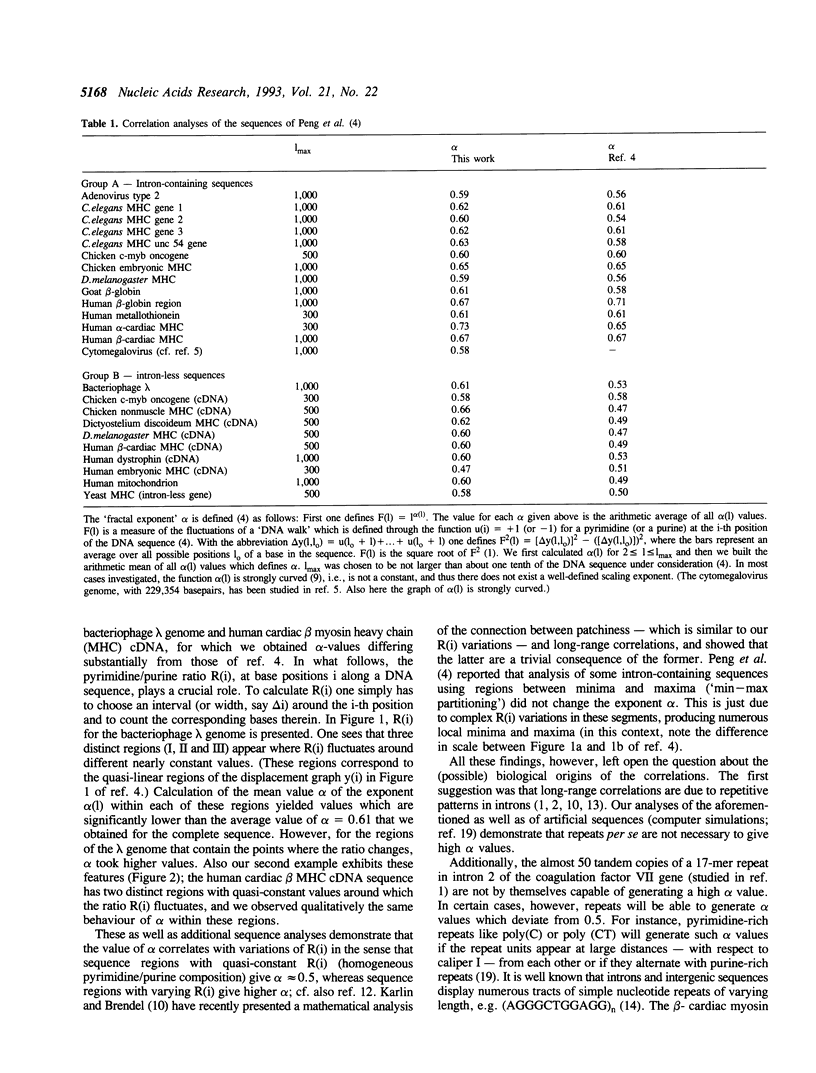
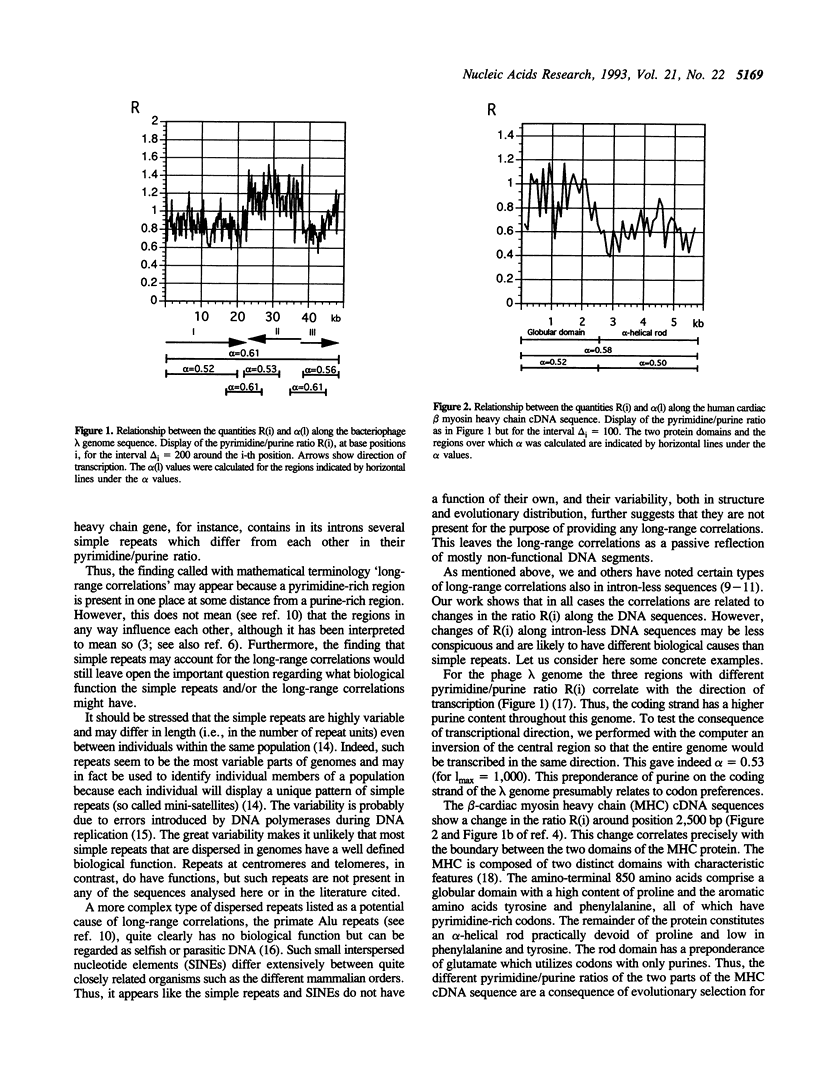
Abstract
The occurrence of certain long-range correlations between nucleotides in DNA sequences of living organisms has recently been reported. The biological origin of these correlations was unknown. The correlations were proposed to be concerned with fractal structure and differences between intron-containing and intron-less sequences. We and others have reported that no consistent difference exists between intron-containing and intron-less sequences. In agreement with this, we demonstrate here that the long-range correlations are trivially equivalent to the varying ratio R between pyrimidines and purines (or any other nucleotide combinations) in different regions of a DNA sequence. Moreover, we show that this variation of R has simple biological explanations: Differences in base composition occur along most DNA sequences and are associated with (i) simple repeats (ii) differences in codon composition (due to the amino acid composition in the encoded protein), (iii) change of the direction of transcription (and thus also translation), and (iv) differences between protein- and rRNA-encoding segments. Seven biological examples are given.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amato I. DNA shows unexplained patterns writ large. Science. 1992 Aug 7;257(5071):747–747. doi: 10.1126/science.1496395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatzidimitriou-Dreismann C. A., Larhammar D. Long-range correlations in DNA. Nature. 1993 Jan 21;361(6409):212–213. doi: 10.1038/361212b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson C. P., Jr, Bernstein S. I. Molecular genetics of myosin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:695–726. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Thein S. L. Individual-specific 'fingerprints' of human DNA. Nature. 