Abstract
Objective
To examine the association between students’ personal characteristics, backgrounds, and medical schools and their intention to enter a family medicine (FM) specialty.
Design
Descriptive study using data from the 2007 National Physician Survey.
Setting
Canada.
Participants
Clinical (n = 1109) and preclinical (n = 829) medical student respondents to the 2007 National Physician Survey.
Main outcome measures
The main variable was hoping to enter an FM specialty, and 40 independent variables were included in regression and classification-tree models.
Results
Fewer than 1 medical student in 3 (30.2% at the preclinical level and 31.4% at the clinical level) hoped to enter into an FM career. Those who did were more likely to be female, were slightly older, were more frequently married or living with partners, were typically born in Canada, and were more likely to have previous exposure to non-urban environments. The most important predictor for both populations was the debt related to medical studies, which acted in the opposite direction of whether or not students were interested in research. Students interested in research were attracted by specialties with high earning potential, while those not interested in research looked for short residency programs, such as FM, so they could begin to pay off debt sooner. Therefore, the interest in research appears to be inversely related to the choice of FM.
Conclusion
Less than one-third of medical students were looking for residencies in FM in Canada. This is far below the goals of 45% set at the national level and 50% set by some provinces like Quebec. Debt and interest in research have strong influences on the choice of residency by medical students.
Résumé
Objectif
Déterminer s’il existe une relation entre les caractéristiques personnelles des étudiants en médecine, leurs antécédents et leurs écoles de médecine, et leur intention de choisir une spécialité de médecine familiale (MF).
Type d’étude
Étude descriptive utilisant les données du Sondage national de 2007 auprès des médecins.
Contexte
Le Canada.
Participants
Un total de 1109 étudiants en médecine du niveau clinique et de 829 du niveau pré-clinique ayant participé au Sondage national 2007 auprès des médecins.
Principaux paramètres à l’étude
La principale variable, l’espoir d’être admis dans une spécialité de MF, a été analysée avec 40 variables indépendantes dans des modèles d’arbre de régression et de classification.
Résultats
Moins d’un étudiant en médecine sur 3 (30,2 % au niveau pré-clinique et 31,4 % au niveau clinique) espérait faire carrière en MF. Ceux qui faisaient ce choix étaient plus souvent des femmes; légèrement plus âgés; plus souvent mariés ou en union libre; typiquement nés au Canada; et plus susceptibles d’avoir été exposés à des milieux non urbains. Le facteur de prédiction le plus important pour les deux groupes était la dette contractée durant les études médicales, qui avait l’effet contraire de l’intérêt manifesté par l’étudiant pour la recherche. Ceux qui étaient intéressés par la recherche étaient attirés vers des spécialités susceptibles de générer des revenus élevés, alors que ceux qui ne l’étaient pas penchaient plutôt pour des programmes de résidence courts comme la MF, de façon à pouvoir commencer à rembourser leur dette plus tôt. Il semble donc exister une relation inverse entre l’intérêt pour la recherche et le choix de la MF.
Conclusion
Moins d’un étudiant sur 3 songeait à une résidence en médecine familiale au Canada, ce qui est de beaucoup inférieur à l’objectif de 45 % établi au niveau national et à celui de 50 % fixé par des provinces comme le Québec. La dette contractée par l’étudiant et son intérêt pour la recherche ont une forte influence sur son choix d’une résidence.
The shortage of family doctors is an important factor responsible for Canadians not having timely access to health care.1 The attractiveness of family medicine (FM) for medical students showed a gradual decline until 2005, followed by a slight increase since then.2–8 In 1997, 45% of Canadian medical school graduates entered residencies in FM compared with only 40% in 2001.9 Scott et al suggested that the lack of a central strategy at the postgraduate training level, coupled with an excess of residency positions, means that the career preferences of medical students have a substantial role in determining the future mix of practising physicians in Canada.8 Rosenblatt and Andrilla came to a similar conclusion about the effects of medical students’ specialty choices on the shape and dynamics of the US medical system.10
Medical work force planning should be based on accurate information, and the College of Family Physicians of Canada, the Canadian Medical Association, and the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada collaboratively collect very detailed information about Canada’s physician resources every 3 years through the National Physician Survey (NPS).11 Separate questionnaires are addressed to physicians, residents, and medical students, with questions about demographics, personal background, satisfaction with medical training and practice, practice interests, and career plans (http://nationalphysiciansurvey.ca).12
The NPS questionnaire for medical students is based on findings from extensive research about the complex process of choosing a medical career.13–17 Personal characteristics and background, lifestyle, expectations, attitudes, and perceptions about the medical profession are all important components of this choice.2,13,14,18–21 Preferences for a particular type of medical career can sometimes be obvious before entering medical school, but they can also be affected by different factors during medical training. Many authors report that characteristics of medical schools and training programs affect students’ choice of specialty14,16,20,22–24: role models,2,17,25–27 internship experiences,28 and the informal climate or hidden curriculum.24,29,30 Contextual factors, such as organizational constraints or the perceived income of physicians, can also affect the choice of medical discipline.7,10,31–34 Bland, Meurer, and Maldonado integrated many of these factors into one of the most complete theoretical models on medical specialty choice.16 Their model showed that medical specialty selection was based on the match between the student’s perceived characteristics of the specialty and his or her career needs. These career needs are determined by the student’s values, which in turn are determined by a combination of pre–medical school life experiences, demographic characteristics, and personality. These values will be shaped by medical school experiences and by the values and culture of the institution in which the student receives medical training.16
With this model as a framework, the aim of this study was to examine the association between students’ values, medical school undergraduate program, and intention to enter an FM specialty in Canada, according to data from the 2007 NPS for medical students.
