Abstract
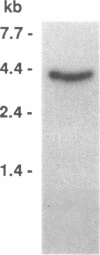
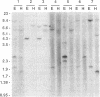
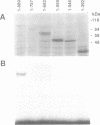
Iron regulatory factor (IRF), also called iron responsive element-binding protein (IRE-BP), is a cytoplasmic RNA-binding protein which regulates post-transcriptionally transferrin receptor mRNA stability and ferritin mRNA translation. By using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and the sequence published by Rouault et al. (1990) a probe was derived which permitted the isolation of three human IRF cDNA clones. Hybridization to genomic DNA and mRNA, as well as sequencing data indicated a single copy gene of about 40 kb specifying a 4.0 kb mRNA that translates into a protein of 98,400 dalton. By in vitro transcription of a assembled IRF cDNA coupled to in vitro translation in a wheat germ extract, we obtained full sized IRF that bound specifically to a human ferritin IRE. In vitro translated IRF retained sensitivity to sulfhydryl oxidation by diamide and could be reactivated by beta-mercaptoethanol in the same way as native placental IRF. An IRF deletion mutant shortened by 132 amino acids at the COOH-terminus was no longer able to bind to an IRE, indicating that this region of the protein plays a role in RNA recognition. Placental IRF has previously been shown to migrate as a doublet on SDS-polyacrylamide gels. After V8 protease digestion the heterogeneity was located in a 65/70 kDa NH2-terminal doublet. The liberated 31 kDa COOH-terminal polypeptide was found to be homogeneous by amino acid sequencing supporting the conclusion of a single IRF gene.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aziz N., Munro H. N. Both subunits of rat liver ferritin are regulated at a translational level by iron induction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 24;14(2):915–927. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.2.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aziz N., Munro H. N. Iron regulates ferritin mRNA translation through a segment of its 5' untranslated region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8478–8482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandziulis R. J., Swanson M. S., Dreyfuss G. RNA-binding proteins as developmental regulators. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):431–437. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton H. A., Eisenstein R. S., Bomford A., Munro H. N. Determinants of the interaction between the iron-responsive element-binding protein and its binding site in rat L-ferritin mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):7000–7008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beinert H., Kennedy M. C. 19th Sir Hans Krebs lecture. Engineering of protein bound iron-sulfur clusters. A tool for the study of protein and cluster chemistry and mechanism of iron-sulfur enzymes. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Dec 8;186(1-2):5–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. H., Daniels-McQueen S., Walden W. E., Patino M. M., Gaffield L., Bielser D., Thach R. E. Requirements for the translational repression of ferritin transcripts in wheat germ extracts by a 90-kDa protein from rabbit liver. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13383–13386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey J. L., Hentze M. W., Koeller D. M., Caughman S. W., Rouault T. A., Klausner R. D., Harford J. B. Iron-responsive elements: regulatory RNA sequences that control mRNA levels and translation. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):924–928. doi: 10.1126/science.2452485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey J. L., Koeller D. M., Ramin V. C., Klausner R. D., Harford J. B. Iron regulation of transferrin receptor mRNA levels requires iron-responsive elements and a rapid turnover determinant in the 3' untranslated region of the mRNA. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3693–3699. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08544.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox T. C., Bawden M. J., Martin A., May B. K. Human erythroid 5-aminolevulinate synthase: promoter analysis and identification of an iron-responsive element in the mRNA. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1891–1902. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07715.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dandekar T., Stripecke R., Gray N. K., Goossen B., Constable A., Johansson H. E., Hentze M. W. Identification of a novel iron-responsive element in murine and human erythroid delta-aminolevulinic acid synthase mRNA. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1903–1909. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07716.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goossen B., Caughman S. W., Harford J. B., Klausner R. D., Hentze M. W. Translational repression by a complex between the iron-responsive element of ferritin mRNA and its specific cytoplasmic binding protein is position-dependent in vivo. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):4127–4133. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07635.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haile D. J., Hentze M. W., Rouault T. A., Harford J. B., Klausner R. D. Regulation of interaction of the iron-responsive element binding protein with iron-responsive RNA elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5055–5061. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haile D. J., Rouault T. A., Harford J. B., Klausner R. D. The inhibition of the iron responsive element RNA-protein interaction by heme does not mimic in vivo iron regulation. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):12786–12789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentze M. W., Argos P. Homology between IRE-BP, a regulatory RNA-binding protein, aconitase, and isopropylmalate isomerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 25;19(8):1739–1740. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.8.1739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentze M. W., Rouault T. A., Caughman S. W., Dancis A., Harford J. B., Klausner R. D. A cis-acting element is necessary and sufficient for translational regulation of human ferritin expression in response to iron. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6730–6734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentze M. W., Rouault T. A., Harford J. B., Klausner R. D. Oxidation-reduction and the molecular mechanism of a regulatory RNA-protein interaction. