Abstract
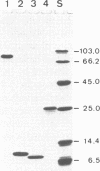
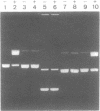
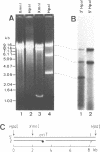
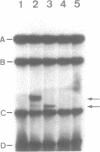
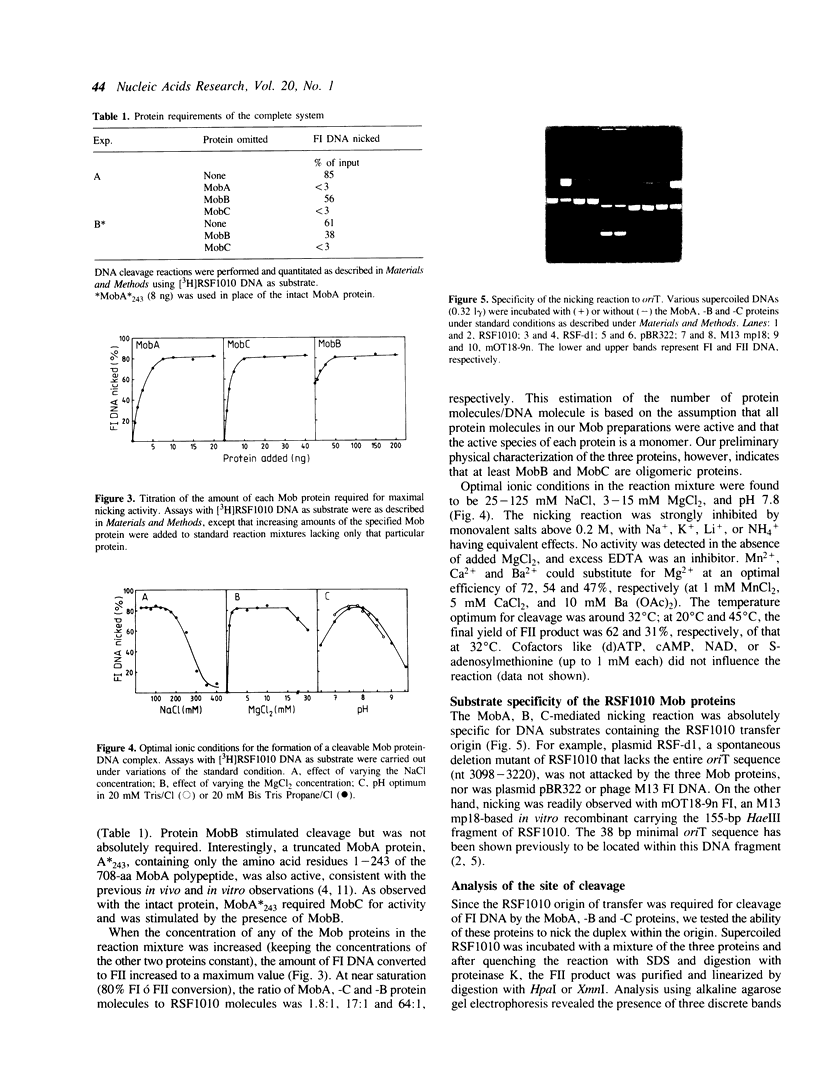
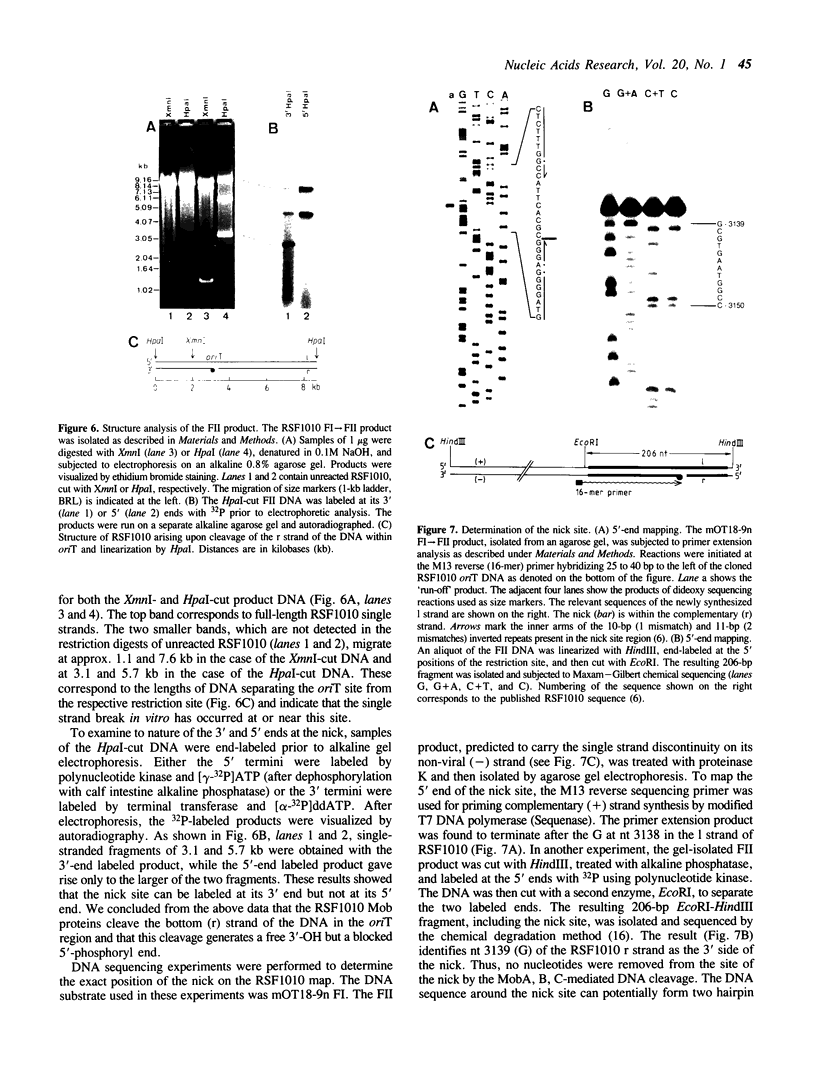
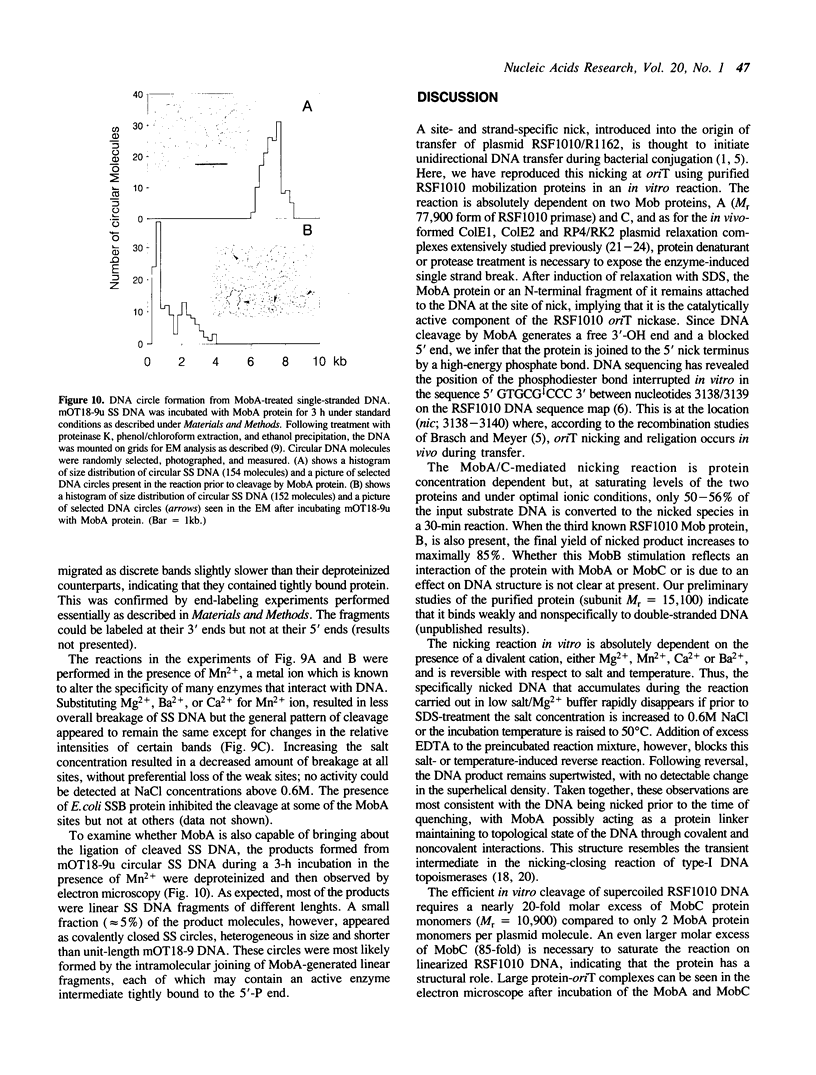
We have used purified RSF1010 mobilization proteins to reproduce in vitro a strand-specific nicking at the plasmid origin of transfer, oriT. In the presence of Mg2+, the proteins MobA (78-kDa form of RSF1010 DNA primase), MobB, and MobC and supercoiled or linear duplex oriT DNA form large amounts of a cleavage complex, which is characterized by its sensitivity to protein-denaturant treatment. Upon addition of SDS to such a complex, a single strand break is generated in the DNA, and MobA is found linked to the 5' nick terminus, presumably covalently. The double-strand nicking activity of MobA requires, in addition to Mg2+, the presence of MobC and is stimulated by the presence of MobB. The nick site has been shown by DNA sequencing to lie at the position cleaved in vivo during transfer, between nucleotides 3138/3139 in the r strand of RSF1010. We have found that MobA will also cleave DNA at sites other than oriT if the DNA is present in single-stranded form. Breakage in this case occurs in the absence of denaturing conditions, and after prolonged incubation, reclosure can be demonstrated.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Been M. D., Champoux J. J. DNA breakage and closure by rat liver type 1 topoisomerase: separation of the half-reactions by using a single-stranded DNA substrate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2883–2887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharjee M. K., Meyer R. J. A segment of a plasmid gene required for conjugal transfer encodes a site-specific, single-strand DNA endonuclease and ligase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 11;19(5):1129–1137. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.5.1129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. G., Helinski D. R. Relaxation complexes of plasmid DNA and protein. I. Strand-specific association of protein and DNA in the relaxed complexes of plasmids ColE1 and ColE2. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 25;250(22):8785–8789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasch M. A., Meyer R. J. A 38 base-pair segment of DNA is required in cis for conjugative mobilization of broad host-range plasmid R1162. J Mol Biol. 1987 Dec 5;198(3):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90286-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasch M. A., Meyer R. J. Genetic organization of plasmid R1162 DNA involved in conjugative mobilization. J Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;167(2):703–710. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.2.703-710.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Holy A. Regulation of ribosomal RNA promoters with a synthetic lac operator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6929–6933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champoux J. J. Strand breakage by the DNA untwisting enzyme results in covalent attachment of the enzyme to DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3800–3804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derbyshire K. M., Hatfull G., Willetts N. Mobilization of the non-conjugative plasmid RSF1010: a genetic and DNA sequence analysis of the mobilization region. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jan;206(1):161–168. doi: 10.1007/BF00326552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derbyshire K. M., Willetts N. S. Mobilization of the non-conjugative plasmid RSF1010: a genetic analysis of its origin of transfer. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jan;206(1):154–160. doi: 10.1007/BF00326551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drolet M., Zanga P., Lau P. C. The mobilization and origin of transfer regions of a Thiobacillus ferrooxidans plasmid: relatedness to plasmids RSF1010 and pSC101. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Aug;4(8):1381–1391. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00717.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürste J. P., Pansegrau W., Ziegelin G., Kröger M., Lanka E. Conjugative transfer of promiscuous IncP plasmids: interaction of plasmid-encoded products with the transfer origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1771–1775. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiney D. G., Helinski D. R. The DNA-protein relaxation complex of the plasmid RK2: location of the site-specific nick in the region of the proposed origin of transfer. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Oct 3;176(2):183–189. doi: 10.1007/BF00273212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halligan B. D., Davis J. L., Edwards K. A., Liu L. F. Intra- and intermolecular strand transfer by HeLa DNA topoisomerase I. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3995–4000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda Y., Sakai H., Hiasa H., Tanaka K., Komano T., Bagdasarian M. Functional division and reconstruction of a plasmid replication origin: molecular dissection of the oriV of the broad-host-range plasmid RSF1010. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):179–183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K., Meyer R. J. Unidirectional transfer of broad host-range plasmid R1162 during conjugative mobilization. Evidence for genetically distinct events at oriT. J Mol Biol. 1989 Aug 5;208(3):501–505. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90513-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Wang J. C. Interaction between DNA and Escherichia coli DNA topoisomerase I. Formation of complexes between the protein and superhelical and nonsuperhelical duplex DNAs. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):11082–11088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett M. A., Helinski D. R. Relaxation complexes of plasmid DNA and protein. II. Characterization of the proteins associated with the unrelaxed and relaxed complexes of plasmid ColE1. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 25;250(22):8790–8795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. Site-specific recombination at oriT of plasmid R1162 in the absence of conjugative transfer. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):799–806. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.799-806.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherzinger E., Haring V., Lurz R., Otto S. Plasmid RSF1010 DNA replication in vitro promoted by purified RSF1010 RepA, RepB and RepC proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 25;19(6):1203–1211. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.6.1203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholz P., Haring V., Wittmann-Liebold B., Ashman K., Bagdasarian M., Scherzinger E. Complete nucleotide sequence and gene organization of the broad-host-range plasmid RSF1010. Gene. 1989 Feb 20;75(2):271–288. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90273-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]