Abstract
In this study, electrostatic interactions between sulfonate groups of an immobilized polymer and the heparin binding domains of growth factors important in cell signaling were exploited to nanopattern the proteins. Poly(sodium 4-styrenesulfonate-co-poly(ethylene glycol) methacrylate) (pSS-co-pPEGMA) was synthesized by reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization using ethyl S-thiobenzoyl-2-thiopropionate as a chain transfer agent and 2,2′azoisobutyronitrile (AIBN) as the initiator. The resulting polymer (1) was characterized by 1H NMR, GPC, FT-IR, and UV-Vis and had a number average molecular weight (Mn) of 24,000 and a polydispersity index (PDI) of 1.17. The dithioester end group of 1 was reduced to the thiol, and the polymer subsequently immobilized on a gold substrate. Binding of basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) to the polymer via the heparin binding domains was then confirmed by surface plasmon resonance (SPR). The interactions were stable at physiological salt concentrations. Polymer 1 was cross-linked onto silicon wafers using an electron beam writer forming micron- and nano- patterns. Resolutions of 100 nm and arbitrary nanoscale features such as concentric circles and contiguous squares and triangles were achieved. Fluorescence microscopy confirmed that bFGF and VEGF were subsequently immobilized to the polymer micro- and nano- patterns.
INTRODUCTION
Patterning cell signaling molecules is important to study cell behavior on surfaces and for directing cell adhesion for applications in biomaterials and tissue engineering.1-3 These surfaces mimic the extracellular matrix (ECM) to enable cell attachment and growth. There are many examples of micropatterning biomolecules found in the ECM such as fibronectin peptide segments and growth factors. However, although it is known that nanoscale presentation of ECM-derived proteins is critical for cellular response,4 only a few examples of patterning these ligands at the nanoscale have been reported to date. In particular, dip-pen lithography5,6 and block-copolymer micelle nanolithography4 have been used to pattern integrin binding peptides such as RGD. These examples nicely demonstrate the importance of nanoscale presentation of these ligands. However, despite the importance of growth factors for stimulating cellular response, to our knowledge there have been no examples of patterning these proteins at the nanoscale. Doing so would provide access to fabricated surfaces that better mimic the ECM in order to improve our understanding and control over cell behavior. Herein, we describe a straightforward way to immobilize growth factors into nanopatterns utilizing electron beam (e-beam) lithography to cross-link a specially designed heparin mimicking polymer into desired features.
Growth factors are proteins that transmit signals to control cellular activities by stimulating or inhibiting cell division, differentiation, migration or gene expression.7 Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) are two important proteins of this class. VEGF stimulates endothelial cell growth, migration, and survival to form new blood vessels.8 bFGF causes migration and proliferation of many cell types important in wound healing.9 Because of these advantageous properties, although nanoscale patterns have yet to be achieved, immobilization of VEGF and bFGF on surfaces either without patterns or in micropatterns has been demonstrated. T. Tagushi, et al. conjugated VEGF by first polymerizing acrylic acid from a poly(ethylene) surface to obtain a poly(acrylic acid)-grafted-poly(ethylene) film.10 VEGF was then immobilized onto the polymeric film by coupling of the amine residues with the carboxylic acids on the surface. It was found that co-immobilization of VEGF with fibronectin resulted in increased cell growth. Backer showed that site-specific conjugation of an active Cys-tagged single chain VEGF to fibronectin followed by its immobilization into tissue culture plastic surfaces was efficient for promoting cell growth.11 Kitajima formed VEGF micropatterns via photolithography by coating a silicon surface with a mixture of VEGF and a photo-reactive gelatin and UV irradiation.12 Matsuda patterned photoactive bFGF and other growth factors onto surfaces using color ink jet printers,13 while Birch and coworkers formed micropatterns of poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) hydrogels with embedded VEGF.14 The patterns were made by coating VEGF, poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate, and 2-2′-dimethoxy-2-phenylacetophenone onto a silicon surface and exposing to UV light. In this report, we describe a new method to pattern bFGF and VEGF at both the micron- and nano-scale that utilizes e-beam lithography.
