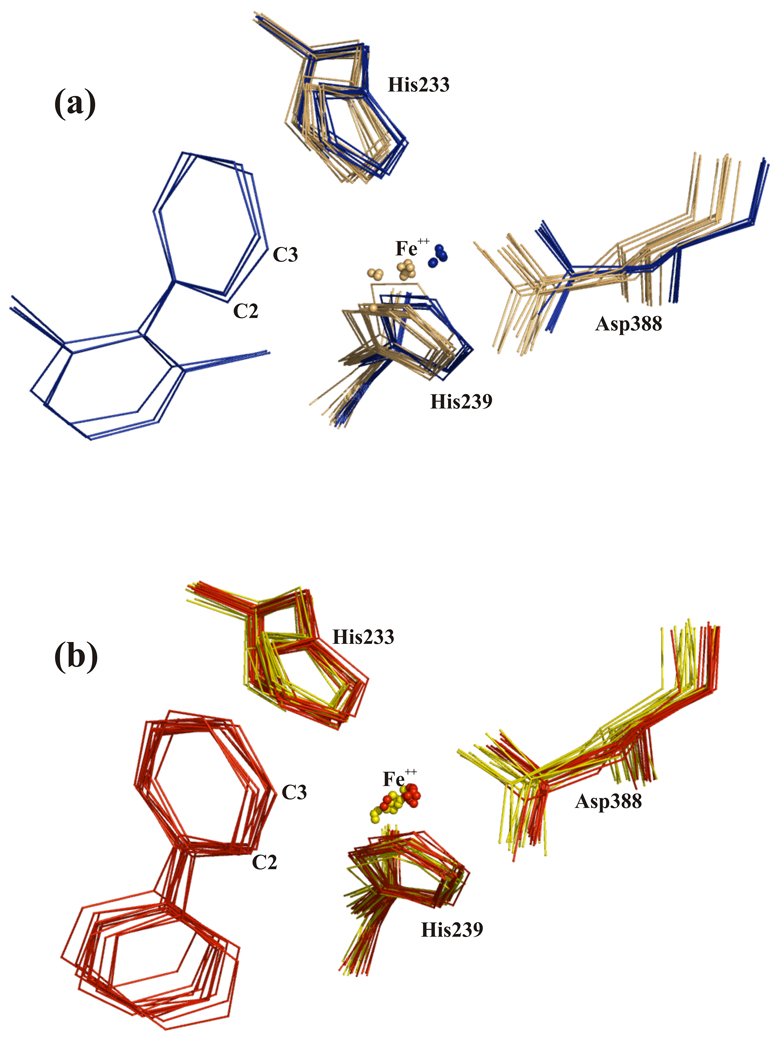
Consistent with an ortho-meta dioxygenation of biphenyl, C-2 and C-3 are the biphenyl atoms closest to the Fe atom and in all active sites they are equidistant to it. A water molecule is directly in line between the Fe atom and C-2 atom of biphenyl (Fig. 3). The separation of the Fe atom from C-2/C-3 is in the range of 3.9–4.1 Å for seven of the twelve dimers (AB, CD, EF, MN, QR, UV, WX). For dimers KL and ST the distance is shorter (3.3–3.5 Å) and for dimers GH, IJ and OP it is longer (4.3–4.5 Å). In this work, BphAELB400 was purified under anaerobic conditions and maintained under these conditions for substrate binding. Therefore, the oxidation state of the catalytic iron should not be the cause of these variations, which suggests some adaptability in the region surrounding the catalytic iron.
Figure 3.
Superposition of the catalytic center of chain AB of BphAELB400 (cyan) and chain AB of BphAELB400 bound to biphenyl (green).
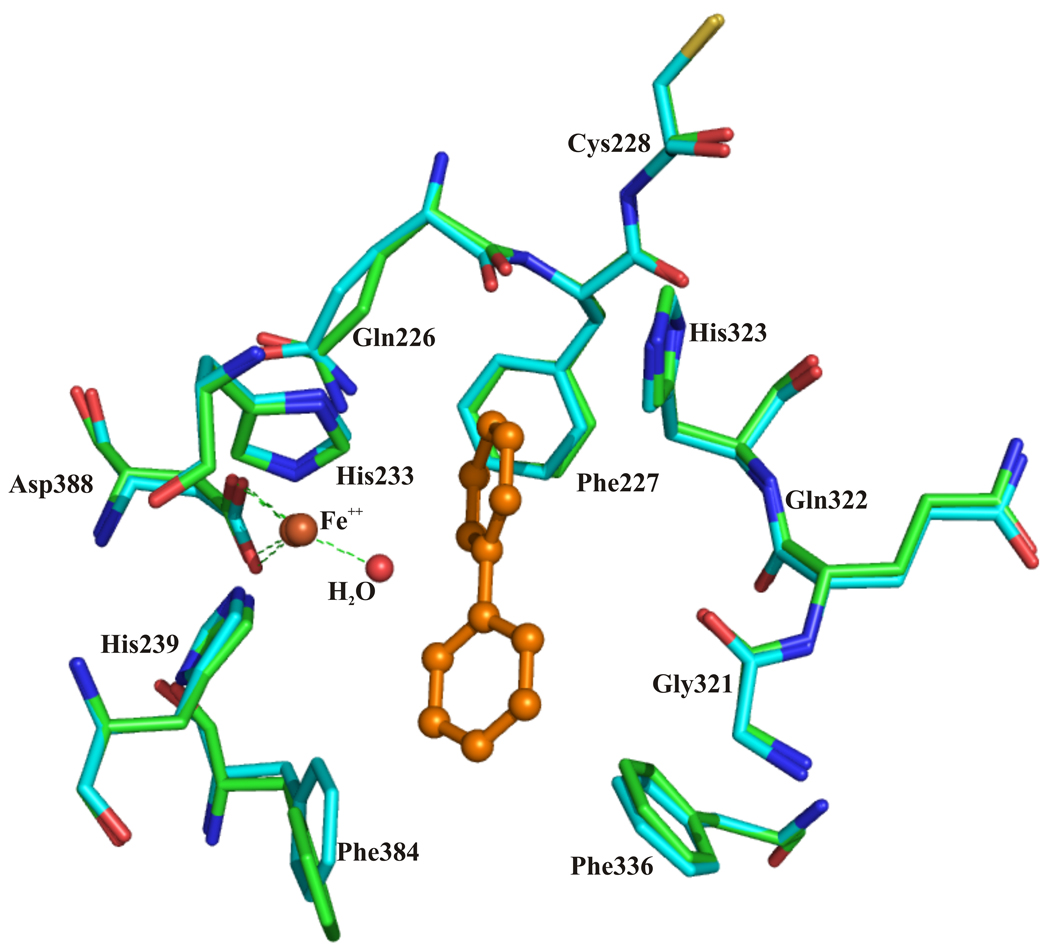
The position and orientation of the reactive ring of biphenyl appear to be tightly constrained by the surrounding protein atoms. Side chains of residues Gln226, Phe227, Asp230, Met231, His233, Ala234, His323 and Leu333 of the α subunit are located within 4.5 Å of atoms of the reactive ring (see supplementary material Fig. 3a).