METHODS
Study design and data source
Data from the 2007 NPS for medical students, a cross-sectional, self-reported online survey, were analyzed in this descriptive study. The survey targeted all the medical students attending Canadian medical schools (N = 9162).11 From February to April 2007, they were contacted and asked to complete the online questionnaire, which was available in English and French. The response rate was 30.8% (N = 2819).11 National level estimates are considered accurate within plus or minus 1.8%, 19 times out of 20.12
Populations studied
Guided by research suggesting that a considerable proportion of students shift their specialty preferences during their undergraduate medical training,3,27,35 we studied 2 populations: students before their clinical clerkship, called preclinical students (targeted population of 2647, 829 of whom responded to the NPS for a response rate of 31.3%; results are considered accurate within plus or minus 3.3%, 19 times out of 2012); and students in their clinical clerkship, called clinical students (targeted population of 3984, 1109 of whom responded to the NPS for a response rate of 27.8%; results are considered accurate within plus or minus 4.2%, 19 times out of 2012). Those who did not answer or who indicated that they were undecided about the medical specialty they hoped to enter (n = 68 preclinical students [8.2%]; n = 54 clinical students [4.8%]) were excluded from our analyses.
Variables studied
The main variable was the hope to enter an FM residency or specialty. Responses were classified into 2 categories: family medicine, when students indicated FM or FM and another discipline in the nonexclusive multiple-choice question, or other specialty, when students indicated disciplines other than FM.
About 40 other variables extracted from NPS questions were analyzed in order to test their association with the main variable. Following the model of Bland, Meurer, and Maldonado, we selected variables related to student characteristics (age, sex, marital status, language, country of birth, exposure to rural or urban environments, parents’ level of education, familiarity with health professions from family members working in health-related jobs, last diploma held at entry into medical school, expected debt at the end of medical training, and current financial situation); students’ values regarding medicine (motivation to select medicine, time when they decided to become a doctor, and interest in FM rotations); medical school characteristics (school of medicine, province where the university was located); and students’ career expectations and needs (principal factors for a satisfying medical practice, plans to repay debt, anticipated type of practice, preferred payment model, and the hope to be involved in specific professional activities such as research, administration, or public health). Except for age, all other explanatory variables were categorical (Table 1).
Table 1.
Covariates and their categories as defined in the models
| COVARIATE | CATEGORIES |
|---|---|
| Age | Continuous |
| Sex | Female, male |
| Language | English, French |
| Marital status | Married or living with partner, single, separated or divorced, widowed |
| Environment before university | Exclusively or predominantly rural, exclusively or predominantly small town, exclusively or predominantly urban, mixture of environments |
| Born in Canada | Yes, no |
| Father’s education (degree or diploma) | No diploma, no university diploma, undergraduate diploma, graduate diploma |
| Mother’s education (degree or diploma) | No diploma, no university diploma, undergraduate diploma, graduate diploma |
| Are any of your immediate family members working in medically related jobs? | |
| • Father | MD, other, NR or NA |
| • Mother | MD, other, NR or NA |
| • Siblings | MD, other, NR or NA |
| Last academic degree before MD program | No university diploma, college, bachelor, master, PhD, other diploma |
| Province of medical school | Ontario, Quebec, British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan, Manitoba, Nova Scotia, Newfoundland |
| Timing of decision to become a doctor | Before high school, during high school, during undergraduate studies, after undergraduate studies, during or after graduate studies, other |
| Of all of the possible careers, what led you to select medicine? | |
| • Mentor | Yes, no |
| • Family | Yes, no |
| • Intellectual stimulation or challenge | Yes, no |
| • Earning potential | Yes, no |
| • Doctor-patient relationship | Yes, no |
| • Research opportunities | Yes, no |
| • Teaching opportunities | Yes, no |
| • Prestige | Yes, no |
| To what extent do you agree that your medical training program has prepared you to select a residency training program? | Strongly agree, agree, neutral, disagree, strongly disagree |
| At this time, in which of the following do you hope to be involved? | |
| • Patient care | Yes, no, unsure |
| • Research | Yes, no, unsure |
| • Administration | Yes, no, unsure |
| • Public health | Yes, no, unsure |
| What factors do you think will be most important in having a satisfying and successful medical practice? | |
| • Flexible work hours | Yes, no |
| • Availability of continuing education resources | Yes, no |
| • Opportunities for research | Yes, no |
| • Opportunities for teaching | Yes, no |
| • Balance between practice and personal life | Yes, no |
| • Sufficient medical competence | Yes, no |
| • Ability to achieve desired income | Yes, no |
| How would you prefer to be paid for your services as a physician? | Blended, capitation, salary, service contract, seasonal or hourly, fee-for-services only, unsure |
| Expected debt upon completion of medical school (directly related to being in medical school) | No debt, < $20 000, $20 000–$80 000, > $80 000, not provided |
| To pay off the debt directly related to being in medical school, do you intend to do any of the following? | |
| • Select a short residency program | Yes, no |
| • Select a specialty you believe will have high earning potential | Yes, no |
| Stress of financial situation | Extremely stressful, very stressful, fairly stressful, minimally stressful, not stressful |
NA—not applicable, NR—no response.
Statistical analyses
Analyses were done separately for each population and included descriptive analysis (with SPSS, version 15.0), univariate and multivariate logistic regressions (with SAS, version 9.1), and classification-tree models (with CART, version 6.0). Univariate regressions were used to identify the covariates significantly associated with the main variable in order to include them in the multivariate regressions and tree models. In logistic regression analyses, the significance level considered was P ≤ .05, and goodness of fit was evaluated by Nagelkerke adjusted R2.36 Backward method was used to obtain parsimonious multivariate models that included age and sex.
