Abstract
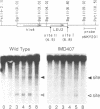
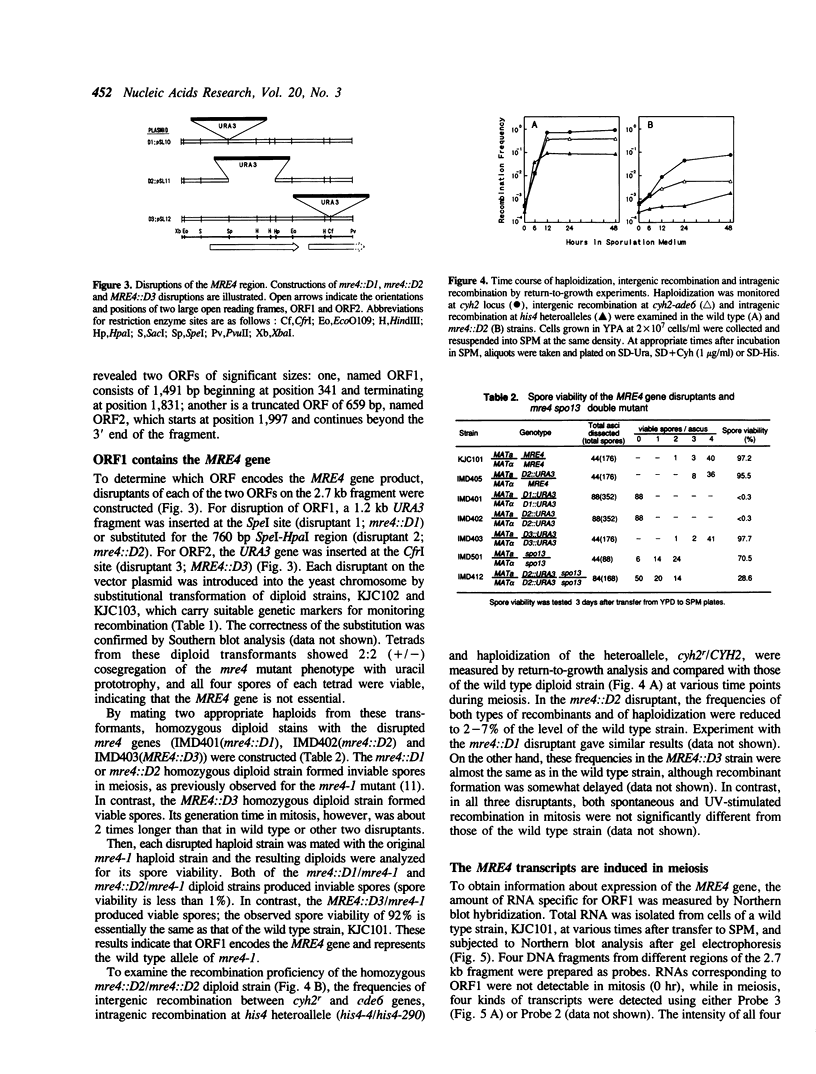
The MRE4 gene was cloned by complementation of the defects of meiotic recombination and haploidization in an mre4-1 mutant. Disruption of MRE4 resulted in reduced meiotic recombination and spore inviability. The mre4 spore lethality can be suppressed by spo13, a mutation that causes cells to bypass the reductional division. Analysis of meiotic DNA extracted from the mre4 mutant cells revealed that double-strand breaks occurred at the two sites of the HIS4-LEU2 recombination hot spot, but at a frequency of about 10-20% of the wild type. Northern blot analysis indicated that the MRE4 gene produces four transcripts of 1.63, 3.2, 4.0 and 6.2 kb. All of these transcripts are absent from mitotic cells and are meiotically induced. The DNA sequence of the MRE4 open reading frame predicts a 497-amino acids protein with a molecular mass of 56.8 kDa. The Mre4 protein contains highly conserved amino acid sequences found specifically in serine-threonine protein kinases. These results suggest that protein phosphorylation is required directly or indirectly for meiotic recombination.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alani E., Padmore R., Kleckner N. Analysis of wild-type and rad50 mutants of yeast suggests an intimate relationship between meiotic chromosome synapsis and recombination. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):419–436. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90524-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker B. S., Carpenter A. T., Esposito M. S., Esposito R. E., Sandler L. The genetic control of meiosis. Annu Rev Genet. 1976;10:53–134. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.10.120176.000413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. K., Kennedy M. B. Deduced primary structure of the beta subunit of brain type II Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase determined by molecular cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1794–1798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckingham L. E., Wang H. T., Elder R. T., McCarroll R. M., Slater M. R., Esposito R. E. Nucleotide sequence and promoter analysis of SPO13, a meiosis-specific gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9406–9410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao L., Alani E., Kleckner N. A pathway for generation and processing of double-strand breaks during meiotic recombination in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1089–1101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90072-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Botstein D. Two differentially regulated mRNAs with different 5' ends encode secreted with intracellular forms of yeast invertase. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90384-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engebrecht J., Hirsch J., Roeder G. S. Meiotic gene conversion and crossing over: their relationship to each other and to chromosome synapsis and segregation. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):927–937. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90267-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engebrecht J., Roeder G. S. MER1, a yeast gene required for chromosome pairing and genetic recombination, is induced in meiosis. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2379–2389. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engebrecht J., Roeder G. S. Yeast mer1 mutants display reduced levels of meiotic recombination. Genetics. 1989 Feb;121(2):237–247. doi: 10.1093/genetics/121.2.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito M. S., Esposito R. E. The genetic control of sporulation in Saccharomyces. I. The isolation of temperature-sensitive sporulation-deficient mutants. Genetics. 1969 Jan;61(1):79–89. doi: 10.1093/genetics/61.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgiev O. I., Nikolaev N., Hadjiolov A. A., Skryabin K. G., Zakharyev V. M., Bayev A. A. The structure of the yeast ribosomal RNA genes. 4. Complete sequence of the 25 S rRNA gene from Saccharomyces cerevisae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6953–6958. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Mason T. Heme regulates transcription of the CYC1 gene of S. cerevisiae via an upstream activation site. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1279–1286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90309-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn S., Hoar E. T., Guarente L. Each of three "TATA elements" specifies a subset of the transcription initiation sites at the CYC-1 promoter of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8562–8566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M. Protein kinase catalytic domain sequence database: identification of conserved features of primary structure and classification of family members. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:38–62. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00126-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra M. F., DeMaggio A. J., Dhillon N. Genetically identified protein kinases in yeast. II: DNA metabolism and meiosis. Trends Genet. 1991 Sep;7(9):293–297. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90311-D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra M. F., Demaggio A. J., Dhillon N. Genetically identified protein kinases in yeast. I: Transcription, translation, transport and mating. Trends Genet. 1991 Aug;7(8):256–261. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90325-K. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingsworth N. M., Byers B. HOP1: a yeast meiotic pairing gene. Genetics. 1989 Mar;121(3):445–462. doi: 10.1093/genetics/121.3.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingsworth N. M., Goetsch L., Byers B. The HOP1 gene encodes a meiosis-specific component of yeast chromosomes. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):73–84. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90216-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapholz S., Esposito R. E. Recombination and chromosome segregation during the single division meiosis in SPO12-1 and SPO13-1 diploids. Genetics. 1980 Nov;96(3):589–611. doi: 10.1093/genetics/96.3.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapholz S., Waddell C. S., Esposito R. E. The role of the SPO11 gene in meiotic recombination in yeast. Genetics. 1985 Jun;110(2):187–216. doi: 10.1093/genetics/110.2.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovari L., Sumrada R., Kovari I., Cooper T. G. Multiple positive and negative cis-acting elements mediate induced arginase (CAR1) gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5087–5097. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford C. J., Klinz F. J., Donath C., Gallwitz D. Point mutations identify the conserved, intron-contained TACTAAC box as an essential splicing signal sequence in yeast. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):645–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90344-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lörincz A. T., Reed S. I. Primary structure homology between the product of yeast cell division control gene CDC28 and vertebrate oncogenes. Nature. 1984 Jan 12;307(5947):183–185. doi: 10.1038/307183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malavasic M. J., Elder R. T. Complementary transcripts from two genes necessary for normal meiosis in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2809–2819. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malone R. E., Esposito R. E. Recombinationless meiosis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;1(10):891–901. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.10.891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Wahl G. Hybridization of nucleic acids immobilized on solid supports. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90808-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menees T. M., Roeder G. S. MEI4, a yeast gene required for meiotic recombination. Genetics. 1989 Dec;123(4):675–682. doi: 10.1093/genetics/123.4.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagawa F., Fink G. R. The relationship between the "TATA" sequence and transcription initiation sites at the HIS4 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8557–8561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Fujii T., Ogita K., Kikkawa U., Igarashi K., Nishizuka Y. The structure, expression, and properties of additional members of the protein kinase C family. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6927–6932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padmore R., Cao L., Kleckner N. Temporal comparison of recombination and synaptonemal complex formation during meiosis in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1239–1256. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90046-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson M., Sclafani R. A., Fangman W. L., Rosamond J. Molecular characterization of cell cycle gene CDC7 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1590–1598. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikielny C. W., Teem J. L., Rosbash M. Evidence for the biochemical role of an internal sequence in yeast nuclear mRNA introns: implications for U1 RNA and metazoan mRNA splicing. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):395–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90373-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rockmill B., Roeder G. S. Meiosis in asynaptic yeast. Genetics. 1990 Nov;126(3):563–574. doi: 10.1093/genetics/126.3.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rockmill B., Roeder G. S. RED1: a yeast gene required for the segregation of chromosomes during the reductional division of meiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6057–6061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. D., Novick P., Thomas J. H., Botstein D., Fink G. R. A Saccharomyces cerevisiae genomic plasmid bank based on a centromere-containing shuttle vector. Gene. 1987;60(2-3):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90232-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R., Fogel S. A system selective for yeast mutants deficient in meiotic recombination. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;112(4):295–305. doi: 10.1007/BF00334431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubtsov P. M., Musakhanov M. M., Zakharyev V. M., Krayev A. S., Skryabin K. G., Bayev A. A. The structure of the yeast ribosomal RNA genes. I. The complete nucleotide sequence of the 18S ribosomal RNA gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 11;8(23):5779–5794. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.23.5779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoji S., Ericsson L. H., Walsh K. A., Fischer E. H., Titani K. Amino acid sequence of the catalytic subunit of bovine type II adenosine cyclic 3',5'-phosphate dependent protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1983 Jul 19;22(15):3702–3709. doi: 10.1021/bi00284a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumrada R. A., Cooper T. G. Point mutation generates constitutive expression of an inducible eukaryotic gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):643–647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumrada R. A., Cooper T. G. Ubiquitous upstream repression sequences control activation of the inducible arginase gene in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):3997–4001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.3997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun H., Treco D., Schultes N. P., Szostak J. W. Double-strand breaks at an initiation site for meiotic gene conversion. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):87–90. doi: 10.1038/338087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. S. cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Model for an enzyme family. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8443–8446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson E. A., Roeder G. S. Expression and DNA sequence of RED1, a gene required for meiosis I chromosome segregation in yeast. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Aug;218(2):293–301. doi: 10.1007/BF00331281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Cameron S., Sass P., Zoller M., Wigler M. Three different genes in S. cerevisiae encode the catalytic subunits of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90223-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. F., Zitomer R. S. A positive regulatory site and a negative regulatory site control the expression of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae CYC7 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):2023–2030. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.2023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
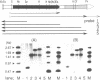
- Yoshida M., Kawaguchi H., Sakata Y., Kominami K., Hirano M., Shima H., Akada R., Yamashita I. Initiation of meiosis and sporulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae requires a novel protein kinase homologue. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Apr;221(2):176–186. doi: 10.1007/BF00261718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Sherman F. DNA sequence required for efficient transcription termination in yeast. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]