For nanopatterning, it is important that the biomolecules are site selectively conjugated to surfaces. Random attachment can lead to reduction in bioactivity of the attached protein,15 and as feature sizes are reduced to the nanoscale, such losses become increasingly significant. VEGF and bFGF bind with high affinity to the polysaccharide heparin, which provides a way for site selective immobilization of these proteins. Heparin is a sulfated polysaccharide with 2-amino-2-deoxyglycose and L-iduronic acid as repeat units and binds to regions of clustered positive charges on the surfaces of the growth factors called the heparin binding domains. In the ECM, heparin stores and protects bFGF and VEGF,7,9,16 and thus could have the additional advantage of stabilizing the growth factors on surfaces. Indeed, this affinity has been exploited to pattern the proteins at the microscale.17-20 We envisioned that this strategy could be employed to pattern proteins at the nanoscale. However, heparin has major limitations in that it is difficult to modify and typically exhibits batch-to-batch variability in structure and bioactivity.16 Such limitations are not a concern with synthetic polymers. We thus examined whether a polymer could be prepared that could bind to the heparin binding domains of bFGF and VEGF and also be readily patterned on a surface.
Heparin can be mimicked by molecules that contain groups similar to those in the polysaccharide, typically sulfonates or sulfates. For example, small molecules, including β-cyclodextrin tetradecasulfate and suramin, exhibit similar biological activities to heparin.21-25 In addition negatively charged polymers and those with side chain amino acids or saccharides have been reported.26-34 We chose to incorporate sodium 4-styrenesulfonate (SS) into our polymer because, like heparin, polySS had been shown to protect growth factors and have anti-angiogenesis behavior.31,32 These results suggested that exhibited activity arose primarily from binding of the polymer to bFGF, although this was not directly shown. Using surface plasmon resonance (SPR), we demonstrated for the first time that a polymer containing 4-styrenesulfonate does indeed bind to bFGF and VEGF at the heparin binding domains. We further exploited this binding to immobilize growth factors onto surfaces.
Electron-beam (e-beam) lithography was employed to prepare patterns of the heparin mimicking polymer. When exposed to focused electron beams, PEG cross-links to surfaces of either the native oxide of silicon35 or a PEG silane,36,37 forming hydrogel materials. The process is believed to occur through hydrogen abstraction and coupling of the resulting polymer radicals.38,39 The mechanism is proposed to be similar for alkoxy radical-mediated cross-linking of PEG.40 Therefore, PEG methacrylate (PEGMA) was incorporated into the heparin mimicking polymer so that the PEG side chains could be exploited to pattern the polymer; the polySS portion of the polymer would in turn bind the growth factors (Figure 1). In this report, the synthesis, heparin mimicking ability, and patterning of poly(sodium 4-styrenesulfonate-co-poly(ethylene glycol) methacrylate) (pSS-co-PEGMA) is described. Subsequent immobilization of VEGF and bFGF into micron and nanometer sized features is also discussed.
Figure 1.
Conjugation of proteins to nanopatterns of a heparin-mimicking polymer. a-b. Films of poly(styrene sulfonate-co-PEG methacrylate) 1 are exposed to electron beams to cross-link the polymer to the surface via radical coupling of the PEG side chains. c. VEGF and d. bFGF are conjugated to the surfaces via interaction of the heparin binding domains with the polymer. Protein representations obtained from the PDB (1VPF, 1BFG).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Synthesis of pSS-co-PEGMA
Reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization was employed to synthesize pSS-co-PEGMA, 1 (Scheme 1). In recent years controlled radical polymerization techniques such as RAFT41,42 polymerization, atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP)43,44, and nitroxide-mediated polymerization (NMP)45 have been widely used for the synthesis of well-defined polymers with defined end groups. Sulfonated styrene has been successfully polymerized utilizing all of these methods.42,46-56 For this particular study, we chose RAFT polymerization for several reasons. First, RAFT is known to be robust, tolerating a wide range of monomers and solvents including water,57,58 which was utilized as a co-solvent in the polymerization. Second, reversible chain transfer agents (CTAs) such as dithioesters or trithiocarbonates are employed in RAFT polymerization. These agents are present at the chain ends of the resultant polymers and can be exploited for further elaboration including immobilization onto gold surfaces.53 This feature was useful for us to investigate the interaction of VEGF and bFGF with the polymer because the polymer could be readily immobilized onto gold coated SPR chips for binding studies, as described below.
Scheme 1.
Synthesis and reduction of pSS-co-PEGMA.