Classification trees allowed a complementary approach to the multivariate regression to easily explore covariate interactions as well as to identify profiles of students according to the probability that they hoped to enter FM residency. This method recursively partitions the observations based on the covariables and forms more homogeneous groups regarding the main variable.37–39 Tree-based models are nonlinear and non-parametric, and explanatory interactions do not need to be explicitly indicated.40 Missing values are handled by developing alternative splits or surrogates for each split for which the primary splitting variable is missing.40
Classification trees were created using the Gini index algorithm, with 10-fold cross-validation, a minimum size of 50 observations to split a node, and 25 observations as the minimum size of a terminal node. The best classification tree was selected by the lower cross-validation relative error in the interval of 1 standard deviation of this value.37
RESULTS
The preclinical sample included 761 medical students and the clinical sample included 1055 students. Among the preclinical sample, 230 (30.2%) students hoped to enter into FM specialties (Table 2); 46 (6.0%) of them indicated FM and 1 or 2 other disciplines, while 184 (24.2%) indicated only FM. Among the clinical sample, 331 (31.4%) students hoped to enter into FM specialties (Table 3); 16 (1.5%) indicated 1 or 2 other disciplines, while 315 (29.9%) indicated only FM.
Table 2.
Characteristics of medical students in the preclinical sample: N = 761; nonresponses were less than 0.3%.
| VARIABLES | FM N = 230 (30.2%) | OS N = 531 (69.8%) | ALL N = 761 (100.0%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Median (range) age, y* | 24 (19–43) | 23 (20–40) | 23 (19–43) |
| Sex, n (%)† | |||
| • Male | 63 (27.4) | 211 (39.7) | 274 (36.0) |
| • Female | 167 (72.6) | 319 (60.1) | 486 (63.9) |
| Marital status, n (%)‡ | |||
| • Single | 184 (80.0) | 464 (87.4) | 648 (85.2) |
| • Married or living with partner | 46 (20.0) | 66 (12.4) | 112 (14.7) |
| • Separated or divorced | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Born in Canada, n (%)§ | 213 (92.6) | 430 (81.0) | 643 (84.5) |
| Environment before university, n (%)§ | |||
| • Exclusively or predominantly rural | 47 (20.4) | 60 (11.3) | 107 (14.1) |
| • Exclusively or predominantly small town | 70 (30.4) | 117 (22.0) | 187 (24.6) |
| • Exclusively or predominantly urban | 93 (40.4) | 311 (58.6) | 404 (53.1) |
| • Mixture of environments | 20 (8.7) | 42 (7.9) | 62 (8.1) |
| Expected debt upon completion of medical school (directly related to being in medical school), n (%) | |||
| • No debt | 21 (9.1) | 66 (12.4) | 87 (11.4) |
| • < $20 000 | 35 (15.2) | 92 (17.3) | 127 (16.7) |
| • $20 000–$80 000 | 84 (36.5) | 162 (30.5) | 246 (32.3) |
| • > $80 000 | 85 (37.0) | 190 (35.8) | 275 (36.1) |
| • Not provided | 3 (1.3) | 16 (3.0) | 19 (2.5) |
| Best description of the financial situation, n (%) | |||
| • Extremely stressful | 6 (2.6) | 19 (3.6) | 25 (3.3) |
| • Very stressful | 16 (7.0) | 36 (6.8) | 52 (6.8) |
| • Fairly stressful | 73 (31.7) | 133 (25.0) | 206 (27.1) |
| • Minimally stressful | 103 (44.8) | 240 (45.2) | 343 (45.1) |
| • Not stressful | 30 (13.0) | 99 (18.6) | 129 (17.0) |
FM—family medicine specialty, OS—other specialty.
Kolmogorov-Smirnov test: P < .05.
χ2 test: P < .01.
χ2 test: P < .05
χ2 test: P < .0001.
Table 3.
Characteristics of medical students in the clinical sample: N = 1055; nonresponses were less than 0.3%.
| VARIABLES | FM N = 331 (31.4%) | OS N = 724 (68.6%) | ALL N = 1055 (100.0%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Median (range) age, y* | 27 (21–50) | 26 (21–44) | 26 (21–50) |
| Sex, n (%)† | |||
| • Male | 80 (24.2) | 260 (35.9) | 340 (32.2) |
| • Female | 251 (75.8) | 463 (64.0) | 714 (67.7) |
| Marital status, n (%)‡ | |||
| • Single | 193 (58.3) | 537 (74.2) | 730 (69.2) |
| • Married or living with partner | 134 (40.5) | 185 (25.6) | 319 (30.2) |
| • Separated or divorced | 4 (1.2) | 2 (0.3) | 6 (0.6) |
| Born in Canada, n (%)§ | 303 (91.5) | 628 (86.7) | 931 (88.2) |
| Environment before university, n (%)‡ | |||
| • Exclusively or predominantly rural | 54 (16.3) | 66 (9.1) | 120 (11.4) |
| • Exclusively or predominantly small town | 114 (34.4) | 167 (23.1) | 281 (26.6) |
| • Exclusively or predominantly urban | 141 (42.6) | 446 (61.6) | 587 (55.6) |
| • Mixture of environments | 21 (6.3) | 43 (5.9) | 64 (6.1) |
| Expected debt upon completion of medical school (directly related to being in medical school), n (%) | |||
| • No debt | 27 (8.2) | 84 (11.6) | 111 (10.5) |
| • < $20 000 | 38 (11.5) | 93 (12.8) | 131 (12.4) |
| • $20 000–$80 000 | 136 (41.1) | 239 (33.0) | 375 (35.5) |
| • > $80 000 | 127 (38.4) | 295 (40.7) | 422 (40.0) |
| • Not provided | 2 (0.6) | 6 (0.8) | 8 (0.8) |
| Best description of the financial situation, n (%) | |||
| • Extremely stressful | 18 (5.4) | 26 (3.6) | 44 (4.2) |
| • Very stressful | 36 (10.9) | 78 (10.8) | 114 (10.8) |
| • Fairly stressful | 86 (26.0) | 242 (33.4) | 328 (31.1) |
| • Minimally stressful | 146 (44.1) | 283 (39.1) | 429 (40.7) |
| • Not stressful | 44 (13.3) | 91 (12.6) | 135 (12.8) |
FM—family medicine specialty, OS—other specialty.
