Abstract
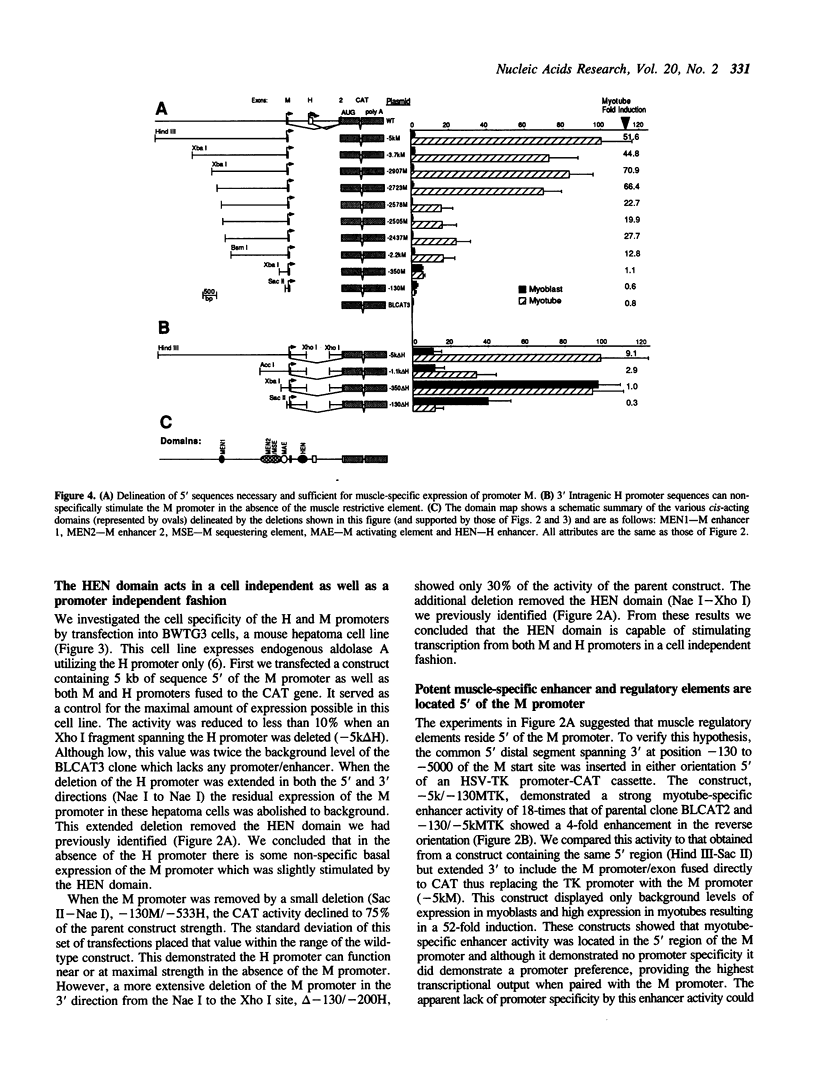
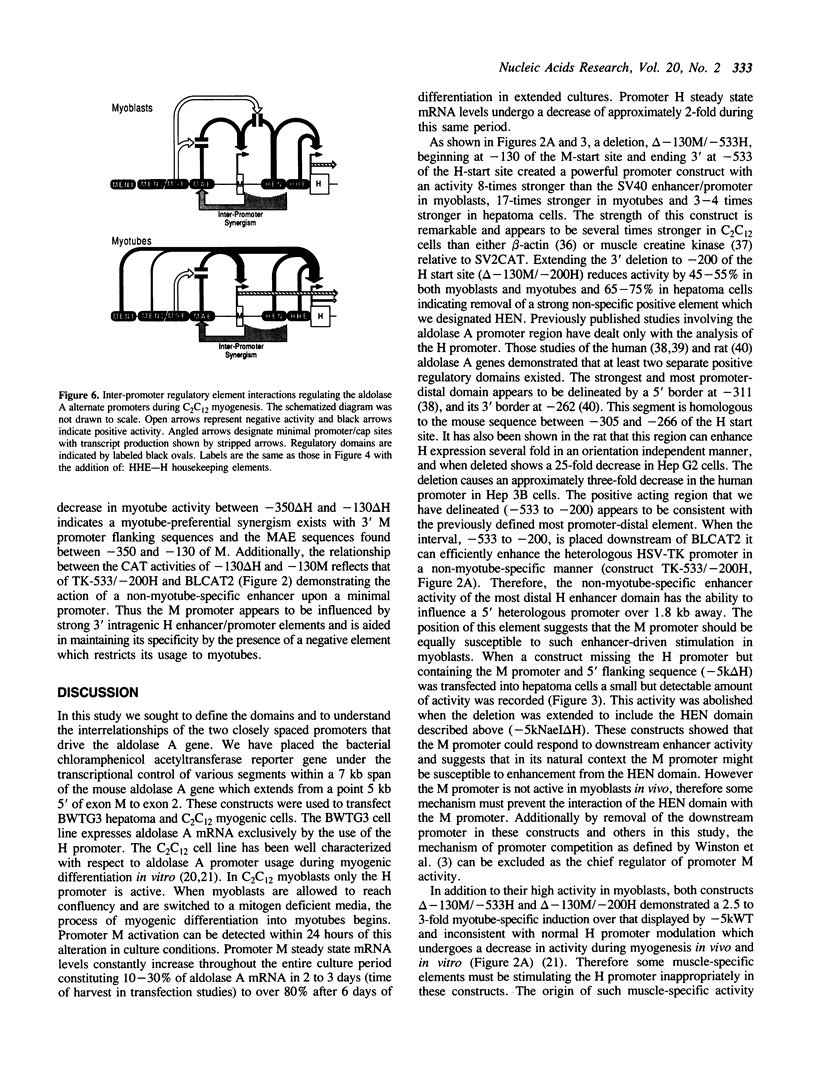
The mouse aldolase A gene contains two closely-spaced alternate promoter/first exons. The more distal of the two, the M promoter, is muscle-specific while the 3' promoter, the H promoter, is expressed constitutively. Various segments from these promoter regions were linked to a reporter gene and used to transfect the myogenic cell line C2C12 and the hepatoma cell line BWTG3. A muscle-specific enhancer, MEN1, responsible for 80% of promoter M activity and containing 4 consensus MyoD binding sites was localized between -2578 to -2723 of the M promoter. Another muscle-specific enhancer and a restrictive element, MEN2/MSE, were found in the interval -1100 to -350. The MSE restrictive element was found to prohibit inappropriate up-regulation of the M promoter by selectively sequestering it from H promoter elements in both myoblasts and myotubes. Among the H promoter elements was found an enhancer, HEN, situated between -533 and -200 which did not function in myotubes. These studies also show that H promoter elements can act synergistically with a non-specific element, MAE, located between -350 and -130 of the M cap site greatly stimulating M promoter transcription in all cell types when the MSE restrictive element was absent. Through the analysis of interactions between these elements and the aldolase A and HSV-TK promoters we showed that neither the enhancers nor the promoter proximal sequences by themselves contain adequate information to reproduce the native pattern of aldolase A promoter modulation. Rather, the sequestering of the M promoter by the MSE restrictive element and the relative positioning and context of promoters M and H appear critical to the regulated expression of aldolase A.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin T. J., Burden S. J. Muscle-specific gene expression controlled by a regulatory element lacking a MyoD1-binding site. Nature. 1989 Oct 26;341(6244):716–720. doi: 10.1038/341716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benyajati C., Spoerel N., Haymerle H., Ashburner M. The messenger RNA for alcohol dehydrogenase in Drosophila melanogaster differs in its 5' end in different developmental stages. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90341-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau H. M., Chiu C. P., Webster C. Cytoplasmic activation of human nuclear genes in stable heterocaryons. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1171–1180. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90300-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvagnet P. F., Strehler E. E., White G. E., Strehler-Page M. A., Nadal-Ginard B., Mahdavi V. Multiple positive and negative 5' regulatory elements control the cell-type-specific expression of the embryonic skeletal myosin heavy-chain gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4377–4389. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chretien S., Dubart A., Beaupain D., Raich N., Grandchamp B., Rosa J., Goossens M., Romeo P. H. Alternative transcription and splicing of the human porphobilinogen deaminase gene result either in tissue-specific or in housekeeping expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):6–10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbert M. C., Ciejek-Baez E. Alternative promoter usage by aldolase A during in vitro myogenesis. Dev Biol. 1988 Nov;130(1):392–396. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90444-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbert M. C., Ciejek-Baez E. The proximal promoter of the aldolase A gene remains active during myogenesis in vitro and muscle development in vivo. Dev Biol. 1992 Jan;149(1):66–79. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90264-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin V., Maniatis T. Role of transcriptional interference in the Drosophila melanogaster Adh promoter switch. Nature. 