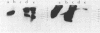Abstract
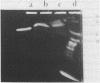
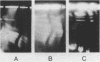
Modifications have been made to standard pulse field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) systems to enable very large DNA molecules to be resolved. The single most important modification was to elevate the temperature of electrophoresis to 35 degrees C. This enabled the largest Saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome to be reproducibly resolved. More impressively, it enabled the DNA of Candida albicans to be clearly resolved into six bands, a feat which was very difficult at lower temperatures. Even so, optimal resolution could only be obtained by carefully adjusting field voltages and switching times. The DNA from the two largest C. albicans chromosomes, which was estimated to be at least 5-10Mbp in size, ran somewhat anomalously, giving fuzzy bands which did not migrate in the direction of the average electric field. That the highest molecular weight band was a distinct chromosome was demonstrated by specific hybridisation to the C. albicans ADE2 gene probe. With further fine tuning, the PFGE system described here should be capable of resolving DNA from the smallest human chromosomes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carle G. F., Olson M. V. Separation of chromosomal DNA molecules from yeast by orthogonal-field-alternation gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5647–5664. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilton C., Markie D., Corner B., Rikkerink E., Poulter R. Heat shock induces chromosome loss in the yeast Candida albicans. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;200(1):162–168. doi: 10.1007/BF00383330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz M. B., Cortelyou M. W., Kirsch D. R. Integrative transformation of Candida albicans, using a cloned Candida ADE2 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):142–149. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggsby W. S. Some recent developments in the molecular biology of medically important Candida. Microbiol Sci. 1985 Sep;2(9):257-8, 261-3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggsby W. S., Torres-Bauza L. J., Wills J. W., Townes T. M. DNA content, kinetic complexity, and the ploidy question in Candida albicans. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jul;2(7):853–862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.7.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Saffran W., Welsh J., Haas R., Goldenberg M., Cantor C. R. New techniques for purifying large DNAs and studying their properties and packaging. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):189–195. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serwer P., Allen J. L. Conformation of double-stranded DNA during agarose gel electrophoresis: fractionation of linear and circular molecules with molecular weights between 3 X 10(6) and 26 X 10(6). Biochemistry. 1984 Feb 28;23(5):922–927. doi: 10.1021/bi00300a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]