Kolmogorov-Smirnov test: P < .05.
χ2 test: P < .01.
χ2 test: P < .0001.
χ2 test: P < .05
Personal characteristics of medical students intending to enter FM were similar in both samples. Most such students were female, slightly older, more frequently married or living with partners, born in Canada, or previously exposed to non-urban environments (Tables 2 and 3).
In the univariate regression among the preclinical students, 19 of the 40 variables were associated with the desire to pursue FM and were included in the multivariate model. The final model included 7 of these covariates, plus age and sex, and explained 43% of the variability (Table 4). A short residency program was the most important predictor, increasing by 9 times the probability of students hoping to enter FM. Both the desire to be involved in public health and the possibility of flexible work hours also increased the chance of a preference for FM, as did exposure to rural or small-town environments before university. Conversely, interest in a specialty with high earning potential and expectations of developing research activities strongly decreased the probability of choosing FM.
Table 4.
Multivariate logistic regression on the hope to enter FM among students from the preclinical sample: N = 612; 149 observations were deleted owing to missing data for the independent variables; Nagelkerke R2 = 0.43.
| COVARIATE | FM N = 196 | OS N = 416 | ODDS RATIO (WALD 95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Median (range) age, y | 24 (19–43) | 23 (20–40) | 1.07 (1.00–1.14) |
| Sex, n (%) | |||
| • Male (reference) | 52 (26.5) | 165 (39.7) | −1.14 (0.71–1.82) |
| • Female | 44 (73.5) | 251 (60.3) | |
| Environment before university, n (%) | |||
| • Urban (reference) | 76 (38.8) | 242 (58.2) | - |
| • Rural | 41 (20.9) | 50 (12.0) | 2.62 (1.43–4.78) |
| • Small town | 61 (31.1) | 89 (21.4) | 1.54 (0.93–2.53) |
| • Mix | 18 (9.2) | 35 (8.4) | 1.67 (0.78–3.56) |
| Hope to be involved in research, n (%) | |||
| • No (reference) | 113 (57.7) | 133 (32.0) | - |
| • Yes | 22 (11.2) | 166 (39.9) | 0.23 (0.10–0.52) |
| • Unsure | 61 (31.1) | 117 (28.1) | 0.56 (0.34–0.91) |
| Hope to be involved in public health, n (%) | |||
| • No (reference) | 44 (22.4) | 142 (34.1) | - |
| • Yes | 84 (42.9) | 114 (27.4) | 3.33 (1.91–5.82) |
| • Unsure | 68 (34.7) | 160 (38.5) | 1.42 (0.83–2.45) |
| Factor for a satisfying medical practice: flexible work hours, n (%) | |||
| • No (reference) | 47 (24.0) | 144 (34.6) | −1.86 (1.16–2.96) |
| • Yes | 149 (76.0) | 272 (65.4) | |
| Factor for a satisfying medical practice: research opportunities, n (%) | |||
| • No (reference) | 176 (89.8) | 269 (64.7) | - |
| • Yes | 20 (10.2) | 147 (35.3) | 0.42 (0.19–0.93) |
| Short residency program to pay off debt, n (%) | |||
| • No (reference) | 136 (69.4) | 391 (94.0) | |
| • Yes | 60 (30.6) | 25 (6.0) | 8.82 (4.49–17.33) |
| Specialty with high earning potential to pay off debt, n (%) | |||
| • No (reference) | 184 (93.9) | 296 (71.2) | - |
| • Yes | 12 (6.1) | 120 (28.8) | −0.07 (0.03–0.16) |
CI—confidence interval, FM–family medicine specialty, OS—other specialty.
In the clinical student sample, 20 covariates were significantly associated with the main variable and were included in the multivariate model. The final model included 10 of these covariates, plus age and sex, and explained 60% of the variability (Table 5). Here again, the most important variable was a short residency program, along with the hope to be involved in public health, availability of continuing education resources, and previous exposure to non-urban environments. As observed in the preclinical student sample, interest in a specialty with a high earning potential strongly decreased the probability of choosing FM, as did the expectation to pursue research, teaching, or administrative roles (Table 5).
Table 5.
Multivariate logistic regression on the hope to enter FM among students from the clinical sample: N = 870; 185 observations were deleted owing to missing data for the independent variables; Nagelkerke R2 = 0.58.
