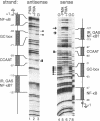
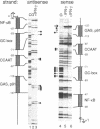
Abstract
GAS (gamma activated sequence) and GAS-like elements are found in a rapidly growing number of genes. Data from EMSA (electromobility shift assay) and transient transfection assays using heterologous promoter systems do not necessarily reflect transcriptional involvement and protein occupation of a binding site in vivo. This has been shown recently by in vivo footprinting of the NF-kappa B site at -40 in the interferon regulatory factor-1 (IRF-1) promoter. Here we show by in vivo footprinting using dimethylsulfate (DMS) that the GAS of the IRF-1 promoter, which also contains an overlapping putative NF-kappa B site, is occupied upon treatment with gamma-interferon (IFN gamma) but not with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA). Irrespective of induction, we detect a very strong DMS hypersensitivity at a guanosine just adjacent to GAS and a less persistent minor DMS hypersensitivity at a central cytosine. Our data confirm the crucial role of GAS in transcriptional activation by IFN gamma and are consistent with induced binding of p91 to GAS. In addition, our data suggest a major conformational distortion of the DNA at the GAS element of the IRF-1 promoter and that this GAS element is not involved in transcriptional activation by PMA.
Full text
PDF

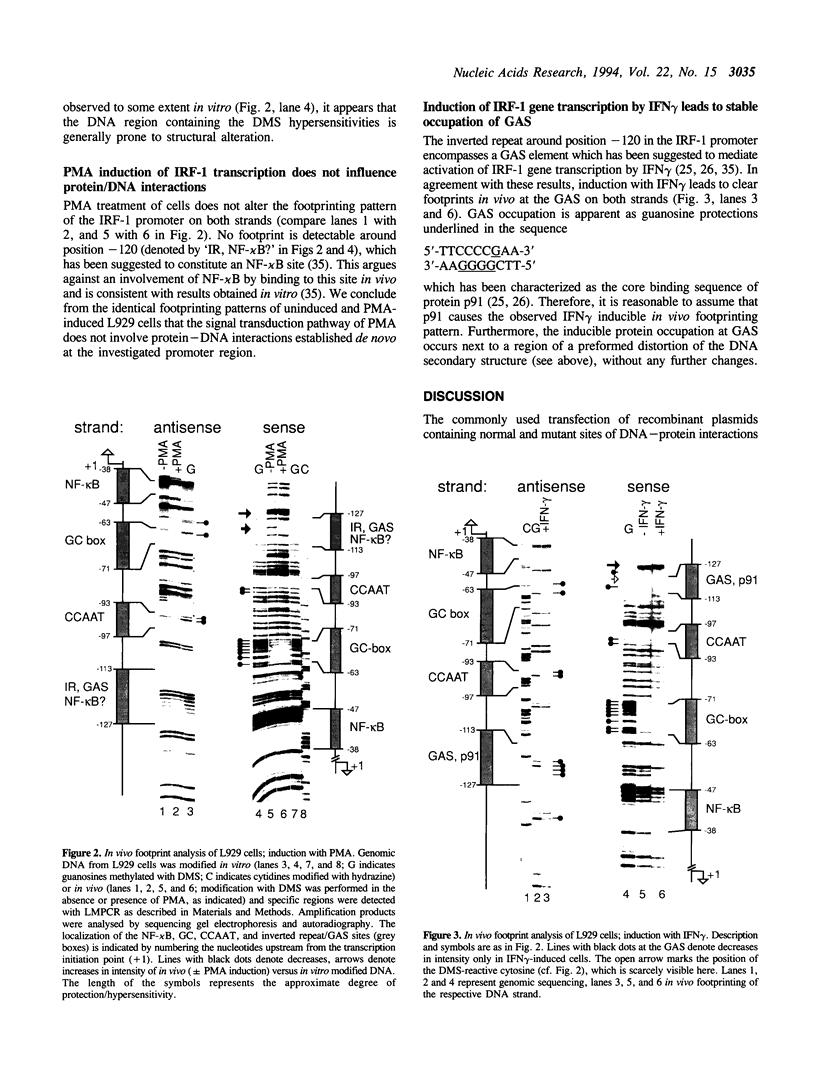


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abravaya K., Phillips B., Morimoto R. I. Heat shock-induced interactions of heat shock transcription factor and the human hsp70 promoter examined by in vivo footprinting. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):586–592. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A. The inducible transcription activator NF-kappa B: regulation by distinct protein subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 16;1072(1):63–80. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Sp1 and the subfamily of zinc finger proteins with guanine-rich binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11109–11110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark L., Matthews J. R., Hay R. T. Interaction of enhancer-binding protein EBP1 (NF-kappa B) with the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 enhancer. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1335–1344. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1335-1344.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker T., Lew D. J., Cheng Y. S., Levy D. E., Darnell J. E., Jr Interactions of alpha- and gamma-interferon in the transcriptional regulation of the gene encoding a guanylate-binding protein. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2009–2014. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03608.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker T., Lew D. J., Mirkovitch J., Darnell J. E., Jr Cytoplasmic activation of GAF, an IFN-gamma-regulated DNA-binding factor. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):927–932. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08026.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du W., Thanos D., Maniatis T. Mechanisms of transcriptional synergism between distinct virus-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90468-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Marty L., Piechaczyk M., el Sabrouty S., Dani C., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Various rat adult tissues express only one major mRNA species from the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase multigenic family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1431–1442. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. Y., Zhang J. J. Transcription factor p91 interacts with the epidermal growth factor receptor and mediates activation of the c-fos gene promoter. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):1135–1145. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90734-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Reis L. F., Watanabe N., Kimura Y., Taniguchi T., Vilcek J. Induction of the transcription factor IRF-1 and interferon-beta mRNAs by cytokines and activators of second-messenger pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9936–9940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Sakakibara J., Sudo Y., Miyamoto M., Kimura Y., Taniguchi T. Evidence for a nuclear factor(s), IRF-1, mediating induction and silencing properties to human IFN-beta gene regulatory elements. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3397–3405. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03213.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrity P. A., Wold B. J. Effects of different DNA polymerases in ligation-mediated PCR: enhanced genomic sequencing and in vivo footprinting. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):1021–1025. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada H., Kitagawa M., Tanaka N., Yamamoto H., Harada K., Ishihara M., Taniguchi T. Anti-oncogenic and oncogenic potentials of interferon regulatory factors-1 and -2. Science. 1993 Feb 12;259(5097):971–974. doi: 10.1126/science.8438157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada H., Takahashi E., Itoh S., Harada K., Hori T. A., Taniguchi T. Structure and regulation of the human interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF-1) and IRF-2 genes: implications for a gene network in the interferon system. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;14(2):1500–1509. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.2.1500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera R. E., Shaw P. E., Nordheim A. Occupation of the c-fos serum response element in vivo by a multi-protein complex is unaltered by growth factor induction. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):68–70. doi: 10.1038/340068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howland R., Decker M. D. Continuous quality improvement and hospital epidemiology: common themes. Qual Manag Health Care. 1992 Fall;1(1):9–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. Signal transduction. Cytokine connections. Nature. 1993 Nov 11;366(6451):114–116. doi: 10.1038/366114a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamijo R., Harada H., Matsuyama T., Bosland M., Gerecitano J., Shapiro D., Le J., Koh S. I., Kimura T., Green S. J. Requirement for transcription factor IRF-1 in NO synthase induction in macrophages. Science. 1994 Mar 18;263(5153):1612–1615. doi: 10.1126/science.7510419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanno Y., Kozak C. A., Schindler C., Driggers P. H., Ennist D. L., Gleason S. L., Darnell J. E., Jr, Ozato K. The genomic structure of the murine ICSBP gene reveals the presence of the gamma interferon-responsive element, to which an ISGF3 alpha subunit (or similar) molecule binds. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):3951–3963. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.3951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan K. D., Shuai K., Lindwall G., Maher S. E., Darnell J. E., Jr, Bothwell A. L. Induction of the Ly-6A/E gene by interferon alpha/beta and gamma requires a DNA element to which a tyrosine-phosphorylated 91-kDa protein binds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6806–6810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Kessler D. S., Pine R., Reich N., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-induced nuclear factors that bind a shared promoter element correlate with positive and negative transcriptional control. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):383–393. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M. DNA--protein interactions. HMG has DNA wrapped up. Nature. 1992 May 28;357(6376):282–283. doi: 10.1038/357282a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Felsenfeld G. Reaction of nucleosome DNA with dimethyl sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2133–2137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto M., Fujita T., Kimura Y., Maruyama M., Harada H., Sudo Y., Miyata T., Taniguchi T. Regulated expression of a gene encoding a nuclear factor, IRF-1, that specifically binds to IFN-beta gene regulatory elements. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):903–913. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91307-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Briscoe J., Laxton C., Guschin D., Ziemiecki A., Silvennoinen O., Harpur A. G., Barbieri G., Witthuhn B. A., Schindler C. The protein tyrosine kinase JAK1 complements defects in interferon-alpha/beta and -gamma signal transduction. Nature. 1993 Nov 11;366(6451):129–135. doi: 10.1038/366129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Laxton C., Briscoe J., Schindler C., Improta T., Darnell J. E., Jr, Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. Complementation of a mutant cell line: central role of the 91 kDa polypeptide of ISGF3 in the interferon-alpha and -gamma signal transduction pathways. EMBO J. 1993 Nov;12(11):4221–4228. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06106.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmieri M., Tovey M. G. Genomic footprinting: detection of putative regulatory proteins in the promoter region of the interferon alpha-1 gene in normal human tissues. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2554–2561. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse R. N., Feinman R., Shuai K., Darnell J. E., Jr, Ravetch J. V. Interferon gamma-induced transcription of the high-affinity Fc receptor for IgG requires assembly of a complex that includes the 91-kDa subunit of transcription factor ISGF3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):4314–4318. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.4314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez C., Wietzerbin J., Benech P. D. Two cis-DNA elements involved in myeloid-cell-specific expression and gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) activation of the human high-affinity Fc gamma receptor gene: a novel IFN regulatory mechanism. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2182–2192. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S., Langer J. A., Zoon K. C., Samuel C. E. Interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:727–777. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine R., Canova A., Schindler C. Tyrosine phosphorylated p91 binds to a single element in the ISGF2/IRF-1 promoter to mediate induction by IFN alpha and IFN gamma, and is likely to autoregulate the p91 gene. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 1;13(1):158–167. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06245.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine R., Decker T., Kessler D. S., Levy D. E., Darnell J. E., Jr Purification and cloning of interferon-stimulated gene factor 2 (ISGF2): ISGF2 (IRF-1) can bind to the promoters of both beta interferon- and interferon-stimulated genes but is not a primary transcriptional activator of either. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2448–2457. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piña B., Brüggemeier U., Beato M. Nucleosome positioning modulates accessibility of regulatory proteins to the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):719–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90087-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter A. C., Chernajovsky Y., Dale T. C., Gilbert C. S., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. Interferon response element of the human gene 6-16. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):85–92. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02786.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis L. F., Harada H., Wolchok J. D., Taniguchi T., Vilcek J. Critical role of a common transcription factor, IRF-1, in the regulation of IFN-beta and IFN-inducible genes. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):185–193. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05041.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond T. J., Finch J. T., Rushton B., Rhodes D., Klug A. Structure of the nucleosome core particle at 7 A resolution. Nature. 1984 Oct 11;311(5986):532–537. doi: 10.1038/311532a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruffner H., Reis L. F., Näf D., Weissmann C. Induction of type I interferon genes and interferon-inducible genes in embryonal stem cells devoid of interferon regulatory factor 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11503–11507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen G. C., Lengyel P. The interferon system. A bird's eye view of its biochemistry. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5017–5020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuai K. Interferon-activated signal transduction to the nucleus. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;6(2):253–259. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90144-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuai K., Schindler C., Prezioso V. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Activation of transcription by IFN-gamma: tyrosine phosphorylation of a 91-kD DNA binding protein. Science. 1992 Dec 11;258(5089):1808–1812. doi: 10.1126/science.1281555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Gilbert W. Contacts between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and an early promoter of phage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):122–126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims S. H., Cha Y., Romine M. F., Gao P. Q., Gottlieb K., Deisseroth A. B. A novel interferon-inducible domain: structural and functional analysis of the human interferon regulatory factor 1 gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):690–702. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka N., Taniguchi T. Cytokine gene regulation: regulatory cis-elements and DNA binding factors involved in the interferon system. Adv Immunol. 1992;52:263–281. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60877-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thanos D., Maniatis T. The high mobility group protein HMG I(Y) is required for NF-kappa B-dependent virus induction of the human IFN-beta gene. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):777–789. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90554-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. H., Elgin S. C. Protein/DNA architecture of the DNase I hypersensitive region of the Drosophila hsp26 promoter. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2191–2201. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03058.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watling D., Guschin D., Müller M., Silvennoinen O., Witthuhn B. A., Quelle F. W., Rogers N. C., Schindler C., Stark G. R., Ihle J. N. Complementation by the protein tyrosine kinase JAK2 of a mutant cell line defective in the interferon-gamma signal transduction pathway. Nature. 1993 Nov 11;366(6451):166–170. doi: 10.1038/366166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegenka U. M., Lütticken C., Buschmann J., Yuan J., Lottspeich F., Müller-Esterl W., Schindler C., Roeb E., Heinrich P. C., Horn F. The interleukin-6-activated acute-phase response factor is antigenically and functionally related to members of the signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) family. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 May;14(5):3186–3196. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.5.3186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willman C. L., Sever C. E., Pallavicini M. G., Harada H., Tanaka N., Slovak M. L., Yamamoto H., Harada K., Meeker T. C., List A. F. Deletion of IRF-1, mapping to chromosome 5q31.1, in human leukemia and preleukemic myelodysplasia. Science. 1993 Feb 12;259(5097):968–971. doi: 10.1126/science.8438156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada G., Ogawa M., Akagi K., Miyamoto H., Nakano N., Itoh S., Miyazaki J., Nishikawa S., Yamamura K., Taniguchi T. Specific depletion of the B-cell population induced by aberrant expression of human interferon regulatory factor 1 gene in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):532–536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan J., Wegenka U. M., Lütticken C., Buschmann J., Decker T., Schindler C., Heinrich P. C., Horn F. The signalling pathways of interleukin-6 and gamma interferon converge by the activation of different transcription factors which bind to common responsive DNA elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):1657–1668. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.1657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou N., Vogel H. J. Two-dimensional NMR and restrained molecular dynamics studies of the hairpin d(T8C4A8): detection of an extraloop cytosine. Biochemistry. 1993 Jan 19;32(2):637–645. doi: 10.1021/bi00053a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorbas H., Rogge L., Meisterernst M., Winnacker E. L. Hydroxyl radical footprints reveal novel structural features around the NF I binding site in adenovirus DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 11;17(19):7735–7748. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.19.7735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]