PEGMA and sodium 4-styrenesulfonate in a DMF:H2O mixture were polymerized at 90 °C with ethyl S-thiobenzoyl-2-thiopropionate as the CTA and 2,2′-azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN) as the initiator. The polymerization was stopped after 18 h, and the polymer was purified by dialysis in water. The copolymer 1 recovered as a pink solid after lyophilization had a number average molecular weight (Mn) by GPC (ESI, Figure S1) of 24,000 Da and a narrow molecular weight distribution (polydispersity index of 1.17). The initial feed ratio of SS to PEGMA was 3:1 and upon close examination of the 1H NMR spectrum of the polymer (ESI, Figure S2) it was determined that the final ratio was approximately 2.2:1. The IR spectrum of polymer 1 (Figure 2a) contained peaks pertaining to both the SS and the C=O stretch of the ester at 1718 cm−1, the C-O stretch of the PEG at 1100 cm−1, and the peaks at 1181, 1123, and 1036 cm−1 corresponding to the aryl SO stretches were visible. Due to peak overlap in the aromatic region of the spectrum, end group analysis of pSS-co-PEGMA was not possible by 1H NMR. Therefore, UV-Vis spectroscopy was employed. The spectrum the dithioester CTA had two peaks corresponding to the thiocarbonyl moiety. A strong absorbance at 301 nm in methanol was attributed to the π-π* transition and a weak absorbance at 497 nm was from the n-π*transition. The π-π* transition was also visible in the polymer at 303 nm indicating that the dithioester group was present in polymer 1. Taken together these results demonstrated that preparation of this polymer, containing both sulfonate and PEG side chain units and a dithioester end group, was readily achieved by RAFT polymerization.
Figure 2.
FT-IR spectra of a) PSS-co-PEGMA 1 powder and b) FT-IR spectrum of PSS-co-PEGMA 2 immobilized on a gold surface.
Binding of bFGF and VEGF to pSS-co-PEGMA
SPR studies were undertaken to confirm binding of bFGF and VEGF to 1. SPR is widely employed to study binding events.59,60 To conduct these studies, the polymer was immobilized onto a gold-coated SPR chip. Polymer 1 was treated with an excess of n-butylamine to reduce the dithioester group to a thiol group (Scheme 1).61 The reaction was stopped after two hours, and after precipitation, pSS-co-PEGMA 2 was recovered as a white powder. The polymer was immediately dissolved in methanol and immobilized onto a gold coated SPR chip. Polymer immobilization was confirmed by surface IR (Figure 2b).
SPR measurements were performed utilizing a Biacore X instrument. For all measurements, 50 μL of the protein sample in phosphate buffer saline (PBS) with 0.1% Triton X was injected. After every protein injection the chip was washed with 40 μL of a regeneration buffer containing high salt (4 M NaCl) to disrupt electrostatic interactions. In this manner, binding of VEGF and bFGF was studied using bovine serum albumin (BSA) as a control.
SPR analysis revealed that both VEGF and bFGF bound to pSS-co-PEGMA in a dose dependent manner (Figure 3). bFGF was injected at different concentrations (Figure 3a): 0.1μg/mL (red line), 0.2 μg/mL (green line) and 0.5 μg/mL (yellow line). As expected, increasing the concentration of bFGF from 0.1 to 0.5 μg/mL resulted in a greater response, which indicated that the protein was binding to the polymer. Moreover, when a solution of 0.2 μg/mL of bFGF containing 20 μg of heparin was injected, the response (blue line) was greatly reduced compared to 0.2 μg/mL of bFGF alone (green line). This result demonstrated that heparin competed with the polymer for binding of bFGF. Control protein BSA, which does not bind to heparin, did not bind to the polymer (Figure 3a, gray line) which further suggested that the heparin binding domain was necessary for binding. SPR studies with VEGF revealed similar results (Figure 3b). Increasing the concentration of VEGF from 0.1 to 0.5 μg/mL resulted in an increased response. When 0.2 μg/mL of VEGF with 20 μg of heparin was injected, a decrease in the response units (RU) was also observed (red compared to green line), which indicated competitive binding. Taken together these data demonstrated that bFGF and VEGF bind to the polymer and that the binding likely occurred at the heparin binding domains. It was not possible to quantify the affinity constants using the experimental configuration utilized to obtain the traces in Figure 3, because the entire chip surface was modified by the polymer; an unmodified control channel is required to determine affinity constants by SPR. We are currently working on obtaining these values by other methods.
Figure 3.
SPR analysis of growth factor binding to immobilized pSS-co-PEGMA. a. Injection of yellow line: 0.5 μg/mL, green line: 0.2 μg/mL, red line: 0.1μg/mL of bFGF, blue line: 0.2 μg/mL bFGF in the presence of 20 μg of heparin, and grey line: 0.2 μg/mL of control protein BSA. b. Injection of yellow line: 0.5 μg/mL, green line: 0.2 μg/mL, blue line: 0.1μg/mL of VEGF, and red line: 0.2 μg/mL VEGF in the presence of 20 μg of heparin. Solution: PBS containing 0.1% Triton X. Surfaces were regenerated with phosphate buffer containing 4 M NaCl. Protein representations were obtained from the PDB (1VPF, 1BFG).