In the distal ring pocket of BphAELB400, five atoms of the non-reactive ring of biphenyl are located within 4.5 Å of multiple protein atoms from Phe384, Phe378, Phe336, His239, Met231, Gly321 and Val287 (see supplementary material Fig 3b). In spite of these multiple contacts, superposition of the twelve αβ dimers clearly illustrates that the non-reactive ring may access different orientations. These variations do not seem to be associated with equivalent variation in the orientation of the reactive ring, especially the ortho-meta C-2/C-3 atoms. Furthermore, the conformations of the residues lining the catalytic pocket remain very similar in all twelve dimers. Altogether, structural analysis shows the catalytic pocket of BphAELB400, as represented by the crystal structure of the substrate-free enzyme, provides enough space to bind biphenyl in a productive manner without major changes in protein conformation within the catalytic pocket.
Comparison of the crystal structure of BphAELB400 with other BPDOs
The superposition of biphenyl-complexed BphAELB400 (dimers AB, CD, EF) with biphenyl-complexed BphA1A2RHA1 shows that the relative positions of the residues that coordinate the catalytic iron, His233, His239 and Asn388 in BphALB400 and His224, His230 and Asn378 in BphA1RHA1, are similar (Supplementary material, Fig. 4). It also shows that carbons C-2 and C-3 of biphenyl align very well although their distance to the catalytic iron is shorter in BphAELB400 than in BphA1A2RHA1 and BphA1A2B118; 24. In the case of BphA1A2RHA1, several residues of the catalytic pocket, such as Leu274 and Ala311, were shown to move significantly after biphenyl binding. Using CASTp27 software, and a probe radius of 1.4Å, we measured an average volume of 1071 Å3 for all twelve αβ dimers of native BphAELB400 and 312 Å3 for BphA1A2RHA1. This suggests the greater side chain displacements observed when BphA1A2RHA1 binds to biphenyl might be caused in part by the smaller cavity volume compared to BphAELB400. Biphenyl-bound BphAELB400 does not superpose as well with BphA1A2B124 which is structurally more similar to naphthalene than to biphenyl dioxygenases.
Crystal structure of BphAEp4: general features
BphAEp4 native crystals were grown in the triclinic space group P1 with unit cell parameters a = 132.6, b = 132.4, c = 133.0 Å, and α = 102.6, β = 102.7 and γ = 104.6°, and they diffracted to 2.2 Å. Crystals of the 2,6-chlorobiphenyl-complex were grown in the monoclinic space group P21 with a = 86.7, b = 276.8, c = 93.3 Å and β = 117.4° and diffracted to comparable resolution (Table 1). The BphAELB400 crystal structure was used as a search model to find initial phases for BphAEp4 and provided the initial model, which was subsequently refined to final R and Rfree values of 21.4 and 26.6% at a resolution of 2.2 Å. The final refined model contains residues Asn18 to Phe143 plus Phe153 to Pro459 of the α subunit, residues Phe9 to Phe188 of the β subunit, 145 water molecules, and one glycerol molecule. Quantities and statistics characterizing the diffraction data and the refined model are provided in Table 1.
The structure of native BphAEp4 is very similar to that of native BphAELB400, where triplets of αβ dimers associate to generate four α3β3 hexamers possessing non-crystallographic three-fold symmetry. Superposition of all Cα atoms for chains AB and chains CD-WX yielded rmsd values of 0.2–0.4 Å2 and the average B-factor was 32.6 Å2 (supplementary material, Table 1). The most disordered residues and protein segments were the same as observed for BphAELB400, including the segments comprising residues Ile247-Lys263 and Glu280-Val287 of the α subunit and 9–17 and 158–164 of the β subunit, as discussed above. In addition, other residues or segments of the α subunit showed variations in position among the twelve dimers. These were His233-His239, Val320-Glu322, Asp388, Lys403-Ala411, Pro423-Tyr433. (supplementary material Fig. 2i–k). As observed for BphAELB400 the flexible N-terminal region (residues 9–17) of the β subunit are having two conformations. In one type of conformation, this segment interacts with the active site mouth of an α subunit belonging to a neighboring α3β3 hexamer. This movement is also observed for the native form of BphAEp4. However, in the case of the 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl-bound form of BphAEp4, no dimer interacts with the active site mouth residue and all of them exhibit the second conformation (supplementary material Fig. 3b). On the basis of this observation, it can be postulated that conformational variations of the N-terminal portion of the β subunit might influence substrate specificity. However, more data is required to support these hypotheses and we will not discuss this further in this work. Nevertheless, the role of the β subunit is not yet clearly understood but, in some experiments, the β subunit was found to influence substrate specificity28; 29.
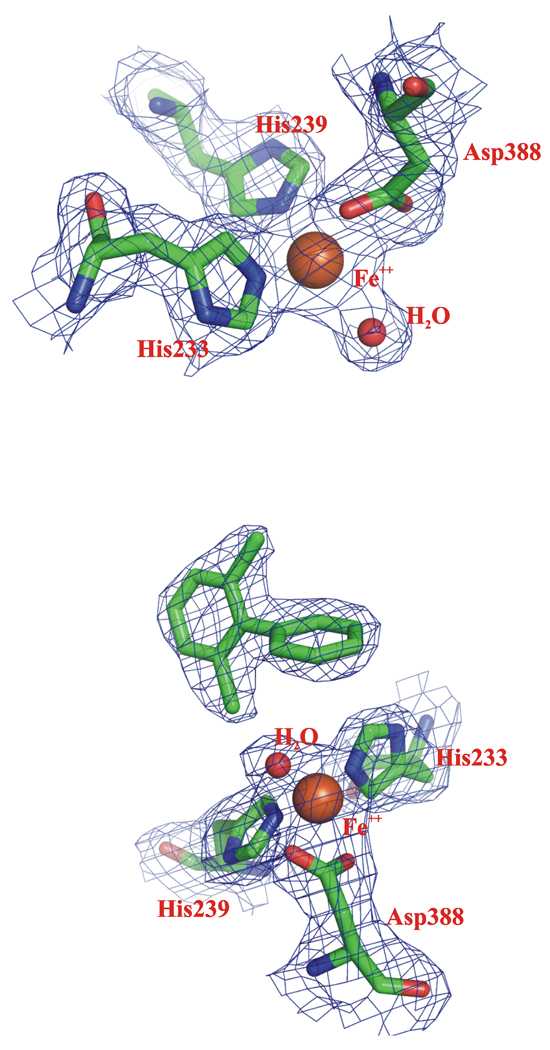
The crystal structure of the BphAEp4:2,6-dichlorobiphenyl complex contains triplets of αβ dimers that associate to generate two (ABCDEF and GHIJKL) hexamers in the asymmetric unit. 2,6-Dichlorobiphenyl could be identified clearly in difference Fourier maps in the active sites of the ABCDEF hexamer. However, the active sites of the GHIJKL hexamer did not have sufficient density to justify modeling the substrate. The electron density maps of the catalytic center residues of the native BphAEp4 and of its 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl-complex are shown in Fig. 4.
