Abstract
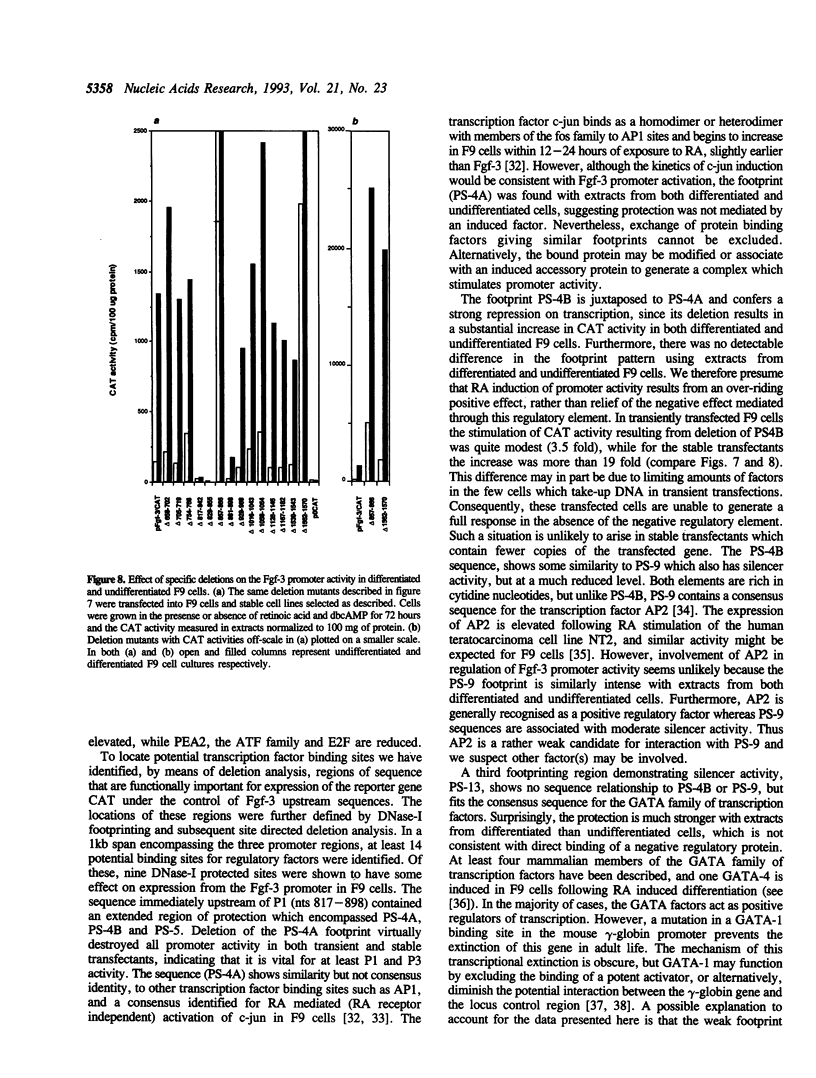
The proto-oncogene Fgf-3 has been implicated as an important signalling molecule in vertebrate development. In the mouse, it is expressed for a limited time at a multitude of sites from embryonic day 7 to birth. Transcription of Fgf-3 initiates at three promoter regions resulting in the generation of various mRNAs which nevertheless all encode the same protein products. A 1.7kb DNA fragment which encompasses these regions was joined to the CAT reporter gene and shown to function as a promoter in embryonal carcinoma cells. In stable transfectants the promoter retains its retinoic acid inducibility, initiating transcription at the same cap-sites as the endogenous gene. In differentiated F9 cells, transient transfection of progressive and targeted deletion mutants of the promoter region has revealed at least two positive and three negative regulatory elements. With one exception, loss of these elements was shown to dramatically affect promoter activity in stable transfectants of F9 cells. However the promoter remained inducible by retinoic acid to differing degrees, apart from deletions encompassing PS-4A which essentially abolished promoter activity in both undifferentiated and differentiated cells. The sequences of these potential regulatory regions were further defined using DNase-I footprinting, revealing some similarities to consensus binding sites for known transcription factors.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arceci R. J., King A. A., Simon M. C., Orkin S. H., Wilson D. B. Mouse GATA-4: a retinoic acid-inducible GATA-binding transcription factor expressed in endodermally derived tissues and heart. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2235–2246. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry M., Grosveld F., Dillon N. A single point mutation is the cause of the Greek form of hereditary persistence of fetal haemoglobin. Nature. 1992 Aug 6;358(6386):499–502. doi: 10.1038/358499a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess W. H., Maciag T. The heparin-binding (fibroblast) growth factor family of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:575–606. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossley M., Orkin S. H. Regulation of the beta-globin locus. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Apr;3(2):232–237. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(93)90028-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darrow A. L., Rickles R. J., Strickland S. Maintenance and use of F9 teratocarcinoma cells. Methods Enzymol. 1990;190:110–117. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)90015-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson C., Deed R., Dixon M., Peters G. The structure and function of the int-2 oncogene. Prog Growth Factor Res. 1989;1(3):123–132. doi: 10.1016/0955-2235(89)90006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson C., Smith R., Brookes S., Peters G. Tumorigenesis by mouse mammary tumor virus: proviral activation of a cellular gene in the common integration region int-2. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):529–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90383-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinberg D., Thurlow J., Watson R., Smith R., Peters G., Dickson C. Transcriptional regulation of the int-2 gene in embryonal carcinoma cells. Cell Growth Differ. 1991 Mar;2(3):137–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman A., Wasylyk B. Nuclear targets for transcription regulation by oncogenes. Trends Genet. 1991 Feb;7(2):49–54. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90231-E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakob H., Boon T., Gaillard J., Nicolas J., Jacob F. Tératocarcinome de la spuris: isolement, culture et propriétés de cellules a potentialités multiples. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1973 Oct;124(3):269–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits A., Shackleford G. M., Varmus H. E., Martin G. R. Two proto-oncogenes implicated in mammary carcinogenesis, int-1 and int-2, are independently regulated during mouse development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7806–7810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitabayashi I., Kawakami Z., Chiu R., Ozawa K., Matsuoka T., Toyoshima S., Umesono K., Evans R. M., Gachelin G., Yokoyama K. Transcriptional regulation of the c-jun gene by retinoic acid and E1A during differentiation of F9 cells. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):167–175. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05039.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Bindereif A., Green M. R. A small-scale procedure for preparation of nuclear extracts that support efficient transcription and pre-mRNA splicing. Gene Anal Tech. 1988 Mar-Apr;5(2):22–31. doi: 10.1016/0735-0651(88)90023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Mitchell P. J., Williams T., Tjian R. Regulation of transcription factor AP-2 by the morphogen retinoic acid and by second messengers. Genes Dev. 1989 Oct;3(10):1507–1517. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.10.1507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour S. L., Goddard J. M., Capecchi M. R. Mice homozygous for a targeted disruption of the proto-oncogene int-2 have developmental defects in the tail and inner ear. Development. 1993 Jan;117(1):13–28. doi: 10.1242/dev.117.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour S. L., Martin G. R. Four classes of mRNA are expressed from the mouse int-2 gene, a member of the FGF gene family. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2035–2041. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03043.