Abstract
An algorithm has been developed for the determination of nucleotide sequence from data produced in fluorescence-based automated DNA sequencing instruments employing the four-color strategy. This algorithm takes advantage of object oriented programming techniques for modularity and extensibility. The algorithm is adaptive in that data sets from a wide variety of instruments and sequencing conditions can be used with good results. Confidence values are provided on the base calls as an estimate of accuracy. The algorithm iteratively employs confidence determinations from several different modules, each of which examines a different feature of the data for accurate peak identification. Modules within this system can be added or removed for increased performance or for application to a different task. In comparisons with commercial software, the algorithm performed well.
Full text
PDF



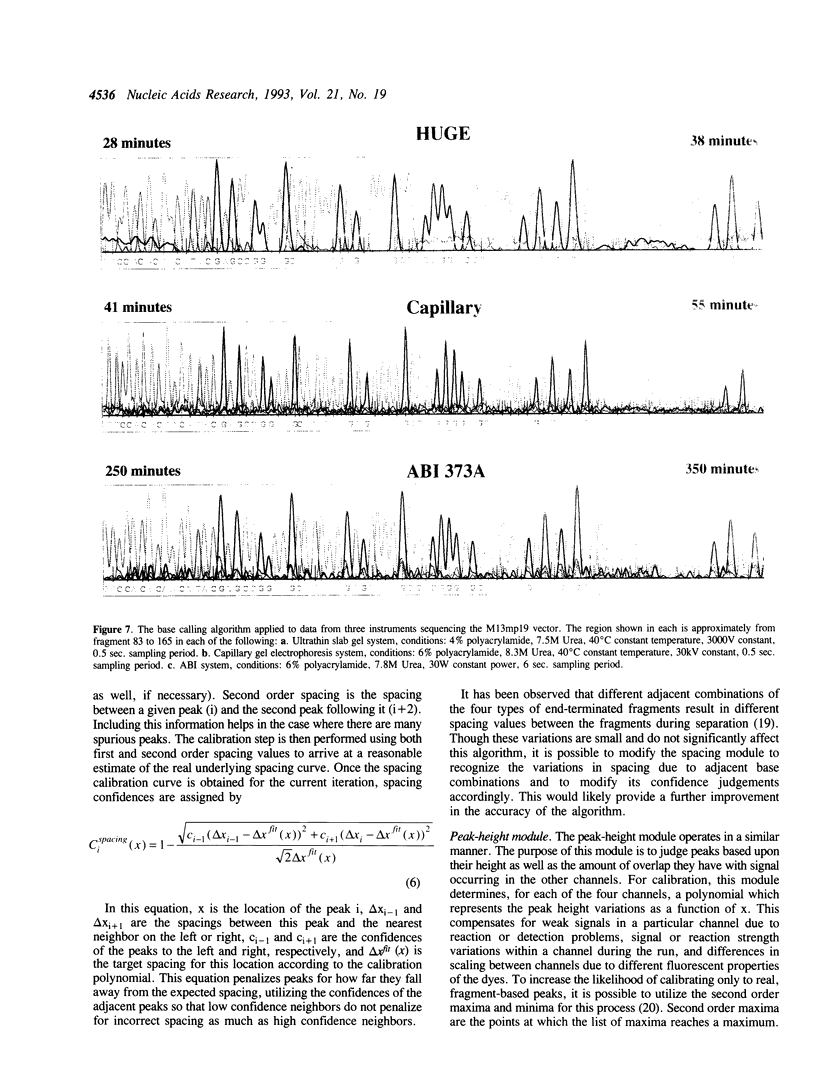

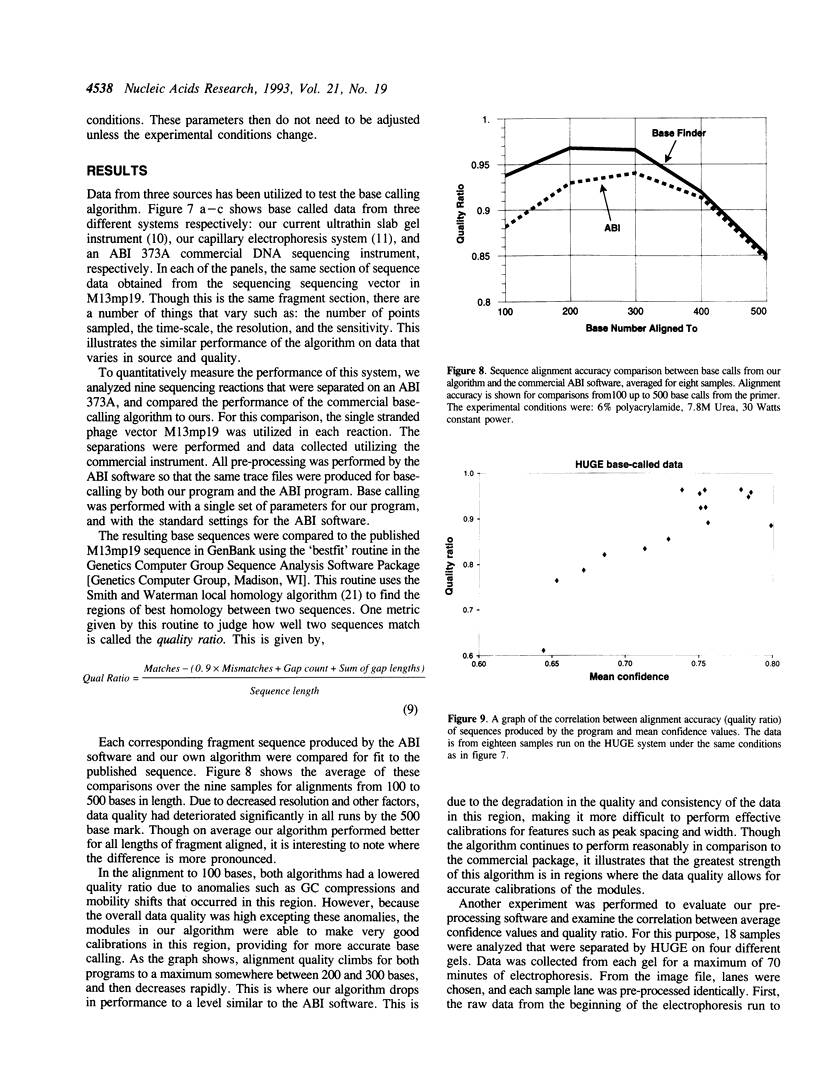


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowling J. M., Bruner K. L., Cmarik J. L., Tibbetts C. Neighboring nucleotide interactions during DNA sequencing gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 11;19(11):3089–3097. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.11.3089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brumley R. L., Jr, Smith L. M. Rapid DNA sequencing by horizontal ultrathin gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 11;19(15):4121–4126. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.15.4121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. K., Green D. K., Southern E. M. Automatic reading of DNA sequencing gel autoradiographs using a large format digital scanner. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):417–424. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii H., Kashiwagi K. Compensation for mobility inequalities between lanes computed from band signals in on-line fluorescence DNA sequencing. Electrophoresis. 