Abstract
The upstream regulatory region (URR) of the human papillomaviruses HPV16 and 18 contains a sequence with a seven out of eight base match to the consensus binding site for octamer binding transcription factors. This motif acts as a target for repression by the Oct-1 transcription factor and therefore inhibits promoter activity in non-cervical cells expressing only Oct-1. In contrast the HPV octamer motif activates promoter activity in cervical cells. Here we show that cervical cells express the activating form of the Oct-2 transcription factor, Oct 2.1 and that this factor can transactivate promoter activity via the HPV16 octamer. This effect is dependent upon both the N and C-terminal activation domains of Oct-2. The expression of specific octamer binding proteins such as Oct-2 in cervical cells thus allows the HPV16 motif to produce opposite effects on gene expression in cervical and non-cervical cells suggesting that it may play a role in the cervical specificity of URR driven gene expression.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan W. K., Chong T., Bernard H. U., Klock G. Transcription of the transforming genes of the oncogenic human papillomavirus-16 is stimulated by tumor promotors through AP1 binding sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):763–769. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan W. K., Klock G., Bernard H. U. Progesterone and glucocorticoid response elements occur in the long control regions of several human papillomaviruses involved in anogenital neoplasia. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3261–3269. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3261-3269.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong T., Apt D., Gloss B., Isa M., Bernard H. U. The enhancer of human papillomavirus type 16: binding sites for the ubiquitous transcription factors oct-1, NFA, TEF-2, NF1, and AP-1 participate in epithelial cell-specific transcription. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5933–5943. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5933-5943.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cripe T. P., Haugen T. H., Turk J. P., Tabatabai F., Schmid P. G., 3rd, Dürst M., Gissmann L., Roman A., Turek L. P. Transcriptional regulation of the human papillomavirus-16 E6-E7 promoter by a keratinocyte-dependent enhancer, and by viral E2 trans-activator and repressor gene products: implications for cervical carcinogenesis. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3745–3753. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02709.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent C. L., McIndoe G. A., Latchman D. S. The constitutively expressed octamer binding protein OTF-1 and a novel octamer binding protein expressed specifically in cervical cells bind to an octamer-related sequence in the human papillomavirus 16 enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 25;19(16):4531–4535. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.16.4531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gloss B., Bernard H. U., Seedorf K., Klock G. The upstream regulatory region of the human papilloma virus-16 contains an E2 protein-independent enhancer which is specific for cervical carcinoma cells and regulated by glucocorticoid hormones. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3735–3743. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02708.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gloss B., Yeo-Gloss M., Meisterenst M., Rogge L., Winnacker E. L., Bernard H. U. Clusters of nuclear factor I binding sites identify enhancers of several papillomaviruses but alone are not sufficient for enhancer function. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3519–3533. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsborough A., Ashworth A., Willison K. Cloning and sequencing of POU-boxes expressed in mouse testis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 25;18(6):1634–1634. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.6.1634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoppe-Seyler F., Butz K., zur Hausen H. Repression of the human papillomavirus type 18 enhancer by the cellular transcription factor Oct-1. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5613–5618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5613-5618.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillycrop K. A., Dent C. L., Wheatley S. C., Beech M. N., Ninkina N. N., Wood J. N., Latchman D. S. The octamer-binding protein Oct-2 represses HSV immediate-early genes in cell lines derived from latently infectable sensory neurons. Neuron. 1991 Sep;7(3):381–390. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90290-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillycrop K. A., Latchman D. S. Alternative splicing of the Oct-2 transcription factor RNA is differentially regulated in neuronal cells and B cells and results in protein isoforms with opposite effects on the activity of octamer/TAATGARAT-containing promoters. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):24960–24965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACPHERSON I., STOKER M. Polyoma transformation of hamster cell clones--an investigation of genetic factors affecting cell competence. Virology. 1962 Feb;16:147–151. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90290-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgenstern J. P., Land H. A series of mammalian expression vectors and characterisation of their expression of a reporter gene in stably and transiently transfected cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):1068–1068. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.1068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
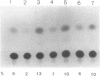
- Morris P. J., Dent C. L., Ring C. J., Latchman D. S. The octamer binding site in the HPV16 regulatory region produces opposite effects on gene expression in cervical and non-cervical cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Feb 25;21(4):1019–1023. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.4.1019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Immerglück M. M., Schaffner W., Matthias P. Transcription factor Oct-2A contains functionally redundant activating domains and works selectively from a promoter but not from a remote enhancer position in non-lymphoid (HeLa) cells. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1625–1634. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08282.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M. M., Ruppert S., Schaffner W., Matthias P. A cloned octamer transcription factor stimulates transcription from lymphoid-specific promoters in non-B cells. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):544–551. doi: 10.1038/336544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royer H. D., Freyaldenhoven M. P., Napierski I., Spitkovsky D. D., Bauknecht T., Dathan N. Delineation of human papillomavirus type 18 enhancer binding proteins: the intracellular distribution of a novel octamer binding protein p92 is cell cycle regulated. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 11;19(9):2363–2371. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.9.2363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Heguy A., Roeder R. G. Identification and purification of a human lymphoid-specific octamer-binding protein (OTF-2) that activates transcription of an immunoglobulin promoter in vitro. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):783–793. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90101-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Hatzopoulos A. K., Balling R., Suzuki N., Gruss P. A family of octamer-specific proteins present during mouse embryogenesis: evidence for germline-specific expression of an Oct factor. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2543–2550. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08392.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Herr W. Differential transcriptional activation by Oct-1 and Oct-2: interdependent activation domains induce Oct-2 phosphorylation. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):375–386. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90589-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]