Abstract
When listing common clinical signs of the spectra of Leishmania-derived diseases, neurologic malfunctions are not commonly included. Despite this, there are multiple reported instances both in human and veterinary medicine where neurologic manifestations, whether central or peripheral, are described. In this review, we describe neurologic manifestations seen during infection with Leishmania spp. with some discussion of the implicit effect of inflammation on the blood brain barrier in both medical and veterinary cases. Taken together, the material discussed here suggests that in patients from Leishmania-endemic areas, when observing neurologic symptoms, causation secondary to infection with Leishmania spp. should be highly considered.
Keywords: leishmaniasis, neurologic, ocular, CNS, macrophage
1 Introduction
Leishmaniasis is a parasitic vector-borne disease caused by a family of obligate intracellular dimorphic protozoa of the genus Leishmania (Figure 1). Although there is a spectra of clinical forms seen with different species of Leishmania parasite, this infection is not classically associated with neurologic manifestations. Despite this, there is a wealth of clinical information on neurological effects of leishmaniasis in animal models [14,15,37] and human case studies [21], which indicates that both central nervous system (CNS) and ocular manifestations are common and often underreported. There are historical [5] and recent reports [1] of both CNS and ocular alterations with visceral leishmaniasis (VL), particularly. In addition to CNS manifestations, there have been studies indicating localized peripheral nerve deficits with cutaneous leishmaniasis [25]. On the whole, neurologic manifestations may occur with Leishmania infection much more frequently than discussed in overview descriptions of this complex infectious disease process.
Figure 1.
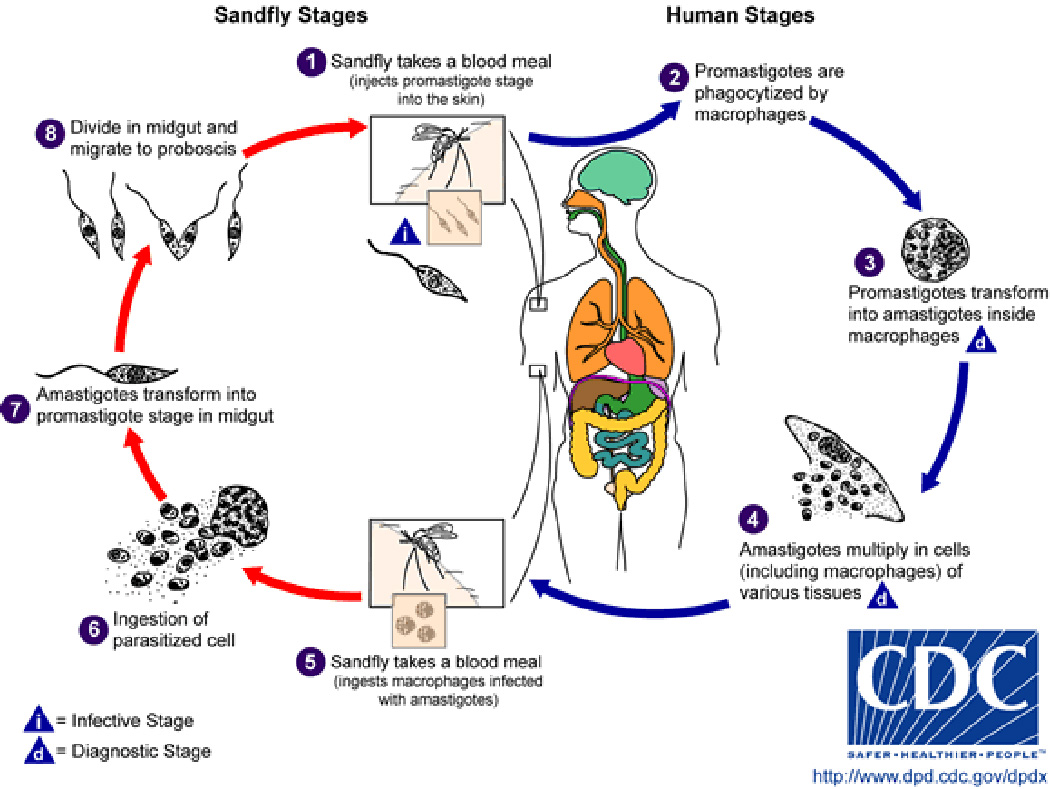
Leishmania life cycle. Credit to CDC.
