Abstract
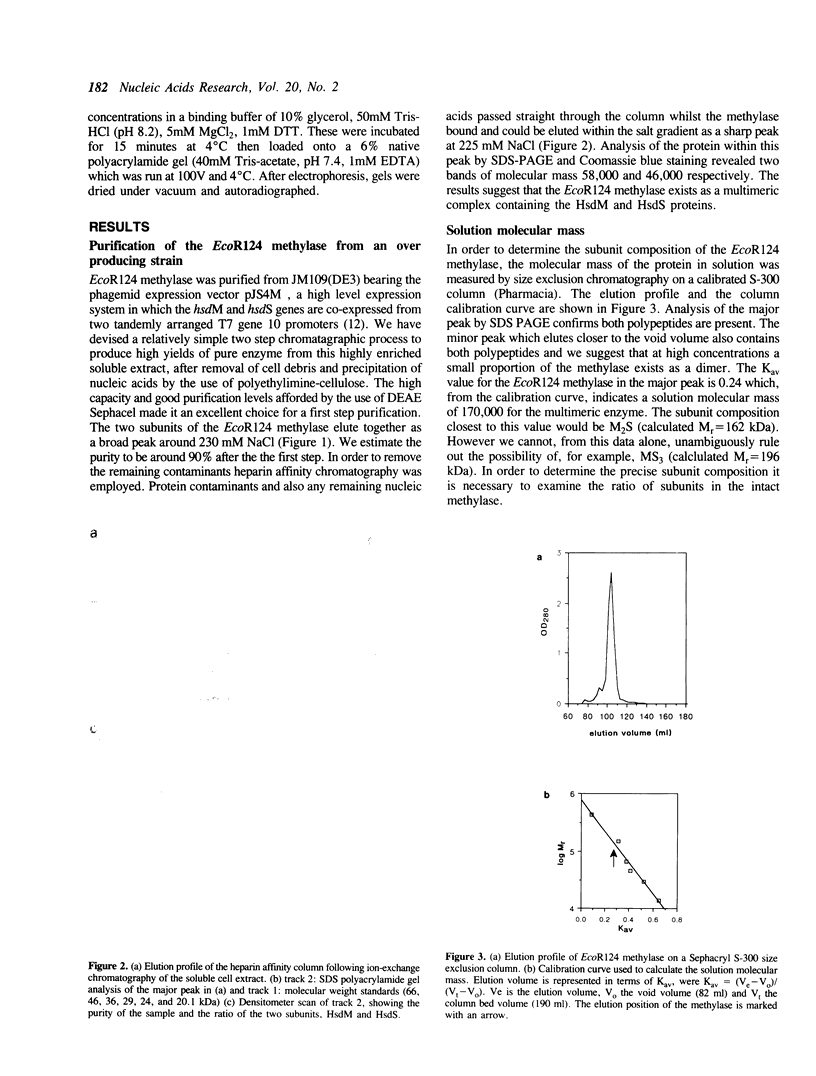
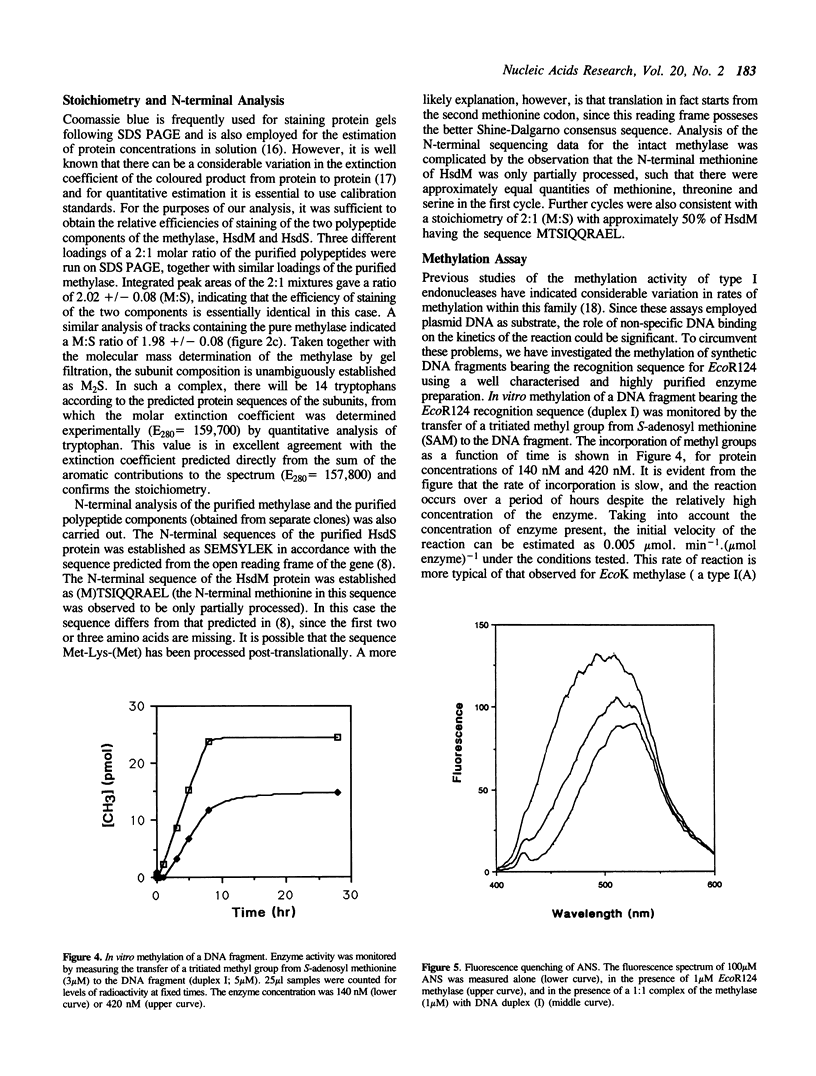
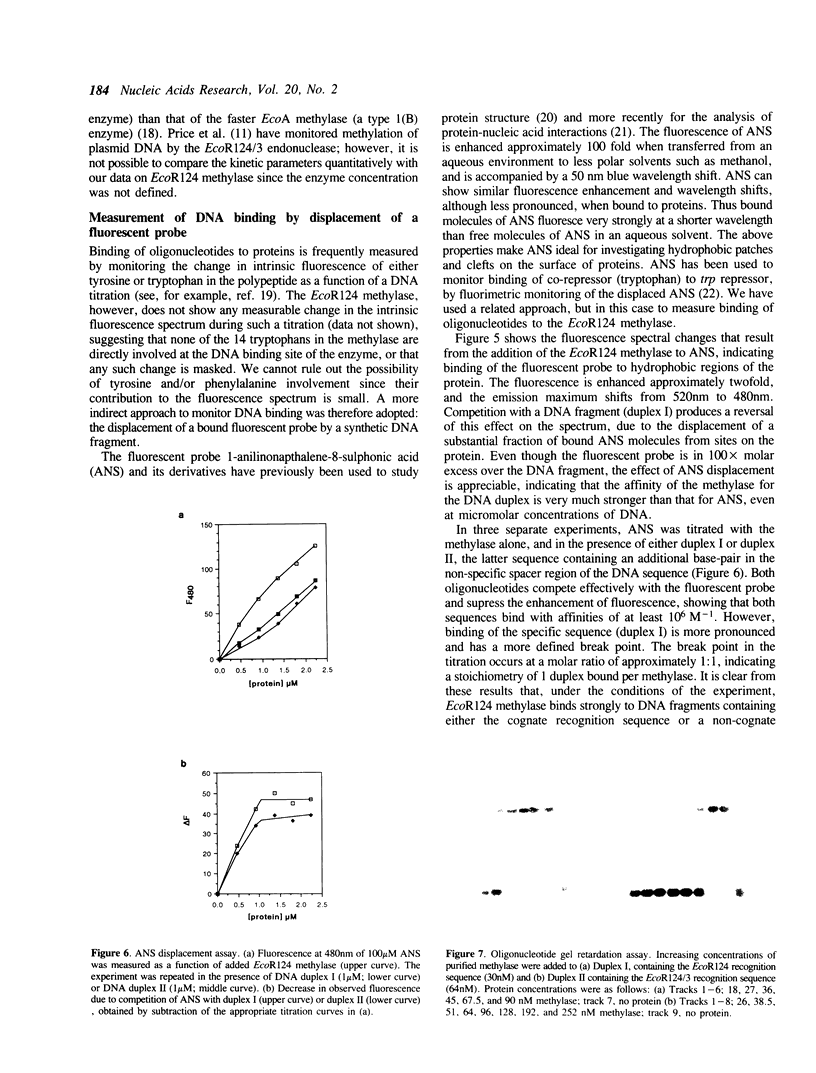
Large scale purification of the type I modification methylase EcoR124 has been achieved from an over-expressing strain by a two step procedure using ion-exchange and heparin chromatography. Pure methylase is obtained at a yield of 30 mg per gm of cell paste. Measurements of the molecular weight and subunit stoichiometry show that the enzyme is a trimeric complex of 162 kDa consisting of two subunits of HsdM (58 kDa) and one subunit of HsdS (46 kDa). The purified enzyme can methylate a DNA fragment bearing its cognate recognition sequence. Binding of the methylase to synthetic DNA fragments containing either the EcoR124 recognition sequence GAAN6RTCG, or the recognition sequence GAAN7RTCG of the related enzyme EcoR124/3, was followed by fluorescence competition assays and by gel retardation analysis. The results show that the methylase binds to its correct sequence with an affinity of the order 10(8) M-1 forming a 1:1 complex with the DNA. The affinity for the incorrect sequence, differing by an additional base pair in the non-specific spacer, is almost two orders of magnitude lower.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argos P. Evidence for a repeating domain in type I restriction enzymes. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1351–1355. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03784.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou W. Y., Bieber C., Matthews K. S. Tryptophan and 8-anilino-1-naphthalenesulfonate compete for binding to trp repressor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18309–18313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrastil J. Spectrophotometric determination of tryptophan and tyrosine in peptides and proteins based on new color reactions. Anal Biochem. 1986 Nov 1;158(2):443–446. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90573-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan G. M., Gann A. A., Murray N. E. Conservation of complex DNA recognition domains between families of restriction enzymes. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):103–109. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90988-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller-Pace F. V., Bullas L. R., Delius H., Murray N. E. Genetic recombination can generate altered restriction specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6095–6099. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gann A. A., Campbell A. J., Collins J. F., Coulson A. F., Murray N. E. Reassortment of DNA recognition domains and the evolution of new specificities. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Jul;1(1):13–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb00521.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough J. A., Murray N. E. Sequence diversity among related genes for recognition of specific targets in DNA molecules. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 5;166(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler M., Bickle T. A. Increased protein flexibility leads to promiscuous protein--DNA interactions in type IC restriction-modification systems. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):951–957. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08029.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannan P., Cowan G. M., Daniel A. S., Gann A. A., Murray N. E. Conservation of organization in the specificity polypeptides of two families of type I restriction enzymes. J Mol Biol. 1989 Oct 5;209(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kneale G. G., Wijnaendts van Resandt R. W. Time-resolved fluorescence of bacteriophage Pf1 DNA-binding protein. Determination of oligonucleotide and polynucleotide binding parameters. Eur J Biochem. 1985 May 15;149(1):85–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08897.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price C., Lingner J., Bickle T. A., Firman K., Glover S. W. Basis for changes in DNA recognition by the EcoR124 and EcoR124/3 type I DNA restriction and modification enzymes. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jan 5;205(1):115–125. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90369-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price C., Pripfl T., Bickle T. A. EcoR124 and EcoR124/3: the first members of a new family of type I restriction and modification systems. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Aug 17;167(1):111–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13310.