Abstract
Gene 1 of bacteriophage T7 early region--the RNA polymerase gene--is very actively translated during the infectious cycle of this phage. A 29 base pair fragment of its ribosome binding site containing the initiation triplet, the Shine-Dalgarno sequence (S-D), 10 nucleotides (nt) upstream and 6 nt downstream of these central elements was cloned into a vector to control the expression of the mouse dihydrofolate reductase gene (dhfr). Although all essential parts of this translation initiation region (TIR) should be present, this fragment showed only very low activity. Computer analysis revealed a potentially inhibitory hairpin binding the S-D sequence into its stem base paired to vector-derived upstream sequences. Mutational alterations demonstrated that this hairpin was not responsible for the low activity. However, addition of 21 nt of the T7 gene 1 upstream sequence to the 29 base pair fragment were capable of increasing the translational efficiency by one order of magnitude. Computer analysis of this sequence, including nucleotide shuffling, revealed that it contains a highly unstructured region lacking mRNA secondary structures but with a hairpin at its 5' end, here formed solely by T7 sequences. There was not much difference in activity whether the mRNA included or lacked vector-derived sequences upstream of the hairpin. Such highly unstructured mRNA regions were found in all very efficiently expressed T7 genes without any obvious sequence homologies. The delta G values of these regions were higher, i.e. potential secondary structural elements were fewer, than in TIR of genes from E. coli. This is likely due to the fact that T7 as a lytic phage is relying for successful infection on much stronger signals which a cell cannot afford because of the indispensable balanced equilibria of its interdependent biochemical processes. When the 5' ends of efficient T7 gene mRNA are formed by the action of RNase III they generally start with an unstructured region. Efficiently expressed T7 genes within a polycistronic mRNA, however, always contain a hairpin preceding the structure free sequence. We suggest that the formation of this 5' hairpin is releasing enough energy to keep the unstructured regions free of secondary RNA structures for sufficient time to give ribosomes and factors a good chance for binding to the TIR. In addition, sequences further downstream of the start codon give rise to an additional increase in efficiency of the TIR by almost two orders of magnitude.
Full text
PDF
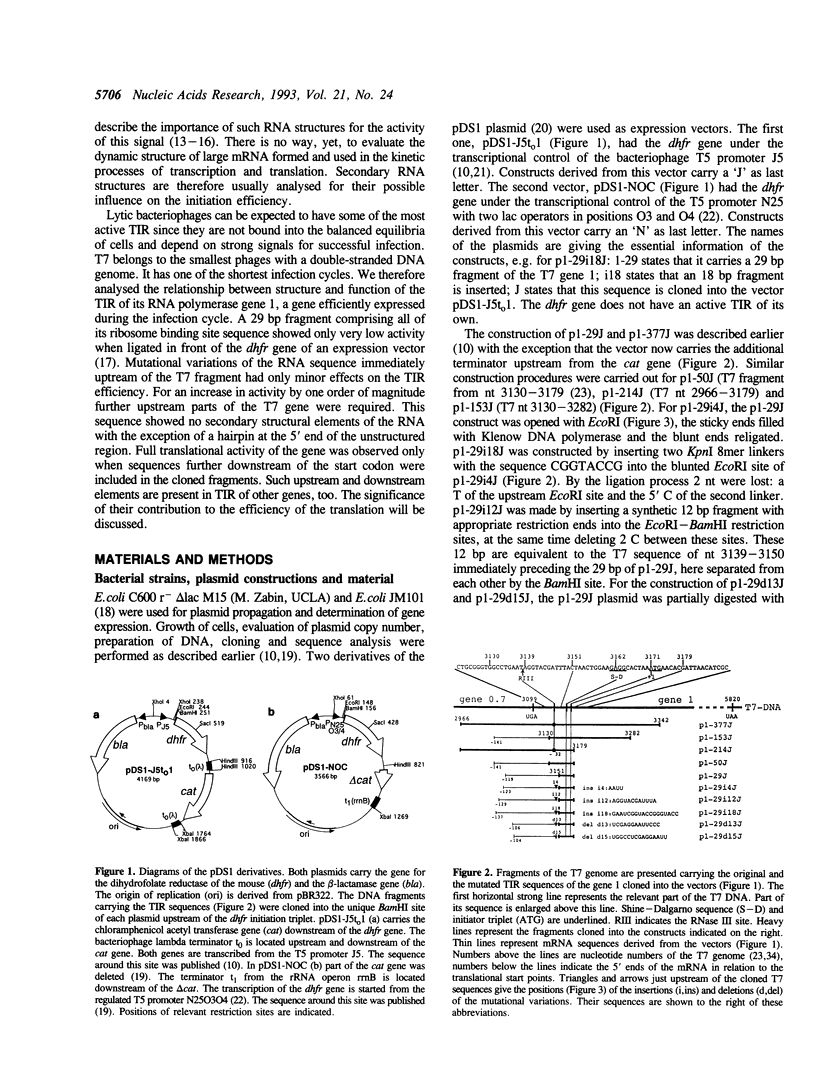

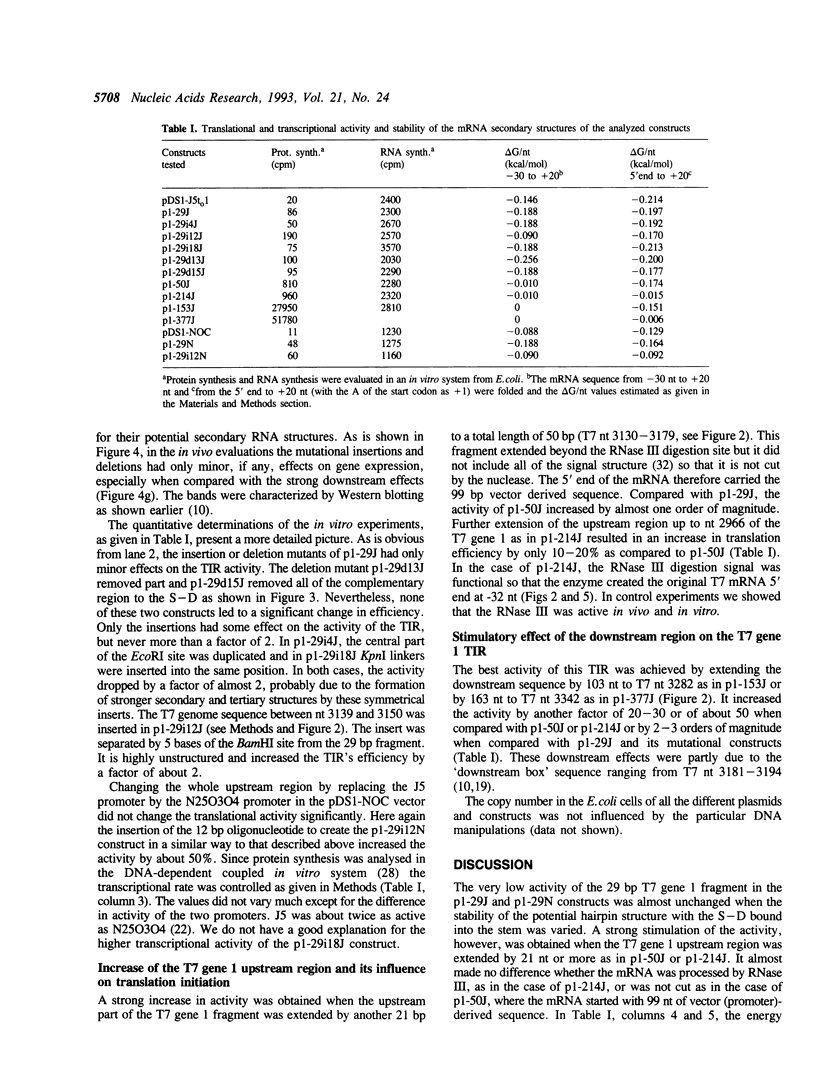
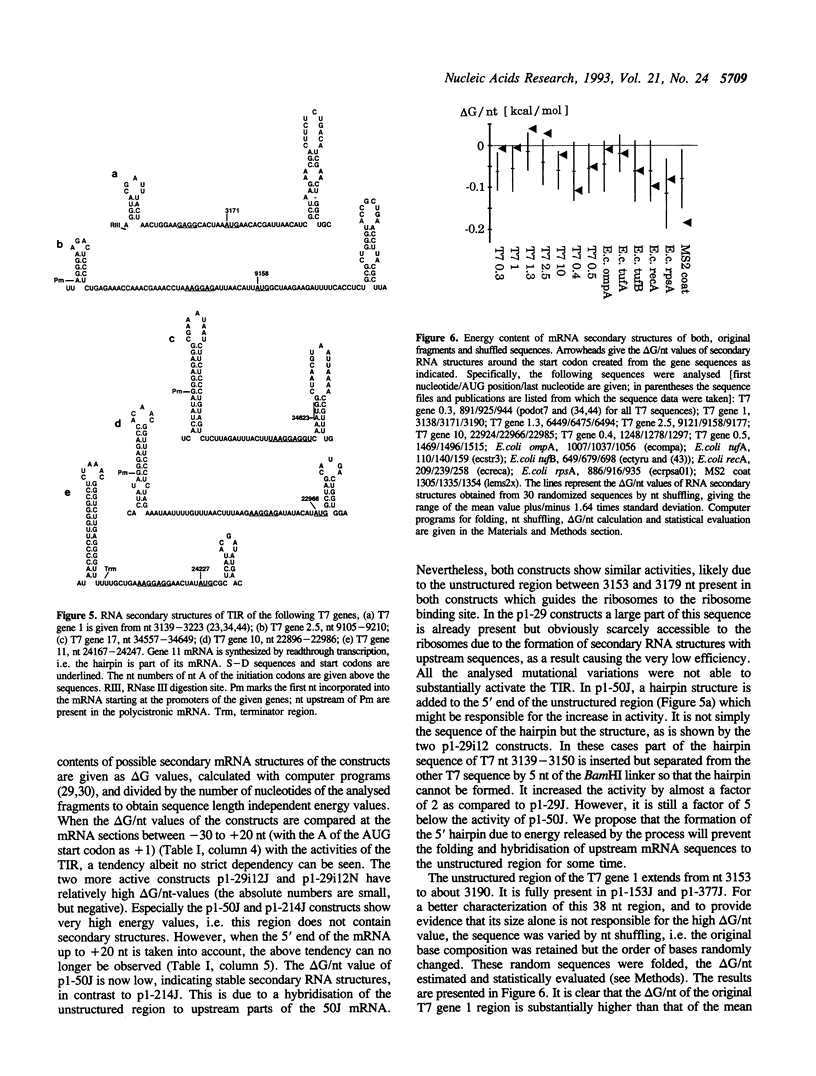


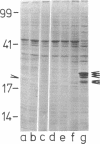
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altuvia S., Kornitzer D., Kobi S., Oppenheim A. B. Functional and structural elements of the mRNA of the cIII gene of bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1991 Apr 20;218(4):723–733. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90261-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- An G., Friesen J. D. The nucleotide sequence of tufB and four nearby tRNA structural genes of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1980 Dec;12(1-2):33–39. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90013-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannwarth W., Iaiza P. A system for the simultaneous chemical synthesis of different DNA fragments on solid support. DNA. 1986 Oct;5(5):413–419. doi: 10.1089/dna.1986.5.