2 Historical case reports of neurologic manifestations during Leishmania infection
Visceral leishmaniasis (VL), also known in humans as Kala-azar, meaning “black sickness” for the increased pigmentation observed on the skin of the face, feet and hands in patients in the Bihar region of India, has been recognized as a disease for centuries. At the turn of the twentieth century, British pathologists studying “dum-dum fever” patients in India reported finding amastigotes in brain meninges [44]. On gross examination of VL patients from East Africa, it is common to find widely disseminated parasites, including in the cerebrospinal fluid and in the endothelia of meningeal vessels [44]. In Northern Africa, paralytic symptoms were reported to be associated with VL, which would resolve after treatment with pentavalent antimony [44]. A report from the mid-1960s described neurologic disturbances in patients infected with VL [36]. Mental changes are also commonly reported; Carswell indicated that “although patients can walk 20 miles to the dispensary, they had a most curious mental depression and were completely apathetic” [5]. “Definite mental changes” in 3 of 18 patients were described in a collection of clinical cases from Ethiopia [29].
Regarding cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL), a report investigating associated distal nerve involvement in cutaneous lesion biopsy specimens in the 14 affected biopsies described an overallperineural inflammatory cell infiltrate consisting of either lymphocytes or a mixture of lymphocytes, plasma cells, and macrophages [25]. In this report, four patients had inflammatory cell invasion of the nerves (neuritis), and in one of them the inflammation was granulomatous and associated with nerve destruction. Amastigotes were seen inside the perineural sheath in two patients. Sensory testing of 50 consecutive patients with cutaneous leishmaniasis identified two patients with diminished sensations in the area of their CL lesions [25]. A study of hyperesthetic CL patients with follow-up mechanistic studies using L. major infection in BALB/c mice, nerve sheath inflammation and parasites within the perineural space occurred with some frequency, though nerve inflammation did not correlate with persistence of the cutaneous lesion [46].
3 Recent case reports of neurologic manifestations during Leishmania infection
More recent case reports from the last two decades also indicated that neurologic abnormalities in Leishmania-infected patients are not unusual. A report from Sudan which followed 111 patients described neurologic signs in 46% of the patients in this study, the most common of which was the sensation of burning feet and foot drop with less frequent to rare deafness and cranial nerve deficits [21]. In most patients these neurological signs diminished or went away altogether after initiation of anti-Leishmania therapy. A separate report of VL in 10-year-old boy who was not responsive to initial therapy indicated that this patient also had parasite-related meningitis. When this patient was treated with an anti-leishmaniacidal regimen of Amphotericin B, his meningitis resolved [43]. Finally, there are reports of patients who have cutaneous and ocular manifestations of leishmaniasis after renal transplant and immunosuppression [20].
4 Evidence in animal models of neurologic manifestations during Leishmania infection
VL transmission is primarily vector borne via the sand fly, with dogs and humans as natural host species [45]. Infected dogs are the primary reservoir for zoonotic visceral leishmaniasis in endemic regions, and are the most significant risk factor predisposing humans to infection [17]. The range of vector-borne canine VL is expanding, leading to new areas where human infection occurs [34]. Chemotherapy of canines is often unsuccessful, providing continued transmission risk from infected dogs to humans. Canine clinical signs often mirror symptoms which are reported in human patients, and neurologic manifestations are no exception.