Fig. 4.
The 2Fobs–Fcalc electron density map of chain AB of substrate-free (upper panel) and of 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl-complex (lower panel) of BphAEp4 contoured at 1.0 σ level.
Comparison of the crystal structures of native and substrate-bound BphAEp4 and BphAELB400
When the six αβ dimers of the BphAEp4:2,6-dichlorobiphenyl complex are superposed, the deviations are small in the core region of the molecule (supplementary material Fig. 1b). The most variable segments are the same as for the native BphAEp4. Superposition of all Cα atoms for chain AB and chains CD-WX yielded rmsd values of 0.25–0.36 Å and the average B-factor value was 49.2 Å2 (supplementary material Fig. 2l–m).
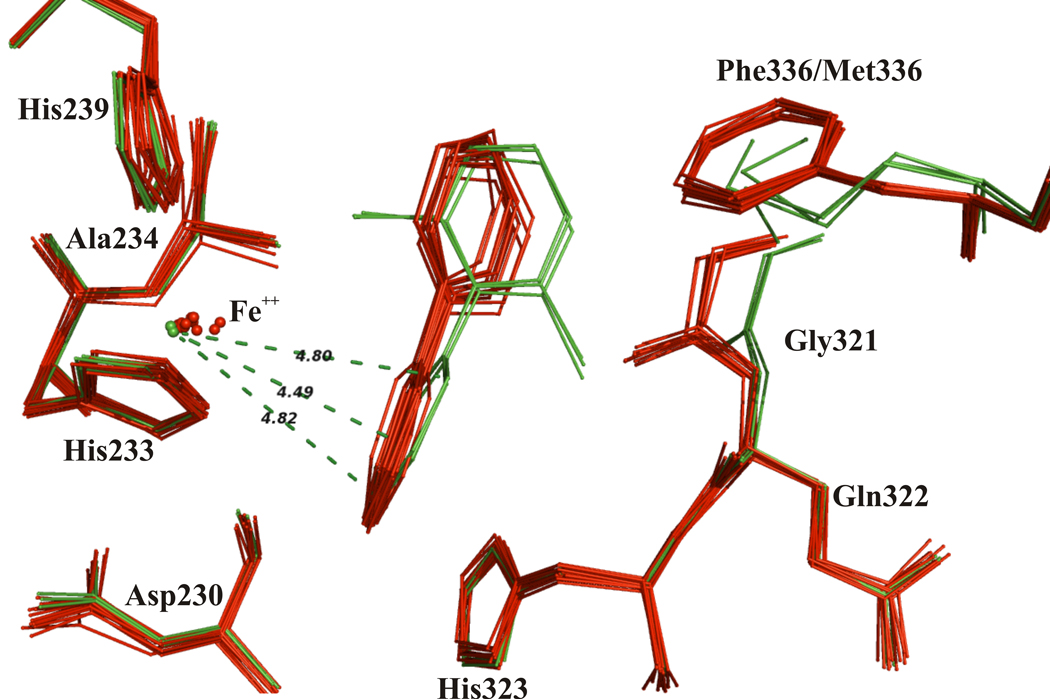
When chains AB, CD, and EF of the BphAEp4:2,6-dichlorobiphenyl complex were superposed with each other and also with the 12 αβ dimers of the biphenyl complex of BphAELB400, it was observed that the orientation of the chlorinated substrate differs from the orientation of biphenyl in BphAELB400. The non-reactive ring of 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl is shifted toward Gly321 and Met336 (Fig. 5). This shift is correlated with a change in the placement of the reactive ring of 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl, such that the relationship of carbons C-2/C-3 to the Fe is altered. In addition, it appears that the Fe atom and Asp388 withdraw from the substrate (see Fig. 6a) when 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl binds BphAEp4. Such a displacement is not observed when BphAELB400 binds biphenyl (Fig. 6b). An interesting consequence of these movements is that carbons C-2 and C-4 of 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl are positioned at a similar distance from the Fe atom: the distances that separate the ortho, meta and para carbons of 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl from the iron of BphAEp4 are on average 4.8 Å, 4.5 Å and 4.9 Å respectively (Fig. 7). As indicated above, the average distances that separate C-2, C-3 and C-4 of biphenyl from the Fe of BphAELB400 are respectively 4 Å, 4 Å and 5 Å. The fact that C-2/C-3/C-4 of 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl are instead at similar distances from the Fe atom of BphAEp4 may explain why BphAEp4 produced a large amount of the 3,4-dihydro-dihydroxy metabolite from 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl.
Figure 5.
Superposition of active site atoms from twelve αβ dimers of BphAELB400 (yellow) and twelve biphenyl-bound dimers (red) with twelve αβ dimers of BphAEp4 (green) and six dimers of 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl-bound BphAEp4 (blue) showing the shift of the distal ring of 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl toward Gly321 and Met336.
Figure 6.
(a) Superposition of active site atoms from twelve BphAEp4 (tan) with six 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl-bound BphAEp4 (blue) αβ dimers and (b) superposition of twelve BphAELB400 (yellow) with twelve biphenyl-bound BphAELB400 (red) dimers showing the displacement of Asp388 after substrate binding.
Figure 7.
Superposition of twelve dimers of biphenyl-bound BphAELB400 (red) with dimers AB, CD and EF of the 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl-bound BphAEp4 (green) showing the distances between C-2, C-3 and C-4 of 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl and the catalytic iron of dimer AB.
The corresponding atoms of both substrates interact with the same residues of BphAEp4 and BphAELB400 α subunits (Leu333, Phe227, Gln226, His323, His233 Ala230, Met231) and they are located at similar distances (closer than 4.5 Å) (Supplementary material Fig. 3c). Most residues that were closer than 4.5 Å from the distal ring in BphAELB400 (Phe384, His239, Phe336, Met231, Gly321, Val287) are at a similar distance from the non-reactive ring of 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl in BphAEp4 (supplementary material Fig. 3d). As noted above, relative to the BphAELB400:biphenyl complex, the non-reactive ring of 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl shifts toward the Val320-Gln322 segment and Met336. As shown in Fig. 5, the Val320-Gln322 segment of BphAEp4 assumes various conformations in the absence of substrate, indicating it is less constrained in BphAEp4 than in BphAELB400. This allows displacement on the order of 2 Å during binding to 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl, generating space for the ortho chlorine. This adjustment did not change the cavity volume of BphAEp4 as the average cavity volume of the αβ dimers of the native enzyme (as calculated using CASTp program) was 1152 Å3 and the average value for dimers GH, IJ, KL of the complexed enzyme was 1159 Å3.
