Abstract
We have developed efficient methodologies for construction and expression of comprehensive phage display libraries of murine Fab antibody fragments in E. coli cells. Our methods optimize several critical steps of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification of transcripts of the re-arranged immunoglobulin genes and of their subsequent assembly and expression: Firstly, we have designed exhaustive sets of PCR primers of low degeneracy for the amplification of transcripts of the Fab region of the heavy and light-chain genes. These primers proved effective in amplification of Fab gene fragments from a large panel of hybridoma cell lines of different specificity and family sub-type. Secondly, we have developed a 'jumping PCR' technique that effectively assembled and recombined the amplified heavy and light-chain gene fragments into a bi-cistronic operon. Thirdly, we have constructed expression vectors for insertion of the combinatorial Fab gene-cassette in fusion with a truncated version of the phage surface protein, gIIIp. The heavy chain and the light chain-gIII fusion are transcribed as a polycistronic mRNA from the lacZ promoter and efficient transcriptional control is provided by wildtype lacI present on the vector. The utility of the system was demonstrated by isolating several antigen-binding clones from hybridomas and libraries made from immunized mice.
Full text
PDF



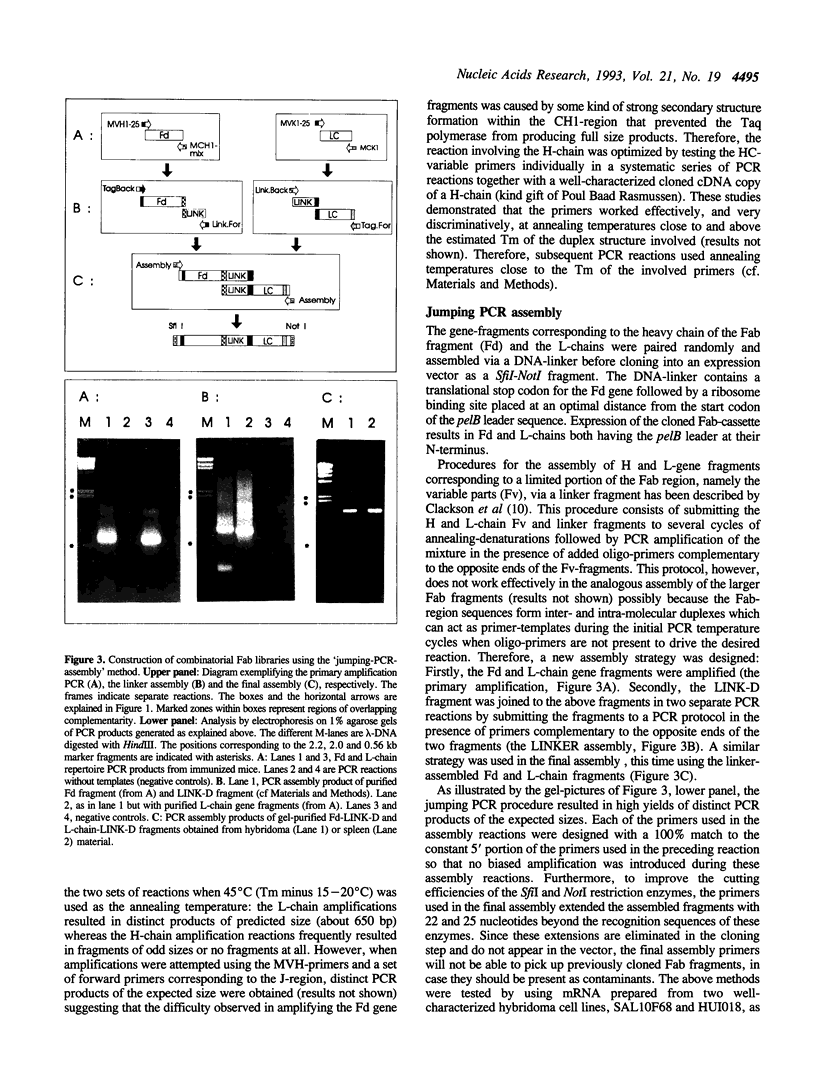
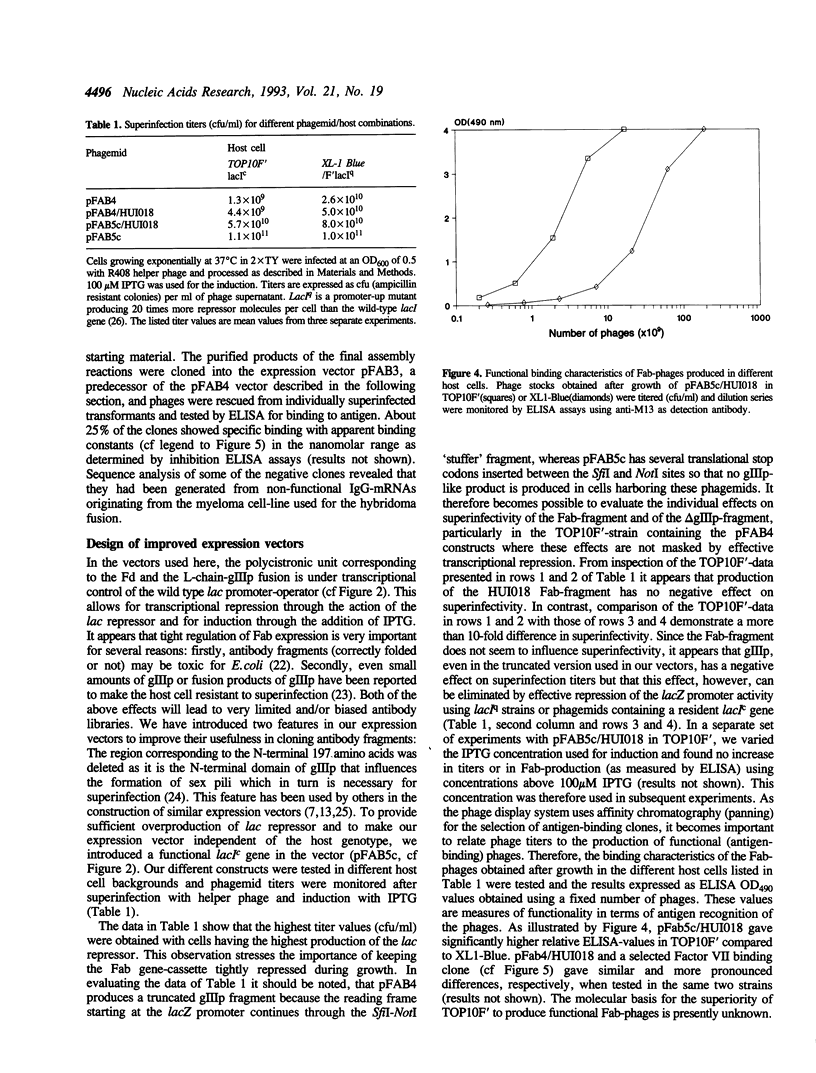
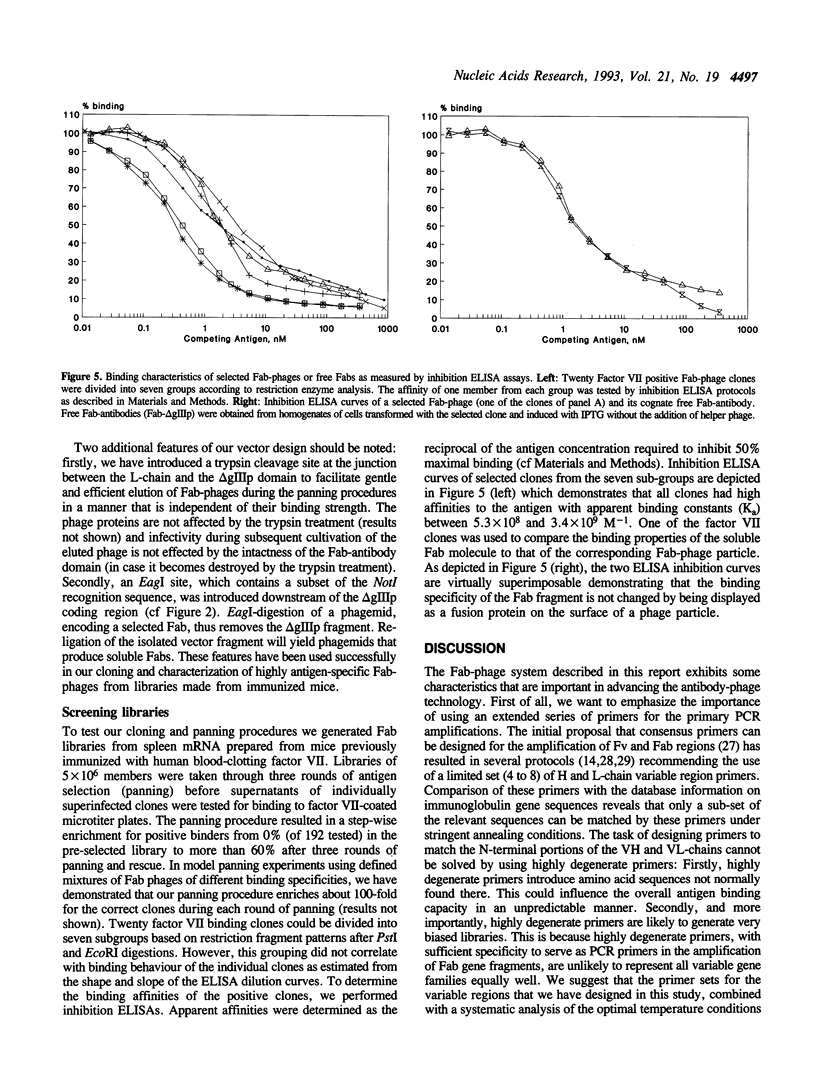

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbas C. F., 3rd, Kang A. S., Lerner R. A., Benkovic S. J. Assembly of combinatorial antibody libraries on phage surfaces: the gene III site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):7978–7982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.7978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass S., Greene R., Wells J. A. Hormone phage: an enrichment method for variant proteins with altered binding properties. Proteins. 1990;8(4):309–314. doi: 10.1002/prot.340080405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Model P., Zinder N. D. Effects of bacteriophage f1 gene III protein on the host cell membrane. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(2):185–192. doi: 10.1007/BF00331849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitling F., Dübel S., Seehaus T., Klewinghaus I., Little M. A surface expression vector for antibody screening. Gene. 1991 Aug 15;104(2):147–153. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90244-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clackson T., Hoogenboom H. R., Griffiths A. D., Winter G. Making antibody fragments using phage display libraries. Nature. 1991 Aug 15;352(6336):624–628. doi: 10.1038/352624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crissman J. W., Smith G. P. Gene-III protein of filamentous phages: evidence for a carboxyl-terminal domain with a role in morphogenesis. Virology. 1984 Jan 30;132(2):445–455. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cwirla S. E., Peters E. A., Barrett R. W., Dower W. J. Peptides on phage: a vast library of peptides for identifying ligands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6378–6382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devlin J. J., Panganiban L. C., Devlin P. E. Random peptide libraries: a source of specific protein binding molecules. Science. 1990 Jul 27;249(4967):404–406. doi: 10.1126/science.2143033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrard L. J., Yang M., O'Connell M. P., Kelley R. F., Henner D. J. Fab assembly and enrichment in a monovalent phage display system. Biotechnology (N Y) 1991 Dec;9(12):1373–1377. doi: 10.1038/nbt1291-1373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gram H., Marconi L. A., Barbas C. F., 3rd, Collet T. A., Lerner R. A., Kang A. S. In vitro selection and affinity maturation of antibodies from a naive combinatorial immunoglobulin library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3576–3580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoogenboom H. R., Griffiths A. D., Johnson K. S., Chiswell D. J., Hudson P., Winter G. Multi-subunit proteins on the surface of filamentous phage: methodologies for displaying antibody (Fab) heavy and light chains. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 11;19(15):4133–4137. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.15.4133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huse W. D., Sastry L., Iverson S. A., Kang A. S., Alting-Mees M., Burton D. R., Benkovic S. J., Lerner R. A. Generation of a large combinatorial library of the immunoglobulin repertoire in phage lambda. Science. 1989 Dec 8;246(4935):1275–1281. doi: 10.1126/science.2531466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang A. S., Barbas C. F., Janda K. D., Benkovic S. J., Lerner R. A. Linkage of recognition and replication functions by assembling combinatorial antibody Fab libraries along phage surfaces. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4363–4366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. A., Kang A. S., Bain J. D., Burton D. R., Barbas C. F., 3rd Antibodies without immunization. Science. 1992 Nov 20;258(5086):1313–1314. doi: 10.1126/science.1455226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowman H. B., Bass S. H., Simpson N., Wells J. A. Selecting high-affinity binding proteins by monovalent phage display. Biochemistry. 1991 Nov 12;30(45):10832–10838. doi: 10.1021/bi00109a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Hill B. Lac repressor and lac operator. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1975;30(2-3):227–252. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(76)90011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlandi R., Güssow D. H., Jones P. T., Winter G. Cloning immunoglobulin variable domains for expression by the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3833–3837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmley S. F., Smith G. P. Antibody-selectable filamentous fd phage vectors: affinity purification of target genes. Gene. 1988 Dec 20;73(2):305–318. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90495-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plückthun A., Skerra A. Expression of functional antibody Fv and Fab fragments in Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1989;178:497–515. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)78036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rath S., Stanley C. M., Steward M. W. An inhibition enzyme immunoassay for estimating relative antibody affinity and affinity heterogeneity. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Feb 10;106(2):245–249. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90204-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. K., Smith G. P. Searching for peptide ligands with an epitope library. Science. 1990 Jul 27;249(4967):386–390. doi: 10.1126/science.1696028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. P. Filamentous fusion phage: novel expression vectors that display cloned antigens on the virion surface. Science. 1985 Jun 14;228(4705):1315–1317. doi: 10.1126/science.4001944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward E. S., Güssow D., Griffiths A. D., Jones P. T., Winter G. Binding activities of a repertoire of single immunoglobulin variable domains secreted from Escherichia coli. Nature. 1989 Oct 12;341(6242):544–546. doi: 10.1038/341544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]