| COVARIATE | FM N = 284 | OS N = 586 | ODDS RATIO (WALD 95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Median (range) age, y | 26 (21–50) | 26 (21–50) | 1.12 (1.00–1.19) |
| Sex, n (%) | |||
| • Male (reference) | 64 (22.5) | 217 (37.0) | - |
| • Female | 220 (77.5) | 369 (63.0) | 1.31 (0.83–2.07) |
| Environment before university, n (%) | |||
| • Urban (reference) | 116 (40.8) | 354 (60.4) | - |
| • Rural | 47 (16.5) | 59 (10.1) | 1.73 (0.97–3.08) |
| • Small town | 104 (36.6) | 141 (24.1) | 2.43 (1.54–3.83) |
| • Mixture | 17 (6.0) | 32 (5.5) | 2.42 (0.96–6.11) |
| What led you to select medicine: doctor-patient relationship, n (%) | |||
| • No (reference) | 34 (12.0) | 131 (22.4) | - |
| • Yes | 250 (88.0) | 455 (77.6) | 1.80 (1.04–3.13) |
| Hope to be involved in research, n (%) | |||
| • No (reference) | 161 (56.7) | 124 (21.2) | - |
| • Yes | 52 (18.3) | 301 (51.4) | 0.09 (0.05–0.16) |
| • Unsure | 71 (25.0) | 161 (27.5) | 0.24 (0.15–0.40) |
| Hope to be involved in administration, n (%) | |||
| • No (reference) | 166 (58.5) | 254 (43.3) | - |
| • Yes | 31 (10.9) | 127 (21.7) | 0.38 (0.20–0.71) |
| • Unsure | 87 (30.6) | 205 (35.0) | 0.62 (0.38–0.99) |
| Hope to be involved in public health, n (%) | |||
| • No (reference) | 103 (36.3) | 282 (48.1) | - |
| • Yes | 81 (28.5) | 136 (23.2) | 3.31 (1.92–5.69) |
| • Unsure | 100 (35.2) | 168 (28.7) | 2.66 (1.58–4.46) |
| Factor for a satisfying medical practice: flexible work hours, n (%) | |||
| • No (reference) | 43 (15.1) | 173 (29.5) | - |
| • Yes | 241 (84.9) | 413 (70.5) | 1.82 (1.12–2.97) |
| Factor for a satisfying medical practice: continuing education resources, n (%) | |||
| • No (reference) | 55 (19.4) | 172 (29.4) | - |
| • Yes | 229 (80.6) | 414 (70.6) | 1.92 (1.18–3.12) |
| Factor for a satisfying medical practice: teaching opportunities, n (%) | |||
| • No (reference) | 130 (45.8) | 164 (28.0) | - |
| • Yes | 154 (54.2) | 422 (72.0) | 0.56 (0.37–0.85) |
| Short residency program to pay off debt, n (%) | |||
| • No (reference) | 172 (60.6) | 555 (94.7) | - |
| • Yes | 112 (39.4) | 31 (5.3) | 14.49 (7.86–26.68) |
| Specialty with high earning potential to pay off debt, n (%) | |||
| • No (reference) | 275 (96.8) | 380 (64.8) | - |
| • Yes | 9 (3.2) | 206 (35.2) | 0.05 (0.02–0.10) |
CI—confidence interval, FM—family medicine specialty, OS—other specialty.
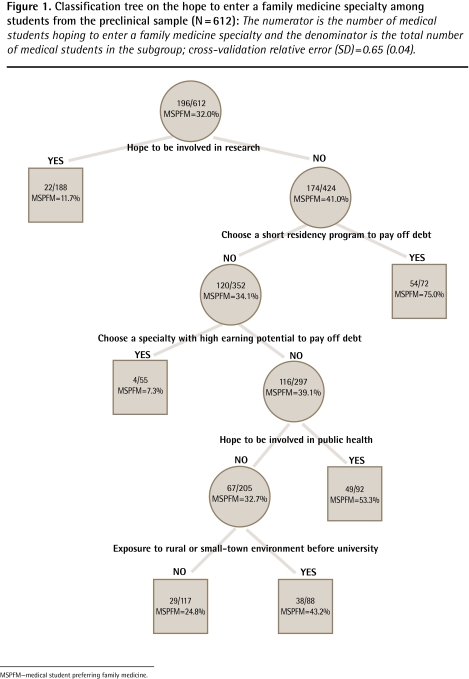
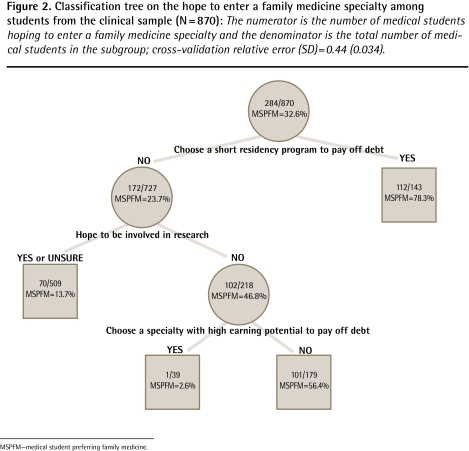
The classification tree explained 35% of the variability for the preclinical medical students according to their probability of being interested in an FM specialty (Figure 1). The highest rate of interest in FM (75.0%) was found among students who were not interested in future research activities and who wanted to complete short residency programs, while the lowest rate (7.3%) was found among students who were not interested in research but who wanted to enter specialties with high earning potential. Expecting to develop a research career was the most important variable that split the sample into 2 homogeneous groups according to the proportion of students interested in FM. Exposure to rural environments before university and hoping to be involved in public health activities acted specifically in the lowest part of the model. There were similar findings among the clinical student sample, with a classification tree that explained 65% of data variability (Figure 2). The highest rate was found among students considering a short residency to pay off their debt (78.3%) and the lowest rate was found among students not interested in research who wanted specialties with high earning potential (2.6%).
Figure 1.
Classification tree on the hope to enter a family medicine specialty among students from the preclinical sample (N = 612): The numerator is the number of medical students hoping to enter a family medicine specialty and the denominator is the total number of medical students in the subgroup; cross-validation relative error (SD) = 0.65 (0.04).
MSPFM—medical student preferring family medicine.
Figure 2.
Classification tree on the hope to enter a family medicine specialty among students from the clinical sample (N = 870): The numerator is the number of medical students hoping to enter a family medicine specialty and the denominator is the total number of medical students in the subgroup; cross-validation relative error (SD) = 0.44 (0.034).
MSPFM—medical student preferring family medicine.