In addition, relative to BphAELB400 the BphAEp4 280–283 segment shows more variation in conformation in the absence of substrate, and this segment clearly shifts by 1 to 2 Å toward the substrate when BphAEp4 binds 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl (Fig.5). Altogether, either because it is larger than biphenyl or as a result of interaction between the two ortho-chlorine atoms of the non-reactive ring with residues lining the distal catalytic pocket, binding of 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl requires or induces more conformational changes than biphenyl binding. The fact that BphAELB400 poorly catalyzes the oxygenation of 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl suggests that in spite of the large size of its catalytic pocket, the space available near the ortho-chlorines is not sufficient to allow productive binding of this substrate. In fact, automated docking of 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl into BphAELB400 places the non-chlorinated ring into the distal pocket of the enzyme and the chlorinated ring into the proximal pocket. In such "flipped" structures, neither the C-2'/C-3' nor C-3'/C-4' carbons of the chlorinated ring align with C-2/C-3 of the BphAELB400:biphenyl complex, and they are very far from the iron atom (not shown).
Aside from the segments comprising residues Glu280-Ser283 and Val320-Glu322 and of residue Asp388, other segments or residues of the α subunit including Tyr277-Val278, Lys403-Ala411, Gly427-Tyr433, His233-His239 are displaced after BphAEp4 binds to 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl (not shown). However, the possible impact of these movements on the catalytic activity toward 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl is not as readily explained.
Effect of the Thr335-to-Ala mutation
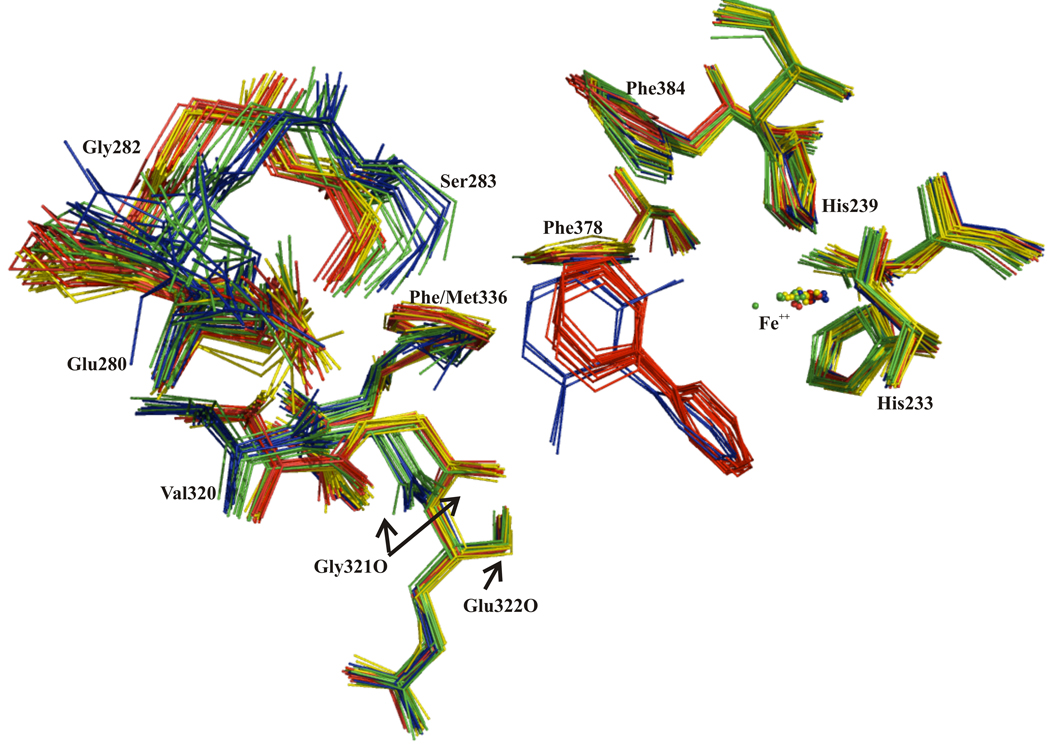
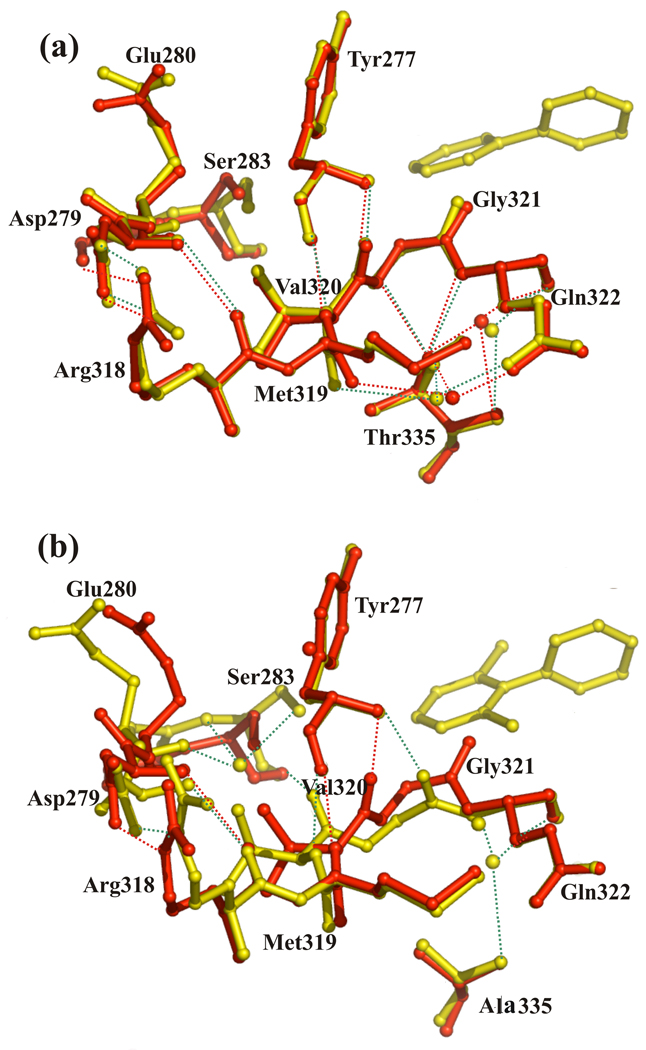
Analysis of the crystal structures of BphAEp4 and BphAELB400 suggests how changing Thr335 to Ala alters the conformational freedom of the Val320-Gly321 segment and some of the other segments of the catalytic pocket. In BphAELB400, the hydroxyl group of Thr335 is within 3.0 Å of the amide groups of Gln322 and of Gly321 and within 3.5 Å of C-1 of Val320. In addition, hydrogen bonds are formed between the amide groups of Gly321 and Gln322 and the hydroxyl group of Thr335. Most of these contacts are lost when Thr335 is replaced by Ala (Fig. 8). This appears to relax conformational constraints for the Val320-Gln322 segment, which allows for greater variation in conformation and displacement of this segment, particularly for the carbonyl group of Gly321. Replacing Thr335 by Ala has other consequences for residues lining the catalytic cavity. Since Gly321 and Val320 form hydrogen bonds with Tyr277, the conformation of the Val320-Gln322 segment influences the conformation of this residue. In addition, although residues Arg318-Met319 do not contact Thr335, their conformation appears to be influenced by the position and orientation of 320–322. Moreover, residues 320–322 can influence indirectly the conformation of the Asn279-Ser283 segment through contacts between the latter and Arg318-Met319 (Fig. 8). Thus the considerable shift of Ser283 and Glu280 after substrate binding can be linked back to the relaxation of conformational restraints for Val320-Gln322. Another consequence of this movement is to close the mouth of the active site, but it is not clear if this shift is required for productive binding of 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl.