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boni I. V., Isaeva D. M., Musychenko M. L., Tzareva N. V. Ribosome-messenger recognition: mRNA target sites for ribosomal protein S1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):155–162. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Buzash-Pollert E., Studier F. W. Mutations of bacteriophage T7 that affect initiation of synthesis of the gene 0.3 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2741–2745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Complete nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage T7 DNA and the locations of T7 genetic elements. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):477–535. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80282-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Effect of RNAase III, cleavage on translation of bacteriophage T7 messenger RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1975 Dec 15;99(3):487–499. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80140-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. T7 early RNAs are generated by site-specific cleavages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1559–1563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fatscher H. P., Geisen R. M., Fuchs E. Only one out of the three strong ribosomal binding sites of the early region of bacteriophage T7 exhibits high translational efficiency in fragments of about 30 base pairs. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Aug 15;175(3):461–465. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14217.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti L., Karnik S. S., Khorana H. G., Nassal M., Oprian D. D. Total synthesis of a gene for bovine rhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):599–603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E., Hirth K. P., Henrich B., Kälberer G. Demonstration of the early--late switch in vitro with bacteriophage T7 DNA as template. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Dec;113(1):61–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganoza M. C., Kofoid E. C., Marlière P., Louis B. G. Potential secondary structure at translation-initiation sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 12;15(1):345–360. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.1.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganoza M. C., Marliere P., Kofoid E. C., Louis B. G. Initiator tRNA may recognize more than the initiation codon in mRNA: a model for translational initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4587–4591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisen R. M., Fatscher H. P., Fuchs E. More than 150 nucleotides flanking the initiation codon contribute to the efficiency of the ribosomal binding site from bacteriophage T7 gene 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 25;15(12):4931–4943. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.12.4931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentz R., Bujard H. Promoters recognized by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase selected by function: highly efficient promoters from bacteriophage T5. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):70–77. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.70-77.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartz D., McPheeters D. S., Gold L. Influence of mRNA determinants on translation initiation in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1991 Mar 5;218(1):83–97. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90875-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hercules K., Jovanovich S., Sauerbrier W. Early gene expression in bacteriophage T7. I. In vivo synthesis, inactivation, and translational utilization of early mRNA's. J Virol. 1976 Feb;17(2):642–658. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.2.642-658.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay G., Khoury G., Seth A. K., Jay E. Construction of a general vector for efficient expression of mammalian proteins in bacteria: use of a synthetic ribosome binding site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5543–5548. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastelein R. A., Berkhout B., Overbeek G. P., van Duin J. Effect of the sequences upstream from the ribosome-binding site on the yield of protein from the cloned gene for phage MS2 coat protein. Gene. 1983 Sep;23(3):245–254. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90015-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang V., Gualerzi C., McCarthy J. E. Ribosomal affinity and translational initiation in Escherichia coli. In vitro investigations using translational initiation regions of differing efficiencies from the atp operon. J Mol Biol. 1989 Dec 5;210(3):659–663. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90140-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzer M., Bujard H. Promoters largely determine the efficiency of repressor action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8973–8977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrs B. L., Yanofsky C. Host and bacteriophage specific messenger RNA degradation in T7-infected Escherichia coli. Nat New Biol. 1971 Dec 8;234(49):168–170. doi: 10.1038/newbio234168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy J. E., Schairer H. U., Sebald W. Translational initiation frequency of atp genes from Escherichia coli: identification of an intercistronic sequence that enhances translation. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):519–526. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03659.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffatt B. A., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1984 Feb 25;173(2):265–269. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90194-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olins P. O., Rangwala S. H. A novel sequence element derived from bacteriophage T7 mRNA acts as an enhancer of translation of the lacZ gene in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):16973–16976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheps R., Zeller H., Revel M. Deficiency in initiation factors of protein synthesis induced by phage T7 in E. coli F(+) strains. FEBS Lett. 1972 Oct 15;27(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80394-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz V. P., Reznikoff W. S. In vitro secondary structure analysis of mRNA from lacZ translation initiation mutants. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jan 20;211(2):427–445. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90363-Q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. Determinant of cistron specificity in bacterial ribosomes. Nature. 1975 Mar 6;254(5495):34–38. doi: 10.1038/254034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprengart M. L., Fatscher H. P., Fuchs E. The initiation of translation in E. coli: apparent base pairing between the 16srRNA and downstream sequences of the mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 11;18(7):1719–1723. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.7.1719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A. Polypeptide chain initiation: nucleotide sequences of the three ribosomal binding sites in bacteriophage R17 RNA. Nature. 1969 Dec 6;224(5223):957–964. doi: 10.1038/224957a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D., Schneider T. D., Gold L. M. Characterization of translational initiation sites in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2971–2996. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D., Schneider T. D., Gold L., Ehrenfeucht A. Use of the 'Perceptron' algorithm to distinguish translational initiation sites in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2997–3011. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strome S., Young E. T. Chemical and functional quantitation of gene 0.3 messenger RNA during T7 infection. J Mol Biol. 1980 Feb 5;136(4):417–432. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90398-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Simon M. N., Dunn J. J. Genetic and physical mapping in the early region of bacteriophage T7 DNA. J Mol Biol. 1979 Dec 25;135(4):917–937. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90520-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stueber D., Bujard H. Transcription from efficient promoters can interfere with plasmid replication and diminish expression of plasmid specified genes. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1399–1404. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01329.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suissa M., Altuvia S., Koby S., Giladi H., Oppenheim A. B. Translational signals of a major head protein gene of bacteriophage lambda. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Nov;214(3):570–573. doi: 10.1007/BF00330496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner D. H., Sugimoto N., Jaeger J. A., Longfellow C. E., Freier S. M., Kierzek R. Improved parameters for prediction of RNA structure. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1987;52:123–133. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1987.052.01.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M. Computer prediction of RNA structure. Methods Enzymol. 1989;180:262–288. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)80106-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Smit M. H., van Duin J. Control of prokaryotic translational initiation by mRNA secondary structure. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1990;38:1–35. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60707-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Smit M. H., van Duin J. Secondary structure of the ribosome binding site determines translational efficiency: a quantitative analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7668–7672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]