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R., Casey G., Brookes S., Dixon M., Peters G., Dickson C. Sequence, topography and protein coding potential of mouse int-2: a putative oncogene activated by mouse mammary tumour virus. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):919–924. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04304.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgenstern J. P., Land H. Advanced mammalian gene transfer: high titre retroviral vectors with multiple drug selection markers and a complementary helper-free packaging cell line. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 25;18(12):3587–3596. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.12.3587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller W. J., Lee F. S., Dickson C., Peters G., Pattengale P., Leder P. The int-2 gene product acts as an epithelial growth factor in transgenic mice. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):907–913. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08188.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornitz D. M., Cardiff R. D., Kuo A., Leder P. Int-2, an autocrine and/or ultra-short-range effector in transgenic mammary tissue transplants. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1992 Jun 3;84(11):887–892. doi: 10.1093/jnci/84.11.887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G., Brookes S., Smith R., Dickson C. Tumorigenesis by mouse mammary tumor virus: evidence for a common region for provirus integration in mammary tumors. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):369–377. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90418-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prosser H. M., Wotton D., Gegonne A., Ghysdael J., Wang S., Speck N. A., Owen M. J. A phorbol ester response element within the human T-cell receptor beta-chain enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9934–9938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risse G., Jooss K., Neuberg M., Brüller H. J., Müller R. Asymmetrical recognition of the palindromic AP1 binding site (TRE) by Fos protein complexes. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3825–3832. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08560.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleigh M. J. A nonchromatographic assay for expression of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene in eucaryotic cells. Anal Biochem. 1986 Jul;156(1):251–256. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90180-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleigh M. J. Differentiation and proliferation in mouse embryonal carcinoma cells. Bioessays. 1992 Nov;14(11):769–775. doi: 10.1002/bies.950141109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R., Peters G., Dickson C. Multiple RNAs expressed from the int-2 gene in mouse embryonal carcinoma cell lines encode a protein with homology to fibroblast growth factors. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1013–1022. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02908.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamp G., Fantl V., Poulsom R., Jamieson S., Smith R., Peters G., Dickson C. Nonuniform expression of a mouse mammary tumor virus-driven int-2/Fgf-3 transgene in pregnancy-responsive breast tumors. Cell Growth Differ. 1992 Dec;3(12):929–938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Mahdavi V. The induction of differentiation in teratocarcinoma stem cells by retinoic acid. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Smith K. K., Marotti K. R. Hormonal induction of differentiation in teratocarcinoma stem cells: generation of parietal endoderm by retinoic acid and dibutyryl cAMP. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):347–355. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90471-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka A., Miyamoto K., Minamino N., Takeda M., Sato B., Matsuo H., Matsumoto K. Cloning and characterization of an androgen-induced growth factor essential for the androgen-dependent growth of mouse mammary carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):8928–8932. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.8928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannahill D., Isaacs H. V., Close M. J., Peters G., Slack J. M. Developmental expression of the Xenopus int-2 (FGF-3) gene: activation by mesodermal and neural induction. Development. 1992 Jul;115(3):695–702. doi: 10.1242/dev.115.3.695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The fibroblast growth factor family. Nomenclature meeting report and recommendations. January 17, 1991. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;638:xiii–xvi. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb49011.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Flores P., Begue A., Leprince D., Stehelin D. The c-ets proto-oncogenes encode transcription factors that cooperate with c-Fos and c-Jun for transcriptional activation. Nature. 1990 Jul 12;346(6280):191–193. doi: 10.1038/346191a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. G., Bhatt S., McMahon A. P. Expression pattern of the FGF-related proto-oncogene int-2 suggests multiple roles in fetal development. Development. 1989 Jan;105(1):131–136. doi: 10.1242/dev.105.1.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. G., Peters G., Dickson C., McMahon A. P. Expression of the FGF-related proto-oncogene int-2 during gastrulation and neurulation in the mouse. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):691–695. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02864.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T., Tjian R. Analysis of the DNA-binding and activation properties of the human transcription factor AP-2. Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):670–682. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]