Although the most common CNS finding is infiltration of inflammatory cells during VL infection of dogs [33], there are reports of presence of amastigotes in both choroid plexus [37] and meninges [49] (which was confirmed via immunohistochemistry in experimental infection [48]). It is also reported to be not uncommon to see ocular changes with canine VL [30]. Similar to the reports of vagueness or apathy in human patients [5,36], in a report of Leishmaniasis in U.S. hunting dogs the dog’s caretaker noted neurological signs including “altered states of mind”, seizures, hind limb paralysis and loss of scenting ability [2]. A diffuse non-supperative meningoencephalitis with scattered areas of necrosis in grey matter and diffuse vacuolation in the white matter with gliosis in both white and grey matters was found in these Leishmania-infected dogs. Previous studies of Foxhounds in early 2000’s found that dogs chronically infected with VL sometimes presented with a chief complaint of atypical behavior, particularly transient aggression, photophobia, hyperesthesia, paralytic episodes and seizures [24]. All dogs were current on their rabies vaccination and were not positive for rabies upon post-mortem analysis. We more recently have noted that loss of balance, particularly in the front end, and disorientation (Petersen, unpublished findings) are not uncommon in foxhound dogs which we observe as part of our ongoing studies [18,41,42]. Beyond these more typical locations of parasites and neurologic malfunction, there is a report of infection of tongue leading to cranial nerve deficits [13].
Rodents are also found to be naturally infected with particularly cutaneous forms of leishmaniasis, although a version of visceralizing disease can be found in BALB/c mice and golden Syrian hamsters. Studies dating back to the 1920’s demonstrated neurologic manifestations of infection with VL in hamsters [31]. Similarly, BALB/c mice have been shown to have CNS-tropic VL [16].
5 Disruption of the blood brain barrier
Reports of neuro-inflammation associated with natural and experimental VL infection [1,33], as well as the presence of Immunoglobulin in aqueous humor and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) [15] suggest a disruption of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), and the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier underlies the CNS manifestation of disease. The BBB functions to exclude microscopic objects and large hydrophilic molecules, and is achieved by endothelial cell specializations including tight junctions between cells, a specialized basal lamina surrounding the vessels in the brain, and an ensheathment of the vessels made of astrocytic endfeet [11]. Under normal physiological conditions, the BBB would prevent the entry of intracellular amastigotes and subsequent inflammatory cells observed with VL (Figure 2). The BBB can be disrupted by matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), which are major extracellular matrix degrading enzymes [4]. There have been reports of MMP 2 and 9 expressions in animals with VL [27,28, 32] though it is unclear if (1) this is the mechanism that underlies BBB disruption and infiltration of leukocytes and (2) what is the underlying cause of MMP expression.
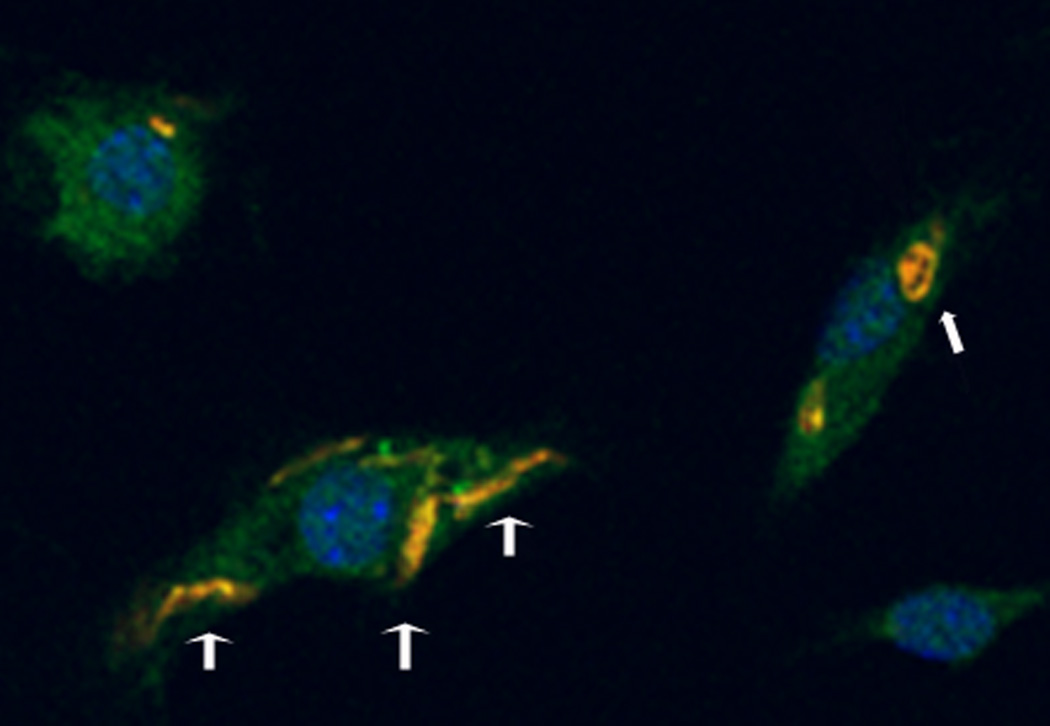
Figure 2.