1992 Aug;13(8):500–505. doi: 10.1002/elps.11501301105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller T., Kaiser R. J., Koop B. F., Hood L. Large-scale and automated DNA sequence determination. Science. 1991 Oct 4;254(5028):59–67. doi: 10.1126/science.1925562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karger A. E., Harris J. M., Gesteland R. F. Multiwavelength fluorescence detection for DNA sequencing using capillary electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 25;19(18):4955–4962. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.18.4955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostichka A. J., Marchbanks M. L., Brumley R. L., Jr, Drossman H., Smith L. M. High speed automated DNA sequencing in ultrathin slab gels. Biotechnology (N Y) 1992 Jan;10(1):78–81. doi: 10.1038/nbt0192-78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckey J. A., Drossman H., Kostichka A. J., Mead D. A., D'Cunha J., Norris T. B., Smith L. M. High speed DNA sequencing by capillary electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 11;18(15):4417–4421. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.15.4417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. M., Fung S., Hunkapiller M. W., Hunkapiller T. J., Hood L. E. The synthesis of oligonucleotides containing an aliphatic amino group at the 5' terminus: synthesis of fluorescent DNA primers for use in DNA sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2399–2412. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. M., Kaiser R. J., Sanders J. Z., Hood L. E. The synthesis and use of fluorescent oligonucleotides in DNA sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:260–301. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. M., Sanders J. Z., Kaiser R. J., Hughes P., Dodd C., Connell C. R., Heiner C., Kent S. B., Hood L. E. Fluorescence detection in automated DNA sequence analysis. Nature. 1986 Jun 12;321(6071):674–679. doi: 10.1038/321674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West J. Automated sequence reading and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 11;16(5):1847–1856. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]