1985 Jul 4;316(6023):76–79. doi: 10.1038/316076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin S., Brendel V. Patchiness and correlations in DNA sequences. Science. 1993 Jan 29;259(5095):677–680. doi: 10.1126/science.8430316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson G., Gutman G. A. Slipped-strand mispairing: a major mechanism for DNA sequence evolution. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 May;4(3):203–221. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W., Kaneko K. DNA correlations. Nature. 1992 Dec 17;360(6405):635–636. doi: 10.1038/360635b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddox J. Long-range correlations within DNA. Nature. 1992 Jul 9;358(6382):103–103. doi: 10.1038/358103a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Taylor R. C., Michaels G. S. DNA correlations. Nature. 1992 Dec 17;360(6405):636–636. doi: 10.1038/360636a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nee S. Uncorrelated DNA walks. Nature. 1992 Jun 11;357(6378):450–450. doi: 10.1038/357450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orgel L. E., Crick F. H. Selfish DNA: the ultimate parasite. Nature. 1980 Apr 17;284(5757):604–607. doi: 10.1038/284604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng C. K., Buldyrev S. V., Goldberger A. L., Havlin S., Sciortino F., Simons M., Stanley H. E. Long-range correlations in nucleotide sequences. Nature. 1992 Mar 12;356(6365):168–170. doi: 10.1038/356168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prabhu V. V., Claverie J. M. Correlations in intronless DNA. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):782–782. doi: 10.1038/359782a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voss RF. Evolution of long-range fractal correlations and 1/f noise in DNA base sequences. Phys Rev Lett. 1992 Jun 22;68(25):3805–3808. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.68.3805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


