Abstract
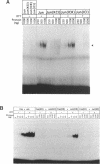
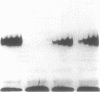
The Fos and Jun family of transcription factors contain an invariant sequence motif lysine-cysteine-arginine (KCR) in the highly conserved DNA-binding region. Reduction of the cysteine residue is necessary to facilitate DNA-binding. Here, we examined the potential dual roles of the flanking lysine and arginine residues in influencing the redox reactivity of the cysteine and the DNA-binding activity of Fos and Jun. Two sets of Fos and Jun mutants were generated: the KCR and KSR series representing proteins capable of redox-dependent and redox-independent DNA-binding activity, respectively. Mutation of the lysine in Fos-Jun heterodimers had no obvious effect on the redox reactivity of the cysteine, suggesting that lysine is not essential in this respect. However, mutation of the arginine but not lysine, in both the KCR and the KSR series abolished DNA-binding activity. Thus, the arginine but not the lysine residue in the KCR motif is critical for both redox-dependent and redox-independent functions in DNA-binding. Surprisingly, the triple substitution, ISI, exhibited high levels of DNA-binding activity. This demonstrates that the effects of amino acid substitutions can be highly dependent on context and that non-basic amino acids can function efficiently in DNA-binding. Analysis of combinations of wild-type and mutant Fos and Jun proteins indicated that Fos was dominant in dictating the DNA-binding ability of Fos-Jun heterodimers. This suggests that the lysine and arginine residues in the KCR region of Fos are not equivalent to those in Jun and that they interact with DNA differently.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abate C., Baker S. J., Lees-Miller S. P., Anderson C. W., Marshak D. R., Curran T. Dimerization and DNA binding alter phosphorylation of Fos and Jun. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6766–6770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abate C., Luk D., Curran T. A ubiquitous nuclear protein stimulates the DNA-binding activity of fos and jun indirectly. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Oct;1(10):455–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abate C., Luk D., Curran T. Transcriptional regulation by Fos and Jun in vitro: interaction among multiple activator and regulatory domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3624–3632. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abate C., Luk D., Gentz R., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Curran T. Expression and purification of the leucine zipper and DNA-binding domains of Fos and Jun: both Fos and Jun contact DNA directly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1032–1036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abate C., Marshak D. R., Curran T. Fos is phosphorylated by p34cdc2, cAMP-dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C at multiple sites clustered within regulatory regions. Oncogene. 1991 Dec;6(12):2179–2185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abate C., Patel L., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Curran T. Redox regulation of fos and jun DNA-binding activity in vitro. Science. 1990 Sep 7;249(4973):1157–1161. doi: 10.1126/science.2118682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. J., Kerppola T. K., Luk D., Vandenberg M. T., Marshak D. R., Curran T., Abate C. Jun is phosphorylated by several protein kinases at the same sites that are modified in serum-stimulated fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4694–4705. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., Smeal T., Defize L. H., Angel P., Woodgett J. R., Karin M., Hunter T. Activation of protein kinase C decreases phosphorylation of c-Jun at sites that negatively regulate its DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):573–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90241-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D., Kelly T. J., Jr Adenovirus DNA replication in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):655–659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chida K., Vogt P. K. Nuclear translocation of viral Jun but not of cellular Jun is cell cycle dependent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4290–4294. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu R., Angel P., Karin M. Jun-B differs in its biological properties from, and is a negative regulator of, c-Jun. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):979–986. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90754-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu R., Boyle W. J., Meek J., Smeal T., Hunter T., Karin M. The c-Fos protein interacts with c-Jun/AP-1 to stimulate transcription of AP-1 responsive genes. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):541–552. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90076-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Franza B. R., Jr Fos and Jun: the AP-1 connection. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):395–397. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellenberger T. E., Brandl C. J., Struhl K., Harrison S. C. The GCN4 basic region leucine zipper binds DNA as a dimer of uninterrupted alpha helices: crystal structure of the protein-DNA complex. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1223–1237. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentz R., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Abate C., Curran T. Parallel association of Fos and Jun leucine zippers juxtaposes DNA binding domains. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1695–1699. doi: 10.1126/science.2494702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T., Curran T. Cross-family dimerization of transcription factors Fos/Jun and ATF/CREB alters DNA binding specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3720–3724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain J., McCaffrey P. G., Valge-Archer V. E., Rao A. Nuclear factor of activated T cells contains Fos and Jun. Nature. 1992 Apr 30;356(6372):801–804. doi: 10.1038/356801a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K., Curran T. DNA bending by Fos and Jun: the flexible hinge model. Science. 1991 Nov 22;254(5035):1210–1214. doi: 10.1126/science.1957173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K., Curran T. Fos-Jun heterodimers and Jun homodimers bend DNA in opposite orientations: implications for transcription factor cooperativity. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):317–326. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90621-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K., Curran T. Selective DNA bending by a variety of bZIP proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5479–5489. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Tzamarias D., Ellenberger T., Harrison S. C., Struhl K. Adaptability at the protein-DNA interface is an important aspect of sequence recognition by bZIP proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4513–4517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzarides T., Ziff E. The role of the leucine zipper in the fos-jun interaction. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):646–651. doi: 10.1038/336646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovary K., Bravo R. Expression of different Jun and Fos proteins during the G0-to-G1 transition in mouse fibroblasts: in vitro and in vivo associations. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2451–2459. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The DNA binding domain of the rat liver nuclear protein C/EBP is bipartite. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1681–1688. doi: 10.1126/science.2494700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maki Y., Bos T. J., Davis C., Starbuck M., Vogt P. K. Avian sarcoma virus 17 carries the jun oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2848–2852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. I., Curran T. Stimulus-transcription coupling in the nervous system: involvement of the inducible proto-oncogenes fos and jun. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1991;14:421–451. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.14.030191.002225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu Y., Ryder K., Nathans D. DNA binding activities of three murine Jun proteins: stimulation by Fos. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):907–915. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90146-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuberg M., Schuermann M., Müller R. Mutagenesis of the DNA contact site in Fos protein: compatibility with the scissors grip model and requirement for transformation. Oncogene. 1991 Aug;6(8):1325–1333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neil K. T., Hoess R. H., DeGrado W. F. Design of DNA-binding peptides based on the leucine zipper motif. Science. 1990 Aug 17;249(4970):774–778. doi: 10.1126/science.2389143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea E. K., Rutkowski R., Stafford W. F., 3rd, Kim P. S. Preferential heterodimer formation by isolated leucine zippers from fos and jun. Science. 1989 Aug 11;245(4918):646–648. doi: 10.1126/science.2503872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuno H., Akahori A., Sato H., Xanthoudakis S., Curran T., Iba H. Escape from redox regulation enhances the transforming activity of Fos. Oncogene. 1993 Mar;8(3):695–701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel L., Abate C., Curran T. Altered protein conformation on DNA binding by Fos and Jun. Nature. 1990 Oct 11;347(6293):572–575. doi: 10.1038/347572a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins K. K., Admon A., Patel N., Tjian R. The Drosophila Fos-related AP-1 protein is a developmentally regulated transcription factor. Genes Dev. 1990 May;4(5):822–834. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.5.822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulverer B. J., Kyriakis J. M., Avruch J., Nikolakaki E., Woodgett J. R. Phosphorylation of c-jun mediated by MAP kinases. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):670–674. doi: 10.1038/353670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Cohen D. R., Curran T., Bos T. J., Vogt P. K., Bohmann D., Tjian R., Franza B. R., Jr Fos-associated protein p39 is the product of the jun proto-oncogene. Science. 1988 May 20;240(4855):1010–1016. doi: 10.1126/science.3130660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Sambucetti L. C., Curran T., Distel R. J., Spiegelman B. M. Common DNA binding site for Fos protein complexes and transcription factor AP-1. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):471–480. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risse G., Jooss K., Neuberg M., Brüller H. J., Müller R. Asymmetrical recognition of the palindromic AP1 binding site (TRE) by Fos protein complexes. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3825–3832. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08560.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryseck R. P., Bravo R. c-JUN, JUN B, and JUN D differ in their binding affinities to AP-1 and CRE consensus sequences: effect of FOS proteins. Oncogene. 1991 Apr;6(4):533–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambucetti L. C., Curran T. The Fos protein complex is associated with DNA in isolated nuclei and binds to DNA cellulose. Science. 1986 Dec 12;234(4782):1417–1419. doi: 10.1126/science.3491427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeal T., Binetruy B., Mercola D. A., Birrer M., Karin M. Oncogenic and transcriptional cooperation with Ha-Ras requires phosphorylation of c-Jun on serines 63 and 73. Nature. 1991 Dec 12;354(6353):494–496. doi: 10.1038/354494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki M. Common features in DNA recognition helices of eukaryotic transcription factors. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3221–3226. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05991.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R., Tjian R. Leucine repeats and an adjacent DNA binding domain mediate the formation of functional cFos-cJun heterodimers. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1689–1694. doi: 10.1126/science.2494701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., Sigler P. B., McKnight S. L. Scissors-grip model for DNA recognition by a family of leucine zipper proteins. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):911–916. doi: 10.1126/science.2683088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. A., Ellenberger T., Wobbe C. R., Lee J. P., Harrison S. C., Struhl K. Folding transition in the DNA-binding domain of GCN4 on specific binding to DNA. Nature. 1990 Oct 11;347(6293):575–578. doi: 10.1038/347575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xanthoudakis S., Curran T. Identification and characterization of Ref-1, a nuclear protein that facilitates AP-1 DNA-binding activity. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):653–665. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05097.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xanthoudakis S., Miao G., Wang F., Pan Y. C., Curran T. Redox activation of Fos-Jun DNA binding activity is mediated by a DNA repair enzyme. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3323–3335. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05411.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]