1989 Jan 19;337(6204):279–282. doi: 10.1038/337279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devlin B. H., Wefald F. C., Kraus W. E., Bernard T. S., Williams R. S. Identification of a muscle-specific enhancer within the 5'-flanking region of the human myoglobin gene. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13896–13901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoghue M., Ernst H., Wentworth B., Nadal-Ginard B., Rosenthal N. A muscle-specific enhancer is located at the 3' end of the myosin light-chain 1/3 gene locus. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1779–1790. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., DeChiara T., Efstratiadis A. A promoter of the rat insulin-like growth factor II gene consists of minimal control elements. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jan 5;199(1):61–81. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90379-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forry-Schaudies S., Maihle N. J., Hughes S. H. Generation of skeletal, smooth and low molecular weight non-muscle tropomyosin isoforms from the chicken tropomyosin 1 gene. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jan 20;211(2):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90354-O. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahlmann R., Kedes L. Cloning, structural analysis, and expression of the human fast twitch skeletal muscle troponin C gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12520–12528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautron S., Maire P., Hakim V., Kahn A. Regulation of the multiple promoters of the human aldolase A gene: response of its two ubiquitous promoters to agents promoting cell proliferation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 25;19(4):767–774. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.4.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossett L. A., Kelvin D. J., Sternberg E. A., Olson E. N. A new myocyte-specific enhancer-binding factor that recognizes a conserved element associated with multiple muscle-specific genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5022–5033. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Leavitt J., Muscat G., Ng S. Y., Kedes L. A human beta-actin expression vector system directs high-level accumulation of antisense transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4831–4835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. V., Jacob P. E., Ringold G. M., Lee F. Expression and regulation of Escherichia coli lacZ gene fusions in mammalian cells. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(1):101–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanke P. D., Storti R. V. The Drosophila melanogaster tropomyosin II gene produces multiple proteins by use of alternative tissue-specific promoters and alternative splicing. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3591–3602. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschman J. E., Durbin K. J., Winston F. Genetic evidence for promoter competition in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4608–4615. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horlick R. A., Hobson G. M., Patterson J. H., Mitchell M. T., Benfield P. A. Brain and muscle creatine kinase genes contain common TA-rich recognition protein-binding regulatory elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4826–4836. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M. T., Gorman C. M. Intervening sequences increase efficiency of RNA 3' processing and accumulation of cytoplasmic RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):937–947. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izzo P., Costanzo P., Lupo A., Rippa E., Paolella G., Salvatore F. Human aldolase A gene. Structural organization and tissue-specific expression by multiple promoters and alternate mRNA processing. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jul 1;174(4):569–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14136.