Figure 8.
(a) Superposition of segments of dimer AB of BphAELB400 and of its biphenyl-bound form and (b) superposition of the corresponding segments of dimer KL of BphAEp4and of dimer AB of its 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl-bound form. Both bound forms of BphAELB400 and BphAEp4 are in yellow, native forms are in red. Dashed lines represent H-bonds of substrate complex forms (green) and of native forms (red), spheres represent water molecules.
Discussion
Examination of the substrate binding interactions and the structural mechanism by which BPDOs can increase their metabolic versatility will advance approaches to engineer better performing biocatalysts. Many investigations have shown that the specificities and regiospecificities of Rieske-type aryl hydroxylating dioxygenases were altered by changing single residues that crystal structures place near the active site22; 30; 31. These studies and many others involving other enzymes30; 31; 32; 33; 34; 35; 36, have demonstrated that these changes can alter the configuration of the space within the catalytic pocket. In the case of versatile enzymes such as aryl hydroxylating dioxygenases and cytochromes P450, many of which can oxygenate a broad range of substrates, induced-fit mechanisms are likely to be required to allow productive substrate binding. One mechanism to enhance the capacity for induced-fit is to lessen the structural constraints imposed on strategic active site residues. Residues lining the catalytic cavity that are less constrained are able to change conformation during substrate binding allowing more space for productive binding of structurally different substrates. Hence changes induced by substrate binding have been observed for several cytochromes P45037. Similarly, in the case of Rieske-type oxygenases, crystallographic studies of NDO38, nitrotoluene dioxygenase39, BphA1A2RHA118 as well as BphA1A2B124 and BphAEp4 showed that some of the residues lining the distal and also the proximal portion of the catalytic pocket can be displaced by substrate binding. Here, structural analysis of native and substrate-bound BphAELB400 and BphAEp4 revealed conformational variations of the carbonyl group of Gly321, which is in direct, non-bonded contact with substrates. The corresponding residue in BphA1A2RHA1 was also shown to be displaced after substrate binding18. Our data also reveal how other residues not in direct contact with the substrate, such as Ala335 of BphAEp4, can influence the adaptability of the catalytic pocket of BPDO and thereby allow productive substrate binding. Thus, changing Thr335 to Ala relaxed constraints on the Val320-Gly321-Gln322 segment allowing displacement of Gly321 during substrate binding and opening space to position and orient the doubly-ortho-chlorinated biphenyl inside the catalytic pocket.
Although Thr335 appears to play a controlling role in the inability of BphAELB400 to oxygenate 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl, the identity of residue 336 also has significant influence on the reaction because BphAEp4 and BphAEp401 have different regiospecificity toward this substrate. The structures suggest differences in side chain interactions between Phe336 or Met336 and the distal ring influence the relationship of the reactive ring relative to the Fe. It is noteworthy that the distances from C-2/C-3 to the Fe atom are significantly larger in the BphAEp4:2,6-dichlorobiphenyl complex compared to the distances in the BphAELB400:biphenyl complex. In addition, in the BphAEp4:2,6-dichlorobiphenyl complex, the C-2 and C-4 carbons are equidistant from the Fe, which may readily explain the enhanced yield of the 3,4-hydroxylated product in Met336 variants. Similarly, Phe336 and Met336 probably interact differently with 2,2'-dichlorobiphenyl since the regiospecificity toward this substrate is changed when Phe336 of BphAELB400 is replaced by Met in BphAEp402 and BphAEp4.
It is also noteworthy that BphAEB-356 and variant BphAEII9, which was obtained by replacing residues 335–341 of BphAELB400 by the corresponding residues of BphAEB-356, can oxygenate 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl16. In this case, Thr335-Phe336 of BphALB400 are replaced by Gly-Ile, and it is most likely that, similar to BphAEp4, the replacement of Thr335 by a Gly reduces constraints on residues 320–322 to facilitate the movement of Gly321. However, BphAEB-356 and BphAEII9, both produce principally the 2,3-dihydro-2,3-dihydroxy-dichlorobiphenyl from 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl. This suggests that Met336 of BphAEp4 and the corresponding residue of BphAEB-356, Thr333, interact differently with the substrate to influence its orientation inside the catalytic cavity. This would not be surprising given the differences in the chemistry and conformation variations of Met and Thr residues.
We recently examined the diversity of the BphA C-terminal domain as represented by PCR products amplified from various PCB degrading bacteria and from DNA extracted from PCB-contaminated soils. The presence of a Thr at position 335 as in BphALB400 was uncommon, and most of the sequences contained the smaller Gly or Ala at that position 40. This leads to the hypothesis that, in most BphAs, the Val320-Gln322 segment is more relaxed than in BphALB400. To our knowledge, no study has examined the effect of replacing Gly321 with larger amino acids in the background of BphALB400, but additional recent observations emphasized the importance of residue 321 as a determinant for substrate specificity40; 41. Thus, Witzig et al.41 amplified the C-terminal portion of genes encoding the α subunit of toluene/biphenyl dioxygenases from isolates growing on benzene-toluene-ethylbenzene and from soil DNA from which they were isolated. The position corresponding to Gly321 was highly variable. However, the isolates harboring a bulkier amino acid at that position were unable to oxygenate toluene41.