Next, SPR was employed to determine the stability of the growth factor-polymer binding to added salt. This stability is important for applications in medicine. After adding the growth factors, solutions of increasing salt concentration were injected. Results indicated that salt concentrations significantly higher than 150 mM, the physiological salt concentration, were necessary to disrupt binding (ESI, Figure S3). This was expected as it is known that high salt is necessary to disrupt the growth factor binding to heparin.62,63 These results bode well for use of these patterned surfaces in cell culture.
Micropatterning
Protein immobilization was first explored on micropatterned substrates. Polymer 1 was spin-coated onto a piranha-cleaned Si wafer from a 1% solution in methanol at 2000 revolutions per minute (RPM). The film was exposed to e-beams with an area dose of 1100 μC/cm2 in order to cross-link the polymer at the sites of exposure. Uncross-linked polymer was removed by washing with methanol and water. The substrate was then incubated with either VEGF or bFGF in PBS for 1 hr followed by rinsing. The immobilized VEGF was labeled with a mouse anti-VEGF antibody for 1 h, while bFGF was labeled with a sheep anti-bFGF antibody for 1 h. Both proteins were visualized with Alexa Fluor 488 secondary antibodies.
Fluorescent microscopy imaging confirmed binding of both bFGF (Figure 4a) and VEGF (Figure 4b) where the antibodies were visible within the polymer patterns. The fluorescence intensity appeared to be different between the two proteins. The proteins were stained with different antibodies; it is not unexpected that variations in antibodies can lead to differences in fluorescent intensities. Controls were performed to elucidate the specificity of binding. First, growth factors patterns were incubated with secondary antibodies, in the absence of the primary antibodies. Polymer patterns without growth factors were also incubated with both antibodies. In both cases, no fluorescence was observed. Binding specificity through the heparin binding domain was also confirmed by adding an excess of heparin to the solutions of VEGF and bFGF prior to incubation on the surfaces. The fluorescence decreased by 55% for VEGF and 66% for bFGF (ESI, Figure S4). This correlated with the SPR results where the heparin decreased the binding, but did not eliminate it (the decrease for VEGF was approximately 50% and for bFGF 80%). Binding of these growth factors to heparin is known to be primarily electrostatic,16 although hydrophobic interactions are thought to play an additional role.62, Thus, the residual binding of the growth factors in the presence of heparin may be due to hydrophobic interactions with the polymer backbone. These results demonstrated that the PEG component of copolymer 1 was effective for radical cross-linking of the polymer to the surface and that the proteins bound to these surface patterns. These data also validate the SPR results that binding of the growth factors to the polymer is primarily through the heparin binding domain.
Figure 4.
Fluorescent images of a. bFGF and b. VEGF immobilized onto pSS-co-PEGMA micropatterns. VEGF and bFGF were visualized with antibody staining. Each patterned square is 5 micron by 5 micron in size.
Nanopatterning
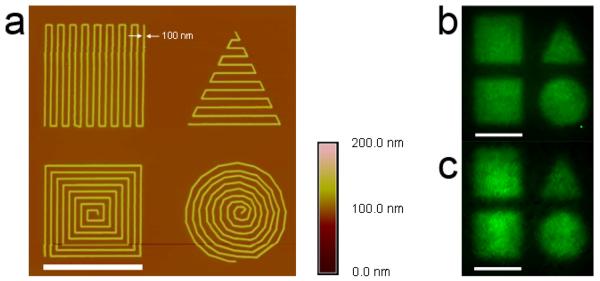
We further fabricated nanopatterns of bFGF and VEGF using these methods. E-beam lithography is a nanofabrication technique that can readily achieve arbitrary shapes, sizes, and curvatures. To demonstrate this versatility, we cross-linked the polymer into 100 nm wide lines with four different shapes, each within an approximately 5 μm2 area. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) images showed nanoscale features forming two different squares, a circle, and a triangle (Figure 5a). Growth factor immobilization to the nanopatterns was investigated in the same fashion as for the micropatterns. Fluorescent microscopy images confirmed binding of bFGF (Figure 5b) and VEGF (Figure 5c) to the pSS-co-PEGMA nanopatterns. The features and spaces between the nanopatterns were below the resolution of the fluorescence microscope, such that the details of the nanopatterns were not resolved in the images. Yet, because the nanometer lines were spaced close together, the overall shapes (squares, triangle, and circle) were visible by fluorescence microscopy. These results illustrated that heparin-mimicking nanopatterns were generated and that growth factors were readily immobilized on the surfaces.
Figure 5.
a. Nanoscale patterns of pSS-co-PEGMA are visible in the height image taken with an atomic force microscope in tapping mode. Lines approximately 100 nm in width forming a square, triangle, concentric square and circle are observed. Fluorescent image of b. bFGF and c. VEGF bound to the nanopatterns with antibody staining. Scale bar = 5 μm.
