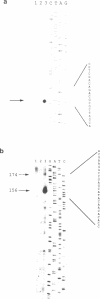
Abstract
A ds/ss-RNA processing activity involved in antisense-RNA mediated gene regulation in the extremely halophilic archaebacterium Halobacterium salinarium was investigated in vivo. H.salinarium cells were transformed with DNA encoding an RNA species complementary to a part of the major lytic transcript, termed T4, of the H.salinarium phage phi H. The transformants transcribing this construct, when infected by phage were able to process T4 in a similar way to the processing of the lytic transcript denoted T1, in the natural sense-antisense system. Processing of T4 was not observed under normal phage growth on wild-type cells. Thus the antisense-RNA mediated processing activity earlier reported is dependent on the presence of an RNA duplex and is not sequence specific.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaseio U., Pfeifer F. Transformation of Halobacterium halobium: development of vectors and investigation of gas vesicle synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6772–6776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline S. W., Doolittle W. F. Efficient transfection of the archaebacterium Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1341–1344. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1341-1344.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline S. W., Lam W. L., Charlebois R. L., Schalkwyk L. C., Doolittle W. F. Transformation methods for halophilic archaebacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Jan;35(1):148–152. doi: 10.1139/m89-022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline S. W., Schalkwyk L. C., Doolittle W. F. Transformation of the archaebacterium Halobacterium volcanii with genomic DNA. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4987–4991. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4987-4991.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eguchi Y., Itoh T., Tomizawa J. Antisense RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:631–652. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gropp F., Grampp B., Stolt P., Palm P., Zillig W. The immunity-conferring plasmid p phi HL from the Halobacterium salinarium phage phi H: nucleotide sequence and transcription. Virology. 1992 Sep;190(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)91191-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hain J., Reiter W. D., Hüdepohl U., Zillig W. Elements of an archaeal promoter defined by mutational analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Oct 25;20(20):5423–5428. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.20.5423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ken R., Hackett N. R. Halobacterium halobium strains lysogenic for phage phi H contain a protein resembling coliphage repressors. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):955–960. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.955-960.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krinke L., Mahoney M., Wulff D. L. The role of the OOP antisense RNA in coliphage lambda development. Mol Microbiol. 1991 May;5(5):1265–1272. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01900.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krinke L., Wulff D. L. OOP RNA, produced from multicopy plasmids, inhibits lambda cII gene expression through an RNase III-dependent mechanism. Genes Dev. 1987 Nov;1(9):1005–1013. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.9.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krinke L., Wulff D. L. RNase III-dependent hydrolysis of lambda cII-O gene mRNA mediated by lambda OOP antisense RNA. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2223–2233. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krinke L., Wulff D. L. The cleavage specificity of RNase III. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 25;18(16):4809–4815. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.16.4809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence N., Wesolowski D., Gold H., Bartkiewicz M., Guerrier-Takada C., McClain W. H., Altman S. Characteristics of ribonuclease P from various organisms. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1987;52:233–238. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1987.052.01.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madon J., Zillig W. A form of the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase of Halobacterium halobium, containing an additional component, is able to transcribe native DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 15;133(2):471–474. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07487.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter W. D., Zillig W., Palm P. Archaebacterial viruses. Adv Virus Res. 1988;34:143–188. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60517-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnabel H. An immune strain of Halobacterium halobium carries the invertible L segment of phage PhiH as a plasmid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1017–1020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolt P., Zillig W. Antisense RNA mediates transcriptional processing in an archaebacterium, indicating a novel kind of RNase activity. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Mar;7(6):875–882. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01178.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolt P., Zillig W. In vivo and in vitro analysis of transcription of the L region from the Halobacterium salinarium phage phi H: definition of a repressor-enhancing gene. Virology. 1993 Aug;195(2):649–658. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolt P., Zillig W. In vivo studies on the effects of immunity genes on early lytic transcription in the Halobacterium salinarium phage phi H. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Nov;235(2-3):197–204. doi: 10.1007/BF00279361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. D., Daniels C. J. Recognition of exon-intron boundaries by the Halobacterium volcanii tRNA intron endonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18104–18111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Stiegler P. Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):133–148. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]