Other residues that line the catalytic cavity were previously found to influence the substrate specificity and regiospecificity. Suenaga et al. 22 found that changing Phe227, Leu333, Phe377 and Phe383 of Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes KF707 BphA1 (BphA1KF707), corresponding to Phe227, Leu333, Phe378 and Phe384 of BphALB400, alter either the range of substrates that the enzyme can oxygenate or the regiospecificity toward ortho-chlorinated biphenyls. Both a homology model of BphA1KF707 based on BphA1RHA1, and our crystal structures of BphALB400 show that these residues line the catalytic pocket and thus may critically influence the enzyme's catalytic properties toward chlorobiphenyls. However, Zielinski et al.23 and Vézina et al.42 identified other residues that are not expected to be in direct contact with the substrate but significantly modified the specificities and/or regiospecificities toward selected substrates. Perhaps some of these residues influence the catalytic properties indirectly by controlling the position and/or conformation of residues lining the catalytic cavity or by altering the level of constraint imposed on protein segments lining the catalytic cavity to allow more movement during substrate binding. The case of Asn377 is of particular interest since the variant obtained by replacing the corresponding Thr376 of BphA1KF707 by Asn of BphALB400 has acquired the ability to oxygenate 2,2’,5,5’-tetrachlorobiphenyl onto carbon atoms 3 and 4 43. An analysis 31 based on a homology model of BphA1KF707 suggested that the loss of a hydrogen bond involving the hydroxyl residue of Thr376 with the carbonyl of Asn373 could be responsible for the different regiospecificities between wild-type BphA1KF707 and its Thr376Asn variant. However, in the absence of crystal structures of BphA1A2KF707 and the variant, the authors were unable to explain how the loss of this hydrogen bond influenced the catalytic properties of the enzyme. Since Phe378 (Phe377 of BphA1KF707) is close to carbon 3 and 4 of biphenyl's distal ring, it is possible that relaxation of constraints on residues 376–377 of BphA1KF707, associated with loss of the hydrogen bond, allows an adaptive response centered on Phe377 that creates more space to accept and position the doubly ortho-meta tetrachlorinated congener.
The results obtained in this work increase our understanding of how amino acid residues within and outside the active site pocket can affect substrate specificity and enzyme activity. Data show how the mutations directed at residues further removed from the substrate can influence the enzyme's specificities. Consistent with induced-fit mechanisms, these mutations can modulate the spatial distribution of residues in direct contact with the substrate or influence the binding-induced changes required to place chlorobiphenyls into productive positions and orientations. Additional effort will be required to determine the precise mechanisms by which additional residues not in direct contact with the substrate influence the enzyme’s specificities. At a fundamental level, our results plead in favor of engineering aryl hydroxylating enzymes through artificial evolutionary approaches that alter all or specific protein segments in the vicinity of the catalytic cavity instead of changing individual residues that are in direct contact with the substrate.
Materials and Methods
Strains, plasmids and chemicals
E. coli DH11S44 and C41(DE3)45 (Statagene, La Jolla, CA) were used in this study. The plasmids used were pT76a 46, pET14b[p4-bphAE] and pET14b[LB400-bphAE]47 and pQE31[LB400-bphAE] and pQE31[p4-bphAE]15. Biphenyl and the chlorobiphenyls used in this work were of the highest purity grade available from AccuStandard (New Haven, CT).
Mutagenesis and cloning
The mutated genes for variants BphAEp401 (T335A) and variant BphAEp402 (F336M) were prepared from LB400 bphAE by the two-step site-directed mutagenesis protocol described previously,42 creating pQE31[LB400-bphAEp401] and pQE31[LB400-bphAEp402]. The resulting plasmids were transformed into E. coli DH11S pDB31[LB400-bphFG]14. DNA protocols were generally according to Sambrook et al.48. DNA from each mutant was sequenced at the Génome Québec DNA Sequencing Center (Montreal, Quebec, Canada).
Whole cell assays to identify metabolites of chlorobiphenyls
Metabolites were analyzed from suspensions of isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG)-induced E. coli DH11S pDB31[LB400-bphFG] harboring appropriate variants of pQE31[bphAE] according to the protocol described previously 15. Level of expression was assessed by inspection of SDS-PAGE gels49. Metabolites were identified by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) analyses of their butylboronate derivatives15. GC-MS peak areas were used to determine the relative activity of each variant enzyme.
Crystallization and crystallographic methods
Purification, crystallization, and preliminary X-ray diffraction properties of BphAELB400 and BphAEp4 have been communicated elsewhere (Kumar et al, submitted). In brief, crystallization conditions for BphAELB400 and BphAEp4 were screened by the sitting-drop vapor-diffusion method at 21°C under an N2 atmosphere (<5 ppm oxygen) in a glove box (Innovative Technologies, Newburyport, MA). BphAELB400 crystals grew in triclinic space group P1 with twelve αβ dimers (i.e., four α3β3 hexamers) in the asymmetric unit at 21°C when the reservoir solution (1000 µl) contained 20–25% (w/v) PEG 8000 or PEG 5000 MME, 50 mM PIPES pH 6.5, 100 mM ammonium acetate, 5% (v/v) glycerol and 0.2% (w/v) agarose. BphAEp4 grew in two different crystal forms at 21°C using a reservoir solution (1000 µl) containing 20–25% (w/v) PEG 8000, 50 mM PIPES pH 6.5 and 100 mM ammonium acetate. Absent substrate, BphAEp4 enzyme crystallized in triclinic space group P1 with twelve αβ dimers in the asymmetric unit, whereas crystals of the BphAEp4:2,6-dichlorobipenyl complex have monoclinic space group P21, with six αβ dimers in the asymmetric unit.
Diffraction data were acquired from cryogenically cooled crystals (100K) using the facilities of SERCAT beamline 22-ID at the Advanced Photon Source (Argonne National Laboratories). The diffraction patterns were indexed, integrated and scaled using the HKL2000 suite50. Initial phases for BphAELB400 and BphAEp4 were obtained by the molecular replacement method using MOLREP51 from the CCP4 v.4.2 software suite52. In case of BphAELB400, the crystal structure of BphAEB35616 was used as the search model. Atomic model refinement was accomplished using the program CNS53 and REFMAC5.254. The programs O55 and COOT56 were used for analysis of electron density maps and model building. Stereochemical properties of models were evaluated using Procheck57 and Ramachandran plots. Several cycles of rigid body refinement and then restrained refinement were used to achieve acceptable Rcryst and Rfree. The CASTp program27 which was available online (http://sts.bioengr.uic.edu/castp/index.php) was used to calculate the catalytic cavity volume using a probe radius of 1.4Å. Figures were prepared using the program PyMOL.