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izzo P., Costanzo P., Lupo A., Rippa E., Salvatore F. In vivo activity of the most proximal promoter of the human aldolase A gene and analysis of transcriptional control elements. FEBS Lett. 1989 Oct 23;257(1):75–80. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81790-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joh K., Arai Y., Mukai T., Hori K. Expression of three mRNA species from a single rat aldolase A gene, differing in their 5' non-coding regions. J Mol Biol. 1986 Aug 5;190(3):401–410. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. C., Rigby P. W., Ziff E. B. Trans-acting protein factors and the regulation of eukaryotic transcription: lessons from studies on DNA tumor viruses. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):267–281. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadesch T., Berg P. Effects of the position of the simian virus 40 enhancer on expression of multiple transcription units in a single plasmid. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2593–2601. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konieczny S. F., Emerson C. P., Jr Complex regulation of the muscle-specific contractile protein (troponin I) gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3065–3075. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korch C. Cross index for improving cloning selectivity by partially filling in 5'-extensions of DNA produced by type II restriction endonucleases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 24;15(8):3199–3220. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.8.3199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., Adashi E. Y., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Isolation of a recombinant copy of the gene encoding C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):786–800. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Buskin J. N., Lockshon D., Davis R. L., Apone S., Hauschka S. D., Weintraub H. MyoD is a sequence-specific DNA binding protein requiring a region of myc homology to bind to the muscle creatine kinase enhancer. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):823–831. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90935-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaigre F. P., Durviaux S. M., Rousseau G. G. Identification of regulatory sequences and protein-binding sites in the liver-type promoter of a gene encoding 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):1099–1106. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.1099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H., Yutzey K. E., Konieczny S. F. Muscle-specific expression of the troponin I gene requires interactions between helix-loop-helix muscle regulatory factors and ubiquitous transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):267–280. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo X. C., Kim K. H. An enhancer element in the house-keeping promoter for acetyl-CoA carboxylase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 11;18(11):3249–3254. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.11.3249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maire P., Gautron S., Hakim V., Gregori C., Mennecier F., Kahn A. Characterization of three optional promoters in the 5' region of the human aldolase A gene. J Mol Biol. 1987 Oct 5;197(3):425–438. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90556-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mar J. H., Ordahl C. P. A conserved CATTCCT motif is required for skeletal muscle-specific activity of the cardiac troponin T gene promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6404–6408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestek A., Stauffer J., Tolan D. R., Ciejek-Baez E. Sequence of a mouse brain aldolase A cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10595–10595. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukai T., Arai Y., Yatsuki H., Joh K., Hori K. An additional promoter functions in the human aldolase A gene, but not in rat. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Feb 14;195(3):781–787. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15766.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muscat G. E., Kedes L. Multiple 5'-flanking regions of the human alpha-skeletal actin gene synergistically modulate muscle-specific expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4089–4099. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J. Transcriptional interference and termination between duplicated alpha-globin gene constructs suggests a novel mechanism for gene regulation. Nature. 1986 Aug 7;322(6079):562–565. doi: 10.1038/322562a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renkawitz R. Transcriptional repression in eukaryotes. Trends Genet. 1990 Jun;6(6):192–197. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90176-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber E., Schaffner W. Long-range activation of transcription by SV40 enhancer is affected by "inhibitory" or "permissive" DNA sequences between enhancer and promoter. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1989 Nov;15(6):591–603. doi: 10.1007/BF01534920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B., Sheen J. Y. A simple phase-extraction assay for chloramphenicol acyltransferase activity. Gene. 1988 Jul 30;67(2):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90403-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauffer J. K., Colbert M. C., Ciejek-Baez E. Nonconservative utilization of aldolase A alternative promoters. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11773–11782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg E. A., Spizz G., Perry M. E., Olson E. N. A ras-dependent pathway abolishes activity of a muscle-specific enhancer upstream from the muscle creatine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):594–601. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strehler E. E., Periasamy M., Strehler-Page M. A., Nadal-Ginard B. Myosin light-chain 1 and 3 gene has two structurally distinct and differentially regulated promoters evolving at different rates. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3168–3182. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szpirer C., Szpirer J. A mouse hepatoma cell line which secretes several serum proteins including albumin and alpha-foetoprotein. Differentiation. 1975 Oct 16;4(2):85–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1975.tb01446.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X. M., Tsay H. J., Schmidt J. Expression of the acetylcholine receptor delta-subunit gene in differentiating chick muscle cells is activated by an element that contains two 16 bp copies of a segment of the alpha-subunit enhancer. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):783–790. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08174.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Davis R., Lockshon D., Lassar A. MyoD binds cooperatively to two sites in a target enhancer sequence: occupancy of two sites is required for activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5623–5627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wentworth B. M., Donoghue M., Engert J. C., Berglund E. B., Rosenthal N. Paired MyoD-binding sites regulate myosin light chain gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1242–1246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R., Urlaub G., Chasin L. DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Y. T., Nadal-Ginard B. Interaction of nuclear proteins with a positive cis-acting element of rat embryonic myosin heavy-chain promoter: identification of a new transcriptional factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):1839–1849. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.1839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yutzey K. E., Kline R. L., Konieczny S. F. An internal regulatory element controls troponin I gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1397–1405. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