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):357–359. doi: 10.1126/science.2711187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentze M. W., Seuanez H. N., O'Brien S. J., Harford J. B., Klausner R. D. Chromosomal localization of nucleic acid-binding proteins by affinity mapping: assignment of the IRE-binding protein gene to human chromosome 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6103–6108. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. C., Emptage M. H., Dreyer J. L., Beinert H. The role of iron in the activation-inactivation of aconitase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11098–11105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeller D. M., Casey J. L., Hentze M. W., Gerhardt E. M., Chan L. N., Klausner R. D., Harford J. B. A cytosolic protein binds to structural elements within the iron regulatory region of the transferrin receptor mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3574–3578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Comparison of initiation of protein synthesis in procaryotes, eucaryotes, and organelles. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):1–45. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.1-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. In vitro RNA synthesis with SP6 RNA polymerase. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:397–415. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55027-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn L. C., Barbosa J. A., Kamarck M. E., Ruddle F. H. An approach to the cloning of cell surface protein genes. Selection by cell sorting of mouse L-cells that express HLA or 4F2 antigens after transformation with total human DNA. Mol Biol Med. 1983 Oct;1(3):335–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibold E. A., Munro H. N. Cytoplasmic protein binds in vitro to a highly conserved sequence in the 5' untranslated region of ferritin heavy- and light-subunit mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2171–2175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. J., Daniels-McQueen S., Gaffield L., Patino M. M., Walden W. E., Thach R. E. Specificity of the induction of ferritin synthesis by hemin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):146–150. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90156-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. J., Daniels-McQueen S., Patino M. M., Gaffield L., Walden W. E., Thach R. E. Derepression of ferritin messenger RNA translation by hemin in vitro. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):74–77. doi: 10.1126/science.2294594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May B. K., Bhasker C. R., Bawden M. J., Cox T. C. Molecular regulation of 5-aminolevulinate synthase. Diseases related to heme biosynthesis. Mol Biol Med. 1990 Oct;7(5):405–421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müllner E. W., Kühn L. C. A stem-loop in the 3' untranslated region mediates iron-dependent regulation of transferrin receptor mRNA stability in the cytoplasm. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):815–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90098-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müllner E. W., Neupert B., Kühn L. C. A specific mRNA binding factor regulates the iron-dependent stability of cytoplasmic transferrin receptor mRNA. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):373–382. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90851-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neupert B., Thompson N. A., Meyer C., Kühn L. C. A high yield affinity purification method for specific RNA-binding proteins: isolation of the iron regulatory factor from human placenta. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 11;18(1):51–55. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen D., Kühn L. C. Noncoding 3' sequences of the transferrin receptor gene are required for mRNA regulation by iron. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1287–1293. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02366.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberger S., Müllner E. W., Kühn L. C. The mRNA-binding protein which controls ferritin and transferrin receptor expression is conserved during evolution. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 11;18(5):1175–1179. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouault T. A., Hentze M. W., Caughman S. W., Harford J. B., Klausner R. D. Binding of a cytosolic protein to the iron-responsive element of human ferritin messenger RNA. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1207–1210. doi: 10.1126/science.3413484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouault T. A., Hentze M. W., Haile D. J., Harford J. B., Klausner R. D. The iron-responsive element binding protein: a method for the affinity purification of a regulatory RNA-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5768–5772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouault T. A., Stout C. D., Kaptain S., Harford J. B., Klausner R. D. Structural relationship between an iron-regulated RNA-binding protein (IRE-BP) and aconitase: functional implications. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):881–883. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90312-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouault T. A., Tang C. K., Kaptain S., Burgess W. H., Haile D. J., Samaniego F., McBride O. W., Harford J. B., Klausner R. D. Cloning of the cDNA encoding an RNA regulatory protein--the human iron-responsive element-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7958–7962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira S., Di Grandi S., Kühn L. C. Primary structure of the human 4F2 antigen heavy chain predicts a transmembrane protein with a cytoplasmic NH2 terminus. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9574–9580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyrrell R. M., Pidoux M. Quantitative differences in host cell reactivation of ultraviolet-damaged virus in human skin fibroblasts and epidermal keratinocytes cultured from the same foreskin biopsy. Cancer Res. 1986 Jun;46(6):2665–2669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walden W. E., Patino M. M., Gaffield L. Purification of a specific repressor of ferritin mRNA translation from rabbit liver. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13765–13769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zähringer J., Baliga B. S., Munro H. N. Novel mechanism for translational control in regulation of ferritin synthesis by iron. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):857–861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]