Leishmania amazonensis amastigote (narrow head arrow) and promastigotes (broad head arrows) within murine dendritic cells, labeled with a parasite specific antibody (yellow), nuclei labeled with DAPI (blue), 100× magnification, fluorescence microscopy. Through infection of monocyte-lineage cells, parasites make their way into the CNS.
6 Ocular manifestations subsequent to neurologic manifestations during Leishmania infection secondary to inflammation
Given the pervasive nature of Leishmania infection and its ability to cause inflammation in the central nervous system, it is not therefore surprising that ocular manifestations are also somewhat common. Most frequently the clinical presentation of ocular leishmaniasis in humans is anterior uveitis either prior to or just after presumed successful treatment of visceral leishmaniasis. Less frequently parasites are found in the orbit [9,10]. Uveitis can progress to secondary glaucoma [9], a disease of retinal cells. Retinal hemorrhages have been observed on fundic examination; in some cases multiple lesions were reported (> 10 lesions in each eye) [8, 35]. In a more severe case, these lesions appeared to be ‘flame-shaped’ potentially arising from hemorrhages from arteriolar capillaries of the nerve fiber layer. In all reported cases, there was a correlation with at least moderate-to-severe anemia with thrombocytopenia. These retinal hemorrhages resolved after treatment for leishmaniasis and improvement of the secondary anemia/thrombocytopenia. In one unusual case, mucosal leishmaniasis presented as optic neuropathy and sinusitis [23].
Similarly, regarding canine visceral leishmaniasis, it is not uncommon to perceive uveitis during chronic systemic canine VL [14,15]. There were measurable levels of anti-Leishmania IgG within the aqueous humor and cerebrospinal fluid as measured by ELISA; these levels did not correlate with serum antibody levels. There was a marked inflammation of multiple ocular structures including the ciliary processes, ciliary body, iris and lacrimal duct and presence of amastigote parasites [14,15].
7 Ocular abnormalities secondary to facial mucocutaneous disease
Within the literature, there are multiple cases of involvement of eyelid during clinical cutaneous or mucocutaneous leishmaniasis [38], with a granulomatous infiltrate in four out of five cases and observable parasites within the touch preparation in two patients. All five patients in this series [38] had positive leishmanin skin tests and eyelid lesions which resolved with anti-Leishmania therapy. Although rare, severe manifestations of eyelid involvement have been described which altered vision. As an example, a lesion which led to bilateral ptosis and lower eyelid ectropion secondary to cutaneous leishmaniasis caused a severe exposure keratopathy [6]. Although not a primary ocular lesion, a chronic dacryocystitis with mucocutaneous leishmaniasis has been described in multiple patients, which led to ocular abnormalities due to problems in tear film formation [3].
8 Endo-ocular parasitism
The first case to report Leishmania sp. isolated from aqueous humor in a (human) patient with disseminated CL and bilateral non-granulomatous iridocyclitis [12] was in Brazil. The ophthalmologic lesions were unresponsive to therapy despite resolution of the other systemic and cutaneous manifestations of this disease, which led to a fine needle aspirate of the anterior eye and isolation of Leishmania sp. This rare finding is in contrast to canine disease where 25% of canine VL cases have ocular manifestations [39], with a range of 16–80% in various case studies [7,19,30,40,47]. In the most recent review, a granulomatous inflammatory infiltrate was found and in 32 of 120 eyes (26.6%) with parasites identified immunohistochemically within the globe [39]. Ocular tissues found to be affected, in order of frequency, were conjunctiva and limbus, ciliary body, iris, cornea, sclera and iridocorneal angle, choroid and the optic nerve sheath. Different histopathological patterns were identified in each of these ocular structures. Leishmania organisms and associated inflammation were found in different ocular tissues, accounting for ocular clinical signs described with canine VL [39]. There have been three cases of feline ocular leishmaniasis reported [22,26]. In the most recent case, initial ophthalmic examination revealed bilateral deep stromal corneal ulcers, exudative panuveitis and secondary glaucoma. Although a specific topical treatment was applied, melting ulcers progressed to corneal perforation and both eyes were enucleated. Ocular histopathology showed large numbers of intracellular organisms compatible with amastigotes of the genus Leishmania in the uvea, cornea, sclera and retina. Results of immunohistochemical staining on ocular samples were positive for Leishmania [26].