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price C., Shepherd J. C., Bickle T. A. DNA recognition by a new family of type I restriction enzymes: a unique relationship between two different DNA specificities. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1493–1497. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02391.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Secnik J., Wang Q., Chang C. M., Jentoft J. E. Interactions at the nucleic acid binding site of the avian retroviral nucleocapsid protein: studies utilizing the fluorescent probe 4,4'-bis(phenylamino)(1,1'-binaphthalene)-5,5'-disulfonic acid. Biochemistry. 1990 Aug 28;29(34):7991–7997. doi: 10.1021/bi00486a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slavík J. Anilinonaphthalene sulfonate as a probe of membrane composition and function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Aug 11;694(1):1–25. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(82)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suri B., Bickle T. A. EcoA: the first member of a new family of type I restriction modification systems. Gene organization and enzymatic activities. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 5;186(1):77–85. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90258-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tal M., Weissman I., Silberstein A. A new method for stoichiometric analysis of proteins in complex mixture--reevaluation of the stoichiometry of E. coli ribosomal proteins. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1990 Sep-Oct;21(3):247–266. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(90)90018-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. D., Badcoe I. G., Clarke A. R., Halford S. E. EcoRV restriction endonuclease binds all DNA sequences with equal affinity. Biochemistry. 1991 Sep 10;30(36):8743–8753. doi: 10.1021/bi00100a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- York S. S., Lawson R. C., Jr, Worah D. M. Binding of recrystallized and chromatographically purified 8-anilino-1-naphthalenesulfonate to Escherichia coli lac repressor. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 17;17(21):4480–4486. doi: 10.1021/bi00614a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]