CONCLUSIONS
Herein, we describe the synthesis of well-defined poly(sodium 4-styrenesulfonate-co-poly(ethylene glycol) methacrylate) by RAFT polymerization and that the polymer bound to the heparin binding domains of bFGF and VEGF. Compared to heparin, pSS-co-PEGMA is significantly easier to modify, is well-defined, and contains biocompatible PEG units. In addition, the sulfonate groups are non-hydrolyzable compared to the acid labile sulfate groups of heparin. Thus, we anticipate that, in addition to utilizing this polymer for surface immobilization of growth factors, this polymer will be useful to replace heparin in hydrogel materials for growth factor delivery or as a soluble drug. We are interested in heparin mimicking materials and are currently investigating this possibility. Our future work will also focus on comparing growth factor-polymer 1 binding to other sulfonated and sulfated polymers.
In this study, cross-linking the polymer via the PEG units to the native oxide of Si using e-beam lithography for micro- and nanopatterning of VEGF and bFGF was illustrated. The polymer bound to the heparin binding domains of bFGF and VEGF and site-selectively anchored the proteins to the surface. Heparin is known to stabilize these growth factors from denaturation and inactivation. This is particularly important for bFGF which is known to degrade upon storage.64 Thus, we anticipate that conjugation of the growth factors to pSS-co-PEGMA features should lead to retention of bioactivity. This point is critical for nanoscale patterning of proteins, and we are currently investigating the bioactivity of these surfaces. In particular, these proteins are known to elicit important biological pathways that involve cell adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation. Immobilization of growth factors at the nanoscale via this heparin binding polymer, alone or in conjunction with integrin binding peptides, should provide surfaces that allow us to probe and control cell behavior. This is important to mimic the ECM and understand critical spacing and separations required to direct cellular response and cell differentiation by nanoscale surface cues, as well as to generate physiologically relevant gradients. Other possible applications include capture agents for proteomics and anticoagulant surfaces.
EXPERIMENTAL SECTION
Materials
AIBN was purified by recrystallization from ethanol. Ethyl S-thiobenzoyl-2-thiopropionate was synthesized using a previously described procedure.65 VEGF refers to the VEGF165 isoform and was expressed from E. coli as previously described.66 bFGF was purchased from R&D Systems. Heparin Sodium Salt grade I-A, 50,000 units, from porcine intestinal mucosa, ~170 USP units/mg was purchased from purchased from Sigma Aldrich. All other reagents were purchased from Aldrich or Acros and utilized as received.
Instrumentation
1H NMR spectra were acquired on a Bruker DRX 500 MHz spectrometer. GPC was conducted on a Shimadzu HPLC system equipped with a refractive index detector RID-10A and two Polymer Laboratories PLgel 5 μm mixed D columns (with guard column). Near-monodisperse poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) standards (Polymer Laboratories) were employed for calibration. Lithium bromide (0.1 M) in N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) at 40 °C was used as the solvent (flow rate: 0.8 mL/min). UV-Vis spectroscopy analysis was performed with a BioMate 5 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Spectronic Instruments). Infrared spectrum of polymer 1 was obtained with a Perkin Elmer Spectrum One instrument equipped with universal ATR accessory. The surface IR spectrum was obtained using a Jasco 670 Plus FTIR spectrometer equipped with a MCT detector and a variable angle ATR-FTIR accessory (Harrick Scientific). The spectrum was recorded over 1000 scans using a hemispherical germanium ATR crystal at an angle of 65°, and a scan resolution of 4 cm−1.
Synthesis
General method for synthesis of pSS-co-PEGMA 1
In an 25 mL air free reaction flask sodium 4-styrenesulfonate (1.13 g, 5.48 mmol), poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate (0.52 mL, 1.83 mmol), ethyl S-thiobenzoyl-2-thiopropionate (0.03 mL. 0.15 mmol) and AIBN (0.012 g, 0.073 mmol) were dissolved in a 1:1 mixture of DMF:H2O (3.2 mL). The mixture was subjected to three freeze/pump/thaw cycles to eliminate oxygen from the reaction flask and then warmed to 90 °C to initiate the polymerization. The polymerization was halted after 18 h by placing the reaction vessel in liquid N2, followed by exposure to air. The polymer was purified by dialysis against water for 2 days. PSS-co-PEGMA 1 was recovered as a pink solid after lyophilization. 1H NMR (D2O): δ 8-6 (4H, aromatic ring), 4.3-2.9 (20.5 H, OCH2), 2.9-0 (8H, polymer backbone). The ratio of SS to PEGMA in the final polymer was 2.2:1. The exact procedure utilized to determine this ratio is discussed in the ESI. FT-IR (cm−1): 3443.5, 2920.1, 1718.0, 1638.3, 1601.5, 1494.5, 1451.5, 1410.9, 1383.5, 1350.8, 1181.7, 1123.9, 1100.0, 1036.4, 1008.9, 947.6, 832.3, 773.7, 670.3 cm−1. Mn(GPC) = 24,000; PDI = 1.17. UV-Vis: λmax (π-π*) = 303 nm.
