Abstract
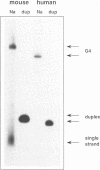
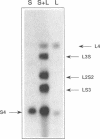
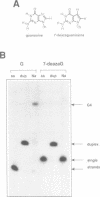
Retinoblastoma susceptibility genes contain significant runs of oligoguanine at their 5' ends. Oligonucleotides having these sequences underwent complex formation in the presence of sodium ions, in which there was association of four strands. Formation of this structure was completely prevented if guanine was replaced by 7-deazaguanine, indicating the importance of guanine N7 in the formation of the complex. Complex formation lead to protection of guanine N7 against methylation by dimethyl sulphate, but thymine bases located between oligoguanine blocks were reactive to osmium tetroxide. There was also some sensitivity to S1 nuclease to the 5' side of the oligoguanine block. The results show that the G-rich regions of the mouse and human retinoblastoma susceptibility genes have a propensity to undergo tetraplex formation of the kind demonstrated in the immunoglobulin switch region.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernards R., Shackleford G. M., Schackleford G. M., Gerber M. R., Horowitz J. M., Friend S. H., Schartl M., Bogenmann E., Rapaport J. M., McGee T. Structure and expression of the murine retinoblastoma gene and characterization of its encoded protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6474–6478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chittenden T., Livingston D. M., Kaelin W. G., Jr The T/E1A-binding domain of the retinoblastoma product can interact selectively with a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1073–1082. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90559-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend S. H., Bernards R., Rogelj S., Weinberg R. A., Rapaport J. M., Albert D. M., Dryja T. P. A human DNA segment with properties of the gene that predisposes to retinoblastoma and osteosarcoma. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):643–646. doi: 10.1038/323643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GELLERT M., LIPSETT M. N., DAVIES D. R. Helix formation by guanylic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Dec 15;48:2013–2018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.12.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson E., Hardin C. C., Walk S. K., Tinoco I., Jr, Blackburn E. H. Telomeric DNA oligonucleotides form novel intramolecular structures containing guanine-guanine base pairs. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):899–908. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90577-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Thein S. L. Hypervariable 'minisatellite' regions in human DNA. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):67–73. doi: 10.1038/314067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin R. Z., Breslauer K. J., Jones R. A., Gaffney B. L. Tetraplex formation of a guanine-containing nonameric DNA fragment. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):543–546. doi: 10.1126/science.2237404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. J., Lee H. D., Robbins P. D., Busam K., Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Regulation of transforming growth factor beta 1 gene expression by the product of the retinoblastoma-susceptibility gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3052–3056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam S. T., Stahl M. M., McMilin K. D., Stahl F. W. Rec-mediated recombinational hot spot activity in bacteriophage lambda. II. A mutation which causes hot spot activity. Genetics. 1974 Jul;77(3):425–433. doi: 10.1093/genetics/77.3.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. Y., To H., Shew J. Y., Bookstein R., Scully P., Lee W. H. Inactivation of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene in human breast cancers. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):218–221. doi: 10.1126/science.3388033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., Shew J. Y., Hong F. D., Sery T. W., Donoso L. A., Young L. J., Bookstein R., Lee E. Y. The retinoblastoma susceptibility gene encodes a nuclear phosphoprotein associated with DNA binding activity. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):642–645. doi: 10.1038/329642a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyutin I. G., Kovalsky O. I., Budowsky E. I., Dickerson R. E., Rikhirev M. E., Lipanov A. A. G-DNA: a twice-folded DNA structure adopted by single-stranded oligo(dG) and its implications for telomeres. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):867–870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins P. D., Horowitz J. M., Mulligan R. C. Negative regulation of human c-fos expression by the retinoblastoma gene product. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):668–671. doi: 10.1038/346668a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen D., Gilbert W. A sodium-potassium switch in the formation of four-stranded G4-DNA. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):410–414. doi: 10.1038/344410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen D., Gilbert W. Formation of parallel four-stranded complexes by guanine-rich motifs in DNA and its implications for meiosis. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):364–366. doi: 10.1038/334364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha N. D., Biernat J., McManus J., Köster H. Polymer support oligonucleotide synthesis XVIII: use of beta-cyanoethyl-N,N-dialkylamino-/N-morpholino phosphoramidite of deoxynucleosides for the synthesis of DNA fragments simplifying deprotection and isolation of the final product. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4539–4557. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. R., Kunes S. M., Schultz D. W., Taylor A., Triman K. L. Structure of chi hotspots of generalized recombination. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90333-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundquist W. I., Klug A. Telomeric DNA dimerizes by formation of guanine tetrads between hairpin loops. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):825–829. doi: 10.1038/342825a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. R., Raghuraman M. K., Cech T. R. Monovalent cation-induced structure of telomeric DNA: the G-quartet model. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):871–880. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90610-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wohlrab F., McLean M. J., Wells R. D. The segment inversion site of herpes simplex virus type 1 adopts a novel DNA structure. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6407–6416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]