PDB accession codes
The coordinates have been deposited with the RCSB Protein Data Bank (http://deposit.rcsb.org/) under accession codes 2xr8 for BphAELB400 and 2xrx for its biphenyl-complex form and 2xso for BphAEp4 and 2xsh for its complex with 2,6-dichlorobiphenyl.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Discovery and Strategic grants from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC). Use of the BioCARS Sector 14 at the Advanced Photon Source (APS), Argonne National Laboratory, was supported by the National Institutes of Health, National Center for Research Resources, under grant number RR007707. Additional X-ray diffraction data were collected at APS using Southeast Regional Collaborative Access Team (SER-CAT) 22-ID beamline; supporting institutions may be found at www.ser-cat.org/members.html. Use of the Advanced Photon Source was supported by the U. S. Department of Energy, Office of Science, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, under Contract No. W-31-109-Eng-38.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
- 1.Aoki Y. Polychlorinated biphenyls, polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, and polychlorinated dibenzofurans as endocrine disrupters--what we have learned from Yusho disease. Environ Res. 2001;86:2–11. doi: 10.1006/enrs.2001.4244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Safe SH. Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) - Environmental impact, biochemical and toxic responses, and implications for risk assessment. Crit Rev Toxicol. 1994;24:87–149. doi: 10.3109/10408449409049308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Misawa N, Nakamura R, Kagiyama Y, Ikenaga H, Furukawa K, Shindo K. Synthesis of vicinal diols from various arenes with a heterocyclic, amino or carboxyl group by using recombinant Escherichia coli cells expressing evolved biphenyl dioxygenase and dihydrodiol dehydrogenase genes. Tetrahedron. 2005;61:195–204. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Resnick SM, Gibson DT. Regio- and stereospecific oxidation of fluorene, dibenzofuran, and dibenzothiophene by naphthalene dioxygenase from Pseudomonas sp strain NCIB 9816-4. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1996;62:4073–4080. doi: 10.1128/aem.62.11.4073-4080.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Seeger M, Gonzalez M, Camara B, Munoz L, Ponce E, Mejias L, Mascayano C, Vasquez Y, Sepulveda-Boza S. Biotransformation of natural and synthetic isoflavonoids by two recombinant microbial enzymes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003;69:5045–5050. doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.9.5045-5050.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ullrich R, Hofrichter M. Enzymatic hydroxylation of aromatic compounds. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007;64:271–293. doi: 10.1007/s00018-007-6362-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Erickson BD, Mondello FJ. Nucleotide sequencing and transcriptional mapping of the genes encoding biphenyl dioxygenase, a multicomponent polychlorinated-biphenyl-degrading enzyme in Pseudomonas strain LB400. J Bacteriol. 1992;174:2903–2912. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.9.2903-2912.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hurtubise Y, Barriault D, Sylvestre M. Characterization of active recombinant his-tagged oxygenase component of Comamonas testosteroni B-356 biphenyl dioxygenase. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:8152–8156. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.14.8152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Karlsson A, Parales JV, Parales RE, Gibson DT, Eklund H, Ramaswamy S. Crystal structure of naphthalene dioxygenase: Side-on binding of dioxygen to iron. Science. 2003;299:1039–1042. doi: 10.1126/science.1078020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mondello FJ, Turcich MP, Lobos JH, Erickson BD. Identification and modification of biphenyl dioxygenase sequences that determine the specificity of polychlorinated biphenyl degradation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1997;63:3096–3103. doi: 10.1128/aem.63.8.3096-3103.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Maltseva OV, Tsoi TV, Quensen JF, Fukuda M, Tiedje JM. Degradation of anaerobic reductive dechlorination products of Aroclor 1242 by four aerobic bacteria. Biodegradation. 1999;10:363–371. doi: 10.1023/a:1008319306757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Rodrigues JLM, Kachel CA, Aiello MR, Quensen JF, Maltseva OV, Tsoi TV, Tiedje JM. Degradation of Aroclor 1242 dechlorination products in sediments by Burkholderia xenovorans LB400(Ohb) and Rhodococcus sp strain RHA1(Fcb) Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006;72:2476–2482. doi: 10.1128/AEM.72.4.2476-2482.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Furukawa K, Tonomura K, Kamibayashi A. Effect of chlorine substitution on the biodegradability of polychlorinated biphenyls. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978;35:223–227. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.2.223-227.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Barriault D, Plante MM, Sylvestre M. Family shuffling of a targeted bphA region to engineer biphenyl dioxygenase. J Bacteriol. 2002;184:3794–3800. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.14.3794-3800.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Barriault D, Sylvestre M. Evolution of the biphenyl dioxygenase BphA from Burkholderia xenovorans LB400 by random mutagenesis of multiple sites in region III. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:47480–47488. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M406805200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gomez-Gil L, Kumar P, Barriault D, Bolin JT, Sylvestre M, Eltis LD. Characterization of biphenyl dioxygenase of Pandoraea pnomenusa B-356 as a potent polychlorinated biphenyl-degrading enzyme. J Bacteriol. 2007;189:5705–5715. doi: 10.1128/JB.01476-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Dong XS, Fushinobu S, Fukuda E, Terada T, Nakamura S, Shimizu K, Nojiri H, Omori T, Shoun H, Wakagi T. Crystal structure of the terminal oxygenase component of cumene dioxygenase from Pseudomonas fluorescens IP01. J Bacteriol. 2005;187:2483–2490. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.7.2483-2490.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Furusawa Y, Nagarajan V, Tanokura M, Masai E, Fukuda M, Senda T. Crystal structure of the terminal oxygenase component of biphenyl dioxygenase derived from Rhodococcus sp. strain RHA1. J Mol Biol. 2004;342:1041–1052. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.07.062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Friemann R, Lee K, Brown EN, Gibson DT, Eklund H, Ramaswamy S. Structures of the multicomponent Rieske non-heme iron toluene 2,3-dioxygenase enzyme system. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2009;65:24–33. doi: 10.1107/S0907444908036524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Yu CL, Liu W, Ferraro DJ, Brown EN, Parales JV, Ramaswamy S, Zylstra GJ, Gibson DT, Parales RE. Purification, characterization, and crystallization of the components of a biphenyl dioxygenase system from Sphingobium yanoikuyae B1. J Ind Microbiol Biot. 2007;34:311–324. doi: 10.1007/s10295-006-0199-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Suenaga H, Goto M, Furukawa K. Emergence of multifunctional oxygenase activities by random priming recombination. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:22500–22506. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M101323200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Suenaga H, Watanabe T, Sato M, Ngadiman, Furukawa K. Alteration of regiospecificity in biphenyl dioxygenase by active-site engineering. J Bacteriol. 2002;184:3682–3688. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.13.3682-3688.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zielinski M, Kahl S, Hecht HJ, Hofer B. Pinpointing biphenyl dioxygenase residues that are crucial for substrate interaction. J Bacteriol. 2003;185:6976–6980. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.23.6976-6980.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ferraro DJ, Brown EN, Yu CL, Parales RE, Gibson DT, Ramaswamy S. Structural investigations of the ferredoxin and terminal oxygenase components of the biphenyl 2,3-dioxygenase from Sphingobium yanoikuyae B1. BMC Struct Biol. 2007;7:10. doi: 10.1186/1472-6807-7-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Jakoncic J, Jouanneau Y, Meyer C, Stojanoff V. The crystal structure of the ring-hydroxylating dioxygenase from Sphingomonas CHY-1. FEBS Journal. 2007;274:2470–2481. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2007.05783.