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR)
SPR measurements were performed using a Biacore X instrument equipped with a gold sensor chip (Biacore). SPR chips coated with PSS-co-PEGMA were prepared as follows. The polymer was first reduced following a literature procedure.61 Briefly, in a 10 mL round bottom flask 1 (0.10 g, 0.0045 mmol) and n-butylamine (0.010 mL, 0.091 mmol) were dissolved in dry methanol and stirred for two hours under argon at 25 °C. The polymer 2 was purified by precipitation from cold ether and dried under vacuum. Freshly reduced polymer was immobilized on a piranha (4:1 sulfuric acid:30% hydrogen peroxide, CAUTION) cleaned SPR chip by incubating the chip with the polymer dissolved in 2 mL of dry methanol for 12 hours. The chip was rinsed with water and dried with a stream of argon. VEGF, bFGF, or BSA were diluted to the appropriate concentration in PBS containing 0.1% Triton X. This solvent was also used as the buffer system for the SPR measurements. For all measurements this regimen was followed: 50 μL of a protein sample were injected at a flow rate of 5 μL/min, followed by 40 μL of phosphate buffer containing 4 M NaCl regenerating buffer at a flow rate of 40 μL/min. One minute after completion of the run, the next sample was injected.
Pattern formation
A 1% solution of 1 in methanol was spin-coated onto a piranha-cleaned Si wafer at 2000 RPM. E-beam lithography was performed with a JEOL 5910 scanning electron beam microscope. Pattern files were created in DesignCAD 2000 and used by a JC Nabity lithography system (Nanometer Pattern Generation System, Ver. 9.0). Micropatterns were exposed using an area dose of 1100 μC/cm2. Nanopatterns were exposed using a line dose of 60 nC/cm. The beam current for both the micro- and nano patterns was 4.8 pA. After exposure, unreacted PSS-co-PEGMA was then rinsed away with methanol and water.
Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
AFM images were taken with a Digital Instruments Dimension 3100 scanning probe microscope (Veeco) equipped with a LIV scanner operating in tapping mode. Images were taken at a scan rate of 1.5 Hz with a resolution of 512 × 512 pixels.
Fluorescence visualization
Patterns were incubated with either VEGF (20 μg/mL) or bFGF (25 μg/mL) for 1 h, and then rinsed for 10 s with PBS. VEGF patterns were labeled with a mouse anti-VEGF antibody (1.3 μg/mL, Zymed) for 1 hour, rinsed for 10 s with PBS, stained with Alexa Fluor 488 goat anti-mouse secondary antibody (10 μg/mL, Invitrogen) for 30 minutes, and then rinsed for 10 s with PBS. bFGF patterns were labeled with a sheep anti-bFGF antibody (1:1000 dilution, Chemicon International) for 1 hour, rinsed for 10 s with PBS, and stained with Alexa Fluor 488 donkey anti-sheep secondary antibody (10 μg/mL, Invitrogen) for 30 minutes, and then rinsed for 10 s with PBS. All samples were visualized by using a Zeiss Axiovert 200 fluorescent microscope equipped with an AxioCam MRm monochrome camera, and pictures were acquired and processed using AxioVision LE 4.1. Signal to noise determination is provided in the ESI.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEGEMENTS
This research was funded by the NIH NIBIB (R21 EB 005838). The authors thank Professor Bruce Dunn for granting access to his surface IR and Steven Jonas for help with the instrument. KLC thanks the NIH NHLBI for a NRSA postdoctoral fellowship. VVD thanks the National Institutes of Health (Grant # F31 GM077086-02) for a pre-doctoral fellowship. CMK appreciates the NSF IGERT: MCTP (Grant # DGE-0114443) and the CNSI for funding. HDM appreciates Amgen (New Faculty Award) and the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation Fellowship for additional funding.
Footnotes
SUPPORTING INFORMATION
Supporting Information Available: GPC trace, 1H NMR spectrum, SPR traces for salt concentration studies, control fluorescent images, procedure for determination of copolymer ratio. This material is available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org.
