Full text
PDF




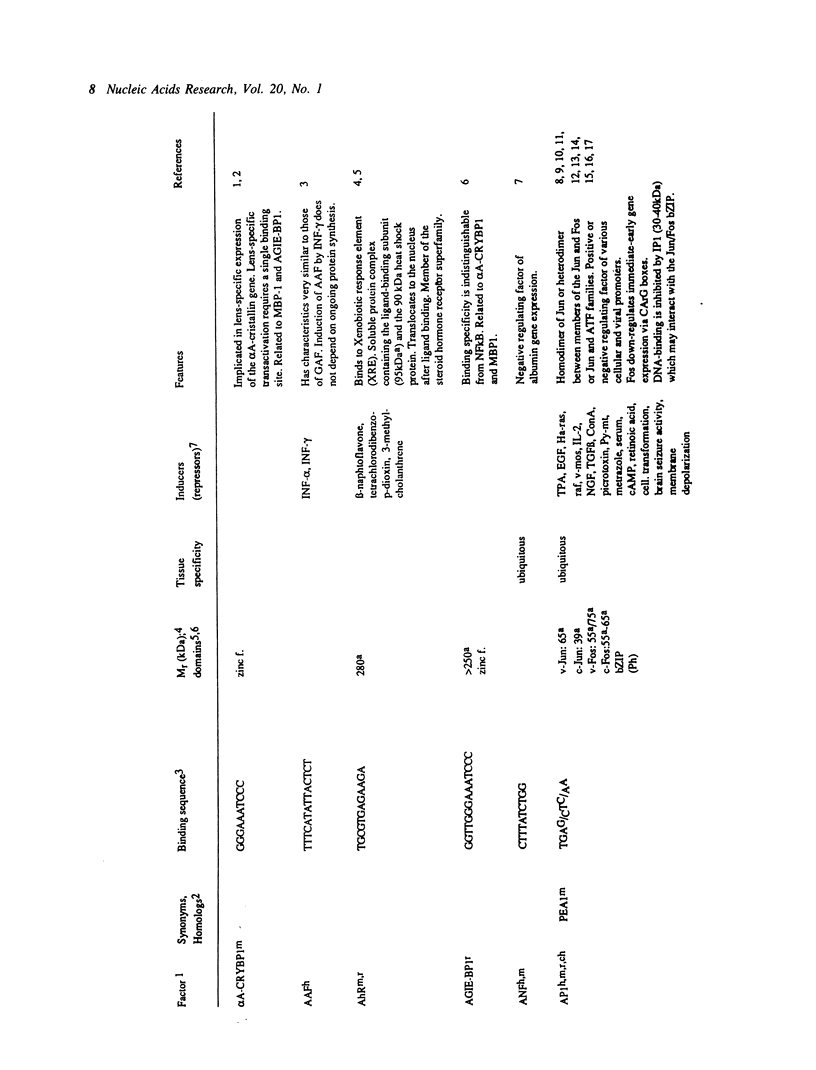
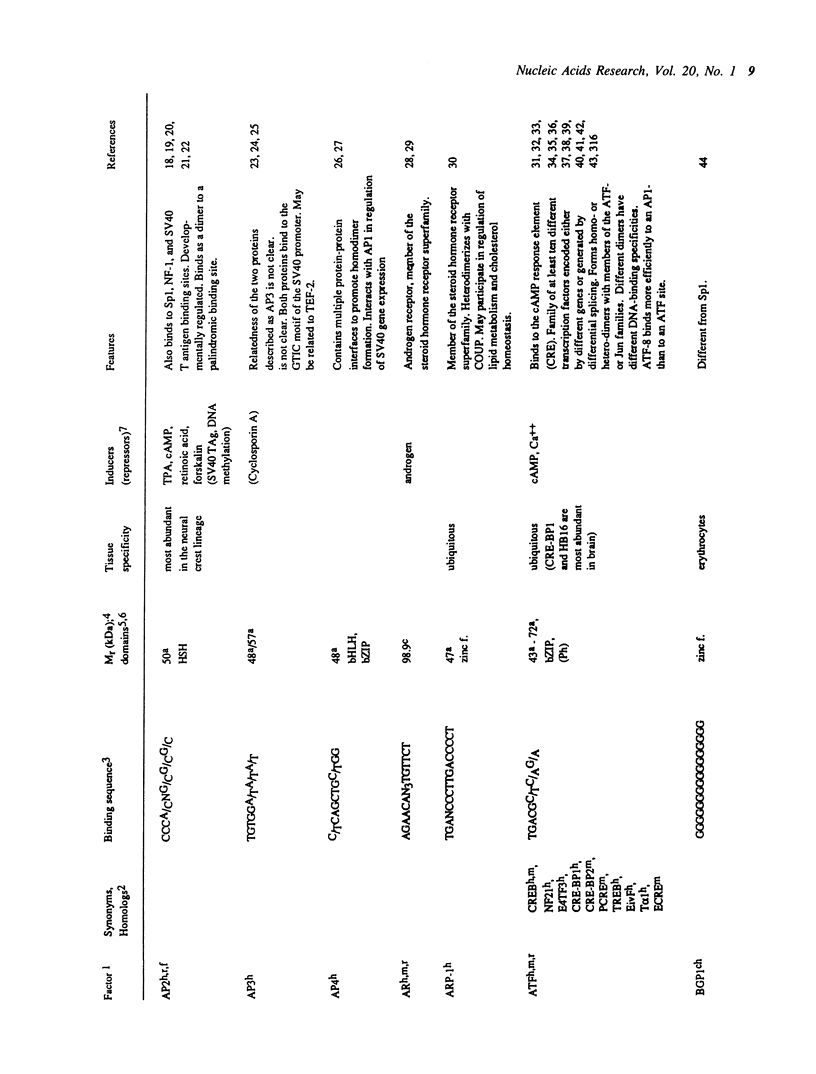
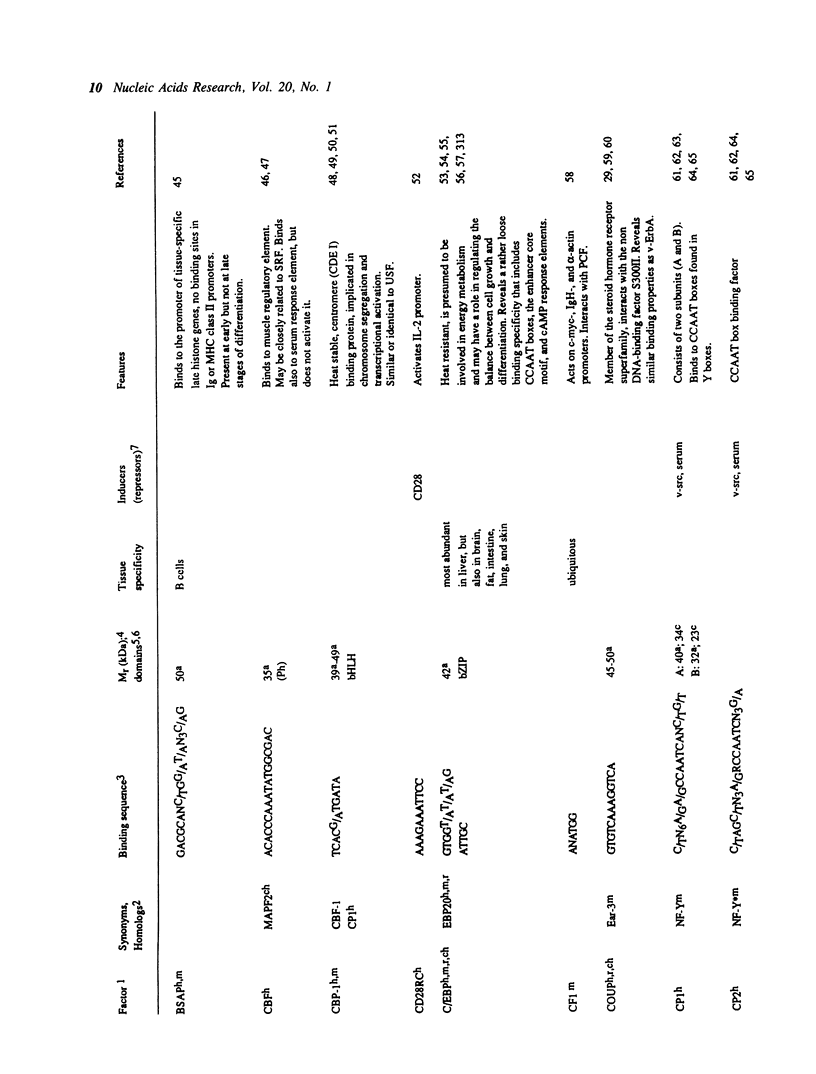
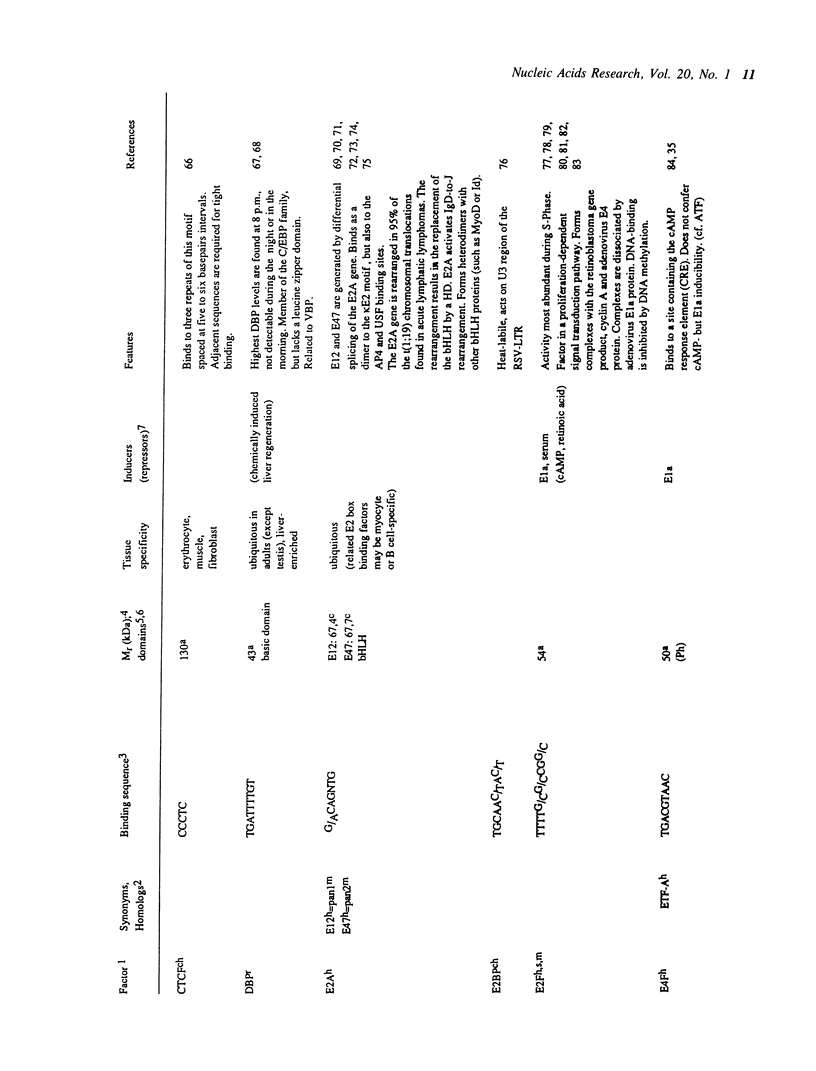



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abravaya K., Phillips B., Morimoto R. I. Heat shock-induced interactions of heat shock transcription factor and the human hsp70 promoter examined by in vivo footprinting. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):586–592. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akira S., Isshiki H., Sugita T., Tanabe O., Kinoshita S., Nishio Y., Nakajima T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. A nuclear factor for IL-6 expression (NF-IL6) is a member of a C/EBP family. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1897–1906. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08316.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Smeal T., Meek J., Karin M. Jun and v-jun contain multiple regions that participate in transcriptional activation in an interdependent manner. New Biol. 1989 Oct;1(1):35–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ariga H., Imamura Y., Iguchi-Ariga S. M. DNA replication origin and transcriptional enhancer in c-myc gene share the c-myc protein binding sequences. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4273–4279. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08613.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arriza J. L., Weinberger C., Cerelli G., Glaser T. M., Handelin B. L., Housman D. E., Evans R. M. Cloning of human mineralocorticoid receptor complementary DNA: structural and functional kinship with the glucocorticoid receptor. Science. 1987 Jul 17;237(4812):268–275. doi: 10.1126/science.3037703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auwerx J., Sassone-Corsi P. IP-1: a dominant inhibitor of Fos/Jun whose activity is modulated by phosphorylation. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):983–993. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90322-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avvedimento V. E., Musti A. M., Ueffing M., Obici S., Gallo A., Sanchez M., DeBrasi D., Gottesman M. E. Reversible inhibition of a thyroid-specific trans-acting factor by Ras. Genes Dev. 1991 Jan;5(1):22–28. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.1.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach I., Mattei M. G., Cereghini S., Yaniv M. Two members of an HNF1 homeoprotein family are expressed in human liver. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 11;19(13):3553–3559. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.13.3553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagchi S., Raychaudhuri P., Nevins J. R. Adenovirus E1A proteins can dissociate heteromeric complexes involving the E2F transcription factor: a novel mechanism for E1A trans-activation. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):659–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90112-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagchi S., Weinmann R., Raychaudhuri P. The retinoblastoma protein copurifies with E2F-I, an E1A-regulated inhibitor of the transcription factor E2F. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1063–1072. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90558-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker A. R., McDonnell D. P., Hughes M., Crisp T. M., Mangelsdorf D. J., Haussler M. R., Pike J. W., Shine J., O'Malley B. W. Cloning and expression of full-length cDNA encoding human vitamin D receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3294–3298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. E., Masison D. C. Isolation of the gene encoding the Saccharomyces cerevisiae centromere-binding protein CP1. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2458–2467. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker O., Parker M. G. CAAT/enhancer binding protein is able to bind to ATF/CRE elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 25;19(6):1213–1217. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.6.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin A. S., Jr, Azizkhan J. C., Jensen D. E., Beg A. A., Coodly L. R. Induction of NF-kappa B DNA-binding activity during the G0-to-G1 transition in mouse fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4943–4951. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin A. S., Jr, LeClair K. P., Singh H., Sharp P. A. A large protein containing zinc finger domains binds to related sequence elements in the enhancers of the class I major histocompatibility complex and kappa immunoglobulin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1406–1414. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard D. W., Walker W. H., Doerre S., Sista P., Molitor J. A., Dixon E. P., Peffer N. J., Hannink M., Greene W. C. The v-rel oncogene encodes a kappa B enhancer binding protein that inhibits NF-kappa B function. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):803–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90146-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
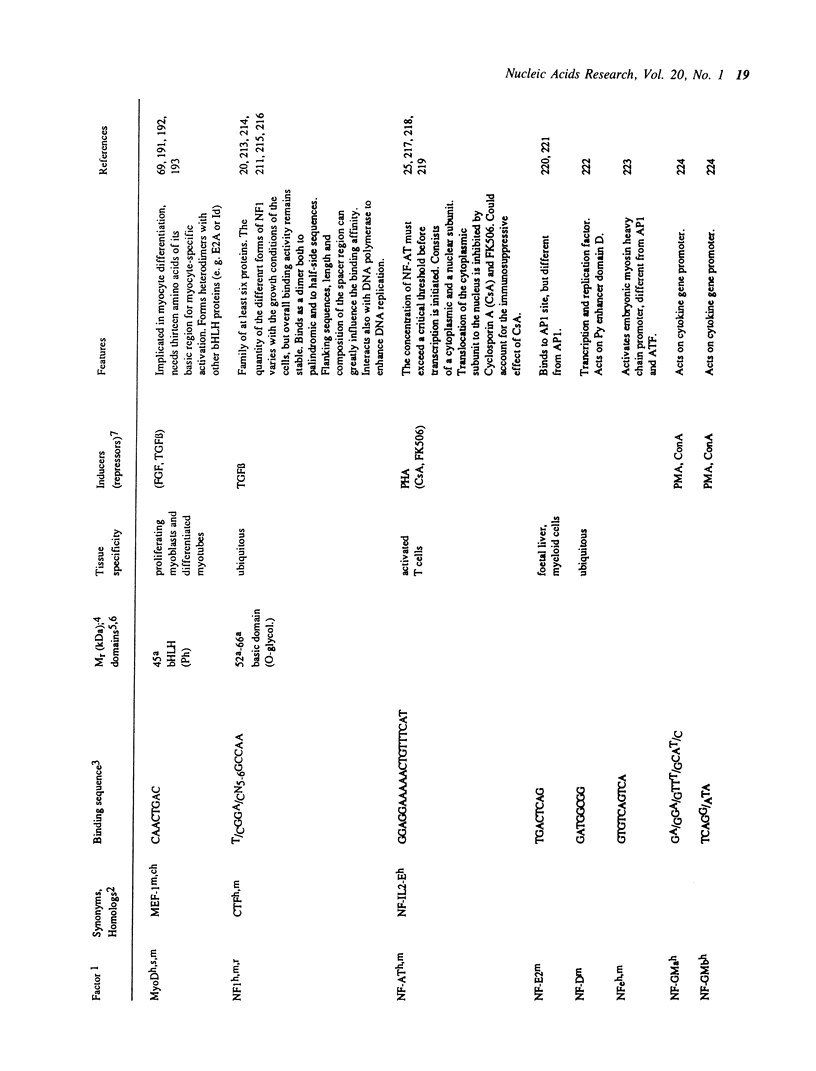
- Baniahmad A., Steiner C., Köhne A. C., Renkawitz R. Modular structure of a chicken lysozyme silencer: involvement of an unusual thyroid hormone receptor binding site. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):505–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90532-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barberis A., Widenhorn K., Vitelli L., Busslinger M. A novel B-cell lineage-specific transcription factor present at early but not late stages of differentiation. Genes Dev. 1990 May;4(5):849–859. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.5.849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnhart K. M., Kim C. G., Sheffery M. Purification and characterization of an erythroid cell-specific factor that binds the murine alpha- and beta-globin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2606–2614. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartel D. P., Sheng M., Lau L. F., Greenberg M. E. Growth factors and membrane depolarization activate distinct programs of early response gene expression: dissociation of fos and jun induction. Genes Dev. 1989 Mar;3(3):304–313. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.3.304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumhueter S., Mendel D. B., Conley P. B., Kuo C. J., Turk C., Graves M. K., Edwards C. A., Courtois G., Crabtree G. R. HNF-1 shares three sequence motifs with the POU domain proteins and is identical to LF-B1 and APF. Genes Dev. 1990 Mar;4(3):372–379. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.3.372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann H., Su L. K., Kadesch T. TFE3: a helix-loop-helix protein that activates transcription through the immunoglobulin enhancer muE3 motif. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):167–179. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Levy R., Faktor O., Berger I., Shaul Y. Cellular factors that interact with the hepatitis B virus enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1804–1809. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat N. K., Thompson C. B., Lindsten T., June C. H., Fujiwara S., Koizumi S., Fisher R. J., Papas T. S. Reciprocal expression of human ETS1 and ETS2 genes during T-cell activation: regulatory role for the protooncogene ETS1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3723–3727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biedenkapp H., Borgmeyer U., Sippel A. E., Klempnauer K. H. Viral myb oncogene encodes a sequence-specific DNA-binding activity. Nature. 1988 Oct 27;335(6193):835–837. doi: 10.1038/335835a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
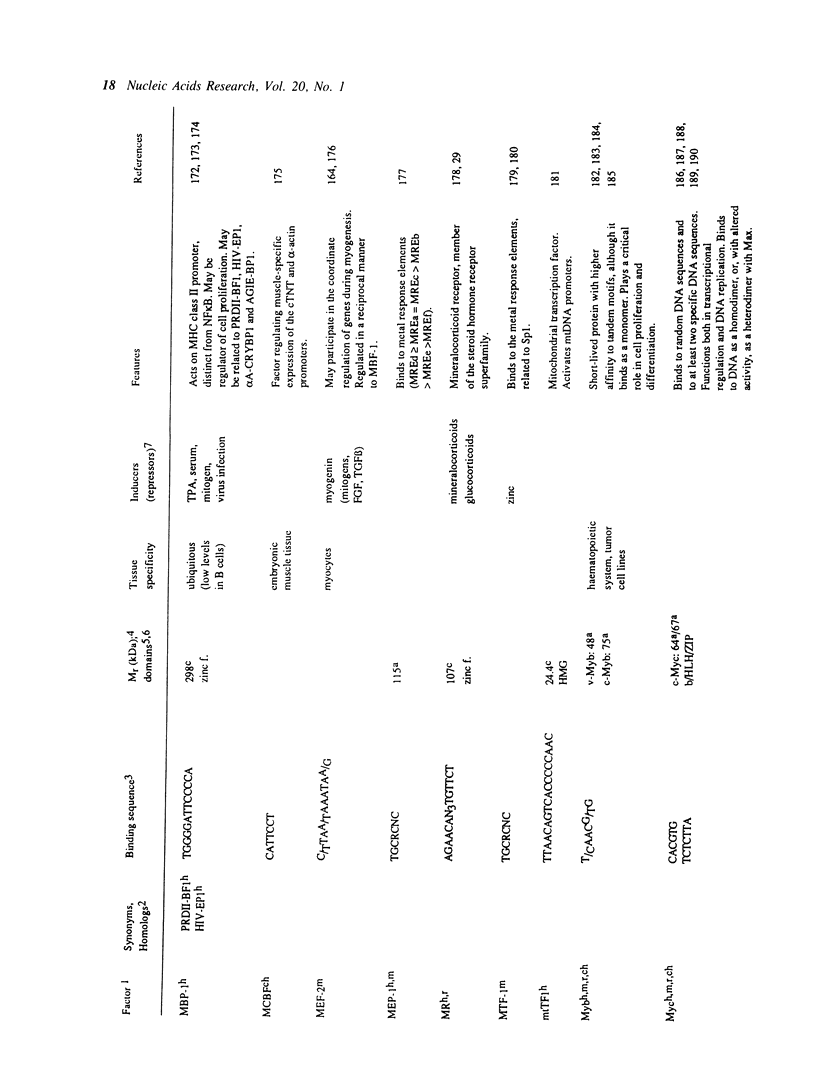
- Blackwell T. K., Kretzner L., Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N., Weintraub H. Sequence-specific DNA binding by the c-Myc protein. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1149–1151. doi: 10.1126/science.2251503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N. Max: a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that forms a sequence-specific DNA-binding complex with Myc. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1211–1217. doi: 10.1126/science.2006410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. C., Jambou R. C., Swick A. G., Kahn J. W., Azizkhan J. C. Transcriptional initiation is controlled by upstream GC-box interactions in a TATAA-less promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6632–6641. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodner M., Castrillo J. L., Theill L. E., Deerinck T., Ellisman M., Karin M. The pituitary-specific transcription factor GHF-1 is a homeobox-containing protein. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):505–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boral A. L., Okenquist S. A., Lenz J. Identification of the SL3-3 virus enhancer core as a T-lymphoma cell-specific element. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):76–84. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.76-84.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxer L. M., Prywes R., Roeder R. G., Kedes L. The sarcomeric actin CArG-binding factor is indistinguishable from the c-fos serum response factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):515–522. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., Smeal T., Defize L. H., Angel P., Woodgett J. R., Karin M., Hunter T. Activation of protein kinase C decreases phosphorylation of c-Jun at sites that negatively regulate its DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):573–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90241-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bram R. J., Kornberg R. D. Isolation of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae centromere DNA-binding protein, its human homolog, and its possible role as a transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):403–409. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brent G. A., Larsen P. R., Harney J. W., Koenig R. J., Moore D. D. Functional characterization of the rat growth hormone promoter elements required for induction by thyroid hormone with and without a co-transfected beta type thyroid hormone receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):178–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruder J. T., Hearing P. Nuclear factor EF-1A binds to the adenovirus E1A core enhancer element and to other transcriptional control regions. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5143–5153. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckler A. J., Pelletier J., Haber D. A., Glaser T., Housman D. E. Isolation, characterization, and expression of the murine Wilms' tumor gene (WT1) during kidney development. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1707–1712. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhnlein E., Lowenthal J. W., Siekevitz M., Ballard D. W., Franza B. R., Greene W. C. The same inducible nuclear proteins regulates mitogen activation of both the interleukin-2 receptor-alpha gene and type 1 HIV. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):827–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90099-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai M., Davis R. W. Yeast centromere binding protein CBF1, of the helix-loop-helix protein family, is required for chromosome stability and methionine prototrophy. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):437–446. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90525-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Call K. M., Glaser T., Ito C. Y., Buckler A. J., Pelletier J., Haber D. A., Rose E. A., Kral A., Yeger H., Lewis W. H. Isolation and characterization of a zinc finger polypeptide gene at the human chromosome 11 Wilms' tumor locus. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):509–520. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90601-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao X. M., Koski R. A., Gashler A., McKiernan M., Morris C. F., Gaffney R., Hay R. V., Sukhatme V. P. Identification and characterization of the Egr-1 gene product, a DNA-binding zinc finger protein induced by differentiation and growth signals. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):1931–1939. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.1931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson P., Eriksson P., Bjursell G. Two nuclear proteins bind to the major positive element of the apolipoprotein B gene promoter. Gene. 1990 Oct 15;94(2):295–301. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90401-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr C. S., Sharp P. A. A helix-loop-helix protein related to the immunoglobulin E box-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4384–4388. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caruso M., Iacobini C., Passananti C., Felsani A., Amati P. Protein recognition sites in polyomavirus enhancer: formation of a novel site for NF-1 factor in an enhancer mutant and characterization of a site in the enhancer D domain. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):947–955. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08193.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Yaniv M., Cortese R. Hepatocyte dedifferentiation and extinction is accompanied by a block in the synthesis of mRNA coding for the transcription factor HNF1/LFB1. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2257–2263. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07396.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalepakis G., Fritsch R., Fickenscher H., Deutsch U., Goulding M., Gruss P. The molecular basis of the undulated/Pax-1 mutation. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):873–884. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90434-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. J., Chen T. T., Lei H. Y., Chen D. S., Lee S. C. Molecular cloning of a transcription factor, AGP/EBP, that belongs to members of the C/EBP family. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6642–6653. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Vesque C., Galliot B., Vigneron M., Dollé P., Duboule D., Charnay P. The segment-specific gene Krox-20 encodes a transcription factor with binding sites in the promoter region of the Hox-1.4 gene. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1209–1218. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08228.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chellappan S. P., Hiebert S., Mudryj M., Horowitz J. M., Nevins J. R. The E2F transcription factor is a cellular target for the RB protein. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1053–1061. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90557-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Baldwin A. S., Carthew R. W., Sharp P. A. Human CCAAT-binding proteins have heterologous subunits. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90483-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Olesen J., Hahn S., Baldwin A. S., Guarente L., Sharp P. A. A yeast and a human CCAAT-binding protein have heterologous subunits that are functionally interchangeable. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90484-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy B., Nathans D. DNA binding site of the growth factor-inducible protein Zif268. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8737–8741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark L., Pollock R. M., Hay R. T. Identification and purification of EBP1: a HeLa cell protein that binds to a region overlapping the 'core' of the SV40 enhancer. Genes Dev. 1988 Aug;2(8):991–1002. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.8.991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockell M., Stevenson B. J., Strubin M., Hagenbüchle O., Wellauer P. K. Identification of a cell-specific DNA-binding activity that interacts with a transcriptional activator of genes expressed in the acinar pancreas. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2464–2476. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comb M., Goodman H. M. CpG methylation inhibits proenkephalin gene expression and binding of the transcription factor AP-2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):3975–3982. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.3975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortes P., Buckbinder L., Leza M. A., Rak N., Hearing P., Merino A., Reinberg D. EivF, a factor required for transcription of the adenovirus EIV promoter, binds to an element involved in EIa-dependent activation and cAMP induction. Genes Dev. 1988 Aug;2(8):975–990. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.8.975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Grayson D. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Multiple hepatocyte-enriched nuclear factors function in the regulation of transthyretin and alpha 1-antitrypsin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1415–1425. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtois S. J., Lafontaine D. A., Lemaigre F. P., Durviaux S. M., Rousseau G. G. Nuclear factor-I and activator protein-2 bind in a mutually exclusive way to overlapping promoter sequences and trans-activate the human growth hormone gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 11;18(1):57–64. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cserjesi P., Olson E. N. Myogenin induces the myocyte-specific enhancer binding factor MEF-2 independently of other muscle-specific gene products. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4854–4862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culotta V. C., Hamer D. H. Fine mapping of a mouse metallothionein gene metal response element. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1376–1380. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunniff N. F., Wagner J., Morgan W. D. Modular recognition of 5-base-pair DNA sequence motifs by human heat shock transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3504–3514. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey L., Roberts S. B., Heintz N. Purification of the human histone H4 gene-specific transcription factors H4TF-1 and H4TF-2. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1700–1712. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang C. V., Barrett J., Villa-Garcia M., Resar L. M., Kato G. J., Fearon E. R. Intracellular leucine zipper interactions suggest c-Myc hetero-oligomerization. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):954–962. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson I., Xiao J. H., Rosales R., Staub A., Chambon P. The HeLa cell protein TEF-1 binds specifically and cooperatively to two SV40 enhancer motifs of unrelated sequence. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):931–942. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90108-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Cheng P. F., Lassar A. B., Weintraub H. The MyoD DNA binding domain contains a recognition code for muscle-specific gene activation. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):733–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90088-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Simone V., De Magistris L., Lazzaro D., Gerstner J., Monaci P., Nicosia A., Cortese R. LFB3, a heterodimer-forming homeoprotein of the LFB1 family, is expressed in specialized epithelia. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1435–1443. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07664.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMarzo A. M., Beck C. A., Onate S. A., Edwards D. P. Dimerization of mammalian progesterone receptors occurs in the absence of DNA and is related to the release of the 90-kDa heat shock protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):72–76. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker T., Lew D. J., Darnell J. E., Jr Two distinct alpha-interferon-dependent signal transduction pathways may contribute to activation of transcription of the guanylate-binding protein gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5147–5153. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker T., Lew D. J., Mirkovitch J., Darnell J. E., Jr Cytoplasmic activation of GAF, an IFN-gamma-regulated DNA-binding factor. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):927–932. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08026.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descombes P., Chojkier M., Lichtsteiner S., Falvey E., Schibler U. LAP, a novel member of the C/EBP gene family, encodes a liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1541–1551. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Didier D. K., Schiffenbauer J., Woulfe S. L., Zacheis M., Schwartz B. D. Characterization of the cDNA encoding a protein binding to the major histocompatibility complex class II Y box. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7322–7326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn A., Benoist C., Mathis D. New B-lymphocyte-specific enhancer-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):312–320. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn A., Bollekens J., Staub A., Benoist C., Mathis D. A multiplicity of CCAAT box-binding proteins. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):863–872. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90513-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutta A., Stoeckle M. Y., Hanafusa H. Serum and v-src increase the level of a CCAAT-binding factor required for transcription from a retroviral long terminal repeat. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):243–254. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellinger-Ziegelbauer H., Dreyer C. A retinoic acid receptor expressed in the early development of Xenopus laevis. Genes Dev. 1991 Jan;5(1):94–104. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.1.94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmel E. A., Verweij C. L., Durand D. B., Higgins K. M., Lacy E., Crabtree G. R. Cyclosporin A specifically inhibits function of nuclear proteins involved in T cell activation. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1617–1620. doi: 10.1126/science.2595372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. J., Scarpulla R. C. NRF-1: a trans-activator of nuclear-encoded respiratory genes in animal cells. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):1023–1034. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.1023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Felsenfeld G. trans-Activation of a globin promoter in nonerythroid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):843–853. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahrner T. J., Carroll S. L., Milbrandt J. The NGFI-B protein, an inducible member of the thyroid/steroid receptor family, is rapidly modified posttranslationally. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6454–6459. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan C. M., Maniatis T. A DNA-binding protein containing two widely separated zinc finger motifs that recognize the same DNA sequence. Genes Dev. 1990 Jan;4(1):29–42. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawell S. E., Lees J. A., White R., Parker M. G. Characterization and colocalization of steroid binding and dimerization activities in the mouse estrogen receptor. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):953–962. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90343-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiering S., Northrop J. P., Nolan G. P., Mattila P. S., Crabtree G. R., Herzenberg L. A. Single cell assay of a transcription factor reveals a threshold in transcription activated by signals emanating from the T-cell antigen receptor. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1823–1834. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan W. M., Corthésy B., Bram R. J., Crabtree G. R. Nuclear association of a T-cell transcription factor blocked by FK-506 and cyclosporin A. Nature. 1991 Aug 29;352(6338):803–807. doi: 10.1038/352803a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman B. M., Samuels H. H. Interactions among a subfamily of nuclear hormone receptors: the regulatory zipper model. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Sep;4(9):1293–1301. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-9-1293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrest D., Hallbök F., Persson H., Vennström B. Distinct functions for thyroid hormone receptors alpha and beta in brain development indicated by differential expression of receptor genes. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):269–275. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07947.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franza B. R., Jr, Josephs S. F., Gilman M. Z., Ryan W., Clarkson B. Characterization of cellular proteins recognizing the HIV enhancer using a microscale DNA-affinity precipitation assay. 1987 Nov 26-Dec 2Nature. 330(6146):391–395. doi: 10.1038/330391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser J. D., Irving B. A., Crabtree G. R., Weiss A. Regulation of interleukin-2 gene enhancer activity by the T cell accessory molecule CD28. Science. 1991 Jan 18;251(4991):313–316. doi: 10.1126/science.1846244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallinari P., La Bella F., Heintz N. Characterization and purification of H1TF2, a novel CCAAT-binding protein that interacts with a histone H1 subtype-specific consensus element. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1566–1575. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaub M. P., Bellard M., Scheuer I., Chambon P., Sassone-Corsi P. Activation of the ovalbumin gene by the estrogen receptor involves the fos-jun complex. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1267–1276. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90422-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T. D. NF-kappa B, KBF1, dorsal, and related matters. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):841–843. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90257-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gius D., Cao X. M., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Cohen D. R., Curran T., Sukhatme V. P. Transcriptional activation and repression by Fos are independent functions: the C terminus represses immediate-early gene expression via CArG elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4243–4255. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. K., Devary O. V., Rosenfeld M. G. Multiple cell type-specific proteins differentially regulate target sequence recognition by the alpha retinoic acid receptor. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):729–738. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90139-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebl M. K. The PU.1 transcription factor is the product of the putative oncogene Spi-1. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1165–1166. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90676-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
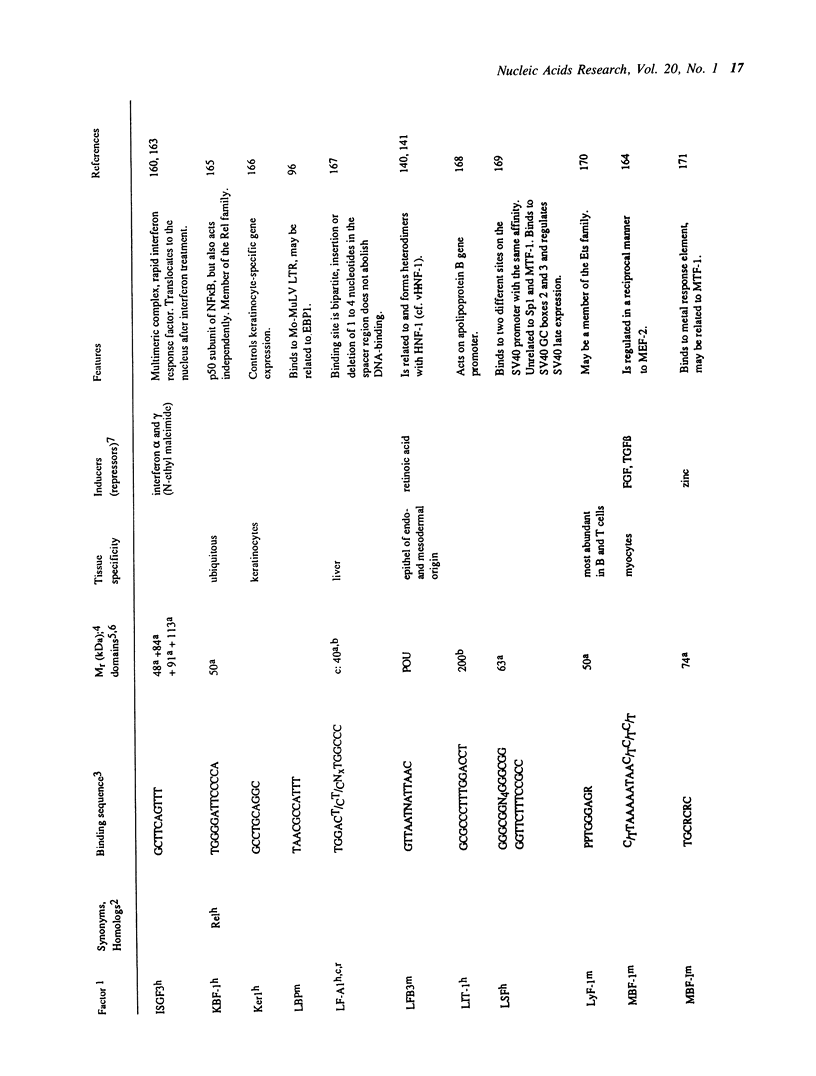
- Goldenberg C. J., Luo Y., Fenna M., Baler R., Weinmann R., Voellmy R. Purified human factor activates heat shock promoter in a HeLa cell-free transcription system. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19734–19739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossett L. A., Kelvin D. J., Sternberg E. A., Olson E. N. A new myocyte-specific enhancer-binding factor that recognizes a conserved element associated with multiple muscle-specific genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5022–5033. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto M., Tamura T., Mikoshiba K., Masamune Y., Nakanishi Y. Transcription inhibition of the somatic-type phosphoglycerate kinase 1 gene in vitro by a testis-specific factor that recognizes a sequence similar to the binding site for Ets oncoproteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):3959–3963. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.3959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gounari F., De Francesco R., Schmitt J., van der Vliet P., Cortese R., Stunnenberg H. Amino-terminal domain of NF1 binds to DNA as a dimer and activates adenovirus DNA replication. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):559–566. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08143.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyal N., Knox J., Gronostajski R. M. Analysis of multiple forms of nuclear factor I in human and murine cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1041–1048. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R., Gilman M. Distinct protein targets for signals acting at the c-fos serum response element. Science. 1991 Jan 11;251(4990):189–192. doi: 10.1126/science.1898992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grange T., Roux J., Rigaud G., Pictet R. Cell-type specific activity of two glucocorticoid responsive units of rat tyrosine aminotransferase gene is associated with multiple binding sites for C/EBP and a novel liver-specific nuclear factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):131–139. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Walter P., Kumar V., Krust A., Bornert J. M., Argos P., Chambon P. Human oestrogen receptor cDNA: sequence, expression and homology to v-erb-A. Nature. 1986 Mar 13;320(6058):134–139. doi: 10.1038/320134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J. Roles of TFIID in transcriptional initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1067–1070. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90027-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregor P. D., Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. The adenovirus major late transcription factor USF is a member of the helix-loop-helix group of regulatory proteins and binds to DNA as a dimer. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1730–1740. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guazzi S., Price M., De Felice M., Damante G., Mattei M. G., Di Lauro R. Thyroid nuclear factor 1 (TTF-1) contains a homeodomain and displays a novel DNA binding specificity. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3631–3639. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07574.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunther C. V., Nye J. A., Bryner R. S., Graves B. J. Sequence-specific DNA binding of the proto-oncoprotein ets-1 defines a transcriptional activator sequence within the long terminal repeat of the Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Genes Dev. 1990 Apr;4(4):667–679. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.4.667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman A., Wasylyk B. The collagenase gene promoter contains a TPA and oncogene-responsive unit encompassing the PEA3 and AP-1 binding sites. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2241–2246. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07394.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T. W., Liu F., Coukos W. J., Green M. R. Transcription factor ATF cDNA clones: an extensive family of leucine zipper proteins able to selectively form DNA-binding heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2083–2090. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada K., Gleason S. L., Levi B. Z., Hirschfeld S., Appella E., Ozato K. H-2RIIBP, a member of the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily that binds to both the regulatory element of major histocompatibility class I genes and the estrogen response element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8289–8293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannon R., Evans T., Felsenfeld G., Gould H. Structure and promoter activity of the gene for the erythroid transcription factor GATA-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3004–3008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada H., Willison K., Sakakibara J., Miyamoto M., Fujita T., Taniguchi T. Absence of the type I IFN system in EC cells: transcriptional activator (IRF-1) and repressor (IRF-2) genes are developmentally regulated. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90163-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa S. L., Doetsch P. W., Hamilton K. K., Martin A. M., Okenquist S. A., Lenz J., Boss J. M. DNA binding properties of YB-1 and dbpA: binding to double-stranded, single-stranded, and abasic site containing DNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 25;19(18):4915–4920. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.18.4915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henseling U., Schmidt W., Schöler H. R., Gruss P., Hatzopoulos A. K. A transcription factor interacting with the class I gene enhancer is inactive in tumorigenic cell lines which suppress major histocompatibility complex class I genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4100–4109. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst R. S., Boczko E. M., Darnell J. E., Jr, Babiss L. E. The mouse albumin enhancer contains a negative regulatory element that interacts with a novel DNA-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):3896–3905. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.3896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho I. C., Bhat N. K., Gottschalk L. R., Lindsten T., Thompson C. B., Papas T. S., Leiden J. M. Sequence-specific binding of human Ets-1 to the T cell receptor alpha gene enhancer. Science. 1990 Nov 9;250(4982):814–818. doi: 10.1126/science.2237431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho I. C., Vorhees P., Marin N., Oakley B. K., Tsai S. F., Orkin S. H., Leiden J. M. Human GATA-3: a lineage-restricted transcription factor that regulates the expression of the T cell receptor alpha gene. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1187–1192. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08059.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman E. C., Reyes H., Chu F. F., Sander F., Conley L. H., Brooks B. A., Hankinson O. Cloning of a factor required for activity of the Ah (dioxin) receptor. Science. 1991 May 17;252(5008):954–958. doi: 10.1126/science.1852076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooft van Huijsduijnen R., Li X. Y., Black D., Matthes H., Benoist C., Mathis D. Co-evolution from yeast to mouse: cDNA cloning of the two NF-Y (CP-1/CBF) subunits. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3119–3127. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07509.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe K. M., Reakes C. F., Watson R. J. Characterization of the sequence-specific interaction of mouse c-myb protein with DNA. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):161–169. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08092.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Y. F., Lüscher B., Admon A., Mermod N., Tjian R. Transcription factor AP-4 contains multiple dimerization domains that regulate dimer specificity. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1741–1752. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang H. C., Sundseth R., Hansen U. Transcription factor LSF binds two variant bipartite sites within the SV40 late promoter. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):287–298. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst H. C., Masson N., Jones N. C., Lee K. A. The cellular transcription factor CREB corresponds to activating transcription factor 47 (ATF-47) and forms complexes with a group of polypeptides related to ATF-43. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6192–6203. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imam A. M., Ackrill A. M., Dale T. C., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Transcription factors induced by interferons alpha and gamma. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6573–6580. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imbert J., Zafarullah M., Culotta V. C., Gedamu L., Hamer D. Transcription factor MBF-I interacts with metal regulatory elements of higher eucaryotic metallothionein genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5315–5323. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
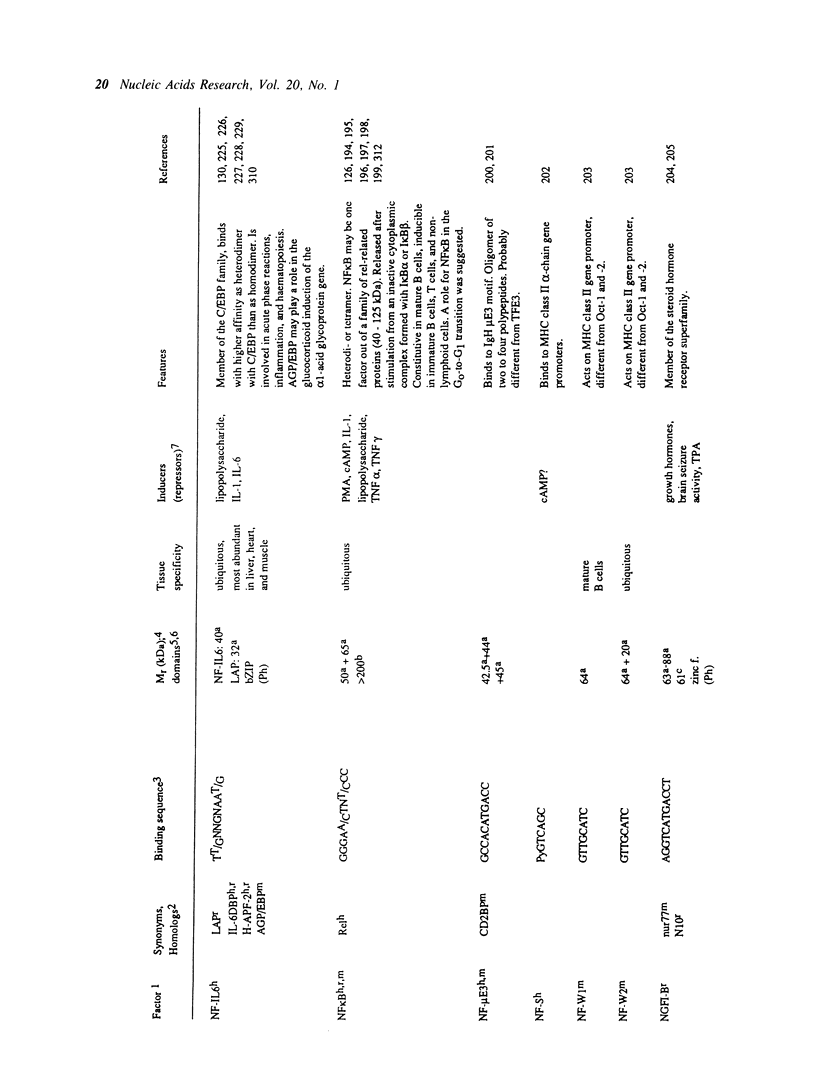
- Ingraham H. A., Flynn S. E., Voss J. W., Albert V. R., Kapiloff M. S., Wilson L., Rosenfeld M. G. The POU-specific domain of Pit-1 is essential for sequence-specific, high affinity DNA binding and DNA-dependent Pit-1-Pit-1 interactions. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1021–1033. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90067-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issemann I., Green S. Activation of a member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily by peroxisome proliferators. Nature. 1990 Oct 18;347(6294):645–650. doi: 10.1038/347645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isshiki H., Akira S., Sugita T., Nishio Y., Hashimoto S., Pawlowski T., Suematsu S., Kishimoto T. Reciprocal expression of NF-IL6 and C/EBP in hepatocytes: possible involvement of NF-IL6 in acute phase protein gene expression. New Biol. 1991 Jan;3(1):63–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivashkiv L. B., Liou H. C., Kara C. J., Lamph W. W., Verma I. M., Glimcher L. H. mXBP/CRE-BP2 and c-Jun form a complex which binds to the cyclic AMP, but not to the 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate, response element. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1609–1621. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyer S. V., Davis D. L., Seal S. N., Burch J. B. Chicken vitellogenin gene-binding protein, a leucine zipper transcription factor that binds to an important control element in the chicken vitellogenin II promoter, is related to rat DBP. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4863–4875. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson S. P., MacDonald J. J., Lees-Miller S., Tjian R. GC box binding induces phosphorylation of Sp1 by a DNA-dependent protein kinase. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):155–165. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90296-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonat C., Rahmsdorf H. J., Park K. K., Cato A. C., Gebel S., Ponta H., Herrlich P. Antitumor promotion and antiinflammation: down-modulation of AP-1 (Fos/Jun) activity by glucocorticoid hormone. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1189–1204. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90395-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph L. J., Le Beau M. M., Jamieson G. A., Jr, Acharya S., Shows T. B., Rowley J. D., Sukhatme V. P. Molecular cloning, sequencing, and mapping of EGR2, a human early growth response gene encoding a protein with "zinc-binding finger" structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7164–7168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joulin V., Bories D., Eléouet J. F., Labastie M. C., Chrétien S., Mattéi M. G., Roméo P. H. A T-cell specific TCR delta DNA binding protein is a member of the human GATA family. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1809–1816. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07706.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kageyama R., Merlino G. T., Pastan I. A transcription factor active on the epidermal growth factor receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5016–5020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kageyama R., Pastan I. Molecular cloning and characterization of a human DNA binding factor that represses transcription. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):815–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90605-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakkis E., Riggs K. J., Gillespie W., Calame K. A transcriptional repressor of c-myc. Nature. 1989 Jun 29;339(6227):718–721. doi: 10.1038/339718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Corcoran L., LeBowitz J. H., Baltimore D. The promoter of the human interleukin-2 gene contains two octamer-binding sites and is partially activated by the expression of Oct-2. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5464–5472. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Look A. T., Baltimore D. The human t(1;19) translocation in pre-B ALL produces multiple nuclear E2A-Pbx1 fusion proteins with differing transforming potentials. Genes Dev. 1991 Mar;5(3):358–368. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.3.358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kara C. J., Liou H. C., Ivashkiv L. B., Glimcher L. H. A cDNA for a human cyclic AMP response element-binding protein which is distinct from CREB and expressed preferentially in brain. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1347–1357. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastner P., Krust A., Turcotte B., Stropp U., Tora L., Gronemeyer H., Chambon P. Two distinct estrogen-regulated promoters generate transcripts encoding the two functionally different human progesterone receptor forms A and B. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1603–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08280.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaulen H., Pognonec P., Gregor P. D., Roeder R. G. The Xenopus B1 factor is closely related to the mammalian activator USF and is implicated in the developmental regulation of TFIIIA gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):412–424. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller A. D., Maniatis T. Identification and characterization of a novel repressor of beta-interferon gene expression. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):868–879. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny S., Guntaka R. V. Localization by mutational analysis of transcription factor binding sequences in the U3 region of Rous sarcoma virus LTR. Virology. 1990 Jun;176(2):483–493. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90018-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler D. S., Veals S. A., Fu X. Y., Levy D. E. Interferon-alpha regulates nuclear translocation and DNA-binding affinity of ISGF3, a multimeric transcriptional activator. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1753–1765. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieran M., Blank V., Logeat F., Vandekerckhove J., Lottspeich F., Le Bail O., Urban M. B., Kourilsky P., Baeuerle P. A., Israël A. The DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B is identical to factor KBF1 and homologous to the rel oncogene product. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90275-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko L. J., Yamamoto M., Leonard M. W., George K. M., Ting P., Engel J. D. Murine and human T-lymphocyte GATA-3 factors mediate transcription through a cis-regulatory element within the human T-cell receptor delta gene enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2778–2784. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobr M., Reith W., Herrero-Sanchez C., Mach B. Two DNA-binding proteins discriminate between the promoters of different members of the major histocompatibility complex class II multigene family. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):965–971. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovesdi I., Reichel R., Nevins J. R. Role of an adenovirus E2 promoter binding factor in E1A-mediated coordinate gene control. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2180–2184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. J., Conley P. B., Hsieh C. L., Francke U., Crabtree G. R. Molecular cloning, functional expression, and chromosomal localization of mouse hepatocyte nuclear factor 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9838–9842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbé S., Prévost J., Remondelli P., Leone A., Séguin C. A nuclear factor binds to the metal regulatory elements of the mouse gene encoding metallothionein-I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 11;19(15):4225–4231. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.15.4225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladias J. A., Karathanasis S. K. Regulation of the apolipoprotein AI gene by ARP-1, a novel member of the steroid receptor superfamily. Science. 1991 Feb 1;251(4993):561–565. doi: 10.1126/science.1899293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E., Prezioso V. R., Smith E., Litvin O., Costa R. H., Darnell J. E., Jr HNF-3A, a hepatocyte-enriched transcription factor of novel structure is regulated transcriptionally. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1427–1436. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E., Prezioso V. R., Tao W. F., Chen W. S., Darnell J. E., Jr Hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 alpha belongs to a gene family in mammals that is homologous to the Drosophila homeotic gene fork head. Genes Dev. 1991 Mar;5(3):416–427. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.3.416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laudet V., Begue A., Henry-Duthoit C., Joubel A., Martin P., Stehelin D., Saule S. Genomic organization of the human thyroid hormone receptor alpha (c-erbA-1) gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 11;19(5):1105–1112. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.5.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazar M. A., Berrodin T. J., Harding H. P. Differential DNA binding by monomeric, homodimeric, and potentially heteromeric forms of the thyroid hormone receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5005–5015. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leask A., Rosenberg M., Vassar R., Fuchs E. Regulation of a human epidermal keratin gene: sequences and nuclear factors involved in keratinocyte-specific transcription. Genes Dev. 1990 Nov;4(11):1985–1998. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.11.1985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Q., Yun Y. D., Hoeffler J. P., Habener J. F. Cyclic-AMP-responsive transcriptional activation of CREB-327 involves interdependent phosphorylated subdomains. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4455–4465. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07896.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Lee T. C., Chow K. L., Fang P., Schwartz R. J. Activation of skeletal alpha-actin gene transcription: the cooperative formation of serum response factor-binding complexes over positive cis-acting promoter serum response elements displaces a negative-acting nuclear factor enriched in replicating myoblasts and nonmyogenic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5090–5100. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaigre F. P., Lafontaine D. A., Courtois S. J., Durviaux S. M., Rousseau G. G. Sp1 can displace GHF-1 from its distal binding site and stimulate transcription from the growth hormone gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1811–1814. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire P., Vesque C., Schmitt J., Stunnenberg H., Frank R., Charnay P. The serum-inducible mouse gene Krox-24 encodes a sequence-specific transcriptional activator. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3456–3467. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M., Rustgi A. K., Schievella A. R., Bernards R. Suppression of MHC class I gene expression by N-myc through enhancer inactivation. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3351–3355. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08497.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leshkowitz D., Walker M. D. Extinction of insulin gene expression in hybrids between beta cells and fibroblasts is accompanied by loss of the putative beta-cell-specific transcription factor IEF1. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1547–1552. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin B. Oncogenic conversion by regulatory changes in transcription factors. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90640-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis C. D., Clark S. P., Felsenfeld G., Gould H. An erythrocyte-specific protein that binds to the poly(dG) region of the chicken beta-globin gene promoter. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):863–873. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leza M. A., Hearing P. Cellular transcription factor binds to adenovirus early region promoters and to a cyclic AMP response element. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):3003–3013. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.3003-3013.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F., Green M. R. A specific member of the ATF transcription factor family can mediate transcription activation by the adenovirus E1a protein. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1217–1224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90686-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo K., Landau N. R., Smale S. T. LyF-1, a transcriptional regulator that interacts with a novel class of promoters for lymphocyte-specific genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5229–5243. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobanenkov V. V., Nicolas R. H., Adler V. V., Paterson H., Klenova E. M., Polotskaja A. V., Goodwin G. H. A novel sequence-specific DNA binding protein which interacts with three regularly spaced direct repeats of the CCCTC-motif in the 5'-flanking sequence of the chicken c-myc gene. Oncogene. 1990 Dec;5(12):1743–1753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lübbert M., Miller C. W., Kahan J., Koeffler H. P. Expression, methylation and chromatin structure of the p53 gene in untransformed and human T-cell leukemia virus type I-transformed human T-lymphocytes. Oncogene. 1989 May;4(5):643–651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Eisenman R. N. New light on Myc and Myb. Part II. Myb. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2235–2241. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden S. L., Cook D. M., Morris J. F., Gashler A., Sukhatme V. P., Rauscher F. J., 3rd Transcriptional repression mediated by the WT1 Wilms tumor gene product. Science. 1991 Sep 27;253(5027):1550–1553. doi: 10.1126/science.1654597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maekawa T., Sakura H., Kanei-Ishii C., Sudo T., Yoshimura T., Fujisawa J., Yoshida M., Ishii S. Leucine zipper structure of the protein CRE-BP1 binding to the cyclic AMP response element in brain. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2023–2028. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03610.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maekawa T., Sakura H., Sudo T., Ishii S. Putative metal finger structure of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 enhancer binding protein HIV-EP1. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14591–14593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majello B., Arcone R., Toniatti C., Ciliberto G. Constitutive and IL-6-induced nuclear factors that interact with the human C-reactive protein promoter. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):457–465. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08131.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maldonado E., Ha I., Cortes P., Weis L., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II: role of transcription factors IIA, IID, and IIB during formation of a transcription-competent complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6335–6347. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manak J. R., Prywes R. Mutation of serum response factor phosphorylation sites and the mechanism by which its DNA-binding activity is increased by casein kinase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3652–3659. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mar J. H., Ordahl C. P. M-CAT binding factor, a novel trans-acting factor governing muscle-specific transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4271–4283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick A., Brady H., Fukushima J., Karin M. The pituitary-specific regulatory gene GHF1 contains a minimal cell type-specific promoter centered around its TATA box. Genes Dev. 1991 Aug;5(8):1490–1503. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.8.1490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Lane M. D., Gluecksohn-Waelsch S. Is CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein a central regulator of energy metabolism? Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2021–2024. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means A. L., Farnham P. J. Transcription initiation from the dihydrofolate reductase promoter is positioned by HIP1 binding at the initiation site. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):653–661. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer D., Graus A., Kraay R., Langeveld A., Mulder M. P., Grosveld G. The octamer binding factor Oct6: cDNA cloning and expression in early embryonic cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7357–7365. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendel D. B., Hansen L. P., Graves M. K., Conley P. B., Crabtree G. R. HNF-1 alpha and HNF-1 beta (vHNF-1) share dimerization and homeo domains, but not activation domains, and form heterodimers in vitro. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):1042–1056. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.1042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercurio F., Karin M. Transcription factors AP-3 and AP-2 interact with the SV40 enhancer in a mutually exclusive manner. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1455–1460. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermod N., O'Neill E. A., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. The proline-rich transcriptional activator of CTF/NF-I is distinct from the replication and DNA binding domain. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):741–753. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90108-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermod N., Williams T. J., Tjian R. Enhancer binding factors AP-4 and AP-1 act in concert to activate SV40 late transcription in vitro. Nature. 1988 Apr 7;332(6164):557–561. doi: 10.1038/332557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignotte V., Wall L., deBoer E., Grosveld F., Romeo P. H. Two tissue-specific factors bind the erythroid promoter of the human porphobilinogen deaminase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):37–54. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. L., Feldhaus A. L., Rooney J. W., Rhodes L. D., Sibley C. H., Singh H. Regulation and a possible stage-specific function of Oct-2 during pre-B-cell differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4885–4894. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Timmons P. M., Hébert J. M., Rigby P. W., Tjian R. Transcription factor AP-2 is expressed in neural crest cell lineages during mouse embryogenesis. Genes Dev. 1991 Jan;5(1):105–119. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.1.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Wang C., Tjian R. Positive and negative regulation of transcription in vitro: enhancer-binding protein AP-2 is inhibited by SV40 T antigen. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):847–861. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90512-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno K., Gonzalez F. J., Kimura S. Thyroid-specific enhancer-binding protein (T/EBP): cDNA cloning, functional characterization, and structural identity with thyroid transcription factor TTF-1. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4927–4933. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molitor J. A., Walker W. H., Doerre S., Ballard D. W., Greene W. C. NF-kappa B: a family of inducible and differentially expressed enhancer-binding proteins in human T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):10028–10032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.10028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncollin V., Stalder R., Verdier J. M., Sentenac A., Egly J. M. A yeast homolog of the human UEF stimulates transcription from the adenovirus 2 major late promoter in yeast and in mammalian cell-free systems. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 25;18(16):4817–4823. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.16.4817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudryj M., Hiebert S. W., Nevins J. R. A role for the adenovirus inducible E2F transcription factor in a proliferation dependent signal transduction pathway. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2179–2184. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07387.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller C. R., Maire P., Schibler U. DBP, a liver-enriched transcriptional activator, is expressed late in ontogeny and its tissue specificity is determined posttranscriptionally. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):279–291. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90808-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P. R., Salser S. J., Wold B. Constitutive and metal-inducible protein:DNA interactions at the mouse metallothionein I promoter examined by in vivo and in vitro footprinting. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):412–427. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mul Y. M., Verrijzer C. P., van der Vliet P. C. Transcription factors NFI and NFIII/oct-1 function independently, employing different mechanisms to enhance adenovirus DNA replication. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5510–5518. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5510-5518.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., Voronova A., Baltimore D. B-cell- and myocyte-specific E2-box-binding factors contain E12/E47-like subunits. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):1156–1160. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.1156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Donovan D. M., Hamada K., Sax C. M., Norman B., Flanagan J. R., Ozato K., Westphal H., Piatigorsky J. Regulation of the mouse alpha A-crystallin gene: isolation of a cDNA encoding a protein that binds to a cis sequence motif shared with the major histocompatibility complex class I gene and other genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3700–3708. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neill S. D., Hemstrom C., Virtanen A., Nevins J. R. An adenovirus E4 gene product trans-activates E2 transcription and stimulates stable E2F binding through a direct association with E2F. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):2008–2012. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neill S. D., Nevins J. R. Genetic analysis of the adenovirus E4 6/7 trans activator: interaction with E2F and induction of a stable DNA-protein complex are critical for activity. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5364–5373. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5364-5373.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson C., Shen L. P., Meister A., Fodor E., Rutter W. J. Pan: a transcriptional regulator that binds chymotrypsin, insulin, and AP-4 enhancer motifs. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):1035–1043. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.1035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ness S. A., Marknell A., Graf T. The v-myb oncogene product binds to and activates the promyelocyte-specific mim-1 gene. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1115–1125. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90767-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan G. P., Ghosh S., Liou H. C., Tempst P., Baltimore D. DNA binding and I kappa B inhibition of the cloned p65 subunit of NF-kappa B, a rel-related polypeptide. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):961–969. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90320-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto K., Okazawa H., Okuda A., Sakai M., Muramatsu M., Hamada H. A novel octamer binding transcription factor is differentially expressed in mouse embryonic cells. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):461–472. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90597-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H. Globin gene regulation and switching: circa 1990. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):665–672. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90133-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostapchuk P., Scheirle G., Hearing P. Binding of nuclear factor EF-C to a functional domain of the hepatitis B virus enhancer region. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2787–2797. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parisi M. A., Clayton D. A. Similarity of human mitochondrial transcription factor 1 to high mobility group proteins. Science. 1991 May 17;252(5008):965–969. doi: 10.1126/science.2035027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park E. A., Roesler W. J., Liu J., Klemm D. J., Gurney A. L., Thatcher J. D., Shuman J., Friedman A., Hanson R. W. The role of the CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein in the transcriptional regulation of the gene for phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP). Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6264–6272. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park R. E., Haseltine W. A., Rosen C. A. A nuclear factor is required for transactivation of HTLV-I gene expression. Oncogene. 1988 Sep;3(3):275–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul R., Schuetze S., Kozak S. L., Kozak C. A., Kabat D. The Sfpi-1 proviral integration site of Friend erythroleukemia encodes the ets-related transcription factor Pu.1. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):464–467. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.464-467.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson K. E., Darnell J. E., Jr, Rushmore T., Pickett C. B. Analysis of the upstream elements of the xenobiotic compound-inducible and positionally regulated glutathione S-transferase Ya gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):1841–1852. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.1841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei D. Q., Shih C. H. Transcriptional activation and repression by cellular DNA-binding protein C/EBP. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1517–1522. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1517-1522.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. L., Calame K. Proteins binding to site C2 (muE3) in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer exist in multiple oligomeric forms. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):776–786. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. L., Eaton S., Calame K. Purified mu EBP-E binds to immunoglobulin enhancers and promoters. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4972–4980. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrucco S., Wellauer P. K., Hagenbüchle O. The DNA-binding activity of transcription factor PTF1 parallels the synthesis of pancreas-specific mRNAs during mouse development. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):254–264. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pevny L., Simon M. C., Robertson E., Klein W. H., Tsai S. F., D'Agati V., Orkin S. H., Costantini F. Erythroid differentiation in chimaeric mice blocked by a targeted mutation in the gene for transcription factor GATA-1. Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):257–260. doi: 10.1038/349257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piette J., Hirai S., Yaniv M. Constitutive synthesis of activator protein 1 transcription factor after viral transformation of mouse fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3401–3405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine R., Decker T., Kessler D. S., Levy D. E., Darnell J. E., Jr Purification and cloning of interferon-stimulated gene factor 2 (ISGF2): ISGF2 (IRF-1) can bind to the promoters of both beta interferon- and interferon-stimulated genes but is not a primary transcriptional activator of either. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2448–2457. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poellinger L., Roeder R. G. Octamer transcription factors 1 and 2 each bind to two different functional elements in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):747–756. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli V., Mancini F. P., Cortese R. IL-6DBP, a nuclear protein involved in interleukin-6 signal transduction, defines a new family of leucine zipper proteins related to C/EBP. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):643–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90459-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postel E. H., Mango S. E., Flint S. J. A nuclease-hypersensitive element of the human c-myc promoter interacts with a transcription initiation factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5123–5133. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Lawe D., Ziff E. B. Association of Myn, the murine homolog of max, with c-Myc stimulates methylation-sensitive DNA binding and ras cotransformation. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):395–407. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90457-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramji D. P., Tadros M. H., Hardon E. M., Cortese R. The transcription factor LF-A1 interacts with a bipartite recognition sequence in the promoter regions of several liver-specific genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 11;19(5):1139–1146. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.5.1139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randak C., Brabletz T., Hergenröther M., Sobotta I., Serfling E. Cyclosporin A suppresses the expression of the interleukin 2 gene by inhibiting the binding of lymphocyte-specific factors to the IL-2 enhancer. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2529–2536. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07433.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Morris J. F., Tournay O. E., Cook D. M., Curran T. Binding of the Wilms' tumor locus zinc finger protein to the EGR-1 consensus sequence. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1259–1262. doi: 10.1126/science.2244209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reith W., Herrero-Sanchez C., Kobr M., Silacci P., Berte C., Barras E., Fey S., Mach B. MHC class II regulatory factor RFX has a novel DNA-binding domain and a functionally independent dimerization domain. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1528–1540. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rey-Campos J., Chouard T., Yaniv M., Cereghini S. vHNF1 is a homeoprotein that activates transcription and forms heterodimers with HNF1. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1445–1457. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07665.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs K. J., Merrell K. T., Wilson G., Calame K. Common factor 1 is a transcriptional activator which binds in the c-myc promoter, the skeletal alpha-actin promoter, and the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1765–1769. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts S. B., Segil N., Heintz N. Differential phosphorylation of the transcription factor Oct1 during the cell cycle. Science. 1991 Aug 30;253(5023):1022–1026. doi: 10.1126/science.1887216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman C., Platero J. S., Shuman J., Calame K. Ig/EBP-1: a ubiquitously expressed immunoglobulin enhancer binding protein that is similar to C/EBP and heterodimerizes with C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1404–1415. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron D., Brasier A. R., Habener J. F. Angiotensinogen gene-inducible enhancer-binding protein 1, a member of a new family of large nuclear proteins that recognize nuclear factor kappa B-binding sites through a zinc finger motif. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2887–2895. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney R. J., Raychaudhuri P., Nevins J. R. E4F and ATF, two transcription factors that recognize the same site, can be distinguished both physically and functionally: a role for E4F in E1A trans activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5138–5149. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner M. H., De Santo R. J., Arnheiter H., Staudt L. M. Oct-3 is a maternal factor required for the first mouse embryonic division. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1103–1110. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90265-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi P., Karsenty G., Roberts A. B., Roche N. S., Sporn M. B., de Crombrugghe B. A nuclear factor 1 binding site mediates the transcriptional activation of a type I collagen promoter by transforming growth factor-beta. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):405–414. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux E., Strubin M., Hagenbüchle O., Wellauer P. K. The cell-specific transcription factor PTF1 contains two different subunits that interact with the DNA. Genes Dev. 1989 Oct;3(10):1613–1624. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.10.1613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe A., Eager N. S., Brickell P. M. A member of the RXR nuclear receptor family is expressed in neural-crest-derived cells of the developing chick peripheral nervous system. Development. 1991 Mar;111(3):771–778. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.3.771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruezinsky D., Beckmann H., Kadesch T. Modulation of the IgH enhancer's cell type specificity through a genetic switch. Genes Dev. 1991 Jan;5(1):29–37. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rustgi A. K., Van 't Veer L. J., Bernards R. Two genes encode factors with NF-kappa B- and H2TF1-like DNA-binding properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8707–8710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saatcioglu F., Perry D. J., Pasco D. S., Fagan J. B. Multiple DNA-binding factors interact with overlapping specificities at the aryl hydrocarbon response element of the cytochrome P450IA1 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6408–6416. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffen D. W., Cole A. J., Worley P. F., Christy B. A., Ryder K., Baraban J. M. Convulsant-induced increase in transcription factor messenger RNAs in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7795–7799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffer J. D., Jackson S. P., Annarella M. B. Developmental expression of Sp1 in the mouse. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2189–2199. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffer J. D., Jackson S. P., Thurston S. J. SV40 stimulates expression of the transacting factor Sp1 at the mRNA level. Genes Dev. 1990 Apr;4(4):659–666. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.4.659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sartorelli V., Webster K. A., Kedes L. Muscle-specific expression of the cardiac alpha-actin gene requires MyoD1, CArG-box binding factor, and Sp1. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1811–1822. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sax C. M., Klement J. F., Piatigorsky J. Species-specific lens activation of the thymidine kinase promoter by a single copy of the mouse alpha A-CRYBP1 site and loss of tissue specificity by multimerization. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6813–6816. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaufele F., West B. L., Reudelhuber T. Somatotroph- and lactotroph-specific interactions with the homeobox protein binding sites in the rat growth hormone gene promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5235–5243. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlissel M., Voronova A., Baltimore D. Helix-loop-helix transcription factor E47 activates germ-line immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene transcription and rearrangement in a pre-T-cell line. Genes Dev. 1991 Aug;5(8):1367–1376. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.8.1367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. C., Zhou Q., Berk A. J. Sp1 activates transcription without enhancing DNA-binding activity of the TATA box factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3299–3307. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber E., Harshman K., Kemler I., Malipiero U., Schaffner W., Fontana A. Astrocytes and glioblastoma cells express novel octamer-DNA binding proteins distinct from the ubiquitous Oct-1 and B cell type Oct-2 proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 25;18(18):5495–5503. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.18.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber E., Matthias P., Müller M. M., Schaffner W. Identification of a novel lymphoid specific octamer binding protein (OTF-2B) by proteolytic clipping bandshift assay (PCBA). EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4221–4229. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03319.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Dressler G. R., Balling R., Rohdewohld H., Gruss P. Oct-4: a germline-specific transcription factor mapping to the mouse t-complex. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2185–2195. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07388.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Umesono K., Mangelsdorf D. J., Bolado J., Pike J. W., Evans R. M. Jun-Fos and receptors for vitamins A and D recognize a common response element in the human osteocalcin gene. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):497–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90531-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon M. F., Gamble J. R., Vadas M. A. Nuclear proteins interacting with the promoter region of the human granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):674–678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P. E., Schröter H., Nordheim A. The ability of a ternary complex to form over the serum response element correlates with serum inducibility of the human c-fos promoter. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):563–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90579-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheng M., Thompson M. A., Greenberg M. E. CREB: a Ca(2+)-regulated transcription factor phosphorylated by calmodulin-dependent kinases. Science. 1991 Jun 7;252(5011):1427–1430. doi: 10.1126/science.1646483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakawa F., Chedid M., Suttles J., Pollok B. A., Mizel S. B. Interleukin 1 and cyclic AMP induce kappa immunoglobulin light-chain expression via activation of an NF-kappa B-like DNA-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):959–964. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladek F. M., Zhong W. M., Lai E., Darnell J. E., Jr Liver-enriched transcription factor HNF-4 is a novel member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2353–2365. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. P., Old R. W. Xenopus laevis Oct-1 does not bind to certain histone H2B gene promoter octamer motifs for which a novel octamer-binding factor has high affinity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 25;19(4):815–821. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.4.815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K. Heat shock factor and the heat shock response. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):363–366. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90452-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su W., Jackson S., Tjian R., Echols H. DNA looping between sites for transcriptional activation: self-association of DNA-bound Sp1. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):820–826. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suva L. J., Ernst M., Rodan G. A. Retinoic acid increases zif268 early gene expression in rat preosteoblastic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2503–2510. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki N., Rohdewohld H., Neuman T., Gruss P., Schöler H. R. Oct-6: a POU transcription factor expressed in embryonal stem cells and in the developing brain. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3723–3732. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07585.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot D., Grosveld F. The 5'HS2 of the globin locus control region enhances transcription through the interaction of a multimeric complex binding at two functionally distinct NF-E2 binding sites. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1391–1398. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07659.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura T., Sumita K., Fujino I., Aoyama A., Horikoshi M., Hoffmann A., Roeder R. G., Muramatsu M., Mikoshiba K. Striking homology of the 'variable' N-terminal as well as the 'conserved core' domains of the mouse and human TATA-factors (TFIID). Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):3861–3865. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.3861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan T. H., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Purification and characterization of multiple nuclear factors that bind to the TAX-inducible enhancer within the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1733–1745. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapscott S. J., Davis R. L., Thayer M. J., Cheng P. F., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. MyoD1: a nuclear phosphoprotein requiring a Myc homology region to convert fibroblasts to myoblasts. Science. 1988 Oct 21;242(4877):405–411. doi: 10.1126/science.3175662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tassios P. T., La Thangue N. B. A multiplicity of differentiation-regulated ATF site-binding activities in embryonal carcinoma cells with distinct sequence and promoter specificities. New Biol. 1990 Dec;2(12):1123–1134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thalmeier K., Synovzik H., Mertz R., Winnacker E. L., Lipp M. Nuclear factor E2F mediates basic transcription and trans-activation by E1a of the human MYC promoter. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):527–536. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornell A., Hallberg B., Grundström T. Differential protein binding in lymphocytes to a sequence in the enhancer of the mouse retrovirus SL3-3. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1625–1637. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilley W. D., Marcelli M., Wilson J. D., McPhaul M. J. Characterization and expression of a cDNA encoding the human androgen receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):327–331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toniatti C., Demartis A., Monaci P., Nicosia A., Ciliberto G. Synergistic trans-activation of the human C-reactive protein promoter by transcription factor HNF-1 binding at two distinct sites. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4467–4475. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07897.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis A., Amsterdam A., Belanger C., Grosschedl R. LEF-1, a gene encoding a lymphoid-specific protein with an HMG domain, regulates T-cell receptor alpha enhancer function [corrected]. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):880–894. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Sagami I., Wang H., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Interactions between a DNA-binding transcription factor (COUP) and a non-DNA binding factor (S300-II). Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):701–709. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90328-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukiyama T., Niwa O., Yokoro K. Mechanism of suppression of the long terminal repeat of Moloney leukemia virus in mouse embryonal carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4670–4676. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban M. B., Schreck R., Baeuerle P. A. NF-kappa B contacts DNA by a heterodimer of the p50 and p65 subunit. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1817–1825. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07707.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaidya T. B., Rhodes S. J., Taparowsky E. J., Konieczny S. F. Fibroblast growth factor and transforming growth factor beta repress transcription of the myogenic regulatory gene MyoD1. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3576–3579. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasios G., Mader S., Gold J. D., Leid M., Lutz Y., Gaub M. P., Chambon P., Gudas L. The late retinoic acid induction of laminin B1 gene transcription involves RAR binding to the responsive element. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1149–1158. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08055.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verrijzer C. P., Kal A. J., Van der Vliet P. C. The DNA binding domain (POU domain) of transcription factor oct-1 suffices for stimulation of DNA replication. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1883–1888. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08314.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada T., Watanabe H., Usuda Y., Handa H. Different biological activities of the hetero- and homodimers formed by the 47- and 43-kilodalton proteins of transcription factor ATF/E4TF3. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):557–564. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.557-564.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner B. J., Hayes T. E., Hoban C. J., Cochran B. H. The SIF binding element confers sis/PDGF inducibility onto the c-fos promoter. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4477–4484. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07898.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh K. Cross-binding of factors to functionally different promoter elements in c-fos and skeletal actin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2191–2201. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Flores P., Begue A., Leprince D., Stehelin D. The c-ets proto-oncogenes encode transcription factors that cooperate with c-Fos and c-Jun for transcriptional activation. Nature. 1990 Jul 12;346(6280):191–193. doi: 10.1038/346191a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk C., Flores P., Gutman A., Wasylyk B. PEA3 is a nuclear target for transcription activation by non-nuclear oncogenes. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3371–3378. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08500.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk C., Gutman A., Nicholson R., Wasylyk B. The c-Ets oncoprotein activates the stromelysin promoter through the same elements as several non-nuclear oncoproteins. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1127–1134. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08053.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk C., Wasylyk B., Heidecker G., Huleihel M., Rapp U. R. Expression of raf oncogenes activates the PEA1 transcription factor motif. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2247–2250. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe H., Wada T., Handa H. Transcription factor E4TF1 contains two subunits with different functions. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):841–847. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08181.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterman M. L., Fischer W. H., Jones K. A. A thymus-specific member of the HMG protein family regulates the human T cell receptor C alpha enhancer. Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):656–669. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterman M. L., Jones K. A. Purification of TCF-1 alpha, a T-cell-specific transcription factor that activates the T-cell receptor C alpha gene enhancer in a context-dependent manner. New Biol. 1990 Jul;2(7):621–636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson M. A., Milbrandt J. The NGFI-B gene, a transcriptionally inducible member of the steroid receptor gene superfamily: genomic structure and expression in rat brain after seizure induction. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4213–4219. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt F., Molloy P. L. High mobility group proteins 1 and 2 stimulate binding of a specific transcription factor to the adenovirus major late promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 25;16(4):1471–1486. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.4.1471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wefald F. C., Devlin B. H., Williams R. S. Functional heterogeneity of mammalian TATA-box sequences revealed by interaction with a cell-specific enhancer. Nature. 1990 Mar 15;344(6263):260–262. doi: 10.1038/344260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinrich S. L., Meister A., Rutter W. J. Exocrine pancreas transcription factor 1 binds to a bipartite enhancer element and activates transcription of acinar genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4985–4997. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelan J., Cordle S. R., Henderson E., Weil P. A., Stein R. Identification of a pancreatic beta-cell insulin gene transcription factor that binds to and appears to activate cell-type-specific expression: its possible relationship to other cellular factors that bind to a common insulin gene sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1564–1572. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P., Ratajczak T., Lee S. C., Ringold G. M. AGP/EBP(LAP) expressed in rat hepatoma cells interacts with multiple promoter sites and is necessary for maximal glucocorticoid induction of the rat alpha-1 acid glycoprotein gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4959–4965. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T., Tjian R. Analysis of the DNA-binding and activation properties of the human transcription factor AP-2. Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):670–682. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winning R. S., Shea L. J., Marcus S. J., Sargent T. D. Developmental regulation of transcription factor AP-2 during Xenopus laevis embryogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 11;19(13):3709–3714. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.13.3709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth T., Priess A., Annweiler A., Zwilling S., Oeler B. Multiple Oct2 isoforms are generated by alternative splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):43–51. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Roeder R. G., Kingston R. E. An upstream transcription factor, USF (MLTF), facilitates the formation of preinitiation complexes during in vitro chromatin assembly. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1299–1308. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08239.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuarin J., Schibler U. Expression of the liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein DBP follows a stringent circadian rhythm. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1257–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90421-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao J. H., Davidson I., Matthes H., Garnier J. M., Chambon P. Cloning, expression, and transcriptional properties of the human enhancer factor TEF-1. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):551–568. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90088-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi Y., Satake M., Ito Y. Two overlapping sequence motifs within the polyomavirus enhancer are independently the targets of stimulation by both the tumor promoter 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate and the Ha-ras oncogene. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1040–1048. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1040-1048.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto M., Ko L. J., Leonard M. W., Beug H., Orkin S. H., Engel J. D. Activity and tissue-specific expression of the transcription factor NF-E1 multigene family. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1650–1662. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan C., Tamm I. Molecular cloning and characterization of interferon alpha/beta response element binding factors of the murine (2'-5')oligoadenylate synthetase ME-12 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):144–148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan D. H., Hung M. C. Identification and characterization of a novel enhancer for the rat neu promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1875–1882. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Yen H. F., Chiu R., Karin M. Elevation of AP1 activity during F9 cell differentiation is due to increased c-jun transcription. New Biol. 1990 Apr;2(4):351–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoza B. K., Roeder R. G. Identification of a novel factor that interacts with an immunoglobulin heavy-chain promoter and stimulates transcription in conjunction with the lymphoid cell-specific factor OTF2. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2145–2153. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu-Lee L. Y., Hrachovy J. A., Stevens A. M., Schwarz L. A. Interferon-regulatory factor 1 is an immediate-early gene under transcriptional regulation by prolactin in Nb2 T cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3087–3094. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Y. T., Nadal-Ginard B. Interaction of nuclear proteins with a positive cis-acting element of rat embryonic myosin heavy-chain promoter: identification of a new transcriptional factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):1839–1849. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.1839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot R. P., Auwerx J., Karperien M., Staels B., Kruijer W. Activation of junB by PKC and PKA signal transduction through a novel cis-acting element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 25;19(4):775–781. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.4.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Verneuil H., Metzger D. The lack of transcriptional activation of the v-erbA oncogene is in part due to a mutation present in the DNA binding domain of the protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 11;18(15):4489–4497. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.15.4489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wijnen A. J., Wright K. L., Massung R. F., Gerretsen M., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. Two target sites for protein binding in the promoter region of a cell cycle regulated human H1 histone gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 25;16(2):571–592. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.2.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Wetering M., Oosterwegel M., Dooijes D., Clevers H. Identification and cloning of TCF-1, a T lymphocyte-specific transcription factor containing a sequence-specific HMG box. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):123–132. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