DISCUSSION
About 30% of medical students responding to the 2007 NPS hoped to enter FM. This rate is consistent with rates reported by the Canadian Resident Matching Service for 2007, 2008, and 2009, when FM was the first choice for 28.9%, 31.0%, and 31.0% of students, respectively.41 This proportion is slightly higher than rates reported by Scott et al in Canadian medical schools between 2002 and 2005.8 However, Wright et al reported a low of 13.7% for students from the University of Alberta in 2002, suggesting wide variability among medical schools.21
Medical students interested in residencies in FM were older, more frequently female, and more often exposed to non-urban environments before university, findings that are similar to those of other studies.10,14,15,21,23,42–44 The most important predictors of interest in FM were similar for preclinical and clinical students, although clinical students were also influenced by the desire to be involved in teaching or administrative activities. Evolution throughout medical training was also manifest in the increasing proportion of students choosing only FM, while the proportions of those not yet decided and those choosing FM and other disciplines decreased.
Following the model of Bland, Meurer, and Maldonado, the predictors reflected the match between the students’ perceptions of the characteristics of FM and the other specialties, and their career needs and expectations. Among their needs, the need to pay off the debt accumulated during medical school was a main factor influencing the choice of a career in FM. Regarding career expectations, desire for research, teaching, and administrative activities appeared to discourage careers in FM, while public health activities, flexible work hours, and continuing education training encouraged FM careers. Age was an additional factor that affected choice, more clearly for clinical students. Classification trees showed the way these factors interacted in the clinical and preclinical groups. For preclinical students the hope to be involved in research was the most important predictor, and choice of a short residency was a predictor only for students not interested in research. For clinical students the order was reversed: the hope to do research was a predictor only for those students who did not want to choose a short residency program.
Findings about students’ plans to pay off debt are consistent with those from other studies.7,31,32,45 Morra et al found the following:
... 54% to 64% of medical students agreed with the statement that if a student has a lot of financial debt, “It is better to do a specialty as you will make more money and be able to pay off your debt faster,” with the remainder agreeing that a student should “Do family medicine as the residency is shorter and you can start paying off your debt faster.”7
That interest in research was inversely related to the choice of FM is consistent with findings from Senf et al in the United States. They suggested that the development of research in FM could attract students who were interested in research but who traditionally associated research with specialties other than FM.44 The College of Family Physicians of Canada’s Clinician Scholar Program,46 for example, might well attract more students to FM in Canada. This is a program that provides a formal postgraduate medical education pathway that fulfils the existing requirements for residency training in FM and also provides integrated, structured, and rigorous research and scholarly training.
Limitations and directions for future research
Response rates to the NPS restrict analyses to the national level to ensure acceptable accuracy in the results. The multivariate regressions employed a subset of students without missing values for covariates, and the classification trees were developed with the same data subsets to allow comparison of results. Results of this study have to be interpreted cautiously because accuracy is lower than would be the case for the entire population. In the same way, data on demographic characteristics of NPS respondents relative to the entire population were not available to evaluate their representativeness. The NPS did not include information on students’ academic performances, medical program curriculum, or descriptors of institutional values and culture. Thus, these important components in the model of Bland, Meurer, and Maldonado were not included in the analyses.
The study presents a cross-sectional picture for 2 populations of students at different times in their medical training. It would be interesting to follow a prospective cohort over their entire medical training and track changes from initial preferences to the final selection of residency. Nevertheless, data from the NPS is to date the most exhaustive, stable, and systematically collected data in Canada to follow medical students’ plans and preferences. To our knowledge, it is internationally one of the most comprehensive recurrent surveys of the medical work force.
Conclusion
According to our study based on the 2007 NPS, only 1 medical student out of 3 in Canada is looking for an FM residency. This is far below the goal of 45% set at the national level1 and even further below some provinces like Quebec, where the goal is 50%.47
The results also show that the opportunity for research and choosing a short residency in order to start to repay debt sooner have strong influences on choice of residency by medical students. Enhancement of the salary earned by family physicians as well as programs to train them in research would contribute to the attractiveness of FM residency programs. This is under consideration at different political levels in Canada but might not be easy to achieve in the short term.
EDITOR’S KEY POINTS
The shortage of family doctors is at the forefront of health care challenges in Canada and is an important factor in the lack of timely access to care by Canadians. The attractiveness of family medicine (FM) for medical students has shown a gradual decline in recent decades. This study aimed to examine the association between students’ personal characteristics, backgrounds, and medical schools and their intention to enter FM specialties, using data from the 2007 Canadian National Physician Survey.
Fewer than 1 medical student in 3 hoped to enter into FM careers. Desire for a short residency program was the most important predictor, increasing by 9 times the probability of students hoping to enter the FM specialty. Both the desire to be involved in public health and the possibility of flexible work hours also increased the chances of a preference for an FM specialty, as did exposure to rural or small-town environments before university.
Conversely, interest in a specialty with high earning potential strongly decreased the probability of choosing FM, as did the hope of pursuing research activities.
The most important predictors of interest in FM were similar for preclinical and clinical students, although clinical students were also influenced by a desire to be involved in teaching or administrative activities.
POINTS DE REPÈRE DU RÉDACTEUR
La pénurie de médecins de famille est l’un des principaux défis auxquels sont confrontés les soins de santé au Canada et c’est une raison majeure pour laquelle les Canadiens ont moins d’accès aux soins en temps opportun. Au cours des dernières décennies, l’attrait de la médecine familiale (MF) pour les étudiants en médecine a connu un déclin progressif. Cette étude cherchait à savoir, grâce aux données du Sondage national 2007 auprès des médecins canadiens, s’il existe un rapport entre les caractéristiques personnelles d’un étudiant, ses antécédents et sa faculté de médecine, et son intention de choisir une spécialité de MF.