9 Conclusions
Although not frequently thought of as “classical” clinical signs or symptoms of clinical leishmaniasis, neurologic manifestations of particularly visceralizing leishmaniasis is not uncommon in either human or other mammalian infection. When determining the cause of visual deficits in either human or canine patients that come from endemic areas for leishmaniasis, a fundic exam may be diagnostic and provide further insight on the overall case. Both central and peripheral nervous system alterations have been shown to occur with leishmaniasis.
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health grant AI50803.
References
- 1.Abreu-Silva AL, Calabrese KS, Tedesco RC, Mortara RA, Gonçalves da Costa SC. Central nervous system involvement in experimental infection with Leishmania (Leishmania) amazonensis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2003;68:661–665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Anderson DC, Buckner RG, Glenn BL, MacVean DW. Endemic canine leishmaniasis. Vet Pathol. 1980;17:94–96. doi: 10.1177/030098588001700110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Baddini-Caramelli C, Matayoshi S, Moura EM, Araf D, Santo R, Ruth MD, et al. Chronic dacryocystitis in American mucocutaneous leishmaniasis. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001;17:48–52. doi: 10.1097/00002341-200101000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Candelario-Jalil E, Yang Y, Rosenberg GA. Diverse roles of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in neuroinflammation and cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience. 2009;158:983–994. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.06.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Carswell J. Kala-azar at Kitui. East Afr Med J. 1953;30:287–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chaudhry IA, Hylton C, DesMarchais B. Bilateral ptosis and lower eyelid ectropion secondary to cutaneous leishmaniasis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1998;116:1244–1245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ciaramella P, Oliva G, De Luna R, Ambrosio R, Cortese L, Persechino A, et al. A retrospective clinical study of canine leishmaniasis in 150 dogs naturally infected by Leishmania infantum. Vet Rec. 1997;141:539–543. doi: 10.1136/vr.141.21.539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.De Cock KM, Rees PH, Klauss V, Kasili EG, Kager PA, Schattenkerk JK. Retinal hemorrhages in kala-azar. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1982;31:927–930. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1982.31.927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Dechant W, Rees PH, Kager PA, Klauss V, Adala H. Post kala-azar uveitis. Br J Ophthalmol. 1980;64:680–683. doi: 10.1136/bjo.64.9.680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.El-Hassan AM, El-Sheikh EA, Eltoum IA, Ghalib HW, Ali MS, Zijlstra E, et al. Post-kala-azar anterior uveitis: demonstration of Leishmania parasites in the lesion. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1991;85:471–473. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(91)90222-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Engelhardt B, Sorokin L. The blood-brain and the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barriers: function and dysfunction. Semin Immunopathol. 2009;31:497–511. doi: 10.1007/s00281-009-0177-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ferrari TC, Guedes AC, Oréfice F, Genaro O, Pinheiro SR, Marra MA, et al. Isolation of Leishmania sp. from aqueous humor of a patient with cutaneous disseminated leishmaniasis and bilateral iridocyclitis (preliminary report) Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 1990;32:296–298. doi: 10.1590/s0036-46651990000400010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Foglia Manzillo V, Paparcone R, Cappiello S, de Santo R, Bianciardi P, Oliva G. Resolution of tongue lesions caused by Leishmania infantum in a dog treated with the association miltefosine-allopurinol. Parasit Vectors. 2009;2 Suppl 1:S6. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-2-S1-S6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.García-Alonso M, Blanco A, Reina D, Serrano FJ, Alonso C, Nieto CG. Immunopathology of the uveitis in canine leishmaniasis. Parasite Immunol. 1996;18:617–623. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3024.1996.d01-39.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.García-Alonso M, Nieto CG, Blanco A, Requena JM, Alonso C, Navarrete I. Presence of antibodies in the aqueous humour and cerebrospinal fluid during Leishmania infections in dogs. Pathological features at the central nervous system. Parasite Immunol. 1996;18:539–546. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3024.1996.d01-28.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Garin YJF, Sulahian A, Méneceur P, Pratlong F, Prina E, Gangneux J-P, et al. Experimental pathogenicity of a presumed monoxenous trypanosomatid isolated from humans in a murine model. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2001;48:170–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.2001.tb00299.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Gavgani AS, Hodjati MH, Mohite H, Davies CR. Effect of insecticide-impregnated dog collars on incidence of zoonotic visceral leishmaniasis in Iranian children: a matched-cluster randomised trial. The Lancet. 2002;360:374–379. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(02)09609-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gibson-Corley KN, Hostetter JM, Hostetter SJ, Mullin K, Ramer-Tait AE, Boggiatto PM, et al. Disseminated Leishmania infantum infection in two sibling foxhounds due to possible vertical transmission. Can Vet J. 2008;49:1005–1008. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ginel PJ, Mozos E, Fernandez A, Martinez A, Molleda JM. Canine pemphigus foliaceus associated with leishmaniasis. Vet Rec. 1993;133:526–527. doi: 10.1136/vr.133.21.526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gontijo CM, Pacheco RS, Oréfice F, Lasmar E, Silva ES, Melo MN. Concurrent cutaneous, visceral and ocular leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania (Viannia) braziliensis in a kidney transplant patient. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2002;97:751–753. doi: 10.1590/s0074-02762002000500029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hashim FA, Ahmed AE, El-Hassan M, El-Mubarak MH, Yagi H, Ibrahim EN, et al. Neurologic changes in visceral leishmaniasis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1995;52:149–154. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1995.52.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hervás J, Chacón-Manrique de Lara F, López J, Gómez-Villamandos JC, Guerrero MJ, Moreno A. Granulomatous (pseudotumoral) iridociclitis associated with leishmaniasis in a cat. Vet Rec. 2001;149:624–625. doi: 10.1136/vr.149.20.624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Huna-Baron R, Warren FA, Miller W, Jacobs J, Green J, Kupersmith MJ. Mucosal leishmaniasis presenting as sinusitis and optic neuropathy. Arch Ophthalmol. 2000;118:852–854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Jackson JE, Iwu MM, Okunji CO, Van Gessel Y, Schantz P, Steurer F, et al. Chronic canine visceral leishmaniasis (VL): prepatent VL neurologic manifestations. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2002;67:222–223. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kubba R, El-Hassan AM, Al-Gindan Y, Omer AHS, Bushra M, Kutty MK. Peripheral nerve involvement in cutaneous Leishmaniasis (old world) Int J Dermatol. 1987;26:527–531. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4362.1987.tb02295.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Leiva M, Lloret A, Peña T, Roura X. Therapy of ocular and visceral leishmaniasis in a cat. Vet Ophthalmol. 2005;8:71–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-5224.2005.00342.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Machado GF, de Melo GD, de Moraes OC, de Souza MS, Marcondes M, Perri SH, et al. Differential alterations in the activity of matrix metalloproteinases within the nervous tissue of dogs in distinct manifestations of visceral leishmaniasis. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2010;136:340–345. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2010.03.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Marangoni NR, de Melo GD, de Moraes OC, de Souza MS, Perri SH, Machado GF. Levels of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and metalloproteinase-9 in the cerebrospinal fluid of dogs with visceral leishmaniasis. Parasite Immunol. 2011;33:330–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.2011.01285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Maru M. Clinical and laboratory features and treatment of visceral leishmaniasis in hospitalized patients in Northwestern Ethiopia. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1979;28:15–18. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1979.28.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.McConnell EE, Chaffee EF, Cashell IG, Garner FM. Visceral leishmaniasis with ocular involvement in a dog. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1970;156:197–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Meleney HE. The histopathology of kala-azar in the hamster, monkey, and man. Am J Pathol. 1925;1:147–168. 11. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Melo GD, Marangoni NR, Marcondes M, Lima VM, Machado GF. High levels of serum matrix metalloproteinases in dogs with natural visceral leishmaniosis: a preliminary report. Vet J. 2011;188:243–245. doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2010.03.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Melo GD, Marcondes M, Vasconcelos RO, Machado GF. Leukocyte entry into the CNS of Leishmania chagasi naturally infected dogs. Vet Parasitol. 2009;162:248–256. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2009.03.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Miro G, Cardoso L, Pennisi MG, Oliva G, Baneth G. Canine leishmaniosis—new concepts and insights on an expanding zoonosis: part two. Trends Parasitol. 2008;24:371–377. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2008.05.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Montero JA, Ruiz-Moreno JM, Sanchis E. Intraretinal hemorrhage associated with leishmaniasis. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging. 2003;34:212–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Mustafa D. Neurological disturbances in visceral leishmaniasis. J Trop Med Hyg. 1965;68:248–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Nieto CG, Vinuelas J, Blanco A, García-Alonso M, Verdugo SG, Navarrete I. Detection of Leishmania infantum amastigotes in canine choroid plexus. Vet Rec. 1996;139:346–347. doi: 10.1136/vr.139.14.346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Oliveira-Neto MP, Martins VJ, Mattos MS, Pirmez C, Brahin LR, Benchimol E. South American cutaneous leishmaniasis of the eyelids: report of five cases in Rio de Janeiro State, Brazil. Ophthalmology. 2000;107:169–172. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(99)00011-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Peña MT, Naranjo C, Klauss G, Fondevila D, Leiva M, Roura X, et al. Histopathological features of ocular leishmaniosis in the dog. J Comp Pathol. 2008;138:32–39. doi: 10.1016/j.jcpa.2007.09.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Pena MT, Roura X, Davidson MG. Ocular and periocular manifestations of leishmaniasis in dogs: 105 cases (1993–1998) Vet Ophthalmol. 2000;3:35–41. doi: 10.1046/j.1463-5224.2000.00106.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Petersen CA. New means of canine leishmaniasis transmission in North America: the possibility of transmission to humans still unknown. Interdiscip Perspect Infect Dis. 2009;2009:802712. doi: 10.1155/2009/802712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Petersen CA, Barr SC. Canine leishmaniasis in North America: emerging or newly recognized? Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 2009;39:1065–1074. doi: 10.1016/j.cvsm.2009.06.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Prasad LS, Sen S. Migration of Leishmania donovani amastigotes in the cerebrospinal fluid. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1996;55:652–654. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1996.55.652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Rees PH, Kager PA. Visceral leishmaniasis and post-kala-azar dermal leishmaniasis. In: Peters W, Killick-Kendrick R, editors. The Leishmaniases in Biology and Medicine. vol. 1. London: Academic Press; 1987. pp. 584–596. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Roberts LJ, Handman E, Foote SJ. Science, medicine, and the future: Leishmaniasis. BMJ. 2000;321:801–804. doi: 10.1136/bmj.321.7264.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Satti MB, El-Hassan A, Al-Gindan Y, Osman MA, Al-Sohaibani MO. Peripheral neural involvement in cutaneous leishmaniasis. A pathologic study of human and experimental animal lesions. Int J Dermatol. 1989;28:243–247. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4362.1989.tb04813.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Slappendel RJ. Canine leishmaniasis. A review based on 95 cases in The Netherlands. Vet Q. 1988;10:1–16. doi: 10.1080/01652176.1988.9694140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Tafuri WL, Santos RL, Arantes RM, Goncalves R, de Melo MN, Michalick MSM. An alternative immunohistochemical method for detecting Leishmania amastigotes in paraffin-embedded canine tissues. J Immunol Methods. 2004;292:17–23. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2004.05.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Viñuelasa J, García-Alonso M, Ferrando L, Navarrete I, Molano I, Mirón C. Meningeal leishmaniosis induced by Leishmania infantum in naturally infected dogs. Vet Parasitol. 2001;101:23–27. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4017(01)00413-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]