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kauppi B, Lee K, Carredano E, Parales RE, Gibson DT, Eklund H, Ramaswamy S. Structure of an aromatic-ring-hydroxylating dioxygenase-naphthalene 1,2- dioxygenase. Structure. 1998;6:571–586. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(98)00059-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Dundas J, Ouyang Z, Tseng J, Binkowski A, Turpaz Y, Liang J. CASTp: computed atlas of surface topography of proteins with structural and topographical mapping of functionally annotated residues. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34:W116–W118. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hurtubise Y, Barriault D, Sylvestre M. Involvement of the terminal oxygenase beta subunit in the biphenyl dioxygenase reactivity pattern toward chlorobiphenyls. J Bacteriol. 1998;180:5828–5835. doi: 10.1128/jb.180.22.5828-5835.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hirose J, Suyama A, Hayashida S, Furukawa K. Construction of hybrid biphenyl (bph) and toluene (tod) genes for functional analysis of aromatic ring dioxygenases. Gene. 1994;138:27–33. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90779-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Parales RE, Lee K, Resnick SM, Jiang HY, Lessner DJ, Gibson DT. Substrate specificity of naphthalene dioxygenase: Effect of specific amino acids at the active site of the enzyme. J Bacteriol. 2000;182:1641–1649. doi: 10.1128/jb.182.6.1641-1649.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Suenaga H, Goto M, Furukawa K. Active-site engineering of biphenyl dioxygenase: effect of substituted amino acids on substrate specificity and regiospecificity. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2006;71:168–176. doi: 10.1007/s00253-005-0135-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bak-Jensen KS, Andre G, Gottschalk TE, Paes G, Tran V, Svensson B. Tyrosine 105 and threonine 212 at outermost substrate binding subsites −6 and +4 control substrate specificity, oligosaccharide cleavage patterns, and multiple binding modes of barley alpha-amylase 1. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:10093–10102. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M312825200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Dietrich M, Do TA, Schmid RD, Pleiss J, Urlacher VB. Altering the regioselectivity of the subterminal fatty acid hydroxylase P450 BM-3 towards gamma-and delta-positions. J Biotechnol. 2009;139:115–117. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2008.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Huang WC, Westlake AC, Marechal JD, Joyce MG, Moody PC, Roberts GC. Filling a hole in cytochrome P450 BM3 improves substrate binding and catalytic efficiency. J Mol Biol. 2007;373:633–651. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.08.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ostrander EL, Larson JD, Schuermann JP, Tanner JJ. A conserved active site tyrosine residue of proline dehydrogenase helps enforce the preference for proline over hydroxyproline as the substrate. Biochemistry. 2009;48:951–959. doi: 10.1021/bi802094k. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Xu D, Enroth C, Lindqvist Y, Ballou DP, Massey V. Studies of the mechanism of phenol hydroxylase: effect of mutation of proline 364 to serine. Biochemistry. 2002;41:13627–13636. doi: 10.1021/bi020446n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Isin EM, Guengerich FP. Substrate binding to cytochromes P450. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2008;392:1019–1030. doi: 10.1007/s00216-008-2244-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Carredano E, Karlsson A, Kauppi B, Choudhury D, Parales RE, Parales JV, Lee K, Gibson DT, Eklund H, Ramaswamy S. Substrate binding site of naphthalene 1,2-dioxygenase: Functional implications of indole binding. J Mol Biol. 2000;296:701–712. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1999.3462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Friemann R, IvkovicJensen MM, Lessner DJ, Yu CL, Gibson DT, Parales RE, Eklund H, Ramaswamy S. Structural insight into the dioxygenation of nitroarene compounds: the crystal structure of nitrobenzene dioxygenase. J Mol Biol. 2005;348:1139–1151. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2005.03.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Vézina J, Barriault D, Sylvestre M. Diversity of the C-terminal portion of the biphenyl dioxygenase large subunit. J Mol Microb Biotech. 2008;15:139–151. doi: 10.1159/000121326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Witzig R, Junca H, Hecht HJ, Pieper DH. Assessment of toluene/biphenyl dioxygenase gene diversity in benzene-polluted soils: links between benzene biodegradation and genes similar to those encoding isopropylbenzene dioxygenases. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006;72:3504–3514. doi: 10.1128/AEM.72.5.3504-3514.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Vézina J, Barriault D, Sylvestre M. Family shuffling of soil DNA to change the regiospecificity of Burkholderia xenovorans LB400 biphenyl dioxygenase. J Bacteriol. 2007;189:779–788. doi: 10.1128/JB.01267-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Suenaga H, Nishi A, Watanabe T, Sakai M, Furukawa K. Engineering a hybrid pseudomonad to acquire 3,4-dioxygenase activity for polychlorinated biphenyls. J Biosci Bioeng. 1999;87:430–435. doi: 10.1016/s1389-1723(99)80090-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Lin JJ, Smith M, Jessee J, Bloom F. DH11s: an E. coli strain for preparation of single-standed DNA from phagemid vectors. BioTechniques. 1992;12:718–721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Miroux B, Walker JE. Over-production of proteins in Escherichia coli: mutant hosts that allow synthesis of some membrane proteins and globular proteins at high levels. J Mol Biol. 1996;260:289–298. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Hofer B, Eltis LD, Dowling DN, Timmis KN. Genetic analysis of a Pseudomonas locus encoding a pathway for biphenyl/polychlorinated biphenyl degradation. Gene. 1993;130:47–55. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90345-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Mohammadi M, Sylvestre M. Resolving the profile of metabolites generated during oxidation of dibenzofuran and chlorodibenzofurans by the biphenyl catabolic pathway enzymes. Chem Biol. 2005;12:835–846. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2005.05.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T. Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1989. [Google Scholar]
- 49.Laemmli CM, Leveau JH, Zehnder AJ, van der Meer JR. Characterization of a second tfd gene cluster for chlorophenol and chlorocatechol metabolism on plasmid pJP4 in Ralstonia eutropha JMP134(pJP4) J Bacteriol. 2000;182:4165–4172. doi: 10.1128/jb.182.15.4165-4172.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Otwinowski Z, Minor W. Processing of X-ray diffraction data collected in oscillation mode. Method Enzymol. 1997;276:307–326. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(97)76066-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Vagin A, Teplyakov A. MOLREP: an automated program for molecular replacement. J Appl Crystallogr. 1997;30:1022–1025. [Google Scholar]
- 52.COLLABORATIVE, COMPUTATIONAL & PROJECT. The CCP4 suite: programs for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1994;50:760–763. doi: 10.1107/S0907444994003112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Brünger AT, Adams PD, Clore GM, DeLano WL, Gros P, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Jiang JS, Kuszewski J, Nilges M, Pannu NS, Read RJ, Rice LM, Simonson T, Warren GL. Crystallography & NMR system: A new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1998;54:905–921. doi: 10.1107/s0907444998003254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Murshudov GN, Vagin AA, Dodson EJ. Refinement of macromolecular structures by the maximum-likelihood method. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1997;53:240–255. doi: 10.1107/S0907444996012255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Jones TA, Zou JY, Cowan SW, Kjeldgaard M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron-density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr A. 1991;47:110–119. doi: 10.1107/s0108767390010224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Emsley P, Cowtan K. Coot: model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2004;60:2126–2132. doi: 10.1107/S0907444904019158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Laskowski RA, Macarthur MW, Moss DS, Thornton JM. Procheck - a program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J Appl Crystallogr. 1993;26:283–291. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.