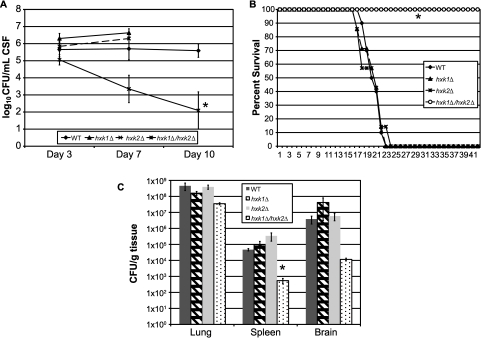
FIG 3 .
Glucose utilization via hexose kinase is required for virulence but not persistence of C. neoformans. (A) NZW rabbits were infected with either the WT, the hxk1∆, the hxk2∆, or the hxk1∆/hxk2∆ strain of C. neoformans as described in Materials and Methods. Differences between strains were assessed by an ANOVA using the fit model process in JMP version 8 (SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC) (*, P = 0.001). Missing data for the hxk1∆ and hxk2∆ strains for day 10 reflect the mortality of all these rabbits before day 10. (B) A/Jcr inbred mice were infected per nasally with the WT, hxk1∆, hxk2∆, or hxk1∆/hxk2∆ strain of C. neoformans. The mice were observed over the course of the experiment for clinical signs correlating with eventual mortality (*, P < 0.0002; log rank test). (C) Fungal burden was assessed for three mice per group from the virulence study described for panel B. Organs were removed at the time of death (~21 days postinfection for the WT, hxk1∆, and hxk2∆ strains; 42 days postinfection for the hxk1∆/hxk2∆ strain) and processed for fungal burden as described elsewhere (70). Differences in numbers of CFU between each mutant strain and the WT for each organ were assessed using Student’s t test (*, P = 0.01).