Abstract
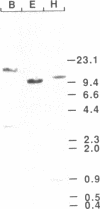
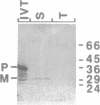
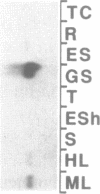
A cDNA encoding a nuclear-encoded chloroplast nucleic acid-binding protein (NBP) has been isolated from maize. Identified as an in vitro DNA-binding activity, NBP belongs to a family of nuclear-encoded chloroplast proteins which share a common domain structure and are thought to be involved in posttranscriptional regulation of chloroplast gene expression. NBP contains an N-terminal chloroplast transit peptide, a highly acidic domain and a pair of ribonucleoprotein consensus sequence domains. NBP is expressed in a light-dependent, organ-specific manner which is consistent with its involvement in chloroplast biogenesis. The relationship of NBP to the other members of this protein family and their possible regulatory functions are discussed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams C. C., Stern D. B. Control of mRNA stability in chloroplasts by 3' inverted repeats: effects of stem and loop mutations on degradation of psbA mRNA in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6003–6010. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandziulis R. J., Swanson M. S., Dreyfuss G. RNA-binding proteins as developmental regulators. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):431–437. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkan A. Proteins encoded by a complex chloroplast transcription unit are each translated from both monocistronic and polycistronic mRNAs. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2637–2644. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03116.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkan A. Tissue-dependent plastid RNA splicing in maize: transcripts from four plastid genes are predominantly unspliced in leaf meristems and roots. Plant Cell. 1989 Apr;1(4):437–445. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.4.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blowers A. D., Ellmore G. S., Klein U., Bogorad L. Transcriptional analysis of endogenous and foreign genes in chloroplast transformants of Chlamydomonas. Plant Cell. 1990 Nov;2(11):1059–1070. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.11.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr B., Burr F. A., Thompson K. H., Albertson M. C., Stuber C. W. Gene mapping with recombinant inbreds in maize. Genetics. 1988 Mar;118(3):519–526. doi: 10.1093/genetics/118.3.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng X. W., Gruissem W. Constitutive transcription and regulation of gene expression in non-photosynthetic plastids of higher plants. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3301–3308. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03200.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng X. W., Gruissem W. Control of plastid gene expression during development: the limited role of transcriptional regulation. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):379–387. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90290-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng X. W., Stern D. B., Tonkyn J. C., Gruissem W. Plastid run-on transcription. Application to determine the transcriptional regulation of spinach plastid genes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9641–9648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng X. W., Tonkyn J. C., Peter G. F., Thornber J. P., Gruissem W. Post-transcriptional control of plastid mRNA accumulation during adaptation of chloroplasts to different light quality environments. Plant Cell. 1989 Jun;1(6):645–654. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.6.645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruissem W. Chloroplast gene expression: how plants turn their plastids on. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):161–170. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90889-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruissem W., Zurawski G. Analysis of promoter regions for the spinach chloroplast rbcL, atpB and psbA genes. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3375–3383. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04093.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffner M. H., Chin M. B., Lane B. G. Wheat embryo ribonucleates. XII. Formal characterization of terminal and penultimate nucleoside residues at the 5'-ends of "capped" RNA from imbibing wheat embryos. Can J Biochem. 1978 Jul;56(7):729–733. doi: 10.1139/o78-109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haley J., Bogorad L. Alternative promoters are used for genes within maize chloroplast polycistronic transcription units. Plant Cell. 1990 Apr;2(4):323–333. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.4.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosler J. P., Wurtz E. A., Harris E. H., Gillham N. W., Boynton J. E. Relationship between Gene Dosage and Gene Expression in the Chloroplast of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 1989 Oct;91(2):648–655. doi: 10.1104/pp.91.2.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen K. H., Herrin D. L., Plumley F. G., Schmidt G. W. Biogenesis of photosystem II complexes: transcriptional, translational, and posttranslational regulation. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1315–1325. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaff P., Gruissem W. Changes in Chloroplast mRNA Stability during Leaf Development. Plant Cell. 1991 May;3(5):517–529. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.5.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchka M. R., Goldschmidt-Clermont M., van Dillewijn J., Rochaix J. D. Mutation at the Chlamydomonas nuclear NAC2 locus specifically affects stability of the chloroplast psbD transcript encoding polypeptide D2 of PS II. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):869–876. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90939-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kück U., Choquet Y., Schneider M., Dron M., Bennoun P. Structural and transcription analysis of two homologous genes for the P700 chlorophyll a-apoproteins in Chlamydomonas reinhardii: evidence for in vivo trans-splicing. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2185–2195. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02489.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leto K. J., Bell E., McIntosh L. Nuclear mutation leads to an accelerated turnover of chloroplast-encoded 48 kd and 34.5 kd polypeptides in thylakoids lacking photosystem II. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1645–1653. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03832.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. Q., Sugiura M. Three distinct ribonucleoproteins from tobacco chloroplasts: each contains a unique amino terminal acidic domain and two ribonucleoprotein consensus motifs. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3059–3066. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07502.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W. A binding consensus: RNA-protein interactions in splicing, snRNPs, and sex. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90164-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullet J. E., Klein R. R. Transcription and RNA stability are important determinants of higher plant chloroplast RNA levels. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1571–1579. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02402.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai K., Oubridge C., Jessen T. H., Li J., Evans P. R. Crystal structure of the RNA-binding domain of the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein A. Nature. 1990 Dec 6;348(6301):515–520. doi: 10.1038/348515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieto-Sotelo J., Vierling E., Ho T. H. Cloning, sequence analysis, and expression of a cDNA encoding a plastid-localized heat shock protein in maize. Plant Physiol. 1990 Aug;93(4):1321–1328. doi: 10.1104/pp.93.4.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Query C. C., Bentley R. C., Keene J. D. A common RNA recognition motif identified within a defined U1 RNA binding domain of the 70K U1 snRNP protein. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):89–101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90175-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochaix J. D., Erickson J. Function and assembly of photosystem II: genetic and molecular analysis. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Feb;13(2):56–59. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90029-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherly D., Boelens W., Dathan N. A., van Venrooij W. J., Mattaj I. W. Major determinants of the specificity of interaction between small nuclear ribonucleoproteins U1A and U2B'' and their cognate RNAs. Nature. 1990 Jun 7;345(6275):502–506. doi: 10.1038/345502a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster G., Gruissem W. Chloroplast mRNA 3' end processing requires a nuclear-encoded RNA-binding protein. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1493–1502. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07669.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieburth L. E., Berry-Lowe S., Schmidt G. W. Chloroplast RNA Stability in Chlamydomonas: Rapid Degradation of psbB and psbC Transcripts in Two Nuclear Mutants. Plant Cell. 1991 Feb;3(2):175–189. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.2.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Clerc R. G., LeBowitz J. H. Molecular cloning of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins using recognition site probes. Biotechniques. 1989 Mar;7(3):252–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. B., Gruissem W. Chloroplast mRNA 3' end maturation is biochemically distinct from prokaryotic mRNA processing. Plant Mol Biol. 1989 Dec;13(6):615–625. doi: 10.1007/BF00016017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. B., Gruissem W. Control of plastid gene expression: 3' inverted repeats act as mRNA processing and stabilizing elements, but do not terminate transcription. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1145–1157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90600-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. B., Jones H., Gruissem W. Function of plastid mRNA 3' inverted repeats. RNA stabilization and gene-specific protein binding. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18742–18750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. B., Radwanski E. R., Kindle K. L. A 3' stem/loop structure of the Chlamydomonas chloroplast atpB gene regulates mRNA accumulation in vivo. Plant Cell. 1991 Mar;3(3):285–297. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.3.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surowy C. S., van Santen V. L., Scheib-Wixted S. M., Spritz R. A. Direct, sequence-specific binding of the human U1-70K ribonucleoprotein antigen protein to loop I of U1 small nuclear RNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4179–4186. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. J., Mosig G. Stimulation of a Chlamydomonas chloroplast promoter by novobiocin in situ and in E. coli implies regulation by torsional stress in the chloroplast DNA. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):281–287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90431-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. C., Howard E. A., Dennis E. S., Peacock W. J. DNA sequences required for anaerobic expression of the maize alcohol dehydrogenase 1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6624–6628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G., Nishikawa K. Chloroplast transit peptides. The perfect random coil? FEBS Lett. 1991 Jan 14;278(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80069-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]