Abstract
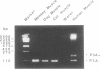
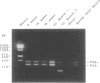
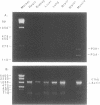
A majority of the autoantibodies in the disease myasthenia gravis (MG) are directed against the alpha-subunit of the muscle nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (AChR). Unlike AChR alpha-subunits previously characterised from other species, the human alpha-subunit exists as two isoforms. The isoforms are generated by alternate splicing of an additional exon located between exons P3 and P4, termed P3A. The 25 amino acids encoded by the P3A exon are incorporated into the extracellular region of the alpha-subunit, and so may be relevant to the pathogenesis of MG. Genomic sequences from rhesus monkey, and from dog and cat, which are susceptible to MG, were characterised between AChR alpha-subunit exons P3 and P4. Although regions homologous to the P3A exon were identified for each of these species, analysis by RT-PCR showed that they are not expressed. At variance with a previous report, constitutive expression of mRNA encoding the human P3A+ alpha-subunit isoform was not detected in heart, kidney, liver, lung or brain. Differential expression of the two alpha-subunit isoforms was not seen during fetal muscle development or in muscle from MG patients. In all cases where mRNAs encoding the two alpha-subunit isoforms have been detected, they are present at an approximate 1:1 ratio.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin T. J., Yoshihara C. M., Blackmer K., Kintner C. R., Burden S. J. Regulation of acetylcholine receptor transcript expression during development in Xenopus laevis. J Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;106(2):469–478. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.2.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beeson D., Morris A., Vincent A., Newsom-Davis J. The human muscle nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunit exist as two isoforms: a novel exon. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2101–2106. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07378.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawkins R. L., Zilko P. J., Carrano J., Garlepp M. J., McDonald B. L. Immunobiology of D-penicillamine. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1981 Jan-Feb;7:56–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garlepp M. J., Dawkins R. L., Christiansen F. T. HLA antigens and acetylcholine receptor antibodies in penicillamine induced myasthenia gravis. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Jan 29;286(6362):338–340. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6362.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D., Boulter J., Heinemann S., Patrick J. Muscle denervation increases the levels of two mRNAs coding for the acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunit. J Neurosci. 1985 Sep;5(9):2553–2558. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-09-02553.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman D. S., Claudio T. Coexpression of two distinct muscle acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunits during development. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):372–375. doi: 10.1038/343372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidenreich F., Vincent A., Roberts A., Newsom-Davis J. Epitopes on human acetylcholine receptor defined by monoclonal antibodies and myasthenia gravis sera. Autoimmunity. 1988;1(4):285–297. doi: 10.3109/08916938809010682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesselmans L. F., Jennekens F. G., Van den Oord C. J., Veldman H., Vincent A. Development of innervation of skeletal muscle fibers in man: relation to acetylcholine receptors. Anat Rec. 1993 Jul;236(3):553–562. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092360315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jermy A., Beeson D., Vincent A. Pathogenic autoimmunity to affinity-purified mouse acetylcholine receptor induced without adjuvant in BALB/c mice. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Apr;23(4):973–976. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao I., Drachman D. B. Thymic muscle cells bear acetylcholine receptors: possible relation to myasthenia gravis. Science. 1977 Jan 7;195(4273):74–75. doi: 10.1126/science.831257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishina M., Takai T., Imoto K., Noda M., Takahashi T., Numa S., Methfessel C., Sakmann B. Molecular distinction between fetal and adult forms of muscle acetylcholine receptor. Nature. 1986 May 22;321(6068):406–411. doi: 10.1038/321406a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A., Beeson D., Jacobson L., Baggi F., Vincent A., Newsom-Davis J. Two isoforms of the muscle acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunit are translated in the human cell line TE671. FEBS Lett. 1991 Dec 16;295(1-3):116–118. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81399-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Furutani Y., Takahashi H., Toyosato M., Tanabe T., Shimizu S., Kikyotani S., Kayano T., Hirose T., Inayama S. Cloning and sequence analysis of calf cDNA and human genomic DNA encoding alpha-subunit precursor of muscle acetylcholine receptor. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):818–823. doi: 10.1038/305818a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick J., Lindstrom J. Autoimmune response to acetylcholine receptor. Science. 1973 May 25;180(4088):871–872. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4088.871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponte P., Ng S. Y., Engel J., Gunning P., Kedes L. Evolutionary conservation in the untranslated regions of actin mRNAs: DNA sequence of a human beta-actin cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 10;12(3):1687–1696. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.3.1687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raftery M. A., Hunkapiller M. W., Strader C. D., Hood L. E. Acetylcholine receptor: complex of homologous subunits. Science. 1980 Jun 27;208(4451):1454–1456. doi: 10.1126/science.7384786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schluep M., Willcox N., Vincent A., Dhoot G. K., Newsom-Davis J. Acetylcholine receptors in human thymic myoid cells in situ: an immunohistological study. Ann Neurol. 1987 Aug;22(2):212–222. doi: 10.1002/ana.410220205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talib S., Okarma T. B., Lebkowski J. S. Differential expression of human nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha subunit variants in muscle and non-muscle tissues. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jan 25;21(2):233–237. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.2.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Seybold M. E., Lindstrom J. M. Specificities of antibodies to acetylcholine receptors in sera from myasthenia gravis patients measured by monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):188–192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wekerle H., Ketelsen U. P., Zurn A. D., Fulpius B. W. Intrathymic pathogenesis of myasthenia gravis: transient expression of acetylcholine receptors on thymus-derived myogenic cells. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Aug;8(8):579–582. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheatley L. M., Urso D., Tumas K., Maltzman J., Loh E., Levinson A. I. Molecular evidence for the expression of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha-chain in mouse thymus. J Immunol. 1992 May 15;148(10):3105–3109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witzemann V., Stein E., Barg B., Konno T., Koenen M., Kues W., Criado M., Hofmann M., Sakmann B. Primary structure and functional expression of the alpha-, beta-, gamma-, delta- and epsilon-subunits of the acetylcholine receptor from rat muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Dec 12;194(2):437–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15637.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]