Abstract
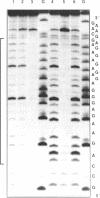
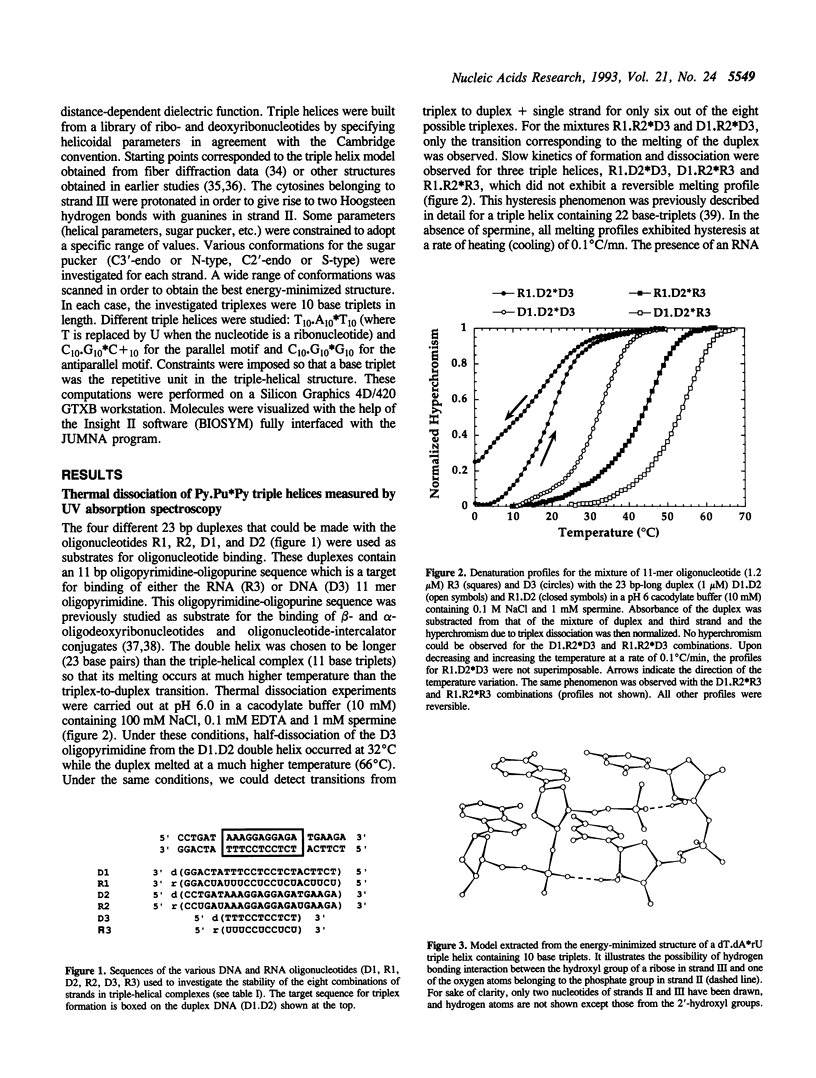
UV-absorption spectrophotometry and molecular modeling have been used to study the influence of the chemical nature of sugars (ribose or deoxyribose) on triple helix stability. For the Pyrimidine.purine* Pyrimidine motif, all eight combinations were tested with each of the three strands composed of either DNA or RNA. The chemical nature of sugars has a dramatic influence on triple helix stability. For each double helix composition, a more stable triple helix was formed when the third strand was RNA rather than DNA. No stable triple helix was detected when the polypurine sequence was made of RNA with a third strand made of DNA. Energy minimization studies using the JUMNA program suggested that interactions between the 2'-hydroxyl group of the third strand and the phosphates of the polypurine strand play an important role in determining the relative stabilities of triple-helical structures in which the polypyrimidine third strand is oriented parallel to the polypurine sequence. These interactions are not allowed when the third strand adopts an antiparallel orientation with respect to the target polypurine sequence, as observed when the third strand contains G and A or G and T/U. We show by footprinting and gel retardation experiments that an oligoribonucleotide containing G and A or G and U fails to bind double helical DNA, while the corresponding DNA oligomers form stable triple-helical complexes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akhebat A., Dagneaux C., Liquier J., Taillandier E. Triple helical polynucleotidic structures: an FTIR study of the C+ .G. Ctriplet. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1992 Dec;10(3):577–588. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1992.10508669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Selsing E. Structures for the polynucleotide complexes poly(dA) with poly (dT) and poly(dT) with poly(dA) with poly (dT). J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 15;88(2):509–521. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90498-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beal P. A., Dervan P. B. Second structural motif for recognition of DNA by oligonucleotide-directed triple-helix formation. Science. 1991 Mar 15;251(4999):1360–1363. doi: 10.1126/science.2003222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor C. R., Warshaw M. M., Shapiro H. Oligonucleotide interactions. 3. Circular dichroism studies of the conformation of deoxyoligonucleotides. Biopolymers. 1970;9(9):1059–1077. doi: 10.1002/bip.1970.360090909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomilier J., Sun J. S., Collier D. A., Garestier T., Hélène C., Lavery R. A computational and experimental study of the bending induced at a double-triple helix junction. Biophys Chem. 1992 Dec;45(2):143–152. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(92)87006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durland R. H., Kessler D. J., Gunnell S., Duvic M., Pettitt B. M., Hogan M. E. Binding of triple helix forming oligonucleotides to sites in gene promoters. Biochemistry. 1991 Sep 24;30(38):9246–9255. doi: 10.1021/bi00102a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duval-Valentin G., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Specific inhibition of transcription by triple helix-forming oligonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):504–508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egli M., Usman N., Rich A. Conformational influence of the ribose 2'-hydroxyl group: crystal structures of DNA-RNA chimeric duplexes. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 6;32(13):3221–3237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escudé C., Sun J. S., Rougée M., Garestier T., Hélène C. Stable triple helices are formed upon binding of RNA oligonucleotides and their 2'-O-methyl derivatives to double-helical DNA. C R Acad Sci III. 1992;315(13):521–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froehler B. C., Ng P. G., Matteucci M. D. Synthesis of DNA via deoxynucleoside H-phosphonate intermediates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5399–5407. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.13.5399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigoriev M., Praseuth D., Guieysse A. L., Robin P., Thuong N. T., Hélène C., Harel-Bellan A. Inhibition of interleukin-2 receptor alpha-subunit gene expression by oligonucleotide-directed triple helix formation. C R Acad Sci III. 1993;316(5):492–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigoriev M., Praseuth D., Robin P., Hemar A., Saison-Behmoaras T., Dautry-Varsat A., Thuong N. T., Hélène C., Harel-Bellan A. A triple helix-forming oligonucleotide-intercalator conjugate acts as a transcriptional repressor via inhibition of NF kappa B binding to interleukin-2 receptor alpha-regulatory sequence. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3389–3395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han H., Dervan P. B. Sequence-specific recognition of double helical RNA and RNA.DNA by triple helix formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):3806–3810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.3806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard F. B., Miles H. T., Liu K., Frazier J., Raghunathan G., Sasisekharan V. Structure of d(T)n.d(A)n.d(T)n: the DNA triple helix has B-form geometry with C2'-endo sugar pucker. Biochemistry. 1992 Nov 10;31(44):10671–10677. doi: 10.1021/bi00159a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hélène C. Sequence-selective recognition and cleavage of double-helical DNA. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 1993 Feb;4(1):29–36. doi: 10.1016/0958-1669(93)90028-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hélène C. The anti-gene strategy: control of gene expression by triplex-forming-oligonucleotides. Anticancer Drug Des. 1991 Dec;6(6):569–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Doan T., Perrouault L., Praseuth D., Habhoub N., Decout J. L., Thuong N. T., Lhomme J., Hélène C. Sequence-specific recognition, photocrosslinking and cleavage of the DNA double helix by an oligo-[alpha]-thymidylate covalently linked to an azidoproflavine derivative. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7749–7760. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liquier J., Coffinier P., Firon M., Taillandier E. Triple helical polynucleotidic structures: sugar conformations determined by FTIR spectroscopy. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1991 Dec;9(3):437–445. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1991.10507927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyamichev V. I., Mirkin S. M., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D., Cantor C. R. A stable complex between homopyrimidine oligomers and the homologous regions of duplex DNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(5):2165–2178. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.2165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macaya R., Wang E., Schultze P., Sklenár V., Feigon J. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance assignments and structural characterization of an intramolecular DNA triplex. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jun 5;225(3):755–773. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90399-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher L. J., 3rd Inhibition of T7 RNA polymerase initiation by triple-helical DNA complexes: a model for artificial gene repression. Biochemistry. 1992 Aug 25;31(33):7587–7594. doi: 10.1021/bi00148a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher L. J., 3rd, Wold B., Dervan P. B. Inhibition of DNA binding proteins by oligonucleotide-directed triple helix formation. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):725–730. doi: 10.1126/science.2549631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A. R., Wells R. D. Specificity of the three-stranded complex formation between double-stranded DNA and single-stranded RNA containing repeating nucleotide sequences. J Mol Biol. 1968 Oct 14;37(1):63–80. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser H. E., Dervan P. B. Sequence-specific cleavage of double helical DNA by triple helix formation. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):645–650. doi: 10.1126/science.3118463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouali M., Letellier R., Adnet F., Liquier J., Sun J. S., Lavery R., Taillandier E. A possible family of B-like triple helix structures: comparison with the Arnott A-like triple helix. Biochemistry. 1993 Mar 2;32(8):2098–2103. doi: 10.1021/bi00059a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilch D. S., Levenson C., Shafer R. H. Structure, stability, and thermodynamics of a short intermolecular purine-purine-pyrimidine triple helix. Biochemistry. 1991 Jun 25;30(25):6081–6088. doi: 10.1021/bi00239a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postel E. H., Flint S. J., Kessler D. J., Hogan M. E. Evidence that a triplex-forming oligodeoxyribonucleotide binds to the c-myc promoter in HeLa cells, thereby reducing c-myc mRNA levels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):8227–8231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.8227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley M., Maling B. Physical and chemical characterization of two- and three-stranded adenine-thymine and adenine-uracil homopolymer complexes. J Mol Biol. 1966 Sep;20(2):359–389. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. W., Crothers D. M. Stability and properties of double and triple helices: dramatic effects of RNA or DNA backbone composition. Science. 1992 Nov 27;258(5087):1463–1466. doi: 10.1126/science.1279808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rougée M., Faucon B., Mergny J. L., Barcelo F., Giovannangeli C., Garestier T., Hélène C. Kinetics and thermodynamics of triple-helix formation: effects of ionic strength and mismatches. Biochemistry. 1992 Sep 29;31(38):9269–9278. doi: 10.1021/bi00153a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu M., Konishi A., Shimada Y., Inoue H., Ohtsuka E. Oligo(2'-O-methyl)ribonucleotides. Effective probes for duplex DNA. FEBS Lett. 1992 May 11;302(2):155–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80428-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skoog J. U., Maher L. J., 3rd Repression of bacteriophage promoters by DNA and RNA oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 May 11;21(9):2131–2138. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.9.2131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stawinski J., Strömberg R., Thelin M., Westman E. Studies on the t-butyldimethylsilyl group as 2'-O-protection in oligoribonucleotide synthesis via the H-phosphonate approach. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 11;16(19):9285–9298. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.19.9285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun J. S., De Bizemont T., Duval-Valentin G., Montenay-Garestier T., Hélène C. Extension of the range of recognition sequences for triple helix formation by oligonucleotides containing guanines and thymines. C R Acad Sci III. 1991;313(13):585–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun J. S., François J. C., Montenay-Garestier T., Saison-Behmoaras T., Roig V., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Sequence-specific intercalating agents: intercalation at specific sequences on duplex DNA via major groove recognition by oligonucleotide-intercalator conjugates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9198–9202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun J. S., Giovannangeli C., François J. C., Kurfurst R., Montenay-Garestier T., Asseline U., Saison-Behmoaras T., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Triple-helix formation by alpha oligodeoxynucleotides and alpha oligodeoxynucleotide-intercalator conjugates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6023–6027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. L., Krawczyk S. H., Matteucci M. D., Toole J. J. Triple helix formation inhibits transcription elongation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10023–10026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]