Abstract
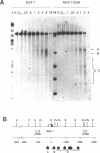
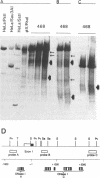
The chromatin structure of the epidermal growth factor receptor gene (EGFR) has been analyzed in several human breast cancer cell lines exhibiting a wide range of EGFR expression. Using DNase I, structural differences were identified in the promoter, first exon, and intron 1 of the EGFR gene that correlate with its expression. Specifically, a DNase I hypersensitive site (DH site) around the exon 1/intron 1 boundary occurred preferentially in estrogen receptor positive breast cancer cell lines with low levels of EGFR expression, while a group of DH sites in intron 1 were observed in estrogen receptor negative, high EGFR expressors. Additionally, a region in the promoter was sensitive to DNase I in all breast cancer cells expressing EGFR, but showed differences in both the level of nuclease sensitivity and the extent of the area that was susceptible. Fine mapping by native genomic blotting revealed the presence of multiple protein footprints in both the promoter and first intron of the EGFR gene in MDA-MB-468 cells, a breast cancer cell line that overexpresses the EGFR gene. The appearance of DH sites in intron 1 associated with high levels of EGFR expression suggests that these regions of the gene contain potential enhancer elements, while the absence of a DH site at the exon 1/intron 1 boundary when the gene is up-regulated suggests the action of a repressor that may block transcriptional elongation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bender T. P., Thompson C. B., Kuehl W. M. Differential expression of c-myb mRNA in murine B lymphomas by a block to transcription elongation. Science. 1987 Sep 18;237(4821):1473–1476. doi: 10.1126/science.3498214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. L., Groudine M. A block to elongation is largely responsible for decreased transcription of c-myc in differentiated HL60 cells. Nature. 1986 Jun 12;321(6071):702–706. doi: 10.1038/321702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthois Y., Katzenellenbogen J. A., Katzenellenbogen B. S. Phenol red in tissue culture media is a weak estrogen: implications concerning the study of estrogen-responsive cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2496–2500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolufer P., Miralles F., Rodriguez A., Vazquez C., Lluch A., Garcia-Conde J., Olmos T. Epidermal growth factor receptor in human breast cancer: correlation with cytosolic and nuclear ER receptors and with biological and histological tumor characteristics. Eur J Cancer. 1990 Mar;26(3):283–290. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(90)90223-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P., McKay J., Liska D. J., Apone S., Devarayalu S. Interactions between the promoter and first intron are involved in transcriptional control of alpha 1(I) collagen gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4851–4857. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R., Stampfer M. R., Milley R., O'Rourke E., Walen K. H., Kriegler M., Kopplin J., McCormick F. Transformation of human mammary epithelial cells by oncogenic retroviruses. Cancer Res. 1988 Aug 15;48(16):4689–4694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Ushiro H., Stoscheck C., Chinkers M. A native 170,000 epidermal growth factor receptor-kinase complex from shed plasma membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1523–1531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulombe B., Ponton A., Daigneault L., Williams B. R., Skup D. Presence of transcription regulatory elements within an intron of the virus-inducible murine TIMP gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3227–3234. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson N. E., Gelmann E. P., Lippman M. E., Dickson R. B. Epidermal growth factor receptor gene expression in estrogen receptor-positive and negative human breast cancer cell lines. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 Mar;1(3):216–223. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-3-216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Fiore P. P., Pierce J. H., Fleming T. P., Hazan R., Ullrich A., King C. R., Schlessinger J., Aaronson S. A. Overexpression of the human EGF receptor confers an EGF-dependent transformed phenotype to NIH 3T3 cells. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1063–1070. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90592-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Yarden Y., Mayes E., Scrace G., Totty N., Stockwell P., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Waterfield M. D. Close similarity of epidermal growth factor receptor and v-erb-B oncogene protein sequences. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):521–527. doi: 10.1038/307521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filmus J., Pollak M. N., Cailleau R., Buick R. N. MDA-468, a human breast cancer cell line with a high number of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptors, has an amplified EGF receptor gene and is growth inhibited by EGF. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Apr 30;128(2):898–905. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90131-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick S. L., Brightwell J., Wittliff J. L., Barrows G. H., Schultz G. S. Epidermal growth factor binding by breast tumor biopsies and relationship to estrogen receptor and progestin receptor levels. Cancer Res. 1984 Aug;44(8):3448–3453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin G. C., Donovan M., Adam G. I., Holmgren L., Pfeifer-Ohlsson S., Ohlsson R. Expression of the human PDGF-B gene is regulated by both positively and negatively acting cell type-specific regulatory elements located in the first intron. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1365–1373. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07656.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasch A., Hinz U., Renkawitz-Pohl R. Intron and upstream sequences regulate expression of the Drosophila beta 3-tubulin gene in the visceral and somatic musculature, respectively. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3215–3218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D. S., Garrard W. T. Nuclease hypersensitive sites in chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:159–197. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullick W. J. Prevalence of aberrant expression of the epidermal growth factor receptor in human cancers. Br Med Bull. 1991 Jan;47(1):87–98. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haley J. D., Waterfield M. D. Contributory effects of de novo transcription and premature transcript termination in the regulation of human epidermal growth factor receptor proto-oncogene RNA synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1746–1753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Epidermal growth factor induces rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of proteins in A431 human tumor cells. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90100-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii S., Xu Y. H., Stratton R. H., Roe B. A., Merlino G. T., Pastan I. Characterization and sequence of the promoter region of the human epidermal growth factor receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4920–4924. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. C., Ishii S., Jinno Y., Pastan I., Merlino G. T. Epidermal growth factor receptor gene promoter. Deletion analysis and identification of nuclear protein binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5693–5699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. C., Jinno Y., Merlino G. T. Modulation of epidermal growth factor receptor proto-oncogene transcription by a promoter site sensitive to S1 nuclease. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4174–4184. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston B. H. The S1-sensitive form of d(C-T)n.d(A-G)n: chemical evidence for a three-stranded structure in plasmids. Science. 1988 Sep 30;241(4874):1800–1804. doi: 10.1126/science.2845572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kageyama R., Merlino G. T., Pastan I. A transcription factor active on the epidermal growth factor receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5016–5020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kageyama R., Merlino G. T., Pastan I. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor gene transcription. Requirement for Sp1 and an EGF receptor-specific factor. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6329–6336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kageyama R., Pastan I. Molecular cloning and characterization of a human DNA binding factor that represses transcription. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):815–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90605-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato M., Kudoh J., Shimizu N. The pyrimidine/purine-biased region of the epidermal growth factor receptor gene is sensitive to S1 nuclease and may form an intramolecular triplex. Biochem J. 1990 May 15;268(1):175–180. doi: 10.1042/bj2680175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. R., Kraus M. H., Williams L. T., Merlino G. T., Pastan I. H., Aaronson S. A. Human tumor cell lines with EGF receptor gene amplification in the absence of aberrant sized mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8477–8486. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus M. H., Popescu N. C., Amsbaugh S. C., King C. R. Overexpression of the EGF receptor-related proto-oncogene erbB-2 in human mammary tumor cell lines by different molecular mechanisms. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):605–610. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04797.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S., Locker A., Todd J. H., Bell J. A., Nicholson R., Elston C. W., Blamey R. W., Ellis I. O. Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor in breast carcinoma. J Clin Pathol. 1990 May;43(5):385–389. doi: 10.1136/jcp.43.5.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. R., Chen W. S., Kruiger W., Stolarsky L. S., Weber W., Evans R. M., Verma I. M., Gill G. N., Rosenfeld M. G. Expression cloning of human EGF receptor complementary DNA: gene amplification and three related messenger RNA products in A431 cells. Science. 1984 May 25;224(4651):843–848. doi: 10.1126/science.6326261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maekawa T., Imamoto F., Merlino G. T., Pastan I., Ishii S. Cooperative function of two separate enhancers of the human epidermal growth factor receptor proto-oncogene. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5488–5494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magin T. M., McEwan C., Milne M., Pow A. M., Selfridge J., Melton D. W. A position- and orientation-dependent element in the first intron is required for expression of the mouse hprt gene in embryonic stem cells. Gene. 1992 Dec 15;122(2):289–296. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90217-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mechti N., Piechaczyk M., Blanchard J. M., Jeanteur P., Lebleu B. Sequence requirements for premature transcription arrest within the first intron of the mouse c-fos gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2832–2841. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson S., Halcrow P., Sainsbury J. R., Angus B., Chambers P., Farndon J. R., Harris A. L. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFr) status associated with failure of primary endocrine therapy in elderly postmenopausal patients with breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 1988 Dec;58(6):810–814. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1988.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson S., Richard J., Sainsbury C., Halcrow P., Kelly P., Angus B., Wright C., Henry J., Farndon J. R., Harris A. L. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFr); results of a 6 year follow-up study in operable breast cancer with emphasis on the node negative subgroup. Br J Cancer. 1991 Jan;63(1):146–150. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1991.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson S., Sainsbury J. R., Halcrow P., Chambers P., Farndon J. R., Harris A. L. Expression of epidermal growth factor receptors associated with lack of response to endocrine therapy in recurrent breast cancer. Lancet. 1989 Jan 28;1(8631):182–185. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91202-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page M. J., Field J. K., Everett N. P., Green C. D. Serum regulation of the estrogen responsiveness of the human breast cancer cell line MCF-7. Cancer Res. 1983 Mar;43(3):1244–1250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauli U., Chrysogelos S., Stein J., Stein G. Native genomic blotting: a novel approach to mapping DNase I hypersensitive sites and protein-DNA interactions at high resolution. Biotechniques. 1988 Feb;6(2):142–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauli U., Chrysogelos S., Stein J., Stein G. Native genomic blotting: high-resolution mapping of DNase I-hypersensitive sites and protein-DNA interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):16–20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sainsbury J. R., Farndon J. R., Sherbet G. V., Harris A. L. Epidermal-growth-factor receptors and oestrogen receptors in human breast cancer. Lancet. 1985 Feb 16;1(8425):364–366. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91385-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sica A., Tan T. H., Rice N., Kretzschmar M., Ghosh P., Young H. A. The c-rel protooncogene product c-Rel but not NF-kappa B binds to the intronic region of the human interferon-gamma gene at a site related to an interferon-stimulable response element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1740–1744. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toi M., Osaki A., Yamada H., Toge T. Epidermal growth factor receptor expression as a prognostic indicator in breast cancer. Eur J Cancer. 1991;27(8):977–980. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(91)90262-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Coussens L., Hayflick J. S., Dull T. J., Gray A., Tam A. W., Lee J., Yarden Y., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J. Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA sequence and aberrant expression of the amplified gene in A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):418–425. doi: 10.1038/309418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushiro H., Cohen S. Identification of phosphotyrosine as a product of epidermal growth factor-activated protein kinase in A-431 cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8363–8365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valverius E. M., Bates S. E., Stampfer M. R., Clark R., McCormick F., Salomon D. S., Lippman M. E., Dickson R. B. Transforming growth factor alpha production and epidermal growth factor receptor expression in normal and oncogene transformed human mammary epithelial cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Jan;3(1):203–214. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-1-203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velu T. J., Beguinot L., Vass W. C., Willingham M. C., Merlino G. T., Pastan I., Lowy D. R. Epidermal-growth-factor-dependent transformation by a human EGF receptor proto-oncogene. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1408–1410. doi: 10.1126/science.3500513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vickers P. J., Dickson R. B., Shoemaker R., Cowan K. H. A multidrug-resistant MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line which exhibits cross-resistance to antiestrogens and hormone-independent tumor growth in vivo. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Oct;2(10):886–892. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-10-886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Y. H., Ishii S., Clark A. J., Sullivan M., Wilson R. K., Ma D. P., Roe B. A., Merlino G. T., Pastan I. Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA is homologous to a variety of RNAs overproduced in A431 carcinoma cells. 1984 Jun 28-Jul 4Nature. 309(5971):806–810. doi: 10.1038/309806a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Y. H., Richert N., Ito S., Merlino G. T., Pastan I. Characterization of epidermal growth factor receptor gene expression in malignant and normal human cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7308–7312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]