Abstract
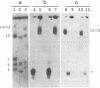
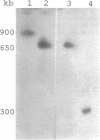
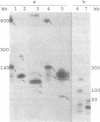
We describe a chromosome translocation in a karyotype mutant of the rodent malarial parasite Plasmodium berghei. In this mutant (named EP) a small chromosome (chromosome 7), which has exhibited a size range between 0.9 and 1.4 Mb in other clones of P. berghei, is translocated to chromosome 13 or 14 with a size of about 3 Mb. By comparison of Apa-I restriction fragments of the chromosomes from mutant EP and from a reference clone (named HP) of P. berghei, we found evidence for a junction of subtelomeric chromosome 7 sequences and internal chromosome 13/14 sequences. In addition, a new chromosome of 1.4 Mb (named EP7) is present in mutant EP, which is (mainly) composed of sequences of chromosome 13/14. EP7 contains one telomeric region derived from chromosome 13/14. We found evidence that internal sequences of chromosome 13/14 are joined to telomeric sequences in the other telomeric region of EP7. The karyotype of mutant EP was stable during asexual and sexual multiplication and we found no indications for phenotypic changes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Corcoran L. M., Thompson J. K., Walliker D., Kemp D. J. Homologous recombination within subtelomeric repeat sequences generates chromosome size polymorphisms in P. falciparum. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):807–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90097-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowman A. F., Lew A. M. Antifolate drug selection results in duplication and rearrangement of chromosome 7 in Plasmodium chabaudi. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5182–5188. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dame J. B., McCutchan T. F. The four ribosomal DNA units of the malaria parasite Plasmodium berghei. Identification, restriction map, and copy number analysis. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6984–6990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dore E., Pace T., Ponzi M., Picci L., Frontali C. Organization of subtelomeric repeats in Plasmodium berghei. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2423–2427. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foote S. J., Thompson J. K., Cowman A. F., Kemp D. J. Amplification of the multidrug resistance gene in some chloroquine-resistant isolates of P. falciparum. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):921–930. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90330-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janse C. J., Boorsma E. G., Ramesar J., Grobbee M. J., Mons B. Host cell specificity and schizogony of Plasmodium berghei under different in vitro conditions. Int J Parasitol. 1989 Aug;19(5):509–514. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(89)90080-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janse C. J., Boorsma E. G., Ramesar J., van Vianen P., van der Meer R., Zenobi P., Casaglia O., Mons B., van der Berg F. M. Plasmodium berghei: gametocyte production, DNA content, and chromosome-size polymorphisms during asexual multiplication in vivo. Exp Parasitol. 1989 Apr;68(3):274–282. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(89)90109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janse C. J., van der Klooster P. F., van der Kaay H. J., van der Ploeg M., Overdulve J. P. DNA synthesis in Plasmodium berghei during asexual and sexual development. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1986 Aug;20(2):173–182. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(86)90029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klar A. J. Determination of the yeast cell lineage. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):433–435. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90442-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mons B., Janse C. J., Boorsma E. G., Van der Kaay H. J. Synchronized erythrocytic schizogony and gametocytogenesis of Plasmodium berghei in vivo and in vitro. Parasitology. 1985 Dec;91(Pt 3):423–430. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000062673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace T., Ponzi M., Dore E., Frontali C. Telomeric motifs are present in a highly repetitive element in the Plasmodium berghei genome. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Jun;24(2):193–202. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90106-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace T., Ponzi M., Dore E., Janse C., Mons B., Frontali C. Long insertions within telomeres contribute to chromosome size polymorphism in Plasmodium berghei. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6759–6764. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patarapotikul J., Langsley G. Chromosome size polymorphism in Plasmodium falciparum can involve deletions of the subtelomeric pPFrep20 sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 25;16(10):4331–4340. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.10.4331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pays E. Expression of variant-specific antigen genes in African trypanosomes. Biol Cell. 1988;64(2):121–130. doi: 10.1016/0248-4900(88)90071-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pologe L. G., Ravetch J. V. A chromosomal rearrangement in a P. falciparum histidine-rich protein gene is associated with the knobless phenotype. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):474–477. doi: 10.1038/322474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pologe L. G., Ravetch J. V. Large deletions result from breakage and healing of P. falciparum chromosomes. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):869–874. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90142-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pologe L. G., de Bruin D., Ravetch J. V. A and T homopolymeric stretches mediate a DNA inversion in Plasmodium falciparum which results in loss of gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3243–3246. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponzi M., Janse C. J., Dore E., Scotti R., Pace T., Reterink T. J., van der Berg F. M., Mons B. Generation of chromosome size polymorphism during in vivo mitotic multiplication of Plasmodium berghei involves both loss and addition of subtelomeric repeat sequences. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1990 Jun;41(1):73–82. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(90)90098-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponzi M., Pace T., Dore E., Frontali C. Identification of a telomeric DNA sequence in Plasmodium berghei. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2991–2995. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04034.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V. Chromosomal polymorphisms and gene expression in Plasmodium falciparum. Exp Parasitol. 1989 Jan;68(1):121–125. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(89)90018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinnis P., Wellems T. E. Long-range restriction maps of Plasmodium falciparum chromosomes: crossingover and size variation among geographically distant isolates. Genomics. 1988 Nov;3(4):287–295. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90117-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernick K. D., Walliker D., McCutchan T. F. Genetic hypervariability of telomere-related sequences is associated with meiosis in Plasmodium falciparum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14B):6973–6985. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.6973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walliker D., Quakyi I. A., Wellems T. E., McCutchan T. F., Szarfman A., London W. T., Corcoran L. M., Burkot T. R., Carter R. Genetic analysis of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Science. 1987 Jun 26;236(4809):1661–1666. doi: 10.1126/science.3299700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellems T. E., Walliker D., Smith C. L., do Rosario V. E., Maloy W. L., Howard R. J., Carter R., McCutchan T. F. A histidine-rich protein gene marks a linkage group favored strongly in a genetic cross of Plasmodium falciparum. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):633–642. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90539-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesseling J. G., de Ree J. M., Ponnudurai T., Smits M. A., Schoenmakers J. G. Nucleotide sequence and deduced amino acid sequence of a Plasmodium falciparum actin gene. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Jan 15;27(2-3):313–320. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90051-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]