REFERENCES
- 1.Jung DR, Kapur R, Adams T, Giuliano KA, Mrksich M, Craighead HG, Taylor DL. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2001;21:111–154. doi: 10.1080/20013891081700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Refai AK, Textor M, Brunette DM, Waterfield JD. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A. 2004;70A:194–205. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.30075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Falconnet D, Csucs G, Grandin HM, Textor M. Biomaterials. 2006;27:3044–3063. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2005.12.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Arnold M, Cavalcanti-Adam EA, Glass R, Blummel J, Eck W, Kantlehner M, Kessler H, Spatz JP. Chemphyschem. 2004;5:383–388. doi: 10.1002/cphc.200301014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lee KB, Park SJ, Mirkin CA, Smith JC, Mrksich M. Science. 2002;295:1702–1705. doi: 10.1126/science.1067172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hoover DK, Chan EWL, Yousaf MN. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008;130:3280–3281. doi: 10.1021/ja711016m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Taipale J, KeskiOja J. Faseb J. 1997;11:51–59. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.11.1.9034166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Elcin YM, Dixit V, Gitnick T. Artificial Organs. 2001;25:558–565. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1594.2001.025007558.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Galzie Z, Kinsella AR, Smith JA. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1997;75:669–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Taguchi T, Kishida A, Akashi M, Maruyama I. J. Bioact. Compat. Pol. 2000;15:309–320. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Backer MV, Patel V, Jehning BT, Claffey KP, Backer JM. Biomaterials. 2006;27:5452–5458. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.06.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ito Y, Hasuda H, Terai H, Kitajima T. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A. 2005;74A:659–665. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.30360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Watanabe K, Miyazaki T, Matsuda R. Zool. Sci. 2003;20:429–434. doi: 10.2108/zsj.20.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Subramani K, Birch MA. Biomed. Mater. 2006;1:144–154. doi: 10.1088/1748-6041/1/3/009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Rao SV, Anderson KW, Bachas LG. Mikrochim. Acta. 1998;128:127–143. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Capila I, Linhardt RJ. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002;41:391–412. doi: 10.1002/1521-3773(20020201)41:3<390::aid-anie390>3.0.co;2-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sato H, Miura Y, Saito N, Kobayashi K, Takai O. Surf. Sci. 2007;601:3871–3875. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sato H, Miura Y, Saito N, Kobayashi K, Takai O. Biomacromolecules. 2007;8:753–756. doi: 10.1021/bm061095l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ohyama T, Nishide T, Iwata H, Sato H, Toda M, Toma N, Taki W. J. Neurosurg. 2005;102:109–115. doi: 10.3171/jns.2005.102.1.0109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ito Y, Hayashi M, Imanishi Y. J. Biomat. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2001;12:367–378. doi: 10.1163/156856201750195270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Folkman J, Weisz P, Joullie M, Li W, Ewing W. Science. 1989;243:1490–1493. doi: 10.1126/science.2467380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Danesi R, Delbianchi S, Soldani P, Campagni A, Larocca RV, Myers CE, Paparelli A, Deltacca M. Br. J. Cancer. 1993;68:932–938. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1993.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Waltenberger J, Mayr U, Frank H, Hombach V. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 1996;28:1523–1529. doi: 10.1006/jmcc.1996.0142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Manetti F, Cappello V, Botta M, Corelli F, Mongelli N, Biasoli G, Borgia AL, Ciomei M. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 1998;6:947–958. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0896(98)00052-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Firsching A, Nickel P, Mora P, Allolio B. Cancer Res. 1995;55:4957–4961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Akashi M, Sakamoto N, Suzuki K, Kishida A. Bioconjugate Chem. 1996;7:393–395. doi: 10.1021/bc960031c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bentolila A, Vlodavsky I, Haloun C, Domb AJ. Polym. Advan. Technol. 2000;11:377–387. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Porte-Durrieu MC, Aymes-Chodur C, Betz N, Baquey C. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A. 2000;52:119–127. doi: 10.1002/1097-4636(200010)52:1<119::aid-jbm15>3.0.co;2-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Benezra M, Vogel T, Ben-Sasson SA, Panet A, Sehayek E, Al-Haideiri M, Decklbaum RJ, Vlodavsky I. J. Cell. Biochem. 2001;81:114–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Papy-Garcia DB-C,V, Rouet V, Keros M, Klochendler C, Tournaire M, Barritault D, Caruelle J, Petit E. Macromolecules. 2005;38:4647–4654. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Liekens S, Neyts J, Degreve B, DeClercq E. Oncol. Res. 1997;9:173–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Liekens S, Leali D, Neyts J, Esnouf R, Rusnati M, Dell'Era P, Maudgal PC, De Clercq E, Presta M. Mol. Pharmacol. 1999;56:204–213. doi: 10.1124/mol.56.1.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Presta M, Leali D, Stabile H, Ronca R, Camozzi M, Coco L, Moroni E, Liekens S, Rusnati M. Curr. Pharm. Design. 2003;9:553–566. doi: 10.2174/1381612033391379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Guan R, Sun XL, Hou SJ, Wu PY, Chaikof EL. Bioconjugate Chem. 2004;15:145–151. doi: 10.1021/bc034138t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Krsko P, Sukhishvili S, Mansfield M, Clancy R, Libera M. Langmuir. 2003;19:5618–5625. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Brough B, Christman KL, Wong TS, Kolodziej CM, Forbes JG, Wang K, Maynard HD, Ho CM. Soft Matter. 2007;3:541–546. doi: 10.1039/b618524j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hong Y, Krsko P, Libera M. Langmuir. 2004;19:5618–5625. doi: 10.1021/la048651m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Sofia SJ, Merrill EW. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1998;40:153–163. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-4636(199804)40:1<153::aid-jbm18>3.0.co;2-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.King PA, Ward JA. J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem. 1970;8:253–262. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Emami SH, Salovey R, Hogen-Esch TE. J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem. 2002;40:3021–3026. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Moad G, Rizzardo E, Thang SH. Aust. J. Chem. 2006;59:669–692. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Chiefari J, Chong YK, Ercole F, Krstina J, Jeffery J, Le TPT, Mayadunne RTA, Meijs GF, Moad CL, Moad G, Rizzardo E, Thang SH. Macromolecules. 1998;31:5559–5562. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Matyjaszewski K, Patten TE, Xia JH. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997;119:674–680. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Matyjaszewski K, Xia JH. Chem. Rev. 2001;101:2921–2990. doi: 10.1021/cr940534g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Hawker CJ, Bosman AW, Harth E. Chem. Rev. 2001;101:3661–3688. doi: 10.1021/cr990119u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Tsarevsky NV, Pintauer T, Matyjaszewski K. Polym. Prepr. (Am. Chem. Soc., Div. Polym. Chem.) 2002;43:203. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Choi CK, Kim YB. Polym. Bull. 2003;49:433–439. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Iddon PD, Robinson KL, Armes SP. Polymer. 2004;45:759–768. [Google Scholar]
- 49.Lienkamp KS, Ingo, Groehn Franziska, Wegner Gerhard. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2006;207:2050–2065. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Baek K-Y, Balsara NP. Polym. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2005;92:7. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Mitsukami Y, Donovan MS, Lowe AB, McCormick CL. Macromolecules. 2001;34:2248–2256. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Sumerlin BS, Donovan MS, Mitsukami Y, Lowe AB, McCormick CL. Macromolecules. 2001;34:6561–6564. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Sumerlin BS, Lowe AB, Stroud PA, Zhang P, Urban MW, McCormick CL. Langmuir. 2003;19:5559–5562. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Lowe AB, McCormick CL. Aust. J. Chem. 2002;55:367–379. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Okamura H, Takatori Y, Tsunooka M, Shirai M. Polymer. 2002;43:3155–3162. [Google Scholar]
- 56.Peng ZP, Wang D, Liu XX, Tong Z. J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem. 2007;45:3698–3706. [Google Scholar]
- 57.McCormack CL, Lowe AB. Acc. Chem. Res. 2004;37:312–325. doi: 10.1021/ar0302484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Mertoglu M, Garnier S, Laschewsky A, Skrabania K, Storsberg J. Polymer. 2005;46:7726–7740. [Google Scholar]
- 59.Huber A, Demartis S, Neri D. J. Mol. Recognit. 1999;12:198–216. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1099-1352(199905/06)12:3<198::AID-JMR458>3.0.CO;2-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Schuck P. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biol. Struct. 1997;26:541–566. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.26.1.541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Qiu XP, Winnik FM. Macromolecules. 2007;40:872–878. [Google Scholar]
- 62.Thompson LD, Pantoliano MW, Springer BA. Biochemistry. 1994;33:3831–3840. doi: 10.1021/bi00179a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Gospodarowicz D, Abraham JA, Schilling J. PNAS. 1989;86:7311–7315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Edelman ER ME, Langer R, Klagsbrun M. Biomaterials. 1991;12:619–626. doi: 10.1016/0142-9612(91)90107-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Farmer SC, Patten TE. J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem. 2002;40:555–563. [Google Scholar]
- 66.Maynard HD, Hubbell JA. Acta Biomaterialia. 2005;1:451–459. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2005.04.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.