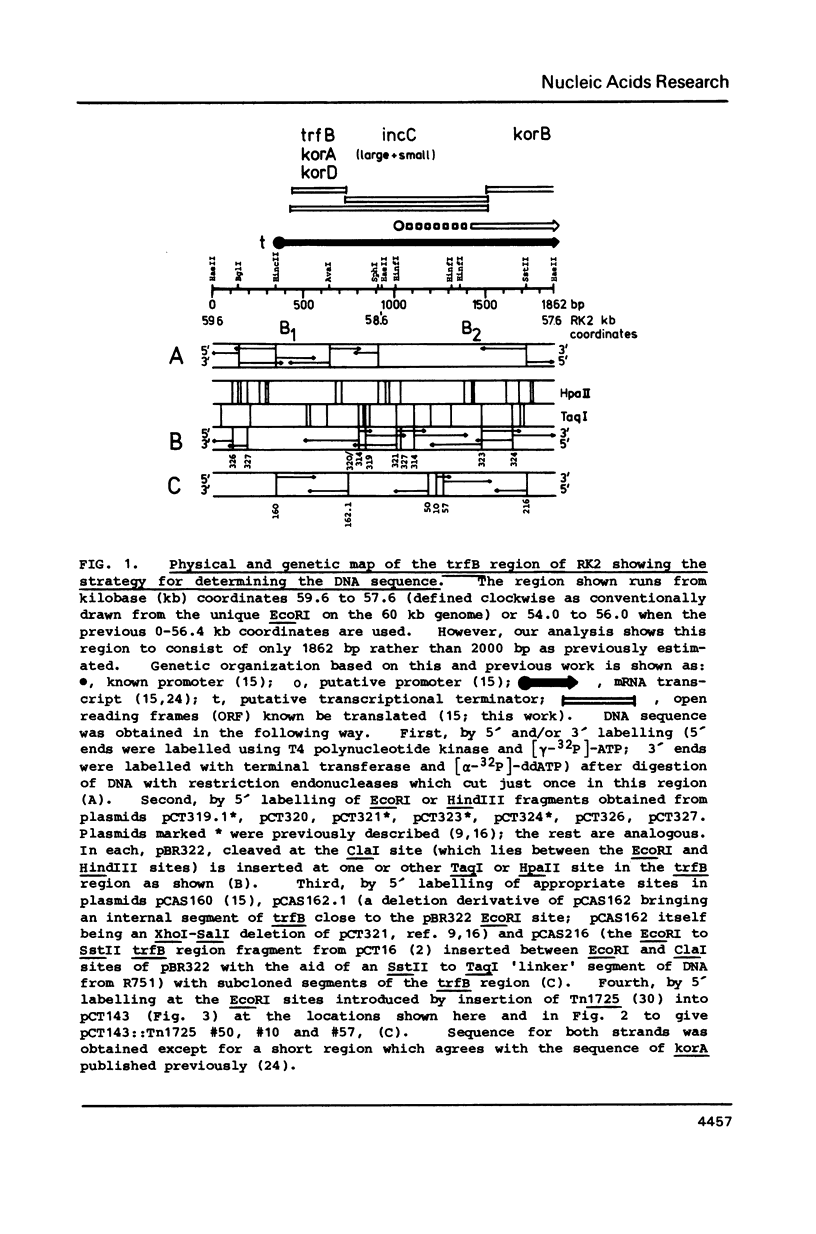
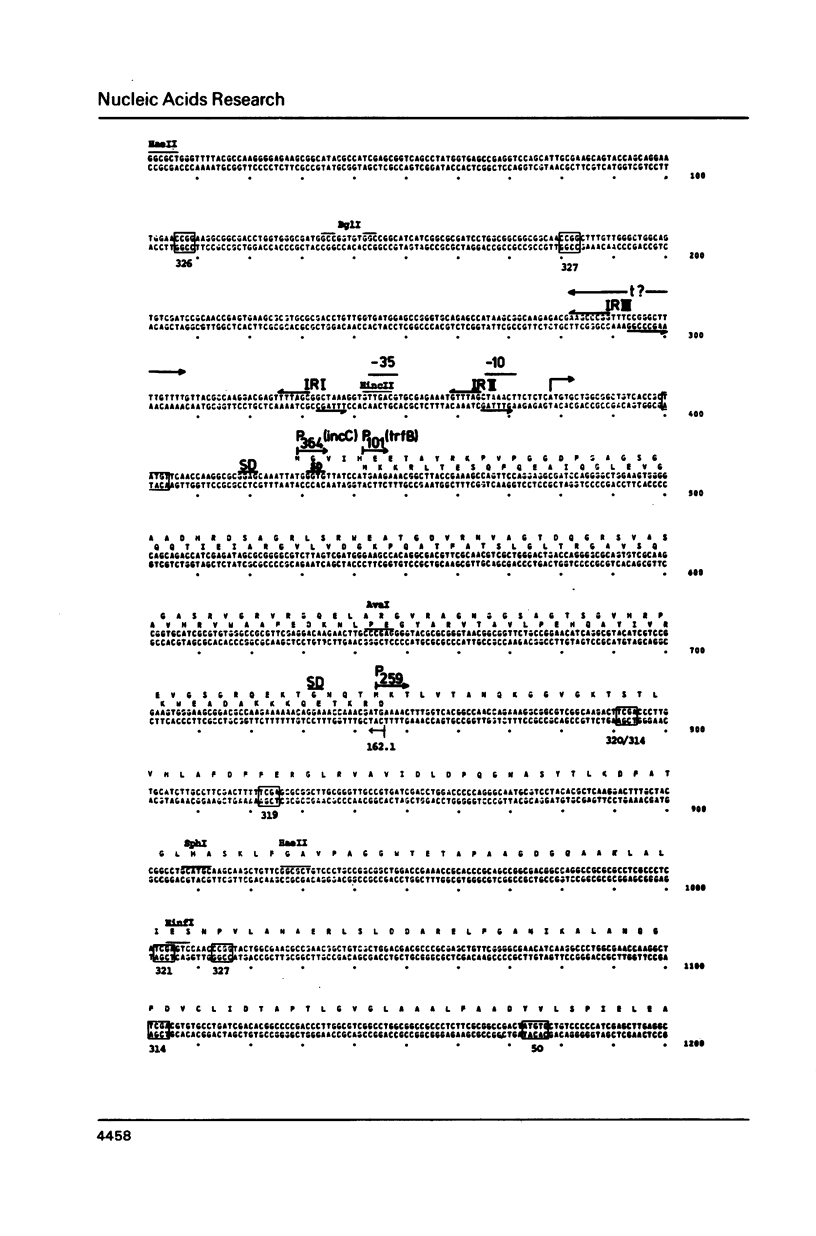
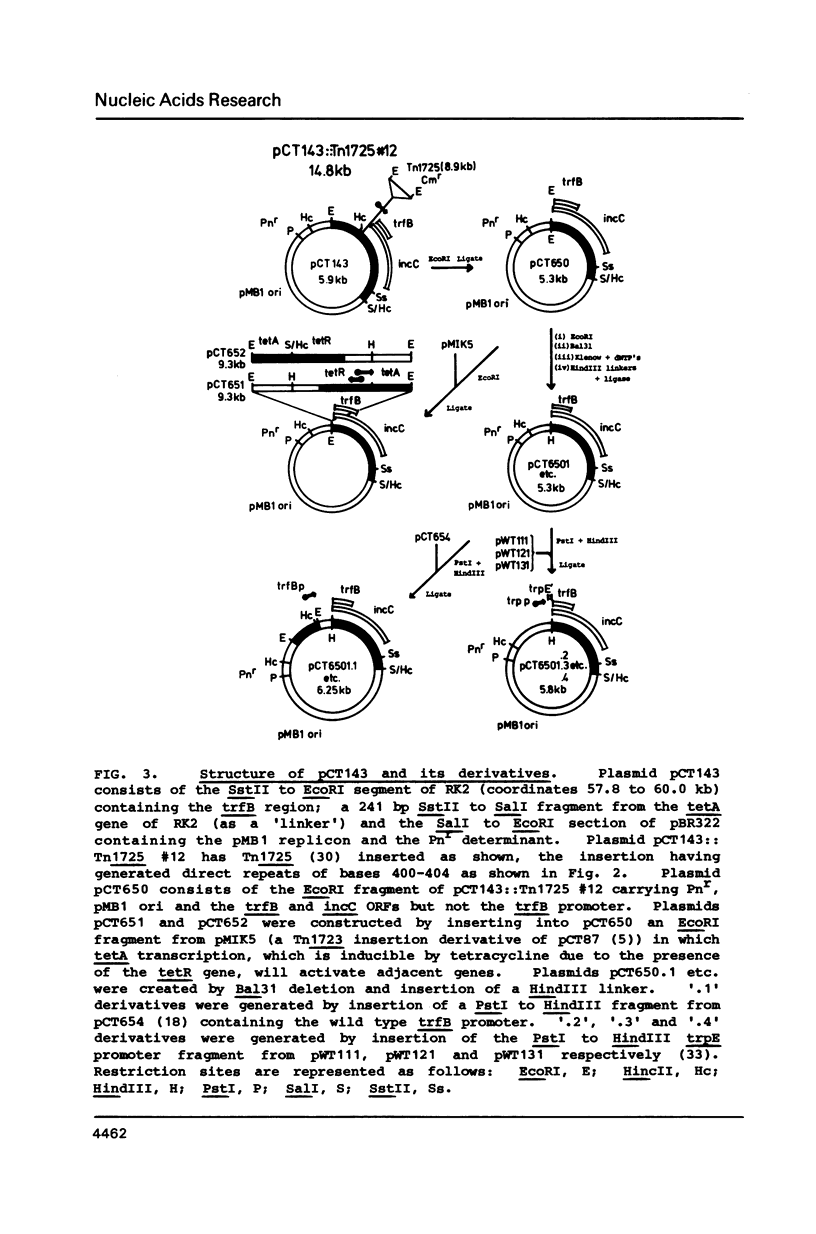
Abstract
We report the nucleotide sequence of the trfB region of broad host range plasmid RK2. This region encodes the following loci: trfB, identical to korA and korD, which encodes a key transcriptional repressor of certain RK2 operons; incC, which appears to be involved in plasmid maintenance, possibley through post-transcriptional regulation of trfA product levels; the start of korB, which encodes a second transcriptional repressor of operons involved in stable inheritance of RK2. These loci are expressed as part of the trfB operon. In combination with deletion analysis, transcriptional and translation fusions and 'maxicell' analysis of polypeptides, the DNA sequence allows a number of conclusions to be drawn. First, the korB ORF start codon overlaps the incC ORF stop codon, suggesting the possibility of translational coupling between these two genes. Second, the trfB ORF lies entirely within the first third of the incC ORF using a different phase. Third, the incC ORF appears to contain a second transcriptional start whose function appears to be coupled to translation of the trfB ORF. Analysis of codon usage in the region of overlap between incC and trfB suggests that the incC gene may have evolved before the trfB gene. Determination of the DNA sequence of a mutant in which the product of trfB is rendered defective for transcriptional repression reveals an amino acid alteration within a region of this polypeptide which exhibits homology to the alpha helix-turn-alpha helix motif characteristic of many DNA binding proteins, and which is probably responsible for recognition of the trfB operator by this protein.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bechhofer D. H., Figurski D. H. Map location and nucleotide sequence of korA, a key regulatory gene of promiscuous plasmid RK2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 11;11(21):7453–7469. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.21.7453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crick F. H., Brenner S., Klug A., Pieczenik G. A speculation on the origin of protein synthesis. Orig Life. 1976 Dec;7(4):389–397. doi: 10.1007/BF00927934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figurski D. H., Helinski D. R. Replication of an origin-containing derivative of plasmid RK2 dependent on a plasmid function provided in trans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1648–1652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figurski D. H., Pohlman R. F., Bechhofer D. H., Prince A. S., Kelton C. A. Broad host range plasmid RK2 encodes multiple kil genes potentially lethal to Escherichia coli host cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1935–1939. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn M., Kolter R., Thomas C., Figurski D., Meyer R., Remaut E., Helinski D. R. Plasmid cloning vehicles derived from plasmids ColE1, F, R6K, and RK2. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:268–280. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. J., Helinski D. R. Unidirectional replication of the P-group plasmid RK2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Sep 6;478(1):109–113. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(77)90249-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R., Hinds M. Multiple mechanisms for expression of incompatibility by broad-host-range plasmid RK2. J Bacteriol. 1982 Dec;152(3):1078–1090. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.3.1078-1090.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normark S., Bergström S., Edlund T., Grundström T., Jaurin B., Lindberg F. P., Olsson O. Overlapping genes. Annu Rev Genet. 1983;17:499–525. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.17.120183.002435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohlman R. F., Figurski D. H. Essential genes of plasmid RK2 in Escherichia coli: trfB region controls a kil gene near trfA. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):584–591. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.584-591.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Hack A. M., Rupp W. D. Simple method for identification of plasmid-coded proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):692–693. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.692-693.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidhauser T. J., Filutowicz M., Helinski D. R. Replication of derivatives of the broad host range plasmid RK2 in two distantly related bacteria. Plasmid. 1983 May;9(3):325–330. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(83)90010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidhauser T. J., Helinski D. R. Regions of broad-host-range plasmid RK2 involved in replication and stable maintenance in nine species of gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):446–455. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.446-455.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd J. C. Method to determine the reading frame of a protein from the purine/pyrimidine genome sequence and its possible evolutionary justification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1596–1600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinger V., Thomas C. M. Transcription in the trfA region of broad host range plasmid RK2 is regulated by trfB and korB. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195(3):523–529. doi: 10.1007/BF00341457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shingler V., Thomas C. M. Analysis of the trfA region of broad host-range plasmid RK2 by transposon mutagenesis and identification of polypeptide products. J Mol Biol. 1984 May 25;175(3):229–249. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90346-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Shingler V., Thomas C. M. The trfA and trfB promoter regions of broad host range plasmid RK2 share common potential regulatory sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 25;12(8):3619–3630. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.8.3619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Thomas C. M. Deletion mapping of kil and kor functions in the trfA and trfB regions of broad host range plasmid RK2. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;190(2):245–254. doi: 10.1007/BF00330647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Thomas C. M. Molecular gentic analysis of the trfB and korB region of broad host range plasmid RK2. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Jul;130(7):1651–1663. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-7-1651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Thomas C. M. Nucleotide sequence of the trfA gene of broad host-range plasmid RK2. J Mol Biol. 1984 May 25;175(3):251–262. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90347-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tacon W., Carey N., Emtage S. The construction and characterisation of plasmid vectors suitable for the expression of all DNA phases under the control of the E. coli tryptophan promoter. Mol Gen Genet. 1980 Feb;177(3):427–438. doi: 10.1007/BF00271481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theophilus B. D., Cross M. A., Smith C. A., Thomas C. M. Regulation of the trfA and trfB promoters of broad host range plasmid RK2: identification of sequences essential for regulation by trfB/korA/korD. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 25;13(22):8129–8142. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.22.8129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. M. Complementation analysis of replication and maintenance functions of broad host range plasmids RK2 and RP1. Plasmid. 1981 May;5(3):277–291. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. M., Hussain A. A. The korB gene of broad host range plasmid RK2 is a major copy number control element which may act together with trfB by limiting trfA expression. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1513–1519. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02004.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. M., Meyer R., Helinski D. R. Regions of broad-host-range plasmid RK2 which are essential for replication and maintenance. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jan;141(1):213–222. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.1.213-222.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. M. Molecular genetics of broad host range plasmid RK2. Plasmid. 1981 Jan;5(1):10–19. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90074-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young C., Bechhofer D. H., Figurski D. H. Gene regulation in plasmid RK2: positive control by korA in the expression of korC. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):247–252. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.247-252.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young C., Prince A. S., Figurski D. H. korA function of promiscuous plasmid RK2: an autorepressor that inhibits expression of host-lethal gene kilA and replication gene trfA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7374–7378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]