Moins d’un étudiant sur 3 espérait choisir une carrière en MF. Le plus important indicateur d’un tel choix, qui augmentait par un facteur 9 la probabilité d’opter pour une spécialité de MF, était le désir d’un programme de résidence court. Le désir de travailler en santé publique et la possibilité de jouir d’heures de travail flexibles augmentaient aussi les chances de choisir une spécialité en MF, de même que le fait d’avoir été exposé à des milieux ruraux ou de petites municipalités avant l’université.
Inversement, l’intérêt pour une spécialité avec revenus éventuels élevés diminuait la probabilité de choisir la MF, tout comme l’espérance de poursuivre une carrière en recherche.
Les meilleurs indicateurs d’un intérêt pour la MF étaient semblables pour les étudiants des niveaux clinique et pré-clinique, quoique au stade clinique, les étudiants étaient aussi influencés par le désir de participer à des activités d’enseignement ou d’administration.
Footnotes
This article has been peer reviewed.
Cet article a fait l’objet d’une révision par des pairs.
Contributors
Drs Vanasse, Orzanco, and Courteau and Ms Scott contributed to the concept and design of the study; data gathering, analysis, and interpretation; and preparing the manuscript for submission.
Competing interests
None declared
References
- 1.College of Family Physicians of Canada . Supporting the future family medicine workforce in Canada. Is enough being done today to prepare for tomorrow? Report card. Mississauga, ON: College of Family Physicians of Canada; 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wright S, Wong A, Newill C. The impact of role models on medical students. J Gen Intern Med. 1997;12(1):53–6. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1497.1997.12109.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bethune C, Hansen PA, Deacon D, Hurley K, Kirby A, Godwin M. Family medicine as a career option. How students’ attitudes changed during medical school. Can Fam Physician. 2007;53:880–5. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Campos-Outcalt D, Senf J, Pugno PA, McGaha AL. Family medicine specialty selection: a proposed research agenda. Fam Med. 2007;39(8):585–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kerr JR, Seaton B, Zimcik H, McCabe J, Feldman K. The impact of interest. How do family medicine interest groups influence medical students? Can Fam Physician. 2008;54:78–9.e2–8. Available from: www.cfp.ca/content/54/1/78.full.pdf+html. Accessed 2011 Apr 20. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.McGaha AL, Schmittling GT, DeVilbiss AD, Pugno PA. Entry of US medical school graduates into family medicine residencies: 2008–2009 and 3-year summary. Fam Med. 2009;41(8):555–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Morra DJ, Regehr G, Ginsburg S. Medical students, money, and career selection: students’ perception of financial factors and remuneration in family medicine. Fam Med. 2009;41(2):105–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Scott IM, Wright BJ, Brenneis FR, Gowans MC. Whether or wither some specialties: a survey of Canadian medical student career interest. BMC Med Educ. 2009;9:57. doi: 10.1186/1472-6920-9-57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Thurber D, Buske L. The class of ’94. What has changed in post-M.D. training since 1989? Ottawa, ON: Canadian Post-M.D. Education Registry; 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Rosenblatt RA, Andrilla AC. The impact of U.S. medical students’ debt on their choice of primary care careers: an analysis of data from the 2002 medical school graduation questionnaire. Acad Med. 2005;80(9):815–9. doi: 10.1097/00001888-200509000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Grava-Gubins I, Scott S. Effects of various methodological strategies. Survey response rates among Canadian physicians and physicians-in-training. Can Fam Physician. 2008;54:1424–30. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.College of Family Physicians of Canada, Canadian Medical Association, Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada . National Physician Survey 2007. Mississauga, ON: College of Family Physicians of Canada; 2007. Available from: www.nationalphysiciansurvey.ca/nps/2007_Survey/2007nps-e.asp. Accessed 2010 Feb 23. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Senf JH, Campos-Outcalt D, Watkins A, Bastacky S, Killian C. A systematic analysis of how medical school characteristics relate to graduates’ choices of primary care specialties. Acad Med. 1997;72(6):524–33. doi: 10.1097/00001888-199706000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Senf JH, Kutob R, Campos-Outcalt D. Which primary care specialty? Factors that relate to a choice of family medicine, internal medicine, combined internal medicine–pediatrics, or pediatrics. Fam Med. 2004;36(2):123–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lawson SR, Hoban JD. Predicting career decisions in primary care medicine: a theoretical analysis. J Contin Educ Health Prof. 2003;23(2):68–80. doi: 10.1002/chp.1340230204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bland CJ, Meurer L, Maldonado G. Determinants of primary care specialty choice: a non-statistical meta-analysis of the literature. Acad Med. 1995;70(7):620–41. doi: 10.1097/00001888-199507000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ciechanowski PS, Worley LL, Russo JE, Katon WJ. Using relationship styles based on attachment theory to improve understanding of specialty choice in medicine. BMC Med Educ. 2006;6:3. doi: 10.1186/1472-6920-6-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Beaulieu MD, Rioux M, Rocher G, Samson L, Boucher L. Family practice: professional identity in transition. A case study of family medicine in Canada. Soc Sci Med. 2008;67(7):1153–63. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2008.06.019. Epub 2008 Jul 20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Beaulieu MD, Dory V, Pestiaux D, Pouchain D, Gay B, Rocher G, et al. General practice as seen through the eyes of general practice trainees: a qualitative study. Scand J Prim Health Care. 2006;24(3):174–80. doi: 10.1080/02813430600795498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gazewood JD, Owen J, Rollins LK. Effect of generalist preceptor specialty in a third-year clerkship on career choice. Fam Med. 2002;34(9):673–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wright B, Scott I, Woloschuk W, Brenneis F. Career choice of new medical students at three Canadian universities: family medicine versus specialty medicine. CMAJ. 2004;170(13):1920–4. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.1031111. Errata in: CMAJ 2004;171(3):222, CMAJ 2004;170(11)1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Meurer LN. Influence of medical school curriculum on primary care specialty choice: analysis and synthesis of the literature. Acad Med. 1995;70(5):388–97. doi: 10.1097/00001888-199505000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lawson SR, Hoban JD, Mazmanian PE. Understanding primary care residency choices: a test of selected variables in the Bland-Meurer model. Acad Med. 2004;79(10 Suppl):S36–9. doi: 10.1097/00001888-200410001-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Campos-Outcalt D, Senf J, Watkins AJ, Bastacky S. The effects of medical school curricula, faculty role models, and biomedical research support on choice of generalist physician careers: a review and quality assessment of the literature. Acad Med. 1995;70(7):611–9. doi: 10.1097/00001888-199507000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ciechanowski PS, Russo JE, Katon WJ, Walker EA. Attachment theory in health care: the influence of relationship style on medical students’ specialty choice. Med Educ. 2004;38(3):262–70. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2923.2004.01767.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kutob RM, Senf JH, Campos-Outcalt D. The diverse functions of role models across primary care specialties. Fam Med. 2006;38(4):244–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Scott IM, Gowans MC, Wright BJ, Brenneis FR. Why medical students switch careers. Changing course during the preclinical years of medical school. Can Fam Physician. 2007;53:94–5.e1–5. Available from: www.cfp.ca/content/53/1/94.full.pdf+html. Accessed 2011 Apr 20. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Bilodeau H, Leduc N, van Schendel N. Analyse des facteurs d’attraction, d’installation et de maintien de la pratique médicale dans les régions éloignées du Québec. Montreal, QC: Groupe de recherche interdisciplinaire en santé; 2006. Report no. R06-02. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Campos-Outcalt D, Senf J, Kutob R. Comments heard by US medical students about family practice. Fam Med. 2003;35(8):573–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hafferty FW, Boulger JG. Medical students view family practice. Fam Med. 1988;20(4):277–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Newton DA, Grayson MS, Thompson LF. Money, lifestyle, or values? Why medical students choose subspecialty versus general pediatric careers. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 2010;49(2):116–22. doi: 10.1177/0009922809350216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Rosenthal MP, Turner TN, Diamond J, Rabinowitz HK. Income expectations of first-year students at Jefferson Medical College as a predictor of family practice specialty choice. Acad Med. 1992;67(5):328–31. doi: 10.1097/00001888-199205000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Rosenthal MP, Rabinowitz HK, Diamond JJ, Markham FW., Jr Medical students’ specialty choice and the need for primary care. Our future. Prim Care. 1996;23(1):155–67. doi: 10.1016/s0095-4543(05)70268-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Rosenthal MP, Diamond JJ, Rabinowitz HK, Bauer LC, Jones RL, Kearl GW, et al. Influence of income, hours worked, and loan repayment on medical students’ decision to pursue a primary care career. JAMA. 1994;271(12):914–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Schafer S, Shore W, French L, Tovar J, Hughes S, Hearst N. Rejecting family practice: why medical students switch to other specialties. Fam Med. 2000;32(5):320–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.SAS Institute Inc . SAS/STAT 9.2 user’s guide. Cary, NC: SAS Institute Inc; 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Breiman L, Friedman JH, Olshen RA, Stone CJ, editors. Classification and regression trees. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth International Group; 1984. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Clark LA, Pregibon D. Statistical models in S. In: Chambers JM, Hastie TJ, editors. Cole computer science series. Pacific Grove, CA: Wadsworth & Brooks; 1992. pp. 377–419. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Venables WN, Ripley BD. Modern applied statistics with S-Plus. 3rd ed. New York, NY: Springer Verlag; 1999. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Zhang H, Tsai CP, Yu CY, Bonney G. Tree-based linkage and association analyses of asthma. Genet Epidemiol. 2001;21(Suppl 1):S317–22. doi: 10.1002/gepi.2001.21.s1.s317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Canadian Resident Matching Service . R-1 match reports. Ottawa, ON: Canadian Resident Matching Service; 2009. Available from: www.carms.ca/eng/operations_R1reports_e.shtml. Accessed 2010 Feb 23. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Kassebaum DG, Szenas PL, Schuchert MK. Determinants of the generalist career intentions of 1995 graduating medical students. Acad Med. 1996;71(2):198–209. doi: 10.1097/00001888-199602000-00030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Jordan J, Brown JB, Russell G. Choosing family medicine. What influences medical students? Can Fam Physician. 2003;49:1131–7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Senf JH, Campos-Outcalt D, Kutob R. Family medicine specialty choice and interest in research. Fam Med. 2005;37(4):265–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Colquitt WL, Zeh MC, Killian CD, Cultice JM. Effect of debt on U.S. medical school graduates’ preferences for family medicine, general internal medicine, and general pediatrics. Acad Med. 1996;71(4):399–411. doi: 10.1097/00001888-199604000-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Clinician scholar program. Mississauga, ON: College of Family Physicians of Canada; 2009. College of Family Physicians of Canada [website] Available from: www.cfpc.ca/local/files/Education/Clinician%20Scholar%20Program%20-%20Final%20January%202009%20(2).pdf. Accessed 2010 Mar 3. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Fédération des médecins omnipraticiens du Québec . Énoncé des principes pour une politique nationale sur la médecine familiale. Montreal, QC: Fédération des médecins omnipraticiens du Québec; 2008. Available from: www.fmoq.org/fr/tagview.aspx?id=4&p=1. Accessed